In this article we will tell you:
- Concept of human needs
- Scientific theories about human needs
- The order of formation of human needs
- Differences between needs and wants
- Specifics of meeting human needs
Human needs are varied and difficult to classify. However, scientists have proposed several methods for grouping and evaluating them. There are several popular theories on this matter.
At first glance, it may seem that needs are a natural part of our lives and we ourselves know our needs best. This is partly true, but understanding how they are formed, what ways exist to satisfy them, and what is the difference between needs and “wants” will help to improve your life qualitatively.
In our article we will tell you what the nature of human desires is, what they are, and also how they can be closed.
Manifestation of need
The need is manifested in the selective attitude of the individual to the existing conditions of the external world and is a dynamic and cyclical quantity. Primary needs relate to biological needs; in addition, a person feels the need to stay in society. The peculiarity of the need is such that it is an internal motivation and stimulus for activity, but at the same time work becomes a subject of necessity.
At the same time, doing something creates new needs, since certain funds and costs are needed to bring the plan to life.
https://youtu.be/CerWUxBS2AM
What alternatives to Maslow's pyramid exist today?
Before we begin a detailed study of the hierarchy of needs according to Maslow’s pyramid, it is worth saying that there are other approaches to assessing human behavior and the incentives that force him to be active. Here are just a few of them:
- Alderfer's theory. It is based on Maslow’s pyramid, but tries to make the system more generalized and simpler, reducing all human needs to the following: the need to exist, the need for connections with others, the need for constant growth;
- McClelland's theory. This researcher believed that in the hierarchy of human needs, only the highest motives are the most important: the desire for power, success, involvement in great deeds and achievements;
- Herzberg's theory. A more applied theory, which is aimed at analyzing people working in a business. Shows that the higher the motivation of employees, the more non-standard tasks they solve, the more responsibility they have for their work, and the more they receive decent remuneration. Otherwise, motivation deteriorates sharply.
There are other theories, but we will look at the 5 steps of Maslow’s pyramid of needs and try to figure out whether all this works today or not.
Needs in society
A society in which human needs are not developed and reproduced is doomed to degradation. The needs of people in different eras correspond to the spirit of entrepreneurship and development, reflect dissatisfaction and despair, express collectivism, a common faith in future affairs, generalize people's aspirations and claims that need periodic satisfaction. The relationship between primary and secondary needs is formed not only in terms of social status, but under the influence of the accepted lifestyle, the level of spiritual development, and the diversity of social and psychological groups in society.
Without satisfying urgent needs, society cannot exist and reproduce social values at the level of historical and cultural standards. Urgent needs for movement, communication, and possession of information require society to develop transport, means of communication, and educational institutions. People care about satisfying primary and secondary needs.
Differences between needs and wants
Needs and desires are not the same thing. There are differences.
| Needs | Desires |
| 1. Needs are always constructive. Human needs indicate the importance and primacy of their satisfaction for the possibility of further functioning and life. 2. The basis of the need is always something important and deep. 3. Thanks to the satisfaction of needs, a person finds harmony with himself. | 1. They are destructive in nature. May harm personal development and life. So, drug addiction is a “wish”, not a need. 2. Other people can impose “wants.” 3. Desires may be superficial and not satisfy the true needs of a person. |
Let's try to figure it out with an example. Imagine that you live in your own apartment and dream of a summer house. You don't have enough money to buy a summer house, so you're angry. In this case, giving is a desire. But if you have nowhere to live, then buying any housing is satisfying a need.
Why is it necessary to distinguish between needs and desires? This is necessary for proper distribution of energy and resources. It also makes it possible to better understand yourself and others. Well, besides, seeing the differences, a person will be able to set priorities correctly.
To make the task easier, just honestly answer the following questions:
- Is it possible to do without this? A fashionable dress is a desire, but not a need. You can put it aside and buy it when there are enough opportunities for this.
- What will I get? The answer to this question will help you understand the nature of the origin of what you want.
- Will this purchase limit me? Desires should not interfere with the satisfaction of needs. Always prioritize.
Types of needs
Human needs are so diverse that to generalize them into different categories requires classification according to several criteria:
- Primary and secondary needs are divided in importance;
- according to the grouping of subjects, collective, individual, public and group are distinguished;
- according to the choice of direction, they are divided into ethical, material, aesthetic and spiritual;
- if possible, there are ideal and real needs;
- by area of activity, the desire to work, physical rest, communication and economic areas are distinguished;
- According to the method of satisfying needs, they are divided into economic, requiring limited material resources for production, and non-economic (need for air, sun, water).
