One of the main areas of work of our clinic is child neurology, psychology and psychiatry, and pediatric epileptology. We work in constant contact with the parents of our little patients: you will be able to keep in touch with your doctor by phone and email. We will be happy to help you and your children!
In most cases, with timely identification of the true causes of asthenia symptoms and the correct approach to rehabilitation, treatment of asthenic and astheno-neurotic syndromes brings positive results. It is important to understand the reason for the development of asthenia. The cause may be, for example, chronic infection in conditions of reduced immunity, anxiety or stress, an imbalance in the endocrine system, overt or hidden epileptic activity of certain parts of the brain.
- Symptoms and causes
- Criteria for the manifestation of asthenic and astheno-neurotic syndrome
- Where to start and who to contact with astheno-neurotic syndrome in a child: a doctor or a psychologist?
Symptoms and causes
Asthenia means fatigue, tiredness, exhaustion. “Pure” asthenia can be caused by illness, injury, surgery, infection (Epstein-Barr virus, herpes type 6, cytomegalovirus, chronic tonsillitis with high antistreptolysin “O”, etc.). Astheno-neurotic syndrome is a state of prolonged, unjustified nervous tension, which leads to overwork and exhaustion of the child’s nervous system. The onset of astheno-neurotic syndrome can be caused by mental stress, nervous tension due to an uncomfortable situation in the family, pressure from older children and other stress factors.
Stimulating the nervous system with asthenic or astheno-neurotic syndrome is a rather thankless task: the nervous system is exhausted and there is nothing to respond to stimulation. It is much more effective not to stimulate the nervous system, but, on the contrary, to relieve nervous tension, nourish the nervous system and help it. So, gradually, the ability of the nervous system to correctly respond to stimuli is restored and asthenia gradually goes away. Astheno-neurotic syndrome very closely overlaps with vegetative-vascular dystonia and practically does not occur without it. But astheno-neurotic syndrome is a broader concept that includes not only vegetative-vascular dystonia, but also fatigue, irritability, nervousness, fatigue, disturbance (exhaustion) of mental functions.
Treatment of neuroses in children
Treatment of neurosis in children is selected individually depending on the symptoms of the disease.
Conservative treatment
The main task of conservative treatment of childhood neuroses is to stabilize the child’s physical and mental state, as well as eliminate specific symptoms. Depending on the situation, the following are prescribed:
- tranquilizers;
- sedatives;
- neuroleptics;
- psychostimulants;
- nootropics;
- vitamins.
Parents are required to strictly observe the daily routine, achieve the correct alternation of work and rest, and provide nutritious, fortified nutrition. If there is evidence, the child may be excused from attending school for a short time.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy plays a leading role in the treatment of childhood neuroses. Depending on the situation, the following types are used:
- gaming;
- sand;
- group psychotherapy, especially MIM theater or adolescent personal growth groups;
- water games;
- psychological techniques aimed at understanding one’s own experiences;
- family therapy.
Play therapy is a method of “pulling” hidden problems out into the open. In the form of a game, the instructor corrects behavior in standard situations: what to do if a stronger peer attacks, how to overcome resentment, how to avoid obviously unsuccessful situations, and the like. Sand therapy allows you to create your own world, making fears and concerns visible, destroying the severity of negative experiences.
Group techniques provide invaluable experience to children with any flaws in character and upbringing. Under the supervision of an instructor, the child understands his place in the human hierarchy and learns to behave accordingly. MIM theater helps shy and hyperactive children overcome communication difficulties. Personal growth classes involve the child’s awareness of his strengths and weaknesses and the development of skills to achieve goals.
Playing with water and other psychological techniques can help cope with stress. This group of techniques teaches a child to get rid of painful emotional experiences. You can draw emotions, observe water or live fire, create a “love medallion” (select any object and mentally charge it with love at the moment of a parent’s hug) and much more. Family therapy is aimed at establishing calm, trusting and fair relationships between children and parents, based on compromise.
Physiotherapy
Used as an auxiliary method of treatment, allowing to reduce the number of medications. The greatest effect is exerted by: exercise therapy, electrophoresis with sedatives, water procedures, relaxing massage.
#Criteria for the manifestation of the syndrome
- The child gets tired quickly not because he worked hard, but because physically he cannot do as much as the average healthy child.
- The child does not sleep well, i.e. either falls asleep with difficulty, or often wakes up at night, or sleeps for a long time, but in a shallow sleep and wakes up in the morning sleep-deprived, tired, and not rested.
