Psychological climate is the mood of the team, the moral and psychological atmosphere that permeates the relationships of its participants. We are not necessarily talking about the work collective, although more often this is the case. The psychological climate exists in an interest group, in the family, in school, and in any collective activity. The success of this activity and the health of each of its participants depend on the atmosphere prevailing in the group. Creating a favorable psychological climate is included in measures to prevent psychosomatic diseases, conflicts, and neuroses.
What it is
The term “psychological climate” was first uttered by N. S. Mansurov in the context of studying a production team. A little later, psychologists began to distinguish between socio-psychological and moral-psychological climate. Psychological climate is a broad concept, the rest are included in it.
Psychological climate is the nature of emotions that arise in relationships between people, based on their sympathies, coincidence of interests, characters and inclinations. The psychological climate includes 3 areas:
- Social climate – awareness of goals and objectives by all participants, respect for rights and responsibilities.
- Moral climate - values accepted in the group. Their unity, acceptance, consistency.
- The actual psychological climate is informal relationships in the team.
There are 4 approaches to studying the psychological climate in a team:
- Climate is a collective consciousness. Awareness by each member of society of relationships in the team, working conditions, methods of stimulating it.
- Climate is the mood of the team. That is, the leading role is given not to consciousness, but to emotions.
- Climate is the style of interaction between people that influences their condition.
- Climate is an indicator of the compatibility of the group, the moral and psychological unity of its participants. The presence of common opinions, traditions and customs.
The peculiarity of the psychological climate as a phenomenon is that it is created by the person himself, he is able to influence the climate, improve and change.
Microclimate assessment and main influencing factors
First, you should find out what is happening in your team at the moment: what prevailing emotions, experiences and moods, whether conflicts occur, whether there is an understanding of the common goal of the company and the desire to realize it.
You can obtain information in several ways:
- At general meetings.
- During personal conversations with individual employees.
- Using an anonymous survey.
It is advisable to perform the analysis regularly, since many factors can dramatically change the current situation. The work environment is affected by:
- group compatibility. Employees operate with their own basic concepts and general ideas and perform a specific task. However, well-coordinated teamwork is built on emotional unity and sharing of company values. If the staff speaks different languages, does not reach a compromise on simple issues, does not understand the main goals, the situation will not allow them to do the work effectively;
- Nature of activity. Each position in the company has its own characteristics - emotional intensity, monotony, increased responsibility, and the presence of stress factors. All this affects the socio-psychological microclimate;
- level of job satisfaction. Ideally, work arouses interest, brings a sense of satisfaction, self-worth, and provides the opportunity for professional development. To maintain a favorable atmosphere, it is necessary to respond to the needs of the team in a timely manner: introduce effective systems of material and non-material motivation, pay attention to training, encourage initiative, and the desire for career growth. Otherwise, enthusiasm in the team will quickly subside;
- working conditions. To get maximum results, it is worth providing employees with a comfortable, specially equipped workplace. Poor lighting, extraneous noise, and stuffiness are a source of stress and irritability for employees. This is incompatible with the concept of a healthy atmosphere;
- leadership style. The formation of a normal microclimate is facilitated by a democratic management style, in which there is no imposition of decisions, friendly, trusting relationships prevail, and team members are equally valued. Permissive and authoritarian styles lead to low productivity, the emergence of hostility, envy, and mistrust;
HR management styles chart
- nuances of the global and local microenvironment. Additionally, the situation is influenced by stability in the political and economic spheres of society, the social and psychological well-being of team members. The structure of the organization, the opportunity to participate in planning and decision-making, and the elimination of functional-role contradictions play a role.
With a normal internal microclimate, employees are satisfied with working conditions and the amount of material remuneration, are focused on results, share common goals, support and respect colleagues, notice prospects for growth, and make long-term plans. Problems on any of the points are a sign that it is time to take appropriate action.
Favorable and unfavorable climate
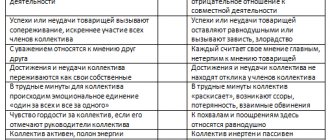
The psychological climate can be favorable or unfavorable. The first is characterized by:
- friendly attitude of participants towards each other;
- camaraderie;
- adequate mutual exactingness, which determines creative and effective activity;
- mutual assistance;
- joy from communication and openness of communications;
- safety and comfort;
- optimism;
- self-confidence and team confidence;
- the opportunity to think freely and creatively, to discover and realize one’s own potential.
But it is worth noting that a combination of mutual demands and mutual assistance is mandatory. Mutual assistance alone will turn into permissiveness, a “brotherly” attitude, which over time will create an unfavorable climate.