Primary and secondary needs
Before moving on to consider the desires and needs unique to the human species, it should be noted that man is a full part of nature. Thus, any individual combines both purely animal needs, focused on survival, and social ones, which can only be realized in society. Modern psychologists, sociologists and biologists highlight the following important points related to biological or primary needs:
- The need for air, food, water, clothing and shelter. Drinking water should not only be uncontaminated, but also taste good. It is necessary to have high-calorie and varied food, saturated with various microelements necessary for a comfortable existence. Clean air composition is important.
- Safety for life, absence of threats from the outside world (including natural disasters).
- Being in thermal, electromagnetic and acoustic comfort.
- Reproduction and procreation, as well as obtaining sexual satisfaction.
Secondary needs include all the standard examples of social needs that can be briefly listed: movement in the hierarchical structure of society (the desire for dominance), the need for work, respect, communication, caring for other people, as well as the desire to comprehend the world and learn new things. Similar examples of social human needs are characteristic of many higher mammals.
There is also a category of pseudo-needs, that is, desires that are present only in the species Homo Sapiens. This may include the need for luxury, excessive aggression in order to gain leadership, or, conversely, the desire to avoid competition and any potentially difficult situations.
Social studies 10 Needs as a motive for activity
Watch this video on YouTube
Primary Needs
This category includes innate physiological needs, without which a person cannot physically exist. These include the desire to eat and drink, the need to breathe clean air, regular sleep, and satisfaction of sexual desires.
Primary needs exist at the genetic level, and secondary needs arise with increasing life experience.
What is the meaning of Maslow's pyramid
If Maslow’s pyramid is considered, the human needs in it are stated rather conditionally, vaguely, the theory is sometimes far from practice. But it has a meaning and it is quite simple - looking at the picture of the pyramid, we must understand that a person is a complex being and there are things that concern him first, and there are things that can be put off until later.
By understanding what motivates people, you can effectively build communication and work process with them, find the right incentives for collaboration and increase the efficiency of employees.
Ideal Needs
This group includes the desire to develop independently, manifested in the desire to receive new information, explore it and navigate in society. The need to study the surrounding reality leads to an awareness of one’s place in the modern world, knowledge of the meaning of life leads to an understanding of one’s purpose and existence. Intertwined with the ideal are primary needs and spiritual desires, which represent the desire for creative activity and awareness of beauty.
A satisfied need ceases to motivate
Another interesting phenomenon is that if a need has already been satisfied, it often ceases to motivate a person. Almost all of us know this, but for some reason Maslow did not take this phenomenon into account in his theory. After all, the system of needs is also conditional in the sense that if a person has achieved what he wants, he does not rejoice at it for long, again falls into boredom, despondency, and looks for new supports for further growth.
We know from our own lives that it is enough to buy, study, build something - interest in it immediately disappears, the faster the more lively, active and ambitious the person is. But this is not reflected in Maslow’s pyramid.
Spiritual aspirations
Spiritual interests develop in a person in connection with the desire to enrich life experience, broaden his horizons, and develop creative abilities.
The growth of personal potential forces an individual not only to be interested in the culture of humanity, but also to care about representing the values of his own civilization. Spiritual aspirations presuppose an increase in psychological tension during emotional experiences, awareness of the value of the chosen ideological goal.
A person with spiritual interests improves his skills and strives for high results in the field of activity and creativity. An individual treats work not only as a means of enrichment, but learns his own personality through work. Spiritual, biological and social needs are closely intertwined. Unlike the animal world, in human society the primary need is for biological existence, but it gradually turns into a social one.
The nature of the human personality is multifaceted, hence the variety of types of needs. The manifestation of aspirations in various social and natural conditions makes their classification and division into groups difficult. Many researchers offer various distinctions, putting motivation at the forefront.
Controversial sides of the pyramid and criticism
Psychologists of many directions actively criticize Maslow’s system, finding in it many discrepancies with real life and specific people. Here are the main statements of critics on this issue:
- History knows a lot of cases when the dissatisfaction of basic needs did not make a person more down-to-earth, but, on the contrary, stimulated him to act and create, write songs, develop, comprehend nature and God;
- Each person has their own level of satisfaction with things. One has enough of the meager lunch, another suffers from the inability to eat in the most expensive restaurant in the city;
- The inability to recognize Maslow’s theory as 100% working is also associated with the fact that many people show insatiable aspirations and cannot satisfy the most basic needs, wanting more and more.
Often brilliant people were poor, physically weak, unhappy and despised by society, but this did not prevent them from remaining in history.
Classification of needs of a different order
Primary human needs are divided into:
- physiological, which consists of the existence and reproduction of offspring, food, breathing, shelter, sleep and other needs of the body;
- existential needs, which are the desire to ensure comfort and safety of living, work to obtain benefits, and confidence in future life.
