Causes of weakness
Wrong daily routine
Natural reasons that cause weakness are non-compliance with the daily routine, working seven days a week for 10-12 hours a day. Malaise is more often observed in middle-aged and older people, whose body is more difficult to adapt to overload. Fatigue occurs in the late afternoon after a hard day of work: general weakness, drowsiness, and heaviness in the muscles of the legs and arms appear. The condition is aggravated by a lack of sleep at night, in which case discomfort and powerlessness persist even in the morning. Similar symptoms occur in people who have to work night shifts.
Dehydration
With a lack of fluid, the work of the heart muscle is disrupted, vascular tone changes, blood circulation in the brain worsens, which is why general malaise develops. Fluid loss of up to 5% of body weight only slightly worsens the general condition: dry mouth, weakness in the legs, and poor exercise tolerance. Massive dehydration is caused by pathological causes: bleeding, generalized hyperhidrosis. In this case, weakness, dizziness and darkening of the eyes are observed; in the most severe cases, the patient cannot move his arms and legs.
Avitaminosis
For coordinated work, the body needs all microelements and vitamins, and the first sign of vitamin deficiency is nonspecific malaise. Most often, symptoms are caused by a lack of vitamin B12, which is involved in the process of hematopoiesis. With hypovitaminosis B12, there is severe weakness, intolerance to physical labor, typically flashing “spots” before the eyes and frequent dizziness. The patient's appearance changes: the skin becomes pale, the tongue becomes bright red, shiny, the nasolabial triangle turns blue.
With vitamin D deficiency, severe weakness in the muscles predominantly develops; muscle tremors appear when trying to play sports or even walk quickly. This cause of malaise is characterized by increased symptoms in the autumn-winter period, when daylight hours are short, and the production of cholecalciferol in the skin under the influence of ultraviolet radiation does not cover the body's needs for the vitamin. Fatigue and powerlessness are accompanied by body aches and joint pain. If you have such signs, you should visit a doctor.
Poisoning
After diarrhea and vomiting stop, toxic compounds circulate in the bloodstream, which are normally eliminated through the gastrointestinal tract. Weakness after poisoning lasts from several days to a week, since the harmful substances remaining in the body are eliminated extremely slowly. Nonspecific symptoms are observed, it is difficult for a person to perform usual work, and fatigue occurs after physical exertion. Characterized by dizziness and dull pressing pain in the head. If you are unable to recover from poisoning within a week, you should consult a doctor.
Allergy
In systemic allergic reactions to food, pollen or animal dander, large amounts of histamine and other active substances are released into the bloodstream. They affect the walls of blood vessels, causing a sharp drop in blood pressure, which is manifested by sudden weakness up to short-term fainting. Mild discomfort persists throughout the duration of the allergen's action; the symptom is often combined with rhinitis, lacrimation, and sore throat.
Vegetative-vascular disorders
The clinical picture of VSD is more common in young people in whom the processes of autonomic nervous regulation are not sufficiently balanced. The appearance of weakness is associated with disturbances in the interaction between the central nervous system and peripheral nerves, decreased vascular tone and circulatory pathology. Fatigue and malaise intensify under the influence of stress, poor nutrition, and physical fatigue. Characterized by periodic dizziness, attacks of weakness in the legs, hyperhidrosis, and presyncope.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
Causes from the heart cause a decrease in effective blood flow and a lack of oxygen in the most important internal organs. There is severe weakness, which is aggravated by physical activity. Worried about severe shortness of breath, interruptions in cardiac output. A similar condition in combination with high body temperature is observed in myocarditis and endocarditis. If, against the background of severe weakness, compressive pain in the heart appears with radiation to the arm, it is necessary to exclude an attack of angina pectoris or an incipient myocardial infarction.
Endocrine pathology
A feeling of weakness in the muscles, when everything literally “falls out of hand,” is characteristic of hypothyroidism. With a lack of thyroid hormones, the basal metabolism slows down, the mental and emotional state is disturbed, which is manifested by depression and apathy for no apparent reason. Malaise accompanied by severe headaches, thirst and polyuria indicates the development of diabetes mellitus. Severe weakness with muscle tremors and attacks of aggression is one of the signs of hypoglycemia caused by improper selection of insulin therapy.
Liver diseases
Asthenovegetative syndrome is the first manifestation of any liver pathology. Symptoms increase gradually, first appearing increased fatigue after a working day, making it difficult to concentrate and think. Then weakness persists constantly, patients refuse their usual physical activity or sports. When walking quickly or with minor exertion, shortness of breath and dizziness bother you. The reasons that cause such a clinical picture:
- Hepatitis
: viral, toxic, autoimmune. - Infiltrative processes
: fatty liver, glycogenosis, amyloidosis. - Vascular damage
: portal hypertension, hepatic vein thrombosis, pylephlebitis. - Hepatobiliary diseases
: cholangitis, bile duct strictures, cholestasis of pregnancy.