An unfavorable or unhealthy climate includes the opposite characteristics:
- pessimism;
- mistrust and disrespect;
- coldness and secrecy in relationships;
- inhibition of personal potential;
- irritability;
- tension and conflict;
- uncertainty;
- misunderstanding;
- fear of error, punishment and rejection;
- suspicion.
It has been noted that a healthy climate increases productivity and labor efficiency. Unfavorable climate causes frequent incidents of safety violations and reduces productivity by 20%.
A healthy climate satisfies the needs of its members and does not conflict with social norms and values. For example, in a criminal group there may be a unity of opinions, views and beliefs, but for society the activities of its members are harmful, in fact, as in the end for the participants themselves (they just don’t know it).
Work strategies
Preventive methods
- It is important to take into account the psychological characteristics of each person when hiring. Therefore, if during the interview some points made you wary, think carefully about whether it is worth letting such a person into your company. Objectively evaluate all the consequences of the manifestation of her character, no matter how professional in her field or close relative she may be.
- Certification of employees should be periodically carried out, especially those who have even a minimum number of people subordinate to them.
- Strict control of the number of employees and vacancies. If there is a shortage, some of the responsibilities have to be distributed among all members of the group, or assigned to one person. And this always threatens the emergence of anger and irritation, which not everyone has the opportunity to express, which is why a tense atmosphere arises. And when there are extra workers, conflicts between them will inevitably arise against the backdrop of competition and clarification of which of them is more important and more valuable.
- One manager should not have more than 6-7 people subordinate to him, otherwise he will not be able to keep track of everyone, and also notice the brewing of a conflict.
- You already know about the value of boundaries from the article about personal space. With their help, the image of another person becomes clearer, what he likes or does not accept, how one can behave with him, and what is best not to do, and so on. The same is true in the work process, if people do not understand what values exist in their company, norms, traditions, plans and attitudes, they may experience anxiety, which will provoke conflicts and feelings of dissatisfaction. Therefore, creating a healthy atmosphere must begin with defining the boundaries of the company.
Conflict situations
They are inevitable, since different people, with different opinions, life and professional experiences, moods and general well-being, are in a single process and space. Are you quarreling with your family members?
This means that you have noticed a difference in something, and do not yet know how to deal with it. It is not the conflict itself that is scary, but what it “results into,” especially if it is hidden.
Measures to improve climate
Organize a joint vacation , and not only on official holidays. This will not only improve the microclimate, but will also help bring all group members closer together, and possibly create more informal relationships.
Collective celebration will help relieve unnecessary stress, improve emotional well-being, perhaps clarify some of the nuances and difficulties in relationships, as well as create common impressions and memories, returning to which over time, employees will feel closeness and unity. The main thing is that they are positive.
And you shouldn’t be forced to attend such events, it can cause a storm of anger. Over time, they themselves will join, as there will be a desire to participate in the general discussion and celebration.
Trainings . Often, various corporations practice the involvement of coaches and psychologists in order to create a harmonious atmosphere in which there will be a desire to work and give all the best. Some trainings allow you to achieve not only professional, but also personal growth. They allow you, for example, to increase your self-esteem, learn to make decisions, cope with tension and aggression, and improve your communication skills.
Climate levels
Climate has two levels: static and dynamic.
Static
This is a stable attitude of employees towards work, constant interpersonal relationships. The climate is stable and tolerates external influences well. It is not easy to create a climate at this level, but then it is easy to maintain. Team members feel this stability, which makes them more confident in their own position. Climate correction is practically not required, control is occasional. This level is also called the socio-psychological climate.
Dynamic
This is the changing nature of the team. The climate changes daily due to the changing moods of its participants. This level is also called the psychological atmosphere. It changes faster and is less felt by the participants. As changes accumulate, it can create an unhealthy climate in the team.
Compatibility of a socio-psychological nature
This type of compatibility includes consistency of interests, social attitudes and roles. In the event that two (or more) individuals are working on a project and each claims a dominant role, it is unlikely that their joint activity will end in success. Most likely, the task will be disrupted.
It would be more advisable to pair a hot-tempered (that is, impulsive) person with an employee who has a calm and balanced disposition, and is also able to listen and be tolerant and trusting of his partner. Everyone will “win” from such a tandem: both the company and both employees who complete the task in the minimum amount of time in a normal psychological environment (and, possibly, receive a reward in monetary terms).
Climate diagnostics
The socio-psychological climate in a team is an indicator of the level of development of the team. Therefore, it is important to regularly carry out diagnostics and monitor dynamics, to identify the properties that hold the team together or destroy it. For this purpose, the method of assessing the level of psychological climate of A. N. Lutoshkin’s team is suitable.
