Double vision is often confused with blurred vision. However, fog in the eyes is a visual impairment in which a person sees one blurry, unclear image, and with double vision, one object is perceived as two images of it.
Diplopia manifests itself in different ways. Some patients report this condition from time to time, others live with it constantly. In some cases, people claim to experience double vision only when they look in a certain direction (vertical or horizontal plane).
1.Why do I see double?
Double vision is a symptom that needs to be treated very carefully. Some causes of double vision may be relatively minor, but others require urgent medical attention. Let's try to figure out why it can cause double vision and what to do about it.
Why do I see double?
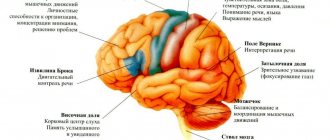
When you open your eyes and see a clear image of the object you are looking at, this is normal. But this seemingly simple and automatic process depends on the coordinated work of several areas of the vision system.
- The cornea
is the “window” of the eyes. The cornea helps focus the light entering the eyes. - The lens behind the pupil
also helps focus light on the retina. - The muscles
of the eyeball allow the eye to turn and look to the sides. - Nerves
are responsible for transmitting visual information from the eyes to the brain. - The brain
processes information received from the eyes.
When you see double, the cause may be problems with any element of this system.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Prevention
Diplopia is an unpredictable visual impairment. Targeted prevention of deviation is impossible. To reduce risks, it is recommended:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly for examination;
- in case of illness, contact a specialized specialist;
- control blood pressure;
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- exercise, take walks;
- Doctors advise regularly checking hormonal levels, glucose and iron levels in the blood.
2. Possible causes of this problem
When you see double, the cause may be problems with any element of this system.
Cornea problems
Problems with the cornea often cause double vision in only one eye. If you close it, you won't see double. Damage to the cornea distorts the incoming light and this becomes the main cause of diplopia. Infection can cause damage to the cornea (for example, shingles can cause distortion of the cornea). Scars on the cornea or dry cornea are other possible causes of double vision.
Problem with the lens of the eye
Cataracts are one of the most common lens problems that cause double vision. If there are cataracts in both eyes, perception will be impaired in each of them. Cataracts can usually be cured with simple surgery.
Eye muscle problems
If the muscles in one eye are weakened, that eye cannot move as smoothly as the healthy eye. And looking in a direction controlled by weak muscles causes double vision. Weakness of the eye muscles may be associated, for example, with myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease that blocks the muscles from stimulating the nerves inside the head. Early signs of myasthenia gravis are double vision and drooping eyelids. Graves' disease is another possible cause of eye muscle weakness. Graves' disease usually causes vertical diplopia, where double vision causes one image to be higher than the other.
Nerve problems
The causes of damage to the nerves that control the eye muscles vary. Multiple sclerosis can damage nerves anywhere in the brain or spinal cord. This means you will see double. Diabetes can affect the nerves connected to the muscles that move the eyeball. And this will also lead to diplopia.
Brain problems
The nerves from the eyes are directly connected to the brain. In addition, the entire process of processing visual information from the eyes also occurs in the brain. Therefore, there can be quite a few causes of double vision - stroke, aneurysm, increased pressure in the brain due to injury, bleeding or infection, as well as brain tumors, headaches and migraines.
What else could it be?
Double vision may begin on its own, without other symptoms. But depending on the causes, other symptoms may be present simultaneously with double vision:
- Strabismus;
- Pain when moving the eyes in one or both eyes;
- Pain around the eyes, for example in the eyebrow area;
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- Weakness in the eye muscles and general weakness;
- Drooping eyelids.
Visit our Neurology page
Conclusion
Diplopia requires careful attention to yourself. In order not to provoke its appearance, you need to take care of your eye health in advance. You can't read too much, especially if the text is too small. It is extremely harmful to work at a computer for a long time. You should always take a break to rest your eyes. After reading or working at the computer, it is useful to do eye exercises.
Girls need to be more careful when using decorative cosmetics. Poor-quality or expired mascara and shadows that get on the mucous membranes of the eyes can cause conjunctivitis. If the disease does develop, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and begin treatment. If you do not get rid of it in time, scars may appear on the cornea, which will lead to poor vision.
3.Diagnostics of double vision
If for some unknown reason you begin to see double, you should immediately consult a doctor. With so many potentially serious causes of double vision, you need to find the cause as soon as possible.
Your doctor will likely use a variety of techniques to determine the cause of double vision. Blood tests, a physical examination, and possibly imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI are the most commonly used.