Gastrointestinal diseases
During inflammatory or dystrophic processes, the intestinal microflora is disrupted, as a result of which a large amount of harmful substances accumulates in the body, causing endogenous intoxication. The situation is aggravated due to insufficient absorption of beneficial food components in the small intestine. Patients feel constant severe weakness, heaviness in their arms and legs, and it becomes difficult for them to cope with their usual work. I am worried about periodic pressing headaches and dizziness, nausea, and lack of appetite. The main gastroenterological causes of weakness:
- Chronic inflammation
: hypoacid gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis. - Functional disorders
: esophageal dyskinesia, dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome. - Malabsorption syndrome
.
Depression
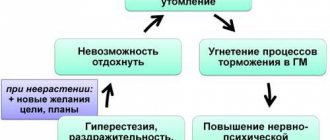
A depressive state is characterized by a variety of complaints: fatigue and weakness, constant muscle weakness up to the inability to move an arm or leg, loss of interest in work and hobbies. In difficult situations, a person lies motionless on the bed all day long, sleeping 14-16 hours a day. Often, weakness due to depression is accompanied by somatic disorders: lack of appetite, constipation, diffuse headaches and abdominal discomfort. Increased discomfort occurs after stress, conflicts with relatives or friends.
Neurological problems
Disorders of the peripheral nerves (plexitis, neuritis, polyneuropathy) cause severe weakness in individual muscle groups or in the entire limb. At the same time, active movements are significantly limited, while passive movements remain normal. If peripheral neuropathies are combined with disorders in the central nervous system, general malaise, apathy, frequent dizziness and darkening of the eyes are observed. Along with subjective symptoms, a slight tremor is felt in the affected muscles, the skin over them turns pale and thins.
Tumors
All oncological causes cause severe intoxication of the body with the decay products of cancer cells, to which brain structures and internal organs react acutely. Patients feel extreme weakness and fatigue not associated with physical activity. The malaise does not disappear even after a long night's sleep; on the contrary, in the morning I am bothered by weakness and headaches. Cancer intoxication leads to loss of appetite, aches throughout the body, and prolonged low-grade fever. Symptoms persist for several months.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Most often, weakness develops after the use of psychotropic drugs - sedatives, tranquilizers and antipsychotics. The drugs selectively inhibit the functioning of brain structures, increase the threshold of excitability of neurons, as a result of which malaise is accompanied by indifference to what is happening around. Symptoms also occur with the use of antihypertensive drugs, especially beta blockers. Weakness is caused by a decrease in cardiac output and changes in the circulation of vital organs.
Rare causes
- Kidney diseases
: chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, initial stage of renal failure. - Postoperative period
. - Brain damage
: severe head injury, meningitis and encephalitis, degenerative processes (Pick's disease, dyscirculatory encephalopathy). - Respiratory tract diseases
: COPD, bronchial asthma, pneumonia in the period of convalescence.
Vitamin deficiency
It is known that asthenia can be caused by a deficiency of certain vitamins and microelements, in particular vitamin D. Low levels of this vital nutrient in the blood can have a negative impact on performance and quality of life in general7. The results of clinical studies indicate that a decrease in the level of sunshine vitamin in the blood of women less than 29 ng/ml is associated with significantly more frequent complaints of increased fatigue compared with a level of more than 30 ng/ml8.
Many biochemical processes occurring in the body every day are accompanied by fluid loss, which is important to compensate. Research shows that even small amounts of fluid loss can lead to decreased energy levels, decreased concentration, and increased fatigue9.
