The appearance of signs of a burning sensation in the head clearly indicates the passage of a pathological process in the body. A burning sensation can occur in any part of the head, gradually gaining strength. Peculiar sensations rarely occur just once; they usually cause anxiety over a long period of time. People who do not pay attention to this symptom because of its relativity greatly risk their health. It is better not to wait for the situation to worsen and the level of performance to decrease, but to immediately seek help from a specialist.
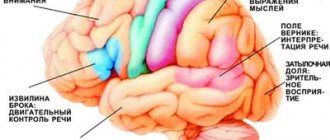
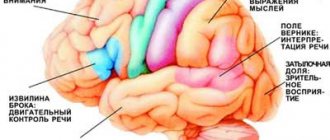
A burning sensation in the head cannot arise out of nowhere; it is usually a symptom of some disease. To understand what kind of disease it is, first of all, you need to determine the localization of this pain syndrome. Pain may occur:
- in the neck area;
- in the crown area;
- in the back of the head;
- in the temporal part of the head;
- on the left or right side of the head;
- at the top or crown of the head.
You may also feel a girdling malaise. It is imperative to consult a specialist if there is a burning sensation from the inside of the crown without clear localization.
Causes of burning in the head
A burning sensation in the head can act as a factor in possible severe consequences. It is necessary to carefully study its origin, since properly structured qualified treatment depends on it.
The most common causes of a burning sensation in the head are:
- Hormonal imbalances . This category includes menstrual irregularities, menopause, improper use of contraceptives, diseases of the paired female reproductive glands, and increased or decreased functioning of the thyroid gland. A failure in the hormonal system can be confirmed by taking hormone tests, as well as consulting a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
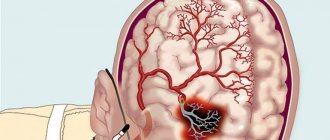
- Osteocondritis of the spine. Osteochondrosis of the spine in the modern world is increasingly occurring in young people. The main sign of its appearance is a burning sensation in the back of the head. The reason for the occurrence of this symptom in osteochondrosis is a violation of blood circulation and nerve transmission, so general therapy for a burning sensation in the head will consist of treating the osteochondrosis itself.
- Overwork of the body. Due to fatigue, stress, lack of sleep, and nervous tension, blood stagnation occurs, leading to a burning sensation in the head.
- Bad habits. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and drugs are factors that cause blood retention in the blood vessels, which contributes to a burning sensation in the head.
- Hypertension. When blood pressure rises, vascular insufficiency occurs, causing a burning sensation in the back of the head.
Treatment of hot flashes
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of hot flashes and is prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis has been established, taking into account all individual aspects. For example, if hot flashes are caused by an overactive thyroid gland, a drug will be prescribed that suppresses the production of the hormone. If a feeling of heat is a harbinger of menopause, estrogen or, if there are contraindications, special non-hormonal therapy may be prescribed. In cases where hot flashes occur as a result of various external and physical factors (being in a stuffy room, intense exercise, stress, eating spicy food, alcohol, etc.), it is enough to eliminate these causes and normalize your daily lifestyle.
General diagnosis for burning in the head area
Based on external and internal manifestations of signs of the disease alone, therapy is not carried out. To establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a number of studies and pass the necessary tests:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- examination by an ophthalmologist;
- echoencephalography of the brain to exclude the presence of tumors;
- monitoring blood pressure levels over the course of a day or several days;
- study of electrical activity of the brain;
- conducting MRI to assess the condition of tissues and blood vessels.
In some cases, consultation with a psychiatrist or psychologist may be necessary.
The modern rhythm of life gives impetus to the development of various diseases based on psycho-emotional instability. Without identifying these problems and starting to work in this direction, treatment will not give the desired effect. Information belongs to the site rew-med.info
How to treat a burning sensation in the head?
There is no general method for getting rid of a burning sensation in the head. Based on the causes and scenarios for the development of this condition, as well as the physiological characteristics of the body, the doctor prescribes individual treatment for each patient.
The most commonly used techniques for a burning sensation in the head:
- Physiotherapy: exposure to magnetic fields, magnetic stimulation of the cerebral cortex, electrosleep therapy, exposure to electric current, medicinal electrophoresis.