General information is very important for diagnosing double vision. Here are some questions your doctor might ask:
- When did the double vision start?
- Have you hit your head, fallen, or been unconscious?
- Have you ever been in an accident?
- Does double vision get worse towards the end of the day or when you are tired?
- Do you have any other symptoms besides double vision?
- Do you have a habit of tilting your head to the side when you look somewhere?
Now focus your vision on some stationary object in your field of vision, for example, a window or a tree behind it.
- Are the two objects that appear as a result of double vision near each other? Or is one higher than the other? Or maybe they are located slightly diagonally? Are any of them larger or smaller?
- Are both images clear? Or is one clear and the other blurry?
- Close one eye and then open it and close the other. Does double vision go away when you look with one eye?
- Imagine that you are looking at a watch dial. Move your eyes in a circle, according to the numbers. Does double vision get worse at certain clock positions? Or is it getting better in some area?
- Tilt your head to the right and then to the left. Does double vision get worse/better in any of these positions?
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Determination of the angle of strabismus
When amblyopia develops against the background of strabismus, the doctor determines the angle of strabismus according to Hirschberg. To do this, the child is asked to look at the ophthalmoscope, after which the doctor records the light reflections. Normally, the glare is projected in the middle of the pupil, but with strabismus - at the edge of the pupil, within or beyond it, which determines the angle of deviation.
Determining the nature of visual fixation is the most important diagnostic procedure for any form of amblyopia, since the treatment regimen depends on visual fixation.
Get a complete vision examination at the Lege Artis Eye Clinic
It's time to correct your vision!
Make an appointment by phone:
8(804) 333-02-14 Free call
4.Treatment
If you see double, the most important thing is to find and treat the cause. In some cases this really helps.
- Eye muscle weakness or injury is treated with eye surgery;
- Myasthenia gravis is treatable with medications;
- Blood sugar levels in diabetes can be controlled with medications or insulin.
If a way to cure double vision has not been found, there are measures that can help reduce this symptom. This sometimes requires wearing an eye patch or special prism glasses to minimize the effect of double vision.
Delfanto® – an innovative product for restoring tear fluid production
Delfanto® capsules are a modern product based on a standardized extract of Aristotelia chilean (MaquiBright®). It contains at least 35% polyphenolic anthocyanins, which help eliminate the effects of oxidative stress and make the tear glands work stably.
Unlike tear substitutes, Delfanto® eliminates not only the signs of dry eye syndrome, but also the causes. The product stimulates the production of your own tears, which provides protection, nutrition, and hydration of eye tissue. Already 14 days after the start of the course of therapy, the first positive changes are noticeable, and after a month, the manifestation of dry eye symptoms is reduced by 45-89% (according to the results of clinical studies).
Examination of a child with amblyopia
Congenital ophthalmic pathology, such as a cataract, cataract or ptosis, is detected immediately after birth if it is pronounced and obvious. However, examination and consultation with a pediatric ophthalmologist, taking into account the above data, is mandatory in any case.
Parents (usually the mother) should be prepared to provide the consultant with the most complete anamnestic information possible: ophthalmic heredity on both lines, the nature of pregnancy and childbirth, infections suffered by the child, injuries, stressful situations; Peculiarities of the child’s behavior observed at home that may be related to vision (squinting, blinking too often, rubbing his eyes, sometimes squinting slightly, etc.); neurological status; previous treatment received and its success, and many others.
Accurate visometry, the measurement of visual acuity, is impossible in early childhood, but these data are necessary to diagnose amblyopia. Pediatric ophthalmologists use indirect assessment techniques and take into account known cause-and-effect relationships (for example, the development of amblyopia is always accompanied by congenital unilateral cataracts).
During the initial ophthalmological examination, attention must be paid to the shape, size and symmetry of the palpebral fissures, the condition and tone of the eyelids, and the consistency of movements of the eyeballs. Pupillary and psychomotor reactions to light are assessed. Using an ophthalmoscope, the condition and light transmittance of transparent ocular structures and media (cornea, lens, vitreous body), as well as the status of the fundus, are examined.
Speaking about indirect, but quite effective methods for assessing refraction, one cannot fail to mention skiascopy - one of the most well-known and widely practiced methods for the early diagnosis of myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism.
