Astheno-neurotic syndrome is a complex disorder of higher nervous activity and cannot be ignored. Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome with sleep disturbance and a feeling of weakness and constant fatigue has its own characteristics. For this purpose, the Transfiguration Clinic uses modernized neurometabolic rehabilitation programs. Therapy is selected and carried out individually, depending on the specifics of the formation and functioning of the body.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome has a cumulative property and occurs as a result of serious psychological and physical stress. The clinic’s specialists effectively combat problems by conducting individual rehabilitation therapy based on identified cause-and-effect relationships.
We select methods for treating astheno-neurotic syndrome strictly individually, so the effectiveness reaches 100%, and the duration of therapy is reduced several times, unlike other methods.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome in the clinic
Astheno-neurotic syndrome can be considered as a pathologically modified version of the adaptation of the nervous system in response to physical and mental stress, intoxication, vascular and hormonal disruptions or disorders. Recently, asthenic and neurotic disorders of the nervous system have become particularly widespread. Therefore, in the treatment of astheno-neurotic conditions, the need to use specific complex drug therapy is of particular importance. Due to the fact that the main leading link of astheno-neurotic syndrome are pathological processes associated with the functioning of higher nervous activity, the need to use complex neurometabolic therapy comes to the fore.
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome requires the use of both medicinal and non-medicinal methods. Biological therapy involves the use of immunomodulators, vitamin therapy and correctors, as well as the use of other means depending on the symptoms and causes of the pathology. In mild cases, staying in sanatorium-resort institutions, where a set of specific procedures are carried out, may be effective.
Non-medicinal methods
Treatment of astheno-neurotic syndrome without the use of medications usually does not bring good, lasting results. However, in a set of measures to combat this pathology, the need for non-drug methods is obvious. The choice of these methods is made together with the attending physician on an individual basis. The range of such tools is quite wide.
Basic non-drug methods of treating astheno-neurotic syndrome
- Psychotherapy;
- Hypnotherapy;
- Selection of daily routine;
- A set of physical activities;
- Music therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Light therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- Water procedures;
- Massage.
Prevention of asthenia
Sarklinik has developed an effective program “ Prevention of asthenia ”, which allows you to avoid future exhaustion of the nervous system. A healthy nervous system is a reality today. The peculiarity of the disease is that the symptoms slowly, gradually, but clearly increase, and the condition worsens sharply. Do not expect dangerous complications of asthenia, asthenic syndrome; contact Sarclinic for timely treatment.
Sign up for a consultation. They have contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: (©) Bds | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Incontinence, treatment of incontinence in Saratov, Russia, symptoms, signs, causes, types
Hypersomnia, doubtfulness, pathological increased sleepiness, treatment
Panic, panic attacks: treatment, symptoms, causes, how to fight, get rid of
Poor attention: absent-mindedness, exhaustion, narrowing of scope, stiffness, distractibility
Depression, treatment of depression, how to get out of depression in Saratov
Comments ()
If astheno-neurotic syndrome is not treated
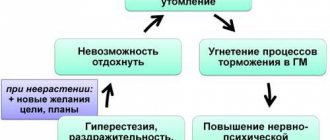
At the time of this disorder, the nervous system is weakened and vulnerable to the formation of various mental pathologies. Sleep disturbances become more severe and enter the chronic phase. The patient's general condition is deteriorating and can already be classified as chronic fatigue syndrome. This is the next phase in the development of the disease.
Efficiency and social activity are greatly reduced. A person feels constant, debilitating fatigue that does not go away even after a long rest. Pain appears in different parts of the body. There is a general feeling of malaise with complaints of various disorders of organs and systems.
Problems arise in the sexual sphere and disruptions in women’s menstrual cycles can often occur. Hormonal metabolism is disrupted.
Symptoms increase and depression, anxiety, and obsessions begin to come to the fore. In extreme states of nervous system depletion, acute psychotic states (psychoses) may occur.
Main causes
- Mental and physical overload;
- Unbalanced diet;
- Having allergies;
- Pregnancy and postpartum period;
- Viral and other infections;
- Surgical interventions;
- Stress;
- Alcoholization;
- Chronic somatic diseases.
Symptoms of astheno-neurotic syndrome
The manifestation of this disease is very diverse and depends on the individual parameters of the formation of the nervous system. However, there are the most common complaints.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome is a pathological condition of higher nervous activity, which manifests itself in the form of a feeling of constant fatigue, complaints of headaches, sleep disturbances, and appetite. A person begins to experience difficulties with memory and concentration, performance decreases, and laziness appears. Rapid depletion of nervous activity resources leads to increased irritability, a decline in mood, and an increased level of anxiety. A person becomes more suspicious, suspicious, loud sounds (music), strong odors (perfumes, deodorants), bright lights begin to irritate him. It is not uncommon for the background mood to have a wave-like character, from elevated to depressive.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome significantly affects the quality of life of a person and the people around him. This is a borderline mental condition that requires the fastest possible contact with a psychiatrist and the need for comprehensive treatment.
Chronic fatigue syndrome can significantly affect the quality of life of the patient and those around him, therefore it is considered a serious psychosomatic disease that requires complex treatment.
Types according to ICD10
The international classification defines two main options for the development of pathology:
- Hyperdynamic. With this nature of the disease, increased excitability, absent-mindedness, disinhibition, and loss of attention are manifested. Also obvious signs are emotional instability and insomnia.
