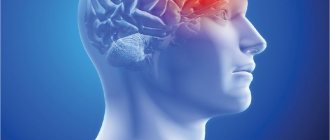
The trigeminal nerve is a ganglion that gives rise to three “branches” that exit directly from the brain stem. Three “branches” reach directly to the human face, supplying it with nerves and connecting it with the central nervous system.
The trigeminal nerve exits the skull through three different foramina. The first “branch” comes out through symmetrical points that are located slightly above the person’s eyebrows (the so-called ocular process). The second, emerging, passes along both sides of the nose (just below the eye area and close to the cheeks) and is therefore called the maxillary, the third “branch” exits in the lower jaw (mandibular) in the direction from the corners of the mouth to its center.
With inflammation of various processes of the trigeminal nerve, pain is observed, localized in various places of the face. When the first “branch” is inflamed, pain occurs above or below the brow ridge, in the forehead and in the front part of the temporal region of the head. When the second and third “branches” of the trigeminal nerve become inflamed, pain occurs in the upper and lower jaws, respectively, which, in turn, causes severe toothache.
Next, we will talk about the types of neuralgia, causes and methods of treatment. But if you are experiencing unbearable pain right now, make an appointment with us. When making an appointment, tell the administrator that you need emergency assistance, and they will find an appointment for you as soon as possible. An appointment with a dentist can be made by calling 8 or using the online appointment form.
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two types. The first, the so-called true trigeminal neuralgia, is a holistic disease caused in most cases by compression of the nerve or disruption of the blood supply. The second type - secondary trigeminal neuralgia - is a symptom of a general disease of the body. It could be a tumor or a serious infection.
In most cases, doctors diagnose inflammation of one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve, but in some situations inflammation of two or three processes occurs at once. Inflammation can affect either one side of the face or both, and in different combinations.
General information about the disease
The auricular autonomic node is called a ganglion. It is a collection of interneurons of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve pathways. Parasympathetic fibers enter the node through the branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve, and sympathetic fibers through the plexus of the middle meningeal artery. Postganglionic fibers are part of the auriculotemporal nerve, which in turn is a branch of the trigeminal nerve. They extend to the temporal region and the ear gland, providing autonomic innervation of the vessels and gland.
Neuralgia of the ear ganglion can be classified as vegetative ganglionitis of the head. This category of pathologies includes:
- Ciliary ganglionitis;
- Neuralgia of the sublingual and submandibular node;
- Cervical truncite;
- Ganglionitis of the superior cervical sympathetic and pterygopalatine nodes.
According to statistics, neuralgia of the auricular nerve most often affects young and middle-aged women.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Doctors believe that the main cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is compression of it either inside the skull or outside it. Inside the skull, the trigeminal nerve can be compressed as a result of the formation of tumors, in most cases resulting from some kind of head injury.
Also a fairly common cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is internal venous or arterial displacement.
Other causes of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, viral or bacterial infection in the body;
- herpes infection (herpes);
- a brain tumor;
- scarring in the brain stem;
- failure of anesthesia during treatment or tooth extraction.
Most often, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve affects women at pre-retirement and retirement age (usually from fifty to seventy years). If trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed in a young man or girl, then most likely its cause is a change in the arteries of a sclerotic nature or a strong dilatation of blood vessels.
Why does this pathology occur?
The etiopathogenetic mechanism of the development of the disease is irritative. /
It develops reflexively if pathological vegetative impulses are received from chronic infectious foci or somatic organs suffering from an inflammatory process.
Diseases that are localized directly next to the ear node are especially dangerous.
These include:
- Periodontitis;
- Gingivitis;
- Stomatitis;
- Periodontitis;
- Ethmoiditis;
- Sinusitis;
- Frontitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Tonsillitis;
- Purulent otitis;
- Stones in the parotid gland;
- Sialadenitis;
- Mumps.
Neuralgia of the auricular nerve, provoked by a general infectious process, is less common. The primary diseases in this case include:
- Syphilis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Protracted sepsis.
Also, the root cause of neuralgia can be a separate infectious focus:
- Urethritis;
- Cystitis;
- Pyelonephritis.
Or somatic diseases:
- Cholecystitis;
- Cirrhosis;
- Gastroduodenitis;
- chronic renal failure;
- Adnexitis.
Sometimes the provoking factor is an endocrine disorder: diabetes mellitus or hyperthyroidism.