Conventional ophthalmic equipment is used: a powerful light source and a head mirror. A directed beam illuminates the pupil; Normally, there is a reflection from the fundus of the eye - the so-called. red reflex. By turning the mirror, the doctor notes the displacement of the shadow (by the way, “skia” means “shadow” in Greek), using special lenses and a ruler, evaluates its direction and deviation. The presence of a refractive error, its nature and severity, including in young children, can be diagnosed using the skiascopic method. The disadvantages are lower measurement accuracy compared to visometry with interchangeable lenses, as well as the need to dilate the pupil. As a mydriatic drug, for children under 1 year of age, a 0.5% solution of tropicamide is usually used 20 minutes before the test; patients from 1 to 3 years of age are instilled with a 0.5% solution of atropine; from 3 years of age, 1% atropine is instilled several days later. before inspection.
Visometric measurement of visual acuity, necessary for the final establishment (or exclusion) of the diagnosis of amblyopia, becomes possible from the moment the child learns to understand and follow simple instructions, answer questions like “What is shown in the picture,” etc. The main diagnostically significant sign of amblyopia is the impossibility or ineffectiveness of correcting impaired vision with glasses.
In addition, the ability of central fixation is examined. The diagnostic method is simple and, like skiascopy, is based on the analysis of the behavior of the shadow under narrowly focused illumination of the fundus through a pre-dilated pupil. An opaque point with a diameter of 3 mm is placed in the center of the ophthalmoscopic lens. The child looks with only one eye (the other is covered) and must focus his gaze on this point. Normally, a reflex is observed from the macular (central and most light-sensitive) zone of the retina, and the shadow is located clearly in the center. Any other position of the shadow indicates impaired fixation. In this case, eccentric fixation can be either stable (the shadow is motionless) or unstable (the shadow is constantly moving).
One of the standard methods for assessing binocular vision is the color test. A special device is used, the main element of which is a disk with four circles illuminated from the inside: two green, red and white. The patient is put on glasses with light filters - red glass on the right eye and green on the left - and placed in front of the disk so that the right eye sees only the red circle, and the left only the other three. With normal binocular vision, a person sees a red circle, both green circles, and a white circle (white may alternately appear red and green). In case of binocularity disturbances, various other options are possible - for example, two red, three green, etc. - each of which is known and informative for the ophthalmologist, who, based on the nature of the picture observed by the patient, establishes the type of dysbinocularity (monocular vision, simultaneous, etc.).
What's next?
Treatment of strabismus cannot be considered complete after the operation is completed. It’s not like with appendicitis - they cut out the inflamed appendix and forgot about it.
Firstly,
Only after 3 months will surgeons be able to finally evaluate its result and decide whether the child needs an additional surgical stage in six months or not.
Secondly,
If a child has strabismus, special exercises are prescribed without fail using a synoptophore apparatus. The course ranges from 10 to 20 sessions.
But it’s too early to stop there - you need to work with the child yourself. For this purpose, there are gymnastics for strabismus in children, which the doctor will familiarize you with in detail before discharge.
Then everything depends only on the patience of the parents and the discipline of the child, but happy children's eyes, capable of seeing all the beauty of the world around them, are worth it!
The material was prepared jointly with the expert:
Leonid Borisovich Kononov, ophthalmologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, head of the department of eye microsurgery of the Morozov Children's City Clinical Hospital
Source:
information project “Moscow is the capital of health”
Types of amblyopia in children
There are several classifications based on various typological criteria. In particular, the classification, which is based on the etiopathogenetic mechanisms of the development of amblyopia, distinguishes its following types.
Obscuration amblyopia, i.e. due to the presence of an optical obstacle. As a rule, this is a cloudy opaque cornea (cataract), congenital cataract (clouding of the lens), ptosis (drooping, “sagging” of the eyelid, usually due to neurological pathology). A feature of this form of amblyopia is the difficulty, and sometimes the impossibility, of restoring vision after a delayed elimination of the immediate cause - in other words, the timeliness of intervention is the decisive factor here.
Refractive amblyopia develops as a result of myopia, farsightedness or astigmatism if the patient ignores the need for optical correction for a long time.
Anisometropic amblyopia occurs when there is a pronounced difference in visual acuity on the right and left. The worse-seeing eye is, as it were, “removed” by the central nervous system from performing visual functions.
Dysbinocular amblyopia is a consequence of strabismus - unilateral and, as a rule, concomitant; The squinting eye gradually turns off and degrades. This is the case when pathological conditions aggravate each other: as the amblyopia caused by strabismus progresses, the strabismus itself worsens.
Hysterical amblyopia is caused by psychopathological reasons and develops with deep hysterical neurosis or decompensation of hysterical psychopathy against the background of imaginary, inorganic blindness (hysterical amaurosis).