- Treatment with drugs: neurometabolic therapy, removal of excess water from the body, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, taking antipsychotics and antidepressants.
- Psychotherapy: emotional-imaginative therapy, trance induction techniques, cognitive behavioral psychotherapy, psychoanalysis.
- Massage, physical therapy and manual pressure.
- Acupuncture.
- Medical nutrition.
- Therapy with mineral waters and medicinal mud.
- Complete lack of sleep.
In most cases, the above treatments help eliminate the burning sensation in the head. Depending on the severity of the condition, three treatment regimens can be recommended: home, inpatient daytime and inpatient permanent.
Preventing a burning sensation in the head
In order not to encounter a painful burning sensation in the head area, you must follow the following preventive recommendations that will help prevent the development of an unpleasant symptom:
- spend more time outdoors;
- walk more;
- watch your posture, try to keep your back straight;
- eat healthy, fresh, vitamin-rich food;
- consult your doctor about taking hormonal medications and contraceptives;
- maintain a good sleep schedule;
- engage in physical activity that has a relaxing effect: Pilates, yoga, qigong gymnastics, calanetics, wushu;
- give up bad habits;
- undergo treatment with a psychotherapist;
- properly treat all diseases of the ear, nose and throat (sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, otitis);
- Learn and practice techniques for quickly calming down in stressful situations (proper breathing, meditation, etc.).
Information belongs to the site rew-med.info
Related posts:
- Hyperkinesis with developmental delay Translated from Greek, “hyperkinesis” means “supermovement”, which accurately reflects...
- Urbach-Wiethe disease Urbach-Wiethe disease is a rare genetic disease that leads to complete...
- Burning in the sternum, what it means and what it can lead to. Pain and burning in the chest are quite common symptoms,…
- The bacterium Helicobacter pylori is the cause of gastritis, cancer and stomach ulcers. Helicobacter pylori is a unique pathogenic microorganism that is the causative agent of such a dangerous...
Why does the crown of my head hurt?
Physiological reasons
Pain may occur the morning after alcohol abuse, due to fatigue, or excessive physical exertion. In some people with weather dependence, painful sensations when the weather changes are localized precisely in the parietal zone, although other options are possible (temples, back of the head, entire head). Sometimes the symptom is triggered by stress. A fairly typical situation is pain in the crown of the head due to overheating or prolonged exposure to the sun without a hat.
Cerebral circulatory disorders
The symptom develops during transient cerebrovascular accidents and pre-stroke conditions. Characterized by a sudden onset and rapid deterioration in well-being. Blurred vision, weakness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, and short-term disturbances of consciousness are observed. The list of possible vegetative-vascular reactions includes sweating, hot flashes, a feeling of heat or chills, trembling throughout the body.
Focal signs are determined by the topic. The duration of the attack ranges from several minutes to several hours. With PNMK, all manifestations completely disappear within 24 hours. In the pre-stroke condition, further aggravation of cerebral and neurological symptoms and transformation into hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke are possible.
Intracranial hypertension
Symmetrical pain in the crown and forehead area is a characteristic manifestation of intracranial hypertension. The type of pain is determined by the rate of progression of liquorodynamic disorders. A rapidly developing disorder is manifested by intense, rapidly increasing pain. Chronic pathology is accompanied by constant dull pain. In some patients, symptoms wax and wane.
Inflammatory processes of the central nervous system
With meningococcal meningitis, the pain is excruciating, pulsating, pressing or bursting, with a maximum in the forehead and crown. Increased intensity is observed when exposed to stimuli (light, sounds), changes in head position, and at night. With other types of meningitis, pain most often occurs in the occipital area, from where it spreads to the crown and other parts of the head. Chills, fever, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, weakness, and positive meningeal symptoms are observed.
Increasing headache is also observed with encephalitis. In patients with arachnoiditis, the pain is bursting, of moderate intensity, aggravated by physical activity, straining, coughing, and in the morning. The connection with increased intracranial pressure causes predominantly parietal localization, a feeling of pressure on the eyes. CSF crises with a sharp increase in pain, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting are possible.