Diagnostics
The primary examination is carried out by a general practitioner. The initial diagnostic stage consists of a detailed collection of all complaints, a history of the development of the disease, on the basis of which the presence of a certain pathology or risk factor is assumed. Then, based on the complaints, special laboratory and instrumental methods are prescribed that make it possible to confirm the probable causes of weakness. The most informative ones are:
- Neurological examination
. To study the functioning of the nervous system, cognitive functions are examined, and the time of occurrence of dermographism is measured. Specific tests (orthostatic and Danini-Aschner) reveal discoordination of sympathetic and parasympathetic regulation. The functional activity of the brain is clarified using EEG. - Blood tests
. A general blood test determines leukocytosis, hemoglobin and red blood cell levels. A biochemical study is carried out to assess liver function, detect signs of inflammation or residual electrolyte disturbances. The content of free T3 and T4 in the blood must be taken into account, and a fasting glucose test is done. - Coprogram
. If weakness occurs after symptoms of poisoning, it is necessary to do a microscopic examination of the stool and culture the material on nutrient media to detect pathogenic microorganisms. In case of prolonged dyspepsia for no apparent reason and malabsorption syndrome, stool is examined for the level of fecal elastase and specific antigen H. pylori. - Ultrasound examination
. If there are complaints from the digestive system, a survey ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space is performed. In women, the pelvic organs are additionally visualized. If there are signs of a pathological process, more informative examinations are recommended - endoscopy, radiography of the intestine using a contrast agent. - ECG
. In middle-aged and elderly patients, an electrocardiogram must be recorded in standard leads and with a load. For a detailed examination of the heart, 24-hour Holter monitoring is effective. To examine the anatomical features of the heart and identify signs of valve damage, echocardiography with vascular Dopplerography is performed. - Additional methods
. To study the respiratory system, a chest x-ray is taken. Spirography helps to assess the function of external respiration. If weakness is caused by a lack of thyroid hormones, scintigraphy of the thyroid gland with iodine is indicated to diagnose organic damage. MRI and CT scan of the brain will help rule out inflammation and degenerative changes.
Unbalanced diet
A number of studies have found that consuming excess amounts of simple carbohydrates can make you feel tired during the day. This is due to the ability of these nutrients to quickly increase blood glucose levels, which in turn leads to the immediate production of large amounts of insulin, which removes sugar from the blood into the cells. A sharp increase and subsequent equally sharp decrease in sugar levels causes a feeling of fatigue4.
Another reason for increased fatigue is a low-calorie diet. When there is a negative balance between calories in food and energy expenditure, metabolism slows down, which can be associated with a feeling of fatigue. To prevent a slow metabolism, most people need to consume at least 1,200 calories per day5.
It is important to consume enough protein, which increases your metabolic rate more than carbohydrates and fats5. In addition, research shows that fatigue is reduced by increasing the content of branched-chain amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. Therefore, to keep your metabolism high enough to prevent fatigue, you should consume protein at every meal6.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If weakness is caused by natural causes, it is enough to normalize your lifestyle. Patients are recommended to get a full night's sleep of at least 7 hours, avoid night shifts at work, and minimize stressful situations and conflicts. A change of environment helps to cope with fatigue - a trip to a sanatorium, a vacation at sea. It is important to provide a nutritious diet high in protein foods, fresh vegetables and fruits. It is advisable to completely avoid alcohol. For prolonged weakness, combined with other symptoms, the doctor selects treatment.
Normalizing your lifestyle is the first step towards combating loss of strength
Conservative therapy
The main treatment for general malaise is therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of symptoms: taking antihistamines for allergic reactions, cardiotropic drugs for cardiovascular diseases, hepatoprotectors for liver damage. For weakness after food poisoning, a diet excluding spicy and smoked foods and extractive substances is recommended. Symptomatic medications are used that improve overall well-being and restore performance. The most effective are:
- Adaptogens
. Concentrated plant extracts of ginseng, eleutherococcus and other medicinal plants tone and invigorate, increase the activity of metabolic processes. Medicines are taken for a long time, they have virtually no contraindications or side effects. - Nootropics
. The drugs stimulate blood circulation in the brain and ensure the delivery of nutrients to neurons. Nootropics improve cognitive functions of the brain, increase memory and concentration. The drugs are used for encephalopathy, the consequences of head injury and encephalitis. - Antidepressants
. Specific serotonin receptor agonists as etiotropic therapy help with depressive disorders. In minimal doses they are indicated for chronic fatigue and malaise caused by severe diseases of the internal organs and endocrine glands. - Vitamins
. For peripheral neuropathies and other neurological disorders, B vitamins are prescribed. To improve general well-being and normalize metabolism, ascorbic acid and the antioxidant tocopherol are used. Vitamin preparations are combined with essential microelements. - Sorbents.
Preparations based on activated carbon are effective for ailments caused by poisoning. The products bind and remove toxins from the gastrointestinal tract. In case of severe intoxication, parenteral administration of infusion saline solutions is necessary.
Physiotherapy
To reduce weakness, various methods of hydrotherapy (Charcot's shower, contrast shower) are useful, which have a general strengthening and tonic effect. A similar effect is observed after using acupuncture and electromagnetic therapy. To improve muscle tone and endurance, a general massage is prescribed and an individual exercise therapy complex is selected. People suffering from depressive conditions require long-term psychotherapy in several areas: auto-training, cognitive behavioral therapy, gestalt therapy.
Sleep disorders
One of the most obvious causes of increased fatigue is chronic lack of sleep. During sleep, hormones are released that regulate metabolism and energy levels, and toxic metabolic products that accumulate during activity are removed. The metabolic rate is significantly reduced, which allows for recovery processes10.