- Hypodynamic. Provokes reduced activity, bad mood, excessive calmness. The child exists inside his own world; he reacts weakly to the changing reality. There may be problems with speech development, inadequate perception of smells and extraneous sounds.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome: diagnosis
Astheno-neurotic syndrome can develop in both children and adults. It is usually very difficult to diagnose due to the presence of somatic complaints that come to the fore. Teenagers often complain of headaches, pain in the heart, fatigue, and drowsiness.
In adults, the symptoms of asthenia are usually much more pronounced and varied. Manifestations of the disease are usually observed more intensely in the afternoon, and reach a maximum in the evening. Weakness and apathy, lack of desire to do any work and decreased concentration are noted. When performing exercises that require mental effort, difficulties in making decisions, absent-mindedness, irritability, and memory impairment are noted.
Emotional stress leads to increased symptoms, which can ultimately provoke the development of depression, neuroses, and neurasthenia.
In addition to the main symptoms, disorders of the autonomic nervous system may come to the fore, such as:
- tachycardia, palpitations, interruptions;
- blood pressure surges;
- increased sweating, feeling of chills and heat;
- decreased appetite, impaired digestive function;
- headache, dizziness;
- decreased libido.
Differential diagnosis
Astheno-neurotic syndrome often accompanies the initial stages of such somatic diseases as: Arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, angina pectoris; cerebrovascular accidents; atherosclerosis and others.
Therefore, we carry out differentiated diagnostics to exclude somatic pathology.
If you notice the above symptoms, then you should not delay. Make an appointment with our specialist and undergo differential diagnostics. Diagnosis of asthenia includes a comprehensive examination, the purpose of which is to identify the pathology that caused the disease.
Symptoms of ANS
Characteristic manifestations of asthenoneurosis are rapid fatigue and chronic fatigue. Children have difficulty shifting their attention, their thinking is inhibited, and their memory is weak. Schoolchildren are unable to concentrate in class, they are fussy, and motor reflexes are noticeable. Teachers usually recognize the initial phases of the syndrome as bad manners, so they complain to parents, but they are in no hurry to visit the clinic.
The next typical category of symptoms is psycho-emotional disorders. The child is subject to sudden mood swings for no apparent reason; he experiences nervousness and increased irritability. Usually there is a pathologically bad mood, which gradually develops into depression. Teenagers react too emotionally to even quite minor events. Typical symptoms of the disease are:
- moodiness;
- enuresis;
- frequent headaches;
- mood swings;
- weak immunity, prone to colds;
- irritability, manifestations of anger, aggression;
- increased sweating;
- loss of appetite;
- low academic performance;
- nausea in transport;
- poor social adaptation.
Asthenoneurosis is manifested by touchiness, the presence of phobias, aggression, and the search for physical ailments. Children feel broken and sick, although in reality there is nothing like that.
Astheno-neurotic syndrome: we recommend
It is recommended to eat foods rich in vitamin B and tryptophan (meat, bananas, beans, cheese and cottage cheese, dairy products, etc.). The amino acid tryptophan is responsible for the normal functioning of the nervous system - sleep, relaxation and emotional state, and is a source of the “happiness hormone” - serotonin.
Qualified specialists at the Transfiguration Clinic will help you create an effective therapeutic program, taking into account both the true cause of the disease and individual factors.
Asthenia, asthenic syndrome, types of asthenia in men and women
Neurologist, neuropathologist, reflexologist, reflexologist distinguish types of asthenia , types of asthenic syndrome : morning (morning), daytime (day), evening (evening), nocturnal (at night) asthenia (neurotics), neurocirculatory asthenia, functional or organic asthenia, mental asthenia ( psychological), psychogenic and physiogenic, cerebral asthenia, infectious (post-infectious), post-viral (post-viral, post-viral asthenia syndrome), alcoholic (post-alcoholic), sexual (post-sexual), tonic, hypersthenic, hyposthenic, somatogenic (somatic), neurocirculatory, agastric, skin , traumatic (post-traumatic), neurasthenia . Reflexotherapists, neurologists, neuropathologists distinguish various variants of asthenic syndrome: astheno-vegetative syndrome, astheno-subdepressive syndrome, astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome.
Astheno-vegetative syndrome is characterized by both manifestations of asthenia and severe autonomic disorders.
Astheno-subdepressive syndrome is a non-psychotic pathological condition characterized by mild melancholy with a feeling of loss of vitality and activity. Physical and mental fatigue, weakness, exhaustion, mental and emotional hyperesthesia, emotional lability, absent-mindedness and distractibility of attention are observed.
Astheno-hypochondriacal syndrome is characterized by a combination of asthenia with exaggerated concern for one’s health.
VSD (vegetative vascular, vegetative vascular dystonia) of mixed, hypotonic, hypertonic type.
List of used literature
- Grishchenko E.V. Methods for correcting asthenic syndrome in outpatient practice // “medical council”, 2012 - p. 36-37
- Kolyutskaya E. V. Modern approaches to psychopharmacotherapy of anxiety disorders // Pharmaceutical Bulletin: information and analytical newspaper. 2005. - p. 112-116
- Vein L. M., Voznesenskaya T. G., Vorobyova O. V. et al. Autonomic disorders: clinical picture, treatment, diagnosis / ed. A. M. Veina. M.: medical information agency. - 1998. - 752 p.