March 15, 2021
When the acute stage after a stroke ends, the patient is discharged from the hospital, then a new period begins - the person’s recovery after a stroke at home.
In this article we tell you how to properly care for victims, restore their movement and cognitive functions, and provide psychological support so that rehabilitation after a stroke at home is systematic and gives the desired effect.
General rules of care
The recovery period after a stroke is divided into early (up to 6 months), late (6-12 months) and residual effects (after 1 year). Ideally, in the early recovery period, the patient is recommended to be treated in palliative hospitals, sanatoriums, in the late recovery period and during the period of residual effects - in a day hospital, rehabilitation department, or by a visiting team at home. In reality, most often patients are at home after an acute period of stroke, and the main question that arises among their loved ones is where to begin rehabilitation. One of the main tasks of the rehabilitation process is to create comfortable conditions that promote relief and speedy recovery.
Preparing the premises
To exclude the impact of external traumatic factors (light, sound, temperature stimuli) on the patient’s psyche, he should be placed in a bright, well-ventilated room, where no extraneous noise can be heard from the street. The room should maintain a comfortable temperature within +18-22 °C.
The room should not be cluttered with furniture or objects that are easily moved out of place. A good alternative to a regular bed would be a functional one - with adjustable height and backrest position, side rails, and lockable wheels. Near the bed you need to place a bedside table with hygiene items, a blood pressure monitor, other necessary things, a wheelchair or other mobility aids (walkers, canes), a portable toilet or a bedpan.
If the person caring for the patient is not always with him, you can equip the room with a call button that the patient can easily reach, or replace it with a regular bell. Patients who can move independently or are beginning to train the skill of walking will find handrails along the walls very useful, and anti-slip mats in the bathroom will prevent injuries.
Body hygiene and bedsore prevention
Adequate prevention of bedsores can prevent their occurrence in 80% of cases.
Preventive measures:
- a special anti-bedsore or foam mattress with a thickness of at least 10 cm;
- soft bed linen without wrinkles;
- special cushions or pads made of foam rubber for vulnerable parts of the body (back of the head, shoulder blades, elbows, sacrum, heels, ankles);
- changing body position every 2-3 hours;
- comfortable underwear;
- prevention of skin trauma - carefully moving or turning over the patient.
It is important to carry out proper hygiene measures and skin care. At least once a day, during hygienic procedures, you should examine the entire surface of the patient’s body, vulnerable areas - every time you turn over. You should use waterproof diapers and diapers and change them as needed. It is necessary to wash the patient with warm water without soap after each bowel movement, washing with soap - no more than once a day, it is better to use liquid soap. After washing, the skin is thoroughly dried with a soft towel. For dry skin, moisturizing and nourishing creams are used; for diaper rash, powders without talc are used.
Nutrition
Food should be comfortable to swallow and easily digestible. The patient needs a sufficient amount of fluid - at least 1.5 liters. in the absence of restrictions. Drinking should not be limited even with urinary incontinence, since with a lack of fluid, urine becomes concentrated and irritates the skin.
The patient's diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein. It can be a soufflé, minced chicken, beef, rabbit, or fish. Patients who have difficulty chewing or swallowing semi-solid foods may be given meat or fish broth.
The menu should include dishes rich in vitamin C, iron, zinc, fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables.
Food is prepared boiled or baked and must be freshly prepared. You should not eat fried foods, pickles, smoked foods, spicy foods, canned food, fast food, carbonated and sweet drinks. You need to eat 4-5 times a day, in small portions.
Prevention of recurrent stroke
The reasons that led to the occurrence of a stroke most often do not disappear anywhere and continue to affect a person. The risk of recurrent stroke depends on their strength and combinations. Prevention of recurrent stroke is called secondary. List of conditions that people pay attention to first:
- Arterial hypertension is the main risk factor for stroke. It increases his risk by 5 times;
- diabetes;
- smoking;
- coronary heart disease (the risk increases by 2-4 times);
- atrial fibrillation (increases the risk by 3-5 times);
- hyperlipidemia (high levels of “bad” cholesterol);
- thrombocytosis;
- overweight.
Accordingly, it is necessary to correct these conditions and bring them back to normal to reduce the risk of recurrent stroke. Drug therapy is only part of the treatment. Diet, exercise, and giving up bad habits are important.
Antihypertensive drugs
It is recommended to reduce blood pressure, even if it is raised very