How does inflammation of the trigeminal nerve manifest?
The main symptom of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is severe pain that occurs in the facial part. The pain really has a powerful force and shooting character, so it is very difficult for the patient to calmly endure painful attacks. The pain intensifies when performing the slightest actions with the facial muscles and jaws - yawning, chewing, laughing, and performing daily oral hygiene. At the same time, the sensitivity of the skin on the inflamed side of the face decreases.
The next painful attack is accompanied by a rapid dilation of the patient’s pupils and the same rapid contraction of facial muscles. Increased tear production may begin.
Pain with trigeminal neuralgia is severe, but not constant. The pain occurs for a few seconds and is interrupted for a while. But if the intervals between painful attacks are short, then it seems that the pain is constant. Trigeminal neuralgia is dangerous because the interval between attacks can be several weeks, and sometimes even several months. But after this period, the pain will certainly return. A long break does not mean that the disease has passed, so if you have already noticed symptoms of neuralgia once, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of neuritis
The main symptoms of neuritis are:
Pain along the nerve
The most common symptom of neuritis is pain along the affected nerve. The pain, as a rule, is dull in nature and intensifies in the cold, with physical activity or uncomfortable body position.
Sensory impairment
Sensory loss in the area of the affected nerve is common. It can manifest itself in the form of numbness, tingling, or “pins and needles.”
Decreased muscle activity
There is a partial decrease in muscle strength (paresis), a decrease or loss of tendon reflexes, and in some cases, muscle paralysis (complete cessation of muscle activity).
Vegetative and trophic disorders
With neuritis, there may be such vegetative and trophic disorders as depigmentation of the skin, the acquisition of a bluish tint, local hair loss, increased sweating and dry skin, swelling.
Why do teeth hurt when the trigeminal nerve is inflamed?
How is inflammation of the trigeminal nerve related to teeth? The connection here is the most direct. Firstly, severe pain during attacks “radiates” to the upper or lower jaw (depending on which nerve extension is inflamed), and sometimes to both jaws. This causes severe and unbearable toothache.
Secondly, those nerves that are found in the upper and lower teeth and gums are directly connected to the trigeminal nerve. The second branch of the trigeminal nerve innervates the upper teeth and gums, and the third, respectively, the lower jaw and gums.
The trigeminal nerve can also be damaged during a number of dental manipulations. Unsuccessful tooth extraction or improper filling, surgical intervention in the jaw structure that ended unsuccessfully, and injuries can cause trigeminal neuralgia.
It is very important to distinguish inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from other diseases of the oral cavity, in particular pulpitis - inflammation of the internal dental tissues. A characteristic sign of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is that, despite severe pain, the sensitivity of the teeth does not increase when they come into contact with cold and hot foods, and hypothermia or heating does not provoke the onset of a new pain attack. Acute tooth sensitivity is a symptom of pulpitis.
When the trigeminal nerve is damaged in the jaw area, acute toothache, pain in the chin, ears and sometimes in the lower lip occurs. The pain may become increasingly intense, and often the patient continues to feel a dull ache after the attack.
Briefly about the ear
Forming an idea of the structure of the ear allows you to understand in which parts pain may occur and what causes it. The organ is one of the most complex in the human body; it consists of three sections:
- Outer ear. This area includes what is accessible for visual inspection without the use of additional devices. We are talking about the concha and the visible part of the ear canal;
- Middle ear. This part is hidden from view and includes the tympanic cavity and the auditory ossicles. Protection of this section is provided by the temporal bone;
- Inner ear. This is the most complex section; its components are represented by bone canals. Its task is to convert incoming sounds into impulses that are transmitted to the brain and recognized there. Also, this department includes the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for human coordination and balance.
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The first stage of treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is medication. It is aimed at reducing the strength and frequency of pain in the patient. Most often, doctors prescribe anticonvulsants to a patient suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. Sedatives are also used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as resorption therapy to relieve the inflammatory process, have a good therapeutic effect. Next, the doctor may recommend the use of laser treatment, in which the laser is directed cutaneously to the area where the processes of the trigeminal nerve exit the skull.
Our clinic is located in the same building as the multidisciplinary clinic “Diamed on Shchelkovskaya”, where special conditions for receiving physiotherapeutic procedures are organized for dental patients. The clinic’s physiotherapy room is equipped with modern equipment, including a laser physiotherapy device, with which you will feel relief after the first procedure. The pain will go away and you can return to normal eating. Make an appointment with a dentist by calling 8 or using the online appointment form. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and refer you for treatment.
