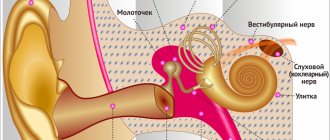
The brain is the main organ of the central nervous system. It consists of more than 35 billion cells. There are 5 parts of the brain that interact with each other using neural connections:
- Oblong. Responsible for protective reflexes (sneezing, coughing, vomiting), food (sucking, salivation, swallowing) and cardiovascular (regulation of the heart and blood vessels, as well as breathing and hearing).
- Posterior section. His “conscience” includes facial expressions, chewing reflexes, balance and muscle function.
- The middle one is responsible for muscle tone and skin pigmentation.
- Intermediate regulates metabolism, cardiovascular activity and sleep.
- The final (large) is the highest center of mental activity. Responsible for smell, hearing, vision, movement.
call me back
Common Causes
At the initial stages of diseases, it is very difficult to detect them, since most of them occur without visible symptoms, or are manifested by minor pain.
The following internal and external causes can lead to the disease:
- severe infections that entered through wounds, insect bites, respiratory tract or blood/lymph from other infected areas of the body;
- trauma to the skull;
- chemical poisoning;
- excessive exposure to radiation;
- adherence to bad habits, systematic intoxication with alcohol, tobacco, drugs or certain medications;
- poor quality of food;
- genetic predisposition to brain destruction;
- congenital disorders.
Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis, determining the type of dementia and the degree of development of the probable causes of the disease, can only be made by a doctor (neurologist or psychiatrist). To do this, data is collected on the signs and course of the disease, the patient himself, close friends and relatives living with him are interviewed. Various medical examinations are carried out: cerebral vascular examination, blood tests, MRI... The patient is tested using neuropsychological screening scales.
Types of diseases
In clinical practice, and then in theory, a huge number of pathologies leading to malfunctions of the central nervous system were identified. The most common of them can be highlighted in a list:
- Vascular aneurysm. It is a pathogenic expansion of the vascular wall, which loses elasticity and risks rupture, leading to internal hemorrhage. It is very difficult to save a person in such cases.
- Atherosclerosis. Appears when there is micro-trauma to the vascular wall, at the site of damage a cholesterol plaque forms, and then a blood clot. The lumen of the blood channel becomes clogged, blocking the path to oxygen and microelement nutrition of neurons, which is why they begin to die.
- Stroke. A vascular anomaly that often develops in old age. Leads to the death of areas of the brain (BM) in which blood circulation is disrupted. In the hemorrhagic form of the attack, the canals rupture, leading to internal hemorrhage, and it is very difficult to save the patient. Ischemic stroke is less dangerous but more common.
- Alcoholic encephalopathy. Systematic drinking of alcohol leads to gradual, non-renewable death of neurons, as a result of which a person loses cognitive abilities, intelligence, and psycho-emotional stability.
- Intracranial hypertension. It manifests itself as high intracranial pressure caused by the growth of a tumor, cyst or aneurysm inside the head.
- Malformation. Congenital defect in the structure of the vascular network.
- Alzheimer's disease. Excessive production of a pathogenic protein enzyme that accumulates in brain tissue and destroys nerve cells. Next, the functioning of internal systems and organs fails, after which death occurs.
- Various tumors. Neoplasms from aggressively growing cells of the body.
- Epilepsy. Impaired bioelectrical function of the brain, as a result of which periodic convulsions develop.
- Hydrocephalus. It is characterized by impaired exchange of cerebrospinal fluid, which begins to accumulate in the intracranial cavities. There is constant pressure on the brain, which causes its functioning to suffer.
The signs of all these diseases are largely similar, if you do not take into account specific manifestations, which almost do not appear in the early stages.
Dementia - senile dementia
Age-related disorders of brain activity, called dementia - acquired (or senile) dementia, are caused by the death of nerve cells in the brain and manifest themselves in a decrease in mental activity, impaired memory, speech, consciousness and behavior of the sick person.
The problem is based on degenerative changes (atrophy) of brain cells and vascular disorders, leading to a lack of blood circulation and oxygen supply to the brain tissue.
According to statistics, the first, subtle symptoms in the form of partial, temporary loss of memory, time orientation and loss of some habitual skills can appear after 50 years. By the age of 60, about 3% of older people have been diagnosed with dementia. By the age of 80, 25% of the inhabitants of our planet suffer from various types of dementia.
When is it time to go to the doctor?
Only a medical specialist can understand what is happening. If discomfort in the head, neck or upper back appears sporadically, for example, when the weather changes, and then disappears without a trace for a long time, there is usually no cause for concern. If you suspect a cold, headache from fatigue, physical or mental stress, just rest. But if you experience the following symptoms, you should definitely go to the doctor:
- previous head injuries with and without complications;
- feverish condition;
- blurred perception;
- muscle tension in the neck or back of the head;
- sudden painful shootings;
- loss of sensation in the arms or legs;
- convulsions;
- problems concentrating your eyes or thoughts;
- bulging of the fontanelle in the newborn period.
