Manifestation of need
The need is manifested in the selective attitude of the individual to the existing conditions of the external world and is a dynamic and cyclical quantity. Primary needs relate to biological needs; in addition, a person feels the need to stay in society. The peculiarity of the need is such that it is an internal motivation and stimulus for activity, but at the same time work becomes a subject of necessity.
At the same time, doing something creates new needs, since certain funds and costs are needed to bring the plan to life.
Needs in society
A society in which human needs are not developed and reproduced is doomed to degradation. The needs of people in different eras correspond to the spirit of entrepreneurship and development, reflect dissatisfaction and despair, express collectivism, a common faith in future affairs, generalize people's aspirations and claims that need periodic satisfaction. The relationship between primary and secondary needs is formed not only in terms of social status, but under the influence of the accepted lifestyle, the level of spiritual development, and the diversity of social and psychological groups in society.
Without satisfying urgent needs, society cannot exist and reproduce social values at the level of historical and cultural standards. Urgent needs for movement, communication, and possession of information require society to develop transport, means of communication, and educational institutions. People care about satisfying primary and secondary needs.
Types of needs
Human needs are so diverse that to generalize them into different categories requires classification according to several criteria:
- Primary and secondary needs are divided in importance;
- according to the grouping of subjects, collective, individual, public and group are distinguished;
- according to the choice of direction, they are divided into ethical, material, aesthetic and spiritual;
- if possible, there are ideal and real needs;
- by area of activity, the desire to work, physical rest, communication and economic areas are distinguished;
- According to the method of satisfying needs, they are divided into economic, requiring limited material resources for production, and non-economic (need for air, sun, water).
Primary Needs
This category includes innate physiological needs, without which a person cannot physically exist. These include the desire to eat and drink, the need to breathe clean air, regular sleep, and satisfaction of sexual desires.
Primary needs exist at the genetic level, and secondary needs arise with increasing life experience.
Why do I even need to know about basic needs, and how will it help me?
Failure to satisfy basic needs leads to the maintenance and activation of maladaptive patterns that begin to control our behavior. Behavior dictated by the schema further interferes with the satisfaction of needs, negatively affects interpersonal relationships, and prevents acting in accordance with internal values. Awareness of basic needs is an important step towards conscious behavior aimed at living a harmonious, satisfying life.
Awareness of basic needs is an important step towards conscious behavior aimed at living a harmonious, satisfying life.
Ideal Needs
This group includes the desire to develop independently, manifested in the desire to receive new information, explore it and navigate in society. The need to study the surrounding reality leads to an awareness of one’s place in the modern world, knowledge of the meaning of life leads to an understanding of one’s purpose and existence. Intertwined with the ideal are primary needs and spiritual desires, which represent the desire for creative activity and awareness of beauty.
Signs of successful implementation of intentions
You can be sure that everything is going right if a person has the following traits:
- harmonious development;
- contact and understanding with nature and the surrounding world;
- respect, love for yourself and people;
- socialization;
- a firm and pragmatic approach to problem solving;
- individuality;
- the ability to experience deep feelings - love, strong friendship.
Spiritual aspirations
Spiritual interests develop in a person in connection with the desire to enrich life experience, broaden his horizons, and develop creative abilities.
The growth of personal potential forces an individual not only to be interested in the culture of humanity, but also to care about representing the values of his own civilization. Spiritual aspirations presuppose an increase in psychological tension during emotional experiences, awareness of the value of the chosen ideological goal.
A person with spiritual interests improves his skills and strives for high results in the field of activity and creativity. An individual treats work not only as a means of enrichment, but learns his own personality through work. Spiritual, biological and social needs are closely intertwined. Unlike the animal world, in human society the primary need is for biological existence, but it gradually turns into a social one.
The nature of the human personality is multifaceted, hence the variety of types of needs. The manifestation of aspirations in various social and natural conditions makes their classification and division into groups difficult. Many researchers offer various distinctions, putting motivation at the forefront.
Basic ways and means of satisfaction
Without the ability to fulfill biological needs, the human species simply cannot survive. Other, higher categories make a person out of an individual, and therefore are also very important. But the more psychologically developed a person is, the more discomfort she experiences when she cannot satisfy spiritual pursuits. If a suitable method has not been discovered, then various reactions begin to operate, for example, rejection or replacement. The first involves giving up (intentionally or uncontrollably) what you want, and the second involves replacing one task with another, less complex one.