If you are in severe pain, but for some reason you have not yet made an appointment with us, then it can be relieved with folk remedies. Take one tablespoon of yarrow, pour a glass of boiling water, let it brew for one hour and strain. The tincture should be taken one tablespoon before meals three to four times a day.
Diagnostic methods
Very often, patients come for help to an otolaryngologist or dentist, and doctors of this specialty refer them to a neurologist. To make a diagnosis, the neurologist collects anamnesis, palpates Richet's points and sclerotomal points of the mandibular, auriculotemporal and mental nerves. On palpation there is a sharp pain. Hyperalgesia of the parotid region confirms neuralgia. To clarify the diagnosis, a lidocaine or novocaine blockade can be performed.
It is very important to correctly determine the etiology of the disease. For this you need:
- Dental examination;
- Audiometry;
- Ultrasound of the parotid salivary gland;
- Rhinoscopy;
- Otoscopy;
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses.
- Pharyngoscopy.
In some cases, consultation with a gastroenterologist, urologist, endocrinologist may be required, as well as gastroscopy, ultrasound of the kidneys or abdominal cavity, and analysis of thyroid hormones.
Neuralgia should be distinguished from otitis media, cysts and stones of the parotid gland, tumors, mumps and eustachitis.
Solving the problem competently: choosing headphone tips
What should a modern person do who cannot imagine his life without listening to music or watching movies on headphones?
To eliminate the problem and minimize the risk of ear pain, we can recommend using quality ear tips. They are made individually from an impression of the ear canal using innovative 3D modeling techniques. Due to the precise repetition of the contours and dimensions of the ear opening, reliable fixation and perfect fit are ensured. As users note, over time you completely forget that there is an accessory in your ears. With such attachments it is very convenient to do your usual work and play sports. They do not fall out even when performing active exercises or intense loads.
The proposed solution has other advantages.
Such accessories:
- perfectly absorb sounds, suppress noise (up to 26 dB);
- allow you to avoid discomfort when wearing;
- significantly improve sound quality;
- delight with a rich palette of colors and long service life;
- can be equipped with a special antibacterial coating;
- pay for themselves in the first year of use.
Custom ear tips are the surest way to eliminate any chance of hearing loss or suffering from hearing aid pain.
Use a safe and comfortable solution!
Therapy
To quickly stop paroxysms of vegetalgia, you need to take analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. These include:
- Acetylsalicylic acid;
- Metamizole sodium;
- Novocaine blockades;
- Aminophenazone.
These drugs are combined with ganglion blockers, sedatives and antispasmodics. If necessary, the patient is prescribed sleeping pills. To achieve an additional analgesic effect, ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone or electrophoresis with novocaine on the ear area is indicated.
Vascular and metabolic therapy is also required:
- A nicotinic acid;
- B vitamins;
- Pentoxifylline.
Antihistamines will help reduce swelling. If symptoms characteristic of irritation of parasympathetic fibers predominate in the clinic, anticholinergic therapy is required: diphenyltropine, platyphylline.
In case of intolerance to drug therapy, the following is required:
- Magnetic puncture;
- Acupuncture;
- Laser punctures.
During convalescence, amplipulse therapy, DDT, and electrophoresis with hyaluronidase can be prescribed.
To effectively treat neuralgia, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of the disease. Treat an inflammatory or infectious focus, regularly carry out sanitation of the oral cavity and therapy for chronic somatic diseases. Correction of endocrine disorders is also necessary. According to indications, surgical dissection of adhesions, removal of tumors and parotid stones, maxillary sinusotomy, ethmoidotomy, etc. may be prescribed.
The following are the causes of ear pain:
- Otitis.
- Presence of sulfur plug.
- Wearing uncomfortable headphones for a long time.
- Listening to music that is too loud.
Prevention
Preventive procedures involve eliminating factors that cause pathology:
- Identify and eliminate pathologies of the ENT organs in a timely manner, without leading to relapses.
- Do not use ototoxic drugs.
- Patients who constantly interact with complex production factors should undergo audiometry 2 times a year.
- We need a healthy lifestyle.
- Multivitamins should be taken in spring and autumn.
- Ears need to be covered with something in production where it is noisy.
- Use a hat in winter.