Diseases of the peripheral nervous system
Neurological Department Peripheral nervous system
- a conventionally distinguished part of the nervous system, the structures of which are located outside the brain and spinal cord, including the cranial nerves, spinal nerves and nerve plexuses.
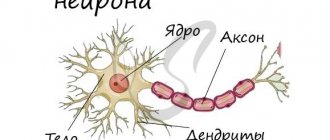
These nerve formations deliver impulses from the central nervous system (CNS) directly to the working organs - muscles and information from the periphery to the CNS. The human peripheral nervous system does not actually have the same protection as the central nervous system, so it can be exposed to toxins and also be damaged mechanically.
Causes of defeat:
- infections;
- intoxication;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- circulatory disorders;
- injuries and other factors.
Classification of diseases of the peripheral nervous system:
1. According to the topographic-anatomical principle:
- radiculitis (inflammation of the roots);
- funiculitis (inflammation of the cords);
- plexitis (inflammation of the plexuses);
- mononeuritis (inflammation of peripheral nerves);
- polyneuritis (multiple inflammation of peripheral nerves).
2. By etiology:
- infectious;
- infectious-allergic (for childhood exanthema infections: measles, rubella, etc.);
- toxic;
- allergic (vaccinal, serum, etc.);
- dysmetabolic (with vitamin deficiency, endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus), etc.);
- discirculatory (for rheumatic and other vasculitis);
- idiopathic and hereditary (neural amyotrophy of Charcot-Marie, etc.);
- compression-ischemic lesions of individual peripheral nerves,
- vertebrogenic lesions (bone, disc, joint, muscle and tendon-ligament formations).
3. According to pathogenesis and pathomorphology:
- neuritis (radiculitis);
- neuropathy (radiculopathy);
- neuralgia.
Group of polyneuropathies (neuropathies)
includes vascular, allergic, toxic, metabolic damage to the peripheral nervous system, as well as damage caused by the influence of various physical factors - mechanical, temperature, radiation.
Neuralgia
– these are painful sensations in the area of innervation of certain nerves and the formation of trigger zones of the skin and mucous membranes, irritation of which, for example, touch causes another attack of pain. In the intervals between attacks, neither subjective nor objective symptoms of irritation or loss of function of the affected nerve are observed.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the peripheral nervous system:
Methods for diagnosing diseases of the peripheral nervous system are aimed at identifying and correcting the underlying disease (for example, damage to peripheral nerves due to diabetes, alcoholism, etc.).
Treatment of these diseases includes medication, non-drug and surgical treatment.
Drug therapy
is aimed at correcting the underlying disease, relieving pain and restoring nerve function.
Non-drug therapy includes the use of physiotherapeutic treatment methods, the selection of which depends on the specific pathology, the severity of the process and concomitant pathology: Surgical treatment methods are used:
- with long-term persistent neurological defect and ineffectiveness of conservative therapy;
- in acute conditions and the presence of absolute indications for surgical treatment.
Treatment of diseases of the peripheral nervous system, as well as therapy of diseases of the central nervous system, must be carried out immediately.
Guillain-Barre syndrome
This is one of the most severe neurological diseases, which in every third patient requires treatment in the intensive care unit at the height of the disease. The term refers to a rapidly progressing neuropathy characterized by flaccid paralysis in the symmetrical muscles of the limbs with sensory and autonomic disturbances. The condition develops acutely, usually after colds and other infections. However, with adequate treatment, complete recovery is possible.
Causes:
Guillain-Barre disease is usually classified as an autoimmune disease.
Having coped with the infection, the human immune system does not recognize this and begins to attack its own body, in particular the nervous tissue. Cells of the immune system produce antibodies that lead to demyelination, that is, damage to the myelin sheath of the nerves. As a result of autoimmune processes, axons, the processes involved in the innervation of muscles and internal organs, can also be damaged. The first signs of the disease are recorded one to three weeks after such infectious diseases as:
- Viral enteritis.
- Respiratory infections (ARVI).
- Cytomegalovirus infection.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Herpetic infection.
Kinds:
Guillain-Barré syndrome is usually divided into two types - demyelinating and axonal; the first variant of damage to peripheral nerves is more common.
- Demyelinating
. Only myelin sheaths are involved in the pathological process; destruction of axon cylinders is not detected. This leads to a slowdown in the speed of impulse conduction, which provokes the development of reversible paralysis. Pathological changes affect the anterior, less often the posterior roots of the spinal cord; damage to other parts of the central nervous system is also possible. The demyelinating type is considered a classic variant of the syndrome.
- In the axonal variant, the axial cylinders of the axons are also affected, which leads to the development of severe paresis and paralysis. The axonal type
of polyneuropathy is considered more severe, after which motor functions are not fully restored.