The subject is asked to answer 13 statements regarding the team in which he is located. The score can be from -3 to 3.
Answer form
22 points and more – highly favorable climate.
8-22 points – moderately favorable climate.
0-8 points – low favorable climate.
From 0 to -8 – initial unfavorability.
From -8 to -10 – moderately unfavorable climate.
From -10 and more – pronounced unfavorability, unhealthy climate.
Each team member takes the questionnaire. When summing up, all points are summed up and divided by the number of people surveyed. The final number is the overall score of the team. You can also calculate an overall score for individual criteria.
Signs characterizing climate
Externally, you can judge the climate of a team by the following signs (useful for those applying for a job):
- staff turnover;
- product quality;
- level of discipline;
- claims and complaints, negative feedback from employees;
- frequent breaks from work;
- negligence and carelessness.
The better these indicators, the more favorable the climate. Signs of a favorable climate also include:
- trust and high demands in relationships;
- kind and constructive criticism;
- freedom of speech and opinion;
- providing initiative to employees, lack of managerial pressure;
- awareness of participants in team issues;
- satisfaction from belonging to this group;
- mutual assistance and highly developed empathy;
- responsibility for yourself and the entire team.
Definition of the concept
The level of favorableness of the work environment is determined by the quality of the psychological climate.
Photo by Canva Studio: Pexels
If we take the most common definitions of the concept of “psychological climate,” we can get something like this:
- Psychological climate is a set of factors that determine the psychological state of the work team participating in the general production process.
- Psychological climate is a qualitative characteristic of interpersonal relationships, which is expressed in the sum of psychological factors that promote or hinder joint activities and personal development in a group.
The harmonious development of a person’s personality is directly related to the ability to realize oneself within a group or team. The processes of development of the individual and the team are very closely interconnected and interdependent: the structure of the team, the rules of relationships, the opportunity for self-expression and development.
What affects climate
The climate is influenced by a number of factors:
- Type of organization, team. Open or closed, private or public, scientific or industrial organization. Family, class, criminal group, charitable association.
- The image and standard of living of the team members.
- Micro (everyday for a particular person) and macro (city, country, culture of society) conditions: normal, complicated, extreme.
- Rational organization of work, compliance with the regime and rights, taking into account the capabilities and characteristics of each team member.
- Team structure.
- Informal leaders or groups in a team.
- Leadership style and features. A favorable climate requires attention from the manager not only to production issues, but also to the personal problems of team members. That is, the democratic style.
- Individual psychological and personal characteristics of team members. Personal opinion, mood and behavior of a person contribute to the overall climate. This is based on passing external factors and events through the prism of one’s own character and personality.
- The combination of the characteristics of all participants forms a new collective quality - the psyche of the collective. Therefore, the psychological compatibility of the participants, primarily in terms of temperament, plays a big role. Psychologically, people must be compatible in terms of psychomotor reactions, emotional and volitional manifestations, the work of thinking and attention, and character. Incompatibility causes antipathy, hostility, and conflicts.
- Self-assessment of each participant. His self-awareness and the correspondence of claims and achievements.
The leader has a great influence on climate formation. You should pay attention to his personal qualities, attitude towards other participants, authority, leadership style. A positive climate is created by a leader who:
- principled;
- responsible;
- active;
- disciplined;
- kind, responsive and sociable;
- has organizational skills.
Rudeness, selfishness, inconsistency, disrespect, and careerism have a negative impact on the health of the climate.
The conditions that dictate the climate also depend on the leader. Necessary:
- be friendly and respectful in relationships;
- provide employees with the opportunity to choose their own area of activity;
- notice and celebrate the activity and creativity of employees;
- promote employee interest in self-development;
- motivate employees for career advancement with the aim of not only material gain, but also to gain prestige and recognition from the team;
- be a good qualified leader and a kind mentor.
What a leader can do for a favorable climate:
- It is justified from a psychological standpoint to select personnel.
- Organize regular training and certification.
- Study and practice the theory of psychological compatibility, that is, have a good understanding of people.
- Contribute through practical activities (through organizing events) to the development of interaction and relationship skills.
Reasons for the deterioration of the emotional climate in the team
The team atmosphere is easy to disrupt. As a rule, this is caused by mistakes on the part of management. According to Irina Avetisyan, there are three main reasons for the development of imbalance.
Imperfection of the personnel management system
If the developer made mistakes at the stage of its formation, there is a high risk of creating a persistent negative atmosphere in the company. It can be formed as a consequence of procedures and mechanisms that systematically cause disputes and conflicts.
