Positive scotomas are rays, glare or flashes of light noticed by the patient in the absence of optical phenomena. This is a response to disruption of the visual system. A single flicker in the eyes may indicate eye fatigue. In this case, just rest and the symptom will go away. If this phenomenon recurs, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an ophthalmological examination to rule out serious pathologies.
Types of violation
Depending on the symptoms the patient experiences, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. Flickering varies in type, strength or intensity. It can be multi-colored, black and white, zigzag, in the form of spots, stripes or black flies. The most common:
- Colored circles and rainbow halos in front of the eyes around light sources, combined with tearing. If they are not accompanied by photophobia, this may be a sign of developing cataracts.
- Multi-colored spots with redness of the eyes and pain occur with fatigue and increased fundus pressure.
- Zigzag spots with a sharp change in head position, sneezing and coughing can occur with iron deficiency anemia, during pregnancy, with a foreign body in the eye, with incorrect selection of glasses or damage to blood vessels. Sometimes accompanied by pain.
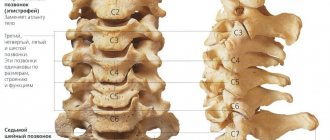
- Glowing flashes of light and bright spots indicate problems with the spine, disruption of brain function, and high blood pressure.
- Laser glare combined with swelling accompany retinal problems. The cause may be retinal detachment, photoburn, or the use of low-quality lenses.
- The appearance of ripples in the eyes occurs with osteochondrosis or eye diseases.
When to see a doctor about floaters
If you experience any of the following symptoms, contact your eye doctor immediately for emergency eye care.
Symptoms that should not be ignored:
- The sudden appearance of floaters accompanied by flashes (which can be of any shape or size).
- An increase in floating particles, accompanied by a darkening of one side of the visual field.
- Shadows in peripheral vision
- Do you see glare all the time?
In many cases, the appearance of floaters before the eyes is not a cause for concern; however, the above symptoms may indicate a retinal detachment, and if left untreated, it can cause permanent vision loss or even blindness.
If you experience the above symptoms, you should see a doctor within 24 hours. You will have to endure the discomfort of having your pupils dilated during an eye exam so that the ophthalmologist can get a good look at the peripheral retina and diagnose or rule out a retinal tear or other serious condition. It is worth finding out whether there is a threat to vision. If it's just an uncomplicated posterior vitreous detachment, which is quite common, or an ocular migraine, then you can breathe a sigh of relief.
Etiology
This symptom can be caused by benign reasons, such as improper selection of glasses and lenses, alcohol abuse, and an unbalanced diet. This effect is sometimes provoked by taking certain medications, heat or sunstroke, and presyncope.
Pathological etiofactors are:
- Migraine;
- Tension headaches;
- Injuries;
- Stenosis of blood vessels in the neck and head;
- Damage to vascular walls;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Hypotension;
- Systemic diseases, for example, diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and so on;
- Hypochromic anemia;
- Tumors of various origins;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- Spinal cord compression;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Inflammatory processes in the eyeball;
- Eclampsia;
- Oscillopsia;
- Drug ototoxicity;
- Retinal detachment or tear;
- Vitreous detachment.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Patients describe eye lightning as "zigzags", reminiscent of flashes during a thunderstorm or shapeless "flashing lights", as well as glowing "pinwheels". In migraine patients, they take a zigzag shape. Flashes are more visible in low light. The following signs may also be present:
- dark dots, spots, lines that appear or are constantly present before the eyes;
- flickering light;
- spider veins.
Recurrent lightning in the eyes should be diagnosed immediately, especially if accompanied by symptoms:
- loss of visual acuity;
- blindness in the center of the visual field, right or left
- loss of the field of vision like a “curtain”.
The appearance of lightning in the eye should prompt a dilated fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy) to identify potential causes. It is useful to conduct tests using a slit lamp, ultrasound, examine the macula, and in some cases, perform optical coherence tomography of the retina. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on a patient interview and clinical examination.
If the test results are in doubt, the ophthalmologist can refer for additional diagnostics, for example, a tomographic examination of the brain, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head and neck, and, when accurately determining the causes of the phenomenon, applies appropriate treatment.
Where to sign up for testing
The easiest way to choose a diagnostic center in St. Petersburg is through our service. There is comprehensive information about addresses, telephone numbers, and opening hours of clinics. You can find out what protocols are used for the examination. Clarify the qualifications of doctors and equipment models. Using the website, it is easy to find out which medical centers are ready to accept patients with limited mobility, and where parking is provided on the territory of the institution. It is convenient to reserve a coupon and receive up to 1000 rubles discount on diagnostics by phone. Our specialists will answer all questions daily from 8:00 to 24:00. The service is free.
Computer vision syndrome in children
Children's eyes are just developing, so any problem can have more serious consequences for vision than in an adult. Moreover, children, due to their studies, are subject to increased visual load.
It is important to recognize the disorder in time and begin to treat it! But the situation is complicated by the fact that children are not always able to recognize their own vision problems. You may suspect CVD in a child based on the following signs:
- Constant redness of the eyes;
- The child complains of pain in the eyes, a feeling as if something was in the eye;
- The child often rubs his eyes;
- Increased tearing and sensitivity to light may occur;
- The child quickly gets tired during visual stress and cannot see objects in the distance.
It is necessary to limit the time a child spends on a computer, tablet or phone. It is better to find safer recreation for children, and also to walk more outside. To maintain healthy vision, it is also important to visit an ophthalmologist annually, even if you have no complaints!