Diagnostics:
The disease can be suspected already by questioning and examining the patient. Guillain-Barré syndrome is characterized by symmetrical damage to the extremities and preservation of the function of the pelvic organs. Of course, there are also atypical signs of the disease, so for differential diagnosis it is necessary to conduct a number of studies.
- Electromyography – determination of the speed of impulse transmission along nerve fibers.
- A spinal tap can detect protein in the cerebrospinal fluid. Its content increases a week after the onset of the disease and reaches its peak by the end of the first month of the disease.
- EGC can detect arrhythmias.
- Blood tests show an increase in ESR and white blood cell count without other signs of infection.
Treatment:
Treatment of Guillain-Barré syndrome is divided into two complementary types: nonspecific and specific therapy.
Treatment of patients with acute development of symptoms, respiratory dysfunction, severe cardiac arrhythmias begins with nonspecific therapy. The patient is admitted to the intensive care unit. In the phase of increasing symptoms, continuous monitoring of respiratory function and cardiac activity is carried out. Specific therapy includes the administration of immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis.
- Immunoglobulin is prescribed intravenously. This is especially necessary for those patients who cannot move without assistance or have difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- Plasmapheresis is prescribed for moderate to severe disease. Its use significantly speeds up recovery time and prevents the development of residual effects. In mild cases of the disease, plasmapheresis is not used.
- For arrhythmias, increased blood pressure and other autonomic disorders, symptomatic therapy is used.
In case of paralysis, bedsores and pneumonia are prevented by turning the patient over, treating the body, and performing a massage.
During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to use sets of physical exercises, physiotherapy, and massage courses. If you have a speech disorder, sessions with a speech therapist are necessary. Information for patients and their relatives
Rules for hospitalization
Services and prices of the department
Symptoms
With neuropathies, symptoms can be different and depend on the affected areas. They cause a lot of discomfort to the patient:
- flaccid muscle paralysis
- pain in limbs
- change in skin sensitivity (there may be a contrast in sensations in one area of the skin compared to another)
- no sensation of pain and more
- amyotrophy
- speech disorder
- feeling of numbness in the face and limbs
- muscle weakness of the limbs
- impaired motor coordination
- dry skin
- focal blanching
- redness and bluish discoloration of the injured area
- Facial asymmetry may occur (if the facial nerves are damaged)
If you find yourself with at least one of the described symptoms, you should immediately seek help from a qualified neurologist.
Diagnostics
Neuropathy is difficult to diagnose; its diagnosis often requires a thorough and comprehensive examination of all organs and systems. The doctor should carefully review the medical history, anamnesis and perform a complete neurological examination, which may include:
- Testing tendon reflexes
- Checking muscle strength and tone
- Ability to sense certain sensations, postures, movements and their coordination
In addition, the doctor may request the following tests:
- Blood tests to check vitamin B12 levels
- Analysis of urine
- Thyroid function test (checking thyroid hormone levels)
- Electromyography (EMG) a procedure that measures electrical discharges produced in muscles
- Nerve conduction study, which evaluates how quickly nerves transmit electrical signals. Nerve conduction studies are commonly used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome and other peripheral nerve disorders.
- In rare cases, your doctor may order a nerve biopsy, a procedure in which a small sample of the nerve is removed and examined for abnormalities. However, even a nerve biopsy cannot always explain the cause of some neuropathies.
Treatment stories
Case No. 1
Patient Yu., 40 years old, noticed sudden facial asymmetry, lacrimation from the right eye and incomplete closure of the eyelids. I contacted a neurologist at the EXPERT Clinic. The patient was diagnosed with acute neuritis of the facial nerve and prescribed treatment and examination. The patient completed a course of intramuscular and intravenous drip injections in the day hospital of the EXPERT Clinic, courses of physical therapy and acupressure self-massage. Movements in the facial muscles have been completely restored. During the examination, the oncological nature of the disease was excluded, but its herpetic nature was revealed against the background of a secondary immunodeficiency state. After consulting an immunologist, patient Yu was prescribed a course of immunomodulatory therapy.
List of sources
- Levin O.S. Polyneuropathy: Clinical Guide / O.S. Levin. - M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2006;
- Angelcheva O.I., Zinovyeva O.E., Yakhno N.N. Neuromuscular disorders in chronic alcoholism. M.: MED-press, 2009;
- Zhulev, N.M. Neuropathies: a guide for doctors / N.M. Zhulev [and others]. -St. Petersburg, 2005;
- Skoromets A.A. Nervous diseases: Textbook. allowance / A.A. Skoromets, A.P. Skoromets, T.A. Skoromets. — Ed. 2nd, revised and additional - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2007;
- Gekht B.M., Merkulova D.M. Practical aspects of the clinic and treatment of polyneuropathies // Nevrol. journal - 1997. - No. 2. - P. 4-9.