- Vegetative-vascular disorders. Increased or decreased blood pressure, rapid or irregular pulse, sweating or dry skin, emotional instability, weather sensitivity (the child does not have time to adapt to changes in atmospheric pressure), irritability, increased excitability, turning into fatigue.
- The child often suffers from colds and often complains of headaches, because his overall health suffers due to constant nervous tension. The immune system works worse, the digestive tract works less coordinated.
The first thing to do is to understand exactly what reasons drove the nervous system into an astheno-neurotic state. It could be a previous trauma, such as a concussion, or perinatal encephalopathy; it could be a banal long-term nervous tension associated with the psychological situation in the family, with relationships with a brother or sister, with difficulties in relationships with parents, with grandparents, with members families. It often happens that parents do not notice this fact, and the child experiences severe, prolonged nervous tension for some reason.
Increased intracranial pressure for a long time, in itself, causes astheno-neurotic syndrome, regardless of the presence/absence of psychological problems.
Asthenia what is it?
Asthenic syndrome is a mental disorder of a child, which is accompanied by behavioral disturbances and is expressed in capriciousness, inattention, reduced physical and mental activity, aggressiveness and prolongation of recovery time after exercise.
The baby is often capricious, does not want to do homework, constantly loses his temper with the people he loves, most likely this is asthenic syndrome.
Asthenia in children develops against the background of neurasthenia, stress, mental illness, as well as mental overstrain. Diseases of internal organs can also be the cause. Sometimes asthenic syndrome in children is an unfavorable prognostic sign of serious infectious diseases, such as tuberculosis or HIV infection.
Asthenia what is it? This is a painful condition that has its own symptoms and treatment.
Asthenia in children can take different forms, for example, cerebrogenic (brain diseases such as traumatic brain injury, infections), somatogenic (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, urinary diseases, blood diseases and various infections), cerebrosomatogenic, overwork and adaptation disorders. Asthenic syndrome in children manifests itself as maladaptation under conditions of extreme stress.
TREATMENT OF ASTHEN-NEUROTIC SYNDROME
An integrated approach is effective in treating neurasthenia. The patient is prescribed a course of drug therapy, psychocorrective and psychotherapeutic sessions.
The main medications for the treatment of neurasthenia are tranquilizers, nootropics, sedatives, drugs to normalize blood circulation, amino acids, and antidepressants. In particularly severe cases, the patient is hospitalized.
UHF, balneotherapy, restorative massage, and light therapy have a positive effect on the nervous system.
From the age of 4, children are prescribed psychotherapy to treat various forms of asthenia. During the classes, the psychotherapist teaches the child to understand and control his emotions, to express his emotional experiences in a socially acceptable way. At the same time, psychological correction is carried out aimed at correcting negative character traits, overcoming fears, and normalizing the psycho-emotional state. Art therapeutic techniques help a child to know and accept himself, and find personal resources. All this facilitates the child’s socialization process.
The conditions for a speedy recovery are:
- the child's adherence to the daily routine;
- systematic exercise, performing a set of morning exercises;
- rational nutrition and use of vitamin and mineral complexes recommended by a doctor;
- daily walks lasting 1–2 hours;
- creation of a favorable psychological atmosphere in the family, attentive and respectful attitude towards the child on the part of parents.
In addition to working with the child, consultation with a psychologist is necessary for parents of a neurasthenic person. In the process of psychological counseling, the specialist teaches parents constructive intra-family interaction, forms in parents a stock of effective coping strategies and teaches methods of conflict-free communication.
Diagnosis of asthenic neurosis
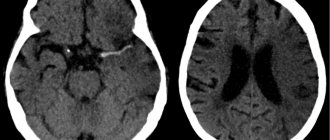
Asthenic neurosis is diagnosed by a neurologist after examining the patient, listening to his complaints and studying the medical record. In some cases, an accurate diagnosis may require a special test. Since the symptoms of asthenic neurosis are similar to the signs of many somatic diseases, primarily brain pathologies, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography, MRI, ultrasound, X-ray, ECG and other studies. These procedures and additional tests will help ensure that headaches and other symptoms are not caused by any diseases, but are a consequence of asthenic neurosis. Treatment is prescribed after examination; if the doctor does not have sufficient information to do this, he may refer the patient to other specialists.
Prevention of asthenic neurosis
To prevent the development of neurasthenia, a person should monitor their daily routine, allocating enough for rest. Sports and outdoor recreation promote rapid recovery after a hard day and recharge the body with energy. Proper nutrition is also important.