I will present the means of realizing intentions:
- formation of a connection between a stimulus and a subsequent event;
- specific assignment of activities to a given goal, that is, the search for a standard solution;
- analysis of what the intention consists of, analysis of its motives into components - they are easier to satisfy;
- socialization, subordination of the individual to the norms and rules of culture and society.
Classification of needs of a different order
Primary human needs are divided into:
- physiological, which consists of the existence and reproduction of offspring, food, breathing, shelter, sleep and other needs of the body;
- existential needs, which are the desire to ensure comfort and safety of living, work to obtain benefits, and confidence in future life.
Secondary needs acquired during the course of life are divided into:
- social aspirations to gain connections in society, to have friendly and personal attachments, to take care of relatives, to gain attention, to participate in joint projects and activities;
- prestigious desires (to respect oneself, to gain recognition from others, to achieve success, high awards, to move up the career ladder);
- spiritual - the need to express oneself, to realize one’s creative potential.
Scientific theories about human needs
Abraham Maslow's theory
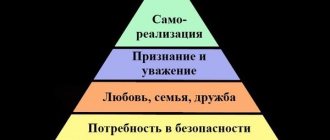
This is the most famous classification of human needs, everyone who has at least once been interested in self-development knows about it. This concept was proposed and developed by the American psychologist Abraham Maslow in a number of his works on motivation. He sorted all human needs by elevation: from lower (biological) to higher (spiritual). Due to the characteristic form of the schematic image, this classification was called “Maslow’s Pyramid”.
The author himself identified 5 levels in his classification:
1. Physiological needs.
In this group he included food, water, sleep, sexual satisfaction - all the basic needs of our body.
2. Safety.
When all physiological needs are satisfied, a person seeks to protect himself and his family. This group includes not only good protection from predators and other dangers, but also confidence in stability and order.
3. Love and belonging.
Here we are talking about good relationships, love, friendship, belonging to a certain social group.
4. Respect and recognition.
If a person is confident in his own well-being in all areas included in the first three levels of the pyramid, he has a strong need for respect and recognition. Here we are not talking about the banal “You respect me, no?!”, but about real respect for actions and achievements.
5. Self-actualization.
Abraham Maslow included in this group self-development, self-education and other ways of working on oneself, one’s skills, knowledge and abilities.
If you look closely at the 5 tiers of Maslow’s pyramid, you will notice that the first two are biological, the third and fourth are social and partially spiritual, and the fifth are purely spiritual needs.
One of the most important statements of Maslow's theory is that each level becomes important only if all the needs located at lower levels are fully satisfied. For example, hunger or unfulfilled sexual instinct (first level) makes a person forget about caution and safety (second level).
If we compare lower needs with higher ones, we can notice several characteristic differences:
- higher needs appear much later (they first appear in adolescence, after which they develop throughout life);
- higher needs are perceived by most people as less important, “optional”;
- the higher the need is in the hierarchy, the easier it is to postpone its implementation to the future in order to solve more pressing problems;
- people living at higher levels of Maslow's pyramid tend to have good health (partly because they take care of it), experience less stress and sleep better;
- a person receives much more joy and pleasure from satisfying higher needs.
The original concept proposed by Abraham Maslow had 5 tiers, which we discussed above. Later, many authors took liberties in its interpretation and introduced additions, increasing the number of levels. Therefore, do not be surprised if you see different variations of the pyramid with 7 or 10 tiers. In any case, the basic concept of Maslow's theory remains.
Read more about Maslow's Pyramid of Needs in this article.
Alderfer's ERG theory
American professor Clayton Alderfer proposed an alternative theory of motivation. It does not contradict Maslow’s theory, but it uses its own classification of needs, which includes 3 groups (the abbreviation ERG is derived from their names):
- Existence (existence, life).
- Relatedness (relationships, communication).
- Growth (personal growth, development).
As you might guess, the first group is represented by physiological needs, the second by social, and the third by spiritual. At the same time, Clayton Alderfer showed that the relationship between these groups is somewhat more complex than Maslow described (priorities are influenced not only by the fact of satisfaction itself, but also by the degree of satisfaction).
In addition, he noticed that dissatisfaction with higher needs increases the desire to satisfy lower ones. For example, it is known that during any crisis the revenue of confectionery stores increases sharply. This is explained by the fact that people, losing a sense of stability, begin to buy more sweets (even those who do not like them at all and usually do not buy them).
Fromm's theory
German psychologist and sociologist Erich Fromm considered social interaction to be a key factor influencing the human psyche. This was reflected in his theory of needs. He proposed a five-point hierarchical scheme:
- Interpersonal connections (love, friendship).