According to modern recommendations, the optimal duration of night sleep for adults should be an average of seven hours. In this case, sleep should be calm and uninterrupted. Taking a short nap during the day can also help boost your energy levels during the day. Studies have proven that a set sleep schedule with a clear time frame for falling asleep and rest duration can reduce fatigue and eliminate sleep problems10.
At the same time, prolonged sleep during daylight hours contributes to disruption of circadian rhythms and disruption of the biological clock. This is another common cause of chronic fatigue. Disturbances in circadian rhythms are also associated with jet lag, night shift work, regular lack of sleep, the habit of falling asleep with a light source, and other factors10.
How does senile asthenia manifest?
This condition does not appear suddenly: at first the elderly person is active, quite energetic, and not physically limited. Then he begins to develop various diseases (of the joints, nervous system, heart, digestive organs), which are practically not expressed, but still somewhat reduce the quality of life. Over time, the symptoms of chronic diseases become more pronounced, worsen the quality of life, but still respond well to therapy.
The stage, which is already considered to be senile preasthenia (that is, which precedes the development of asthenia), looks like frequent exacerbations of chronic diseases, decompensation of some of them, because of which the quality of life begins to suffer more severely.
Mild senile asthenia then develops: the person loses weight, his memory, vision or hearing deteriorate, and it becomes more difficult for him to walk within his usual route. But he can still have difficulty going out and even going to the store.
Moderate frailty is when weakness and impairment of either the ability to think well or coordination result in an older person requiring long-term care. Relatives can no longer simply prepare food for him and leave: they need to feed him, take him outside (to a bench), and walk him to his bed. If such a person is hospitalized, his condition also requires the almost constant presence of relatives (unless we are talking about a specialized boarding house).
The progression of asthenia leads to a severe decrease in memory, constant coordination problems, as a result of which the person becomes very unstable. He can no longer go outside, he needs to be taken to the toilet and to bed, put food on a plate and pour water, help him eat and perform hygiene procedures. Such a person needs to wear a diaper, as he suffers from constant urinary and sometimes fecal incontinence. He also needs to either be given laxatives (from time to time or constantly) or have enemas.
Prevention of chronic fatigue syndrome
The occurrence of chronic fatigue syndrome can be prevented if you properly organize your lifestyle: nutrition should be healthy and balanced, psychological and physical stress should be adequate, and the daily routine should be proportional.
In any work process it is necessary to take short breaks, i.e. They worked for an hour or two and broke off for a short rest. This is especially necessary for those who are engaged in monotonous work. And, of course, don’t forget about vacations, during which you can travel to change your surroundings and get a lot of new experiences.
Primary appointment with a neurologist: 1850 RUR.
Sign up Online 5% discount when registering from the site
What is senile asthenia
Senile asthenia syndrome is a condition characterized by age-related changes in the body, primarily in the musculoskeletal, immune, central nervous and endocrine systems.
It includes more than 85 different syndromes, which are manifested by such main symptoms as:
- general weakness;
- slowness;
- loss of more than 4.5 kg of weight without dieting in a year;
- deterioration of memory and ability to analyze;
- falls;
- depression;
- urinary incontinence;
- sensitivity disorders;
- deterioration of hearing and vision.
All these symptoms usually appear against the background of various diseases, which makes diagnosis difficult. In addition, senile asthenia itself is often the cause of mental disorders, the manifestations of which can be very similar to diseases of the heart, nervous system, intestines or other organs. Therefore, the main treatment of older people should be carried out by a geriatrician. Only he can isolate individual diseases from the “bouquet” and prescribe their treatment. In addition, it is this doctor who must monitor the many prescriptions of narrow specialists and reduce them to a minimum so as not to overload the liver, which also experiences age-related changes.
In the English-language literature, senile asthenia syndrome is called “frailty,” and older people in whom it manifests itself are called “frail.”
Anemia
Anemia (anemia) is a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells and a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein that gives blood its red color. It helps cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
The body of a person suffering from anemia simply does not receive enough oxygen, which is why one feels general weakness, fatigue, sudden changes in mood and “fog” in the head.
Common symptoms of anemia
Here are some of the most common symptoms of anemia that adults typically experience:
- fatigue, lethargy, lack of energy;
- pale skin;
- fast or irregular heartbeat;
- shortness of breath, breathing problems;
- chest pain;
- dizziness or loss of stability;
- decreased concentration;
- decreased body temperature;
- headache.
Treatment of anemia
First of all, the cause of regular fatigue should be clarified with your doctor. People tend to self-medicate, which is absolutely not worth doing.
Treatment of anemia can be either therapeutic or surgical. Therefore, you should not delay your visit to the doctor and turn a blind eye to general malaise.