Secondary needs acquired during the course of life are divided into:
- social aspirations to gain connections in society, to have friendly and personal attachments, to take care of relatives, to gain attention, to participate in joint projects and activities;
- prestigious desires (to respect oneself, to gain recognition from others, to achieve success, high awards, to move up the career ladder);
- spiritual - the need to express oneself, to realize one’s creative potential.
Theory and practice
In theory, everything looks quite interesting. Maslow's coherent theory of needs is very logical; it really describes reality and nature well for most people around. But over time, there were many critics of this theory, since in practice it began to increasingly diverge from reality.
The theoretical calculations of A. Maslow began to be actively applied in practice. Here are just a few areas of activity where they were adopted:
- Psychology and sociology. Researchers began to look at society and typical human needs with greater understanding and began to see patterns in all this;
- Maslow's theory is applied in human resource management systems to increase employee motivation and increase their ability to work and efficiency;
- There are many tips on how you can use Maslow’s pyramid in marketing, where it allows you to attract attention and encourage people to make purchases and orders.
Also, the theory continues to interest theoretical researchers who are trying to clarify and supplement it to this day.
Classification of desires according to A. Maslow
If you find out that a person has a need for shelter, food and a healthy lifestyle, then you have identified a primary need. Need forces an individual to strive to obtain essential benefits or change an undesirable situation (disrespect, shame, loneliness, danger). The need is expressed in motivation, which, depending on the level of personal development, takes on a specific and definite form.
Primary needs include physiological needs, for example, procreation, the desire to drink water, breathe, etc. A person wants to protect himself and his loved ones from enemies, help them treat diseases, and protect them from poverty. The desire to get into a certain social group sends the researcher to another category - social needs. In addition to these aspirations, the individual feels a desire to be liked by others and demands respectful treatment.
Human needs are constantly changing; in the process of human evolution, motivation is gradually being revised. E. Engel's law states that the demand for low-quality food products decreases as income increases. At the same time, the demand for food products, which are required of increased quality while improving the standard of human life, is increasing.
How not to become addicted
Sometimes a person experiences a constant desire that develops into addiction, for example: to eat or sleep a lot. This is facilitated by psychological and physical health problems. There is a whole list of mental illnesses that are associated with food. Such diseases have the abbreviation Eating Disorder, which stands for eating disorder. This includes:
- excessive thinness (anorexia);
- bulimia with unhealthy weight control;
- binge eating;
- desire for healthy and proper nutrition;
- bigorexia.
A specialist will help you cope with such deviations. If you do not contact him in time, additional mental disorders may occur:
- depression;
- neurosis;
- anxiety;
- PTSD.
Excessive appetite also indicates hormonal diseases in the body that occur when taking any medications. If you notice a constant craving for food and this has been going on for a long time, immediately consult a doctor for help. Such a frequent need for food and sleep is a sign of various kinds of psychological or physical disorders. For example, people suffering from chronic health problems need rest more than healthy individuals. However, in a strong body, a condition such as hypersomnia (excessive sleep and the manifestation of constant drowsiness) can occur. It manifests itself after stressful situations, during a long period without relaxation, or when taking medications. It can also occur for the following reasons:
- head injury;
- depression;
- uremia;
- apnea.
In order not to be a hostage to the needs of physiology, listen to your body and prevent alarming signals by contacting a doctor or psychotherapist.
Motive of behavior
The existence of needs is judged by a person’s deeds and behavior. Needs and aspirations are referred to as quantities that cannot be directly measured and observed. Researchers in the field of psychology have determined that certain needs motivate an individual to act. The feeling of need forces a person to act to satisfy needs.
Drive is defined as a lack of something that turns into a certain course of action and a person concentrates on achieving the result. The result in its final manifestation means a means to satisfy desire. If you achieve a certain goal, it may mean complete satisfaction, partial or incomplete. Then determine the ratio of primary and secondary needs and try to change the direction of the search, while leaving the motivation the same.
The amount of satisfaction obtained as a result of an activity leaves a mark on memory and determines the behavior of the individual in the future under similar circumstances. A person repeats those actions that caused the satisfaction of primary needs, and does not commit actions leading to failure to fulfill his plans. This law is called the law of result.
Managers in modern society model situations that allow people to feel satisfaction through behavior that benefits them. For example, a person in the process of production activity must imagine the completion of work in the form of a meaningful result. If the technological process is structured in such a way that the individual does not see the final result of the work, this will lead to the disappearance of interest in the activity, violation of discipline and absenteeism. This rule requires the administration to develop the production sector in such a way that technology does not conflict with human needs.
How did the image of the pyramid of needs come about?
The theory of needs was developed by Abraham Maslow, but he was not involved in the creation of the pyramid. There was not a single graph in the psychologist’s work.