- Creativity (any creative activity, regardless of type).
- Feeling of strong and deep roots (stability).
- Search for the ideal and assimilation to it (self-improvement).
- Knowledge of the world (spiritual improvement).
As one of the founders of neo-Freudianism, Fromm believed that our basic needs are controlled by the unconscious. But since the unconscious often encounters such obstacles as taboos, stereotypes, logic, rationality, etc., needs remain unfulfilled.
McClelland's theory of acquired needs
American writer and psychologist David McClelland proposed his theory of motivation. He believed that all needs are formed in childhood. At the same time, he divided them into three groups, explaining the mechanism of formation of each of them:
- Involvement.
This need arises in children who were engaged in collective activities and played team games. As a result, even in adulthood, they feel the need to be part of a group, to participate in a socially significant project or movement. - Power.
If in childhood one way or another is encouraged to control other children, in adulthood such a person needs a sense of power. Also, this need can be formed under the influence of the family atmosphere. - Success.
If a child is taught to be independent, to achieve something, to receive prizes and certificates, as an adult he will also need success.
Classification of desires according to A. Maslow
If you find out that a person has a need for shelter, food and a healthy lifestyle, then you have identified a primary need. Need forces an individual to strive to obtain essential benefits or change an undesirable situation (disrespect, shame, loneliness, danger). The need is expressed in motivation, which, depending on the level of personal development, takes on a specific and definite form.
Primary needs include physiological needs, for example, procreation, the desire to drink water, breathe, etc. A person wants to protect himself and his loved ones from enemies, help them treat diseases, and protect them from poverty. The desire to get into a certain social group sends the researcher to another category - social needs. In addition to these aspirations, the individual feels a desire to be liked by others and demands respectful treatment.
Human needs are constantly changing; in the process of human evolution, motivation is gradually being revised. E. Engel's law states that the demand for low-quality food products decreases as income increases. At the same time, the demand for food products, which are required of increased quality while improving the standard of human life, is increasing.
Motive of behavior
The existence of needs is judged by a person’s deeds and behavior. Needs and aspirations are referred to as quantities that cannot be directly measured and observed. Researchers in the field of psychology have determined that certain needs motivate an individual to act. The feeling of need forces a person to act to satisfy needs.
Drive is defined as a lack of something that turns into a certain course of action and a person concentrates on achieving the result. The result in its final manifestation means a means to satisfy desire. If you achieve a certain goal, it may mean complete satisfaction, partial or incomplete. Then determine the ratio of primary and secondary needs and try to change the direction of the search, while leaving the motivation the same.
The amount of satisfaction obtained as a result of an activity leaves a mark on memory and determines the behavior of the individual in the future under similar circumstances. A person repeats those actions that caused the satisfaction of primary needs, and does not commit actions leading to failure to fulfill his plans. This law is called the law of result.
Managers in modern society model situations that allow people to feel satisfaction through behavior that benefits them. For example, a person in the process of production activity must imagine the completion of work in the form of a meaningful result. If the technological process is structured in such a way that the individual does not see the final result of the work, this will lead to the disappearance of interest in the activity, violation of discipline and absenteeism. This rule requires the administration to develop the production sector in such a way that technology does not conflict with human needs.
Concept and signs of need
Need represents the need for certain things, these can be objects of the material world, objects, people, social criteria. In their absence, the individual feels uncomfortable.
If we take into account this definition of need, then a need, in order to become a need, must meet several criteria:
- The presence of a shortage of an item of need, which causes dissatisfaction (need as a desired good);
- The presence of appropriate emotions (from negative emotions at the first stage to positive ones after the need is realized);
- Fixation on the subject of need, when consciousness can snatch from reality things that can satisfy a person (for example, when experiencing a feeling of hunger, an individual will focus on products and the smell of food).
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
The need system is created according to special rules. Need is inherent in all living beings on the planet, but the more developed the species, the higher the level of needs will be. The tree needs nutrients from the earth, sunlight, and watering from rain. Man, as a highly developed animal, requires much more.
The older the individual, the more extensive the list of his needs becomes. A child can completely do without things that an adult needs. Needs represent a strictly hierarchical structure (some are primary, others are secondary).
People's actions are caused by the existence of a certain need, which is the main motive for activity. The motivation to get what you want can move an individual forward, forcing him to take appropriate actions. Everything that man has created throughout history within the framework of politics, economics, art and science is considered the result of activity in the sphere of satisfying needs.