“When processes become more complicated, when a complex hierarchy is added to resolve even simple issues, if there are no standards of behavior in emergency situations and there are no regulations for actions in regular ones, conflicts and discontent in the team are inevitable,” the expert notes.
Personal qualities of a leader
Leadership style inevitably affects the morale of the team. The personal qualities of not only the heads of departments are important. The manager’s rudeness, disrespect for his subordinates, his commitment to act on the “divide and conquer” principle, multiplied by incompetence in the field of psychology of labor relations, destroy a favorable microclimate. Another dangerous flaw of management is inattention to the processes occurring within the team.
“It is important for a leader to be able to consider and extinguish a conflict at the stage of its inception,” clarifies Irina Avetisyan. “After all, it’s always easier to prevent a fire than to put it out.”
pixabay.com/
Presence of “troublemakers”
These are employees who, due to their own character or due to dissatisfaction with the conditions in the team, bring discord into its ranks:
- create in leadership;
- initiate “actions of intolerance” against another employee and remove him from the team;
- sow an atmosphere of hostility and dissatisfaction with working conditions;
- their actions lead to disorganization not only of their own working time, but also of other team members.
“You need to be able to spot such employees at the selection stage,” the expert notes. “And it is extremely important to identify “troublemakers” by monitoring the state of the psychological climate.”
Creating a favorable climate
A favorable climate is formed where participants clearly see the goals of the team, clearly understand and accept them. At the same time, they have a flexible system of means and ways to achieve them.
The higher the level of development of the team, the more favorable the climate. However, even at a low level of development, a favorable climate can be created.
It is important to maintain the unity of motives, interests, beliefs, ideals, attitudes, needs of the participants and correctly combine their individual characteristics.
A favorable psychological climate cannot arise by itself. This is the product of the coordinated and hard work of the entire team, and the competent organizational activities of the leader.
Purposeful work must be carried out to create a favorable climate. This is a responsible and creative undertaking that requires knowledge of human psychology, the ability to predict likely situations in relationships, and understand emotions and their regulation.
Creating climate begins with changes in each individual person. In order for interpersonal relationships to develop favorably, you need to:
- work on your own negative character traits;
- to form positive moral qualities (respect for people, recognition of their dignity and honor, attention, recognition of the beliefs and interests of other people, trust, observance of politeness and rules of behavior, objective assessment and self-esteem, tact);
- use polite words and phrases, observe etiquette;
- master methods of emotional and mental self-regulation (necessary for the prevention and elimination of irritation, resentment, burnout, nervousness, anger, fatigue, agitation, apathy);
- know strategies for behavior in conflict situations and be able to resolve them competently;
- avoid maximalism in judgment and behavior, egocentrism, labeling, categoricalness, inflated expectations and ideas.
Each member of the team should be valuable, unique and positive in their own way, and in a group setting they should complement each other, not interfere or overshadow each other.
Satisfaction as a criterion
The basis for climate assessment is people’s satisfaction/dissatisfaction with relationships in the team and the activity itself. However, you need to understand that satisfaction can be subjective and objective.
It often happens that one person is completely satisfied with the team, while another is not at all satisfied with the working conditions. This is subjectivity in assessment. Differences in experience, conditions and quality of life, interests, character of people and other individual characteristics contribute. The principle of subjective satisfaction is the relationship between the parameters “I give” and “I receive”.
Dissatisfaction with delayed wages, regular punishments, non-compliance with labor standards, violation of rights is an objective indicator.
Afterword
Psychological climate is sometimes identified with socio-psychological or moral-psychological, which further emphasizes its basis. The basis of a favorable climate is the unity and similarity of values among team members.
The nature of the climate affects the individual: whether or not it stimulates work, joint activities, raises or lowers the mood, instills faith or self-doubt in one’s own strength, cheerfulness or despondency, stimulates or suppresses activity.
It is very easy to guess the nature of the climate. It is enough for its participants to only answer the questions “like - don’t like”, “satisfied - doesn’t suit”, “would like - don’t want to be in a team.”
Learn about what the psychological climate in a team is and how to create a favorable climate from the specialists of the Synergy University of Self-Development.
Authoritarian style
It is based on the dominance of unity of command, which is expressed in the fact that only the leader himself makes all important decisions (without consulting anyone). The opinion of the team in this case is not taken into account.
The main methods of management are orders, instructions, reprimands, comments and punishments. Communication between a manager and his subordinates occurs in a rude and harsh manner. In the team, “ear-mongering” and widespread control are encouraged. Any employee initiatives are not supported, and the interests of the company are placed above the interests of people.
Such a leadership style can generate in the team a feeling of some psychological discomfort, conflict, fear, envy, ingratiation and hostility.