Pain in the crown
Traumatic injuries
The mildest injury is a bruise of the crown. The pain is moderate, local, and its intensity quickly decreases. With a hematoma, a limited swelling forms with an area of fluctuation, which then either resolves within a few weeks or needs to be opened. Fractures of the calvarium are also accompanied by the formation of a hematoma, but with them the pain is sharp, explosive, does not subside over time, spreading to the entire head. An indentation may be felt. The general condition is variable - from satisfactory health to shock or coma.
Pain in the crown of the head may also result from injuries to the upper cervical vertebrae. The symptom is most pronounced with damage to C2, observed with fractures, fracture dislocations, subluxations, displacement of the vertebrae, including as a result of whiplash injury. There are limited movements, neck pain, and possible neurological disorders (numbness, weakness of the limbs, pelvic dysfunction).
Otolaryngological diseases
The symptom is quite widespread in diseases of the paranasal sinuses, nose, ear and complications of these pathologies. It is predominantly radiating in nature, accompanied by pain in the projection of the forehead or ear. It is observed in the following diseases:
- Frontit.
In patients with a mild form, the pain syndrome is mild. In the moderate form, patients complain of severe arching, throbbing pain in the projection of the eyebrow, radiating to the crown and temporal region. The severe form is accompanied by very intense, sometimes unbearable, painful sensations. Other manifestations include hyperthermia, intoxication syndrome, nasal congestion, photophobia, and lacrimation. - Pansinusitis.
The spread of the inflammatory process to all paranasal sinuses is fraught with the occurrence of very severe pain in the eyebrows, under the eyes, in the back of the head, crown, forehead, and orbits. There is an increase in pain during movement and palpation, and severe intoxication. The condition is serious. - Thornwald's cyst.
A congenital pathology characterized by the presence of a cyst-like formation on the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. The main clinical manifestations are pain in the occipital and parietal region, impaired nasal breathing, and bad breath. When infected, an increase in body temperature is detected. - Acute otitis media.
The epicenter of pain in this disease is in the projection of the ear. Irradiation to the parietal and temporal regions is typical. Congestion, tinnitus, hearing impairment, and deterioration in general condition are observed. - Mastoiditis.
It occurs simultaneously with acute otitis media or a little later. It manifests itself as a rapid deterioration in health, severe intoxication, severe pain in the ear and behind the ear, radiating to the crown, orbit, temple, and upper jaw. In some cases, the pain spreads to the entire half of the head.
Rhinogenic and otogenic intracranial complications are accompanied by pain in the frontoparietal region against the background of increased intracranial pressure. They are provoked by acute and chronic otitis media, epi- and mesotympanitis, purulent labyrinthitis. Other possible causes include respiratory infections with the development of acute forms of rhinitis, sinusitis or exacerbation of chronic pathologies, trauma, boils and carbuncles of the nose, abscesses of the nasal septum.
When the infection spreads, arachnoiditis, meningitis, and brain abscesses are observed. With sinusitis, thrombosis of the cavernous sinus is possible. The clinical picture is determined by the nature of the complication. Common manifestations, along with pain, are intoxication, vestibular disorders, insomnia, irritability, visual disturbances, and a feeling of pressure from inside the eyes.
Spinal diseases
Pain in the crown of the head often occurs with radicular syndrome caused by pathologies of the cervical spine, combined with hypoesthesia of the skin of the occipital region, limitation of tilting and turning the head. The most common cause is osteochondrosis. The likelihood of pain increases with the formation of a hernia. In addition, compression of the roots can be observed with spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis.
Muscle pathologies
With myositis of the cervical muscles, pain first appears in the neck, and from there spreads to the back of the head, crown, and upper back. There is increased pain during movements. Another possible cause is myalgia due to muscle strain during prolonged driving, working at a computer or sewing machine.
Other reasons
Other pathological conditions that can cause pain in the crown include:
- Infectious toxic syndrome.
Headaches can be widespread or local with the epicenter in the crown. Accompanied by influenza, ARVI, inflammatory diseases of the kidneys and respiratory tract, local purulent processes. - Endogenous and exogenous intoxications
. The symptom is observed in acute alcohol intoxication and food poisoning. It becomes a side effect or the result of an overdose of drugs, occurs in patients with malignant tumors, and in specialists who work in hazardous chemical industries. - Vegetative-vascular, neurotic disorders
. Pain in the projection of the crown sometimes bothers patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, and is observed in people with anxiety disorders, hypochondria, and hysteria.