Even short-term loss of vision or hearing is also a serious reason for medical intervention.
Signs of dementia
The aging process is always accompanied by various changes in human behavior, but changes are different from changes. Indirect signs of senile dementia in a person may include the following behavioral deviations:
- Experiences temporary memory lapses;
- Forgets the location of ordinary things in the house, while accusing loved ones of theft;
- Experiences frequent sudden changes in mood;
- Often becomes depressed and loses interest in life;
- Loses simple household skills (tying shoelaces, boiling a kettle, turning on the TV...);
- Experiences problems with speech (slowness, distortion of speech);
- Ceases to understand interlocutors, repeatedly asks to repeat what was said;
- Loses orientation in time and space;
If you notice such symptoms in a loved one, you should contact specialized institutions. According to doctors, the progression of the disease can be slowed down with proper medical care.
How to correctly identify the disease?
As soon as a preliminary history is collected, complaints are heard, first assumptions about a possible disease are made, a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed, which includes the following procedures:
- Laboratory blood analysis.
- Radiography.
- Electroencephalography.
- Angiography.
- MRI of the brain.
- CT scan of the skull or cervical spine.
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck.
The most informative techniques are tomographic sessions. They give a complete picture of the existing changes in tissues and the root cause of the pathology. Even microscopic abnormalities, precancerous stages, and vascular abnormalities clearly appear on scans in one short procedure.
To undergo a full examination at a specialized tomography center, just contact our service, which works free of charge. Choose CT or MRI services, consider offers from different clinics in the city, compare options based on prices, equipment, ratings and other criteria. Here you can remotely consult on existing questions and sign up at your favorite institution with discounts from the service. Contact us, we will be happy to help you.
Treatment of organic pathology and mental disorders
First of all, the cause of organic pathology should be established. Treatment tactics will depend on this.
In case of infectious pathology, antibiotics sensitive to the pathogen should be prescribed. For viral infections - antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. For hemorrhagic strokes, surgical removal of the hematoma is indicated, and for ischemic strokes, decongestant, vascular, nootropic, and anticoagulant therapy is indicated. For Parkinson's disease, specific therapy is prescribed - levodopa-containing drugs, amantadine, etc.
Correction of mental disorders can be medicinal and non-medicinal. The best effect is shown by a combination of both methods. Drug therapy includes the prescription of nootropic (piracetam) and cerebroprotective (citicoline) drugs, as well as tranquilizers (lorazepam, tofisopam) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine). To correct sleep disturbances, hypnotics (bromizoval, phenobarbital) are used.
Psychotherapy plays an important role in treatment. Hypnosis, auto-training, Gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, and art therapy have proven themselves well. This is especially important when treating children due to possible side effects of drug therapy.
Information for relatives
It should be remembered that patients with organic brain damage often forget to take prescribed medications and attend a psychotherapy group. You should always remind them of this and ensure that all doctor’s instructions are followed in full.
If you suspect a psychoorganic syndrome in your relatives, contact a specialist (psychiatrist, psychotherapist or neurologist) as soon as possible. Early diagnosis is the key to successful treatment of such patients.
Restoring brain function after coronavirus
The ability to objectively assess a patient's brain function helps to avoid misdiagnosis and provide appropriate treatment if necessary. Doctors emphasize that with timely detection of changes and proper treatment, the patient can quickly return to normal life.
Recovery at home is ineffective; only a doctor should be involved in diagnosis and treatment.
The doctor begins treatment for headaches after coronavirus with a comprehensive examination of the patient. Additionally, an encephalogram or magnetic resonance imaging may be prescribed as a diagnosis. In transcripts of studies, focal lesions of different lobes of the brain are often indicated. Most often, deformations cover the temporal region, in which there are centers responsible for the ability to perceive tastes and smells, analyze and understand speech.
Brain dysfunction is usually recoverable. Drug treatment is primarily aimed at improving blood circulation in the brain. In severe cases, complete rehabilitation becomes more difficult, but treatment and continuous memory development can improve the condition. Studies have found that constant brain training, including a series of special exercises, can achieve structural changes in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. The development of memory and attentiveness contribute to an increase in the density of contact of gray cells.
Care, recovery, rehabilitation, elderly people with dementia
Our boarding house staff have the necessary skills and experience working with patients suffering from various cognitive impairments. Our nurses and carers know how to care for older people with memory loss and ensure their safety. We provide:
- adapted, safe premises for people with brain disorders;
- constant supervision by trained staff of the boarding house;
- balanced dietary nutrition, taking into account age needs and medical recommendations;
- assistance to residents of the boarding house in eating, hygiene procedures, careful care for bedridden patients;
- necessary medical procedures, exercises to support cognitive skills, motor skills;
- psychological assistance during rehabilitation.