It is believed that the first graphic representation of the hierarchy of needs was published in 1975 - in the textbook by W. Stopp. Since then, the scheme has been used inextricably with Maslow’s theory. That’s what they call it: Maslow’s pyramid or pyramid of needs.
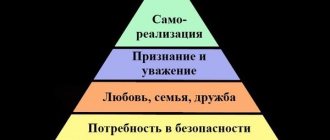
The pyramid is often depicted in the shape of a triangle. The lowest wide part covers basic needs, then the following levels are displayed towards the top:
- Physiology (hunger, thirst and other natural needs).
- Security (feeling of security, lack of fear).
- Belonging and love.
- Respect and recognition (fame, success, prestigious status).
- Cognition (gaining knowledge, skills and abilities).
- Aesthetics (striving for beauty, searching for ideals).
- Self-actualization (realization of abilities and desires).
Schematic representation of Maslow's pyramid
In 2010, a group of scientists from the USA and Canada updated the pyramid taking into account modern realities. In their opinion, basic needs remained the same. In the same way, people need food, security, belonging and love. As for the upper levels, reproductive goals come to the fore: maintaining relationships, finding a suitable partner and raising children. Self-actualization is combined with recognition. At the same time, scientists note that needs sometimes shift and are interchanged.
Updated pyramid of needs
However, Maslow himself did not rule out deviations from the hierarchy. Some people may stop at the lowest level, others are more in need of self-actualization than security or recognition. Maslow considered such exceptions to be features of a person’s personality or a consequence of unfavorable external circumstances.
The hierarchy of needs remains popular in psychology, within the framework of sociology research, and in management training. However, Maslow's pyramid is often criticized and called outdated.
Some interesting facts about Maslow's theory
Here are examples of interesting facts about the issue under consideration that will be of interest to readers:
- Maslow himself was only interested in very strong personalities like Abraham Lincoln and believed that, despite all the efforts of an individual, only 2% of people can achieve maximum personality development, or self-actualization;
- In Abraham Maslow's basic article on the hierarchy of human needs there is no image of a pyramid - it was completed later by other researchers of the issue;
- The unspoken truth of the scientist’s theory is that a person can develop and move higher and higher in life only under one condition - he is driven by higher values and there is a need to achieve a dream, a higher goal of existence.
In general, Maslow’s theory of needs is very interesting, well-known, and will probably cause controversy for decades to come, both among psychologists, marketers and scientists, and among ordinary people interested in this issue.
See also:
Who is a marketer and what does he do?
complete guide Freelancing - what kind of profession is it and who are freelancers?
How to write articles correctly: stages, methods with examples and important details
Setting up Yandex.Direct yourself 2019
Setting up Yandex.Direct in a day, step by step instructions
Guerrilla marketing - how does the technique work?
Application of Maslow's pyramid
Maslow's pyramid can be most successfully applied in certain areas, such as:
- marketing
- life
- work and business
- when building a career
- running a company
Let's expand on each topic a little for a broader understanding.
Application in marketing
Maslow shows human needs in the form of a hierarchy, so marketing companies and marketers can rely on this theory in order to understand exactly how to attract this or that category of people. If it is necessary to motivate, say, employees, then lower incentives such as increasing salaries or reducing working hours work here; management employees are already concerned about other issues: comfort, conditions for career growth, respect from management.
Application in life
The application of this theoretical concept in life is quite limited, but it can be useful for every person. We must not only look at what is at the top of Maslow's pyramid, but also cover basic needs if there are problems there. This will help relieve stress and tension, cope with professional burnout, and open up mental strength for new and greater achievements.
Maslow's pyramid in work and business
In these areas, the use of the theory under consideration comes down to competently stimulating your employees, understanding how to properly influence their performance, attitude towards work and work responsibilities. By managing to some extent the basic needs of people and clients, we can make ourselves more attractive in their eyes and offer solutions to specific pressing problems. After all, a business is more successful the more effectively it solves a client’s problem.
In building a career
In career matters, we should always remember what is at the top of Maslow's pyramid, but not try to jump straight there, since such a “maneuver” is available to very few geniuses. In a career, the pyramid will always help you remember that there are basic things that we cannot turn a blind eye to, so that they do not drag us down and close off the possibility of further growth. For example, if we work in conditions of low wages and cannot provide for our family, we work without respect from colleagues and superiors - this will greatly hinder or even slow down our growth.
In the practice of enterprise management
You can use Maslow's theory in business management. Here, too, everything is simple: each subordinate at his level and the ability to satisfy his needs must be selected with optimal incentives, satisfy these basic needs, or be given a real hope of satisfying them. If you add some qualities to your work that cover higher levels, you can also reduce stress from problems at lower levels. For example, a job where the boss respects and treats his subordinates well will be more interesting to many people than a high salary, but a bad attitude, which can lead to causes of professional burnout.