FAQ
Three fingers on my right hand are numb and painful. What to do?
It is necessary to consult a neurologist to exclude carpal tunnel syndrome and treatment.
I had an attack of trigeminal neuralgia for a long time. Should I take something preventative to prevent another one?
It is imperative to see a neurologist. The doctor will select medications for you that need to be taken on a regular basis and prescribe preventive courses of injections (if necessary, drips in a day hospital) and tablet medications.
Severe burning pain appeared in the right half of the chest and some bubbles appeared. Which doctor should I see?
Similar manifestations, as you describe, can be observed with herpetic ganglioneuritis, the so-called. herpes zoster. This disease is treated by a neurologist.
After about 2 months, my legs began to go numb and weak. Why could this be?
Weakness and sensory disturbances in the limbs can be observed with polyneuropathies of various natures. For example, as a result of diabetes or intoxication. To establish the cause and select adequate therapy, you need to consult a neurologist. There may be a need for additional laboratory and instrumental examinations.
I developed weakness in my right hand after sleeping. Is it from the spine?
The cause of sudden weakness in the arm may also be diseases of the spine. However, a vascular cause or compression of the nerve trunk (nerve plexus) cannot be excluded. To find out the cause and prescribe treatment, you should consult a neurologist.
Can alcoholic neuropathy be cured?
Toxic and dysmetabolic polyneuropathies, incl. alcoholic diseases are most often chronic diseases. With adequate therapy, it is possible to achieve long-term and stable remission
Treatment
In our clinic, traditional and alternative medicine methods are used to treat neuropathies. Complex treatment is selected only individually and depends entirely on the degree of damage to the nerve(s).
Initial treatment will be aimed at restoring the functions of the peripheral nerves, therefore, the cause will be eliminated.
An integrated approach is important in the treatment of neuropathies! Our specialists will take into account all the nuances of the damage and may prescribe:
- medications that improve metabolism, blood circulation and restoration processes in nervous tissue. Medicines can also be used in injection form, including intravenous drips in a cozy day hospital
- hormonal drugs (steroids) - in some cases
- therapeutic drug blockades
- certain types of physiotherapeutic treatment
- manual therapy (osteopathy)
- classic massage
Classification
Assessing the course of the disease, experts distinguish between acute , subacute and chronic polyneuropathies. In the acute form of the disease, its symptoms become most pronounced several days or weeks after the onset of the disease. Subacute polyneuropathies are characterized by an increase in symptoms over several weeks. But at the same time they take place no more than two months. Chronic polyneuropathies can develop over several years.
There are also toxic polyneuropathies (another name for the disease is Guillain-Barre syndrome ), in which a monophasic course is observed. Consequently, the symptoms worsen once, after which the disease gradually regresses. Initially, the patient may show signs of an infectious gastrointestinal or respiratory disease.
There are also porphyritic polyneuropathy and inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy , which occur with periodic relapses and remissions. When the next exacerbation of the disease occurs, the neurological defect becomes more profound each time.
With axonal polyneuropathies, the disease develops gradually, and first of all, the distal parts of the legs are involved. With this type of polyneuropathy, trophic changes very quickly appear in the patient’s muscles, pain, and impaired autonomic functions are bothersome. The patient has sensory and motor impairment.
With demyelinating polyneuropathies, the patient exhibits early tendon reflexes. The sensitivity of muscles and joints is impaired. Both the proximal and distal parts of the limbs are involved in the process, with paresis more pronounced, but muscle atrophy manifests itself less.
So what is stimulation ENMG?
The standard method for studying motor and sensory fibers of peripheral nerves looks simple on the surface. Electrodes are applied over the surface of the muscle or on the area of skin innervated by the nerve being studied (most often they look like a small patch or sticker), and the electrodes are connected to equipment (electroneuromyograph). In areas where the nerve is not very deep, using a special stimulator (vaguely reminiscent of the plug of any electrical appliance), the nerve is irritated by electric current discharges. The current is weak and absolutely safe, although the sensations may be unpleasant. As a result of electrical stimulation, a muscle contracts or a response occurs in the skin (in the case of studying sensory fibers). This response, or muscle contraction, is recorded by electrode stickers. The data obtained is analyzed by a doctor.
Recommendations and prevention
The main prevention of most diseases of the nervous system is maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, timely and adequate treatment of infectious and non-infectious diseases.
If any neurological symptoms occur, do not delay contacting a doctor. Early diagnosis and timely treatment will help prevent the development of complications, prolongation of treatment and the consequences of uncontrolled use of medications. The most complete program of preventive measures is drawn up by a neurologist for each individual patient.