Make an appointment for your child with a doctor
Folk remedies
Traditional methods will help reduce swelling and inflammation of the eye mucosa. These include cool compresses on the eyelids. And:
- Chamomile decoction;
- Cucumber juice mixed one to one with water.
We must remember that these methods also have contraindications. Therefore, it is better to first consult with a specialist. If attacks recur, it is necessary to undergo examination.
What is computer vision syndrome and why does it appear?
KZS is a complex disorder associated with long-term (more than 2 hours a day) work on a PC and mobile gadgets. The development of KZS is based on two problems at once - dry eye syndrome and spasm of accommodation.
Normally, a person blinks approximately 18 times per minute. But with visual concentration, the frequency of blinking is sharply reduced to 4-5 times per minute, as a result of which the cornea of the eyes dries out. This ultimately leads to the development of dry eye syndrome, a chronic condition in which there is not enough moisture on the surface of the eye.
Computer vision syndrome is a complex disorder that occurs with prolonged use of a computer or gadgets.
Another problem concerns accommodation - the eye's ability to focus vision at different distances. Accommodation spasm occurs due to prolonged tension of the ciliary muscle, which is responsible for the ability of the eye to change focus. This happens when a person focuses on objects at the same distance for a long time - near or far. Due to overwork and accommodation spasm, visual acuity decreases; it is difficult for a person to move focus from closer to distant objects; the image on the monitor begins to blur.
A spasm of accommodation can slow down and even stop metabolic processes in the eye structures necessary for healthy vision.
Who is affected by computer vision syndrome?
Office workers are primarily at risk. Working at a computer for a long time can be detrimental to your eyesight, especially if you do not comply with the requirements for organizing your workplace. Constantly running air conditioners that dry out the air only aggravate the problem.
Children who spend a lot of time on the computer or other gadgets also often suffer from CVD. In general, any person who spends 4-5 hours a day on mobile gadgets or a computer screen (regardless of whether he is working, watching videos, reading or playing) is at risk of developing computer vision syndrome. And if he uses contact lenses at the same time, the problem becomes even more acute.
Prevention
As preventive measures it is necessary:
- Maintaining daily routine and visual hygiene;
- Correctly selected lighting during work;
- Healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits;
- Balanced diet;
- Moderate physical activity;
- Reduction of psycho-emotional stress;
- Timely medical examination by a neurologist and ophthalmologist.
The article is for informational purposes only. If initial symptoms are detected, you should consult a doctor.
Cobwebs before my eyes
In the eye, the space between the lens and the retina is filled with a clear, jelly-like substance called the vitreous. In newborns, the vitreous body has a homogeneous structure and is tightly adjacent to the retina. As the body ages, the vitreous body is divided into two fractions - liquid (practically water) and fibrous, formed by protein molecules glued together - and detaches from the retina. This process is very common, usually not dangerous, and is called vitreous detachment.
A person may feel this detachment by noticing floaters (floaters) and lightning (bright flashes of light, often from the side) before the eyes. Floaters are caused by the opaque fibers of the vitreous casting a shadow on the retina. Lightning appears as a result of the traction that the detached vitreous body exerts on the retina in places where they are tightly attached. The retinal photoreceptors in this area perceive mechanical stimulation as a bright flash of light, which the patient feels.
There are also more dangerous reasons for the appearance of flies and lightning. Retinal tears and detachments, infection, inflammation, bleeding, or trauma such as a blow to the head can cause floaters and lightning. Sometimes lightning flashes in front of the eyes can be caused by neurological disorders such as migraines. In migraines, flashes of light are visible in front of both eyes a few minutes before the onset of a severe and prolonged headache.
Signs (symptoms)
- Black dots or cobwebs that float together or separately in the field of view, sway when you move your eyes
- Flashes of light, similar to lightning, that are most noticeable when looking at a uniform background, such as a clear sky
Symptoms that may be a sign of a more serious condition
- A sharp deterioration in vision along with lightning and floaters
- A curtain that obscures part or all of the field of vision in front of one eye
- A sharp increase in the number of floaters
Diagnostics
Contact your ophthalmologist immediately if you notice a sudden appearance of a large number of floaters, new flashes, or a curtain blocking your vision. The doctor will use drops to dilate the pupils and examine the vitreous body and retina using an ophthalmoscope and a slit lamp with a special lens.
Treatment
Vitreous detachment itself almost never requires treatment, much less surgery, since over time (weeks to months) the interference from the floaters becomes less as they descend below the optical axis. Only in cases of significant vision loss can surgical treatment be justified. In such cases, surgical removal of the vitreous body is performed - vitrectomy.
If the cause of floaters and lightning is not due to vitreous detachment, surgery may be necessary.
Take active control of your vision
It is very important to periodically check the vision of each eye separately. Many eye diseases can be detected early by simply comparing vision between eyes. It often happens that a person notices a significant deterioration in vision in one eye with a healthy second eye only after some time. This reduces the chances of successful treatment.
To test your vision:
1. Close one eye and look at some point directly in front of you.
2. Assess the quality of your central and peripheral vision, paying attention to changes since the previous test
3. Check for interference and curtains in the periphery of the field of view
4. Pay attention to flies and lightning
5. If symptoms are present, assess their duration and severity
6. Close the other eye and repeat the same with it
Report new symptoms to your ophthalmologist