Doctors note that asthenic neurosis is most easily treated if detected in a timely manner. However, if you delay in seeing a doctor, the disease may develop into a chronic form, which will be much more difficult to treat.
Symptoms of illness in a child
Signs of neurosis in a child are often ignored or perceived incorrectly - as a lack of upbringing or character traits. There are a number of basic signs that need to be paid attention to, especially if they appear over a long period of time and in the aggregate.
- The physiological complex of symptoms includes sleep disturbances (nightmares, tremors, insomnia, enuresis and daytime sleepiness), poor appetite, weakness, and rapid fatigue. In more advanced forms, these symptoms may be accompanied by abdominal and heart pain, headaches, and dizziness.
- Psychological symptoms include sudden, causeless mood swings, increased vulnerability and sensitivity, isolation and reluctance to make contact, too strong a reaction to failures, the emergence of fears and anxieties.
Neuroses usually manifest themselves with several symptoms at once, so you need to be careful to pay attention to them in time.
COMPLICATIONS OF THE DISEASE
Common complications of astheno-neurotic disorder are:
- hormonal disorders that increase the risk of pathology of the digestive tract, acceleration or slowdown of puberty;
- lack of reproductive capacity in adult life;
- socialization difficulties;
- depression, suicidal thoughts;
If you start treatment for a neurotic disorder at the initial stage, negative consequences and complications can be avoided.
Classification of asthenic neuroses
There are three stages of neurasthenia in total. In the absence of treatment for asthenic neurosis, they consistently
transform into one another, however, given certain characteristics of a person’s character, they can develop independently.
- Hypersthenic form
This stage of neurasthenia occurs most often, since it is the initial form of asthenic neurosis. Treatment in this case almost always gives a 100% result if it was started on time.
A feature of hypersthenic neurasthenia is increased excitability and irritability of the patient. It is very easy to anger such people by talking to them louder or quieter than usual. They also can't stand loud noises and hate it when things don't work out for them. It costs them nothing to shout or insult a relative, colleague or friend, but they quickly waste their emotional strength and lose the ability to work and mental activity.
People with the hypersthenic form of asthenic neurosis work ineffectively, as they are constantly distracted by conversations, rest and any other reasons not related to work. Absent-mindedness, inattention and lack of concentration lead to the fact that by the end of the working day such employees do not have time to complete even half of the tasks assigned to them.
In everyday life, patients experience problems with sleep, when a person has nightmares or cannot sleep at all. It is clear that in the morning such a person gets up tired and irritable, and in this state goes to work. After this, everything starts all over again and only goes away by the weekend, when after rest the headaches subside a little and strength returns.
- Irritability and weakness
If neurasthenia is not cured in its hypertensive form, it may progress to the next stage. People with a pronounced temperament and a strong nervous system are especially susceptible to it. They react even more strongly to external stimuli, but the outbreak of emotions quickly turns into a state of devastation and powerlessness, which is often accompanied by crying. However, a reverse change of state is also possible - the main feature of this stage is precisely the unpredictability of mood changes.
Such jumps immediately affect the general condition of the body: a person quickly “runs out of steam” both morally and physically. It is very difficult for him to start work, and if he does start something, he soon gives up. When trying to continue working through force, internal tension increases more and more, which ultimately leads to severe headaches. After resting for a while, the patient can try to start working again, but the strength gained does not last long. Moreover, short breaks do not contribute to improving a person’s general condition, but only aggravate the situation. In the absence of timely treatment, asthenic neurosis leads to the fact that the patient loses the ability to perform any adequate activity at all.
- Hyposthenic stage
Unlike the previous form of neurasthenia, which is characteristic mainly of choleric people, the hyposthenic stage is observed in weak-willed, inactive and suspicious people. Explosive expression of emotions in such patients is extremely rare, but a state of constant drowsiness and lethargy is constantly present. The picture of the disease is complemented by low mood, constant anxiety and bouts of crying. There can be no talk of any work, since the person is not able to concentrate on any task. In addition, there is increased suspiciousness and a tendency to discover various diseases in oneself that in reality do not exist.
Any form of asthenic neurosis can be successfully treated, especially if the disorder is detected in advance. If treatment was not started on time, attacks of neurasthenia will become more frequent, and their duration will increase each time. This condition is dangerous because even after completing the course of treatment, attacks of asthenic neurosis can recur after a long period of time. This phenomenon is called periodic neurasthenia and requires great effort by the doctor and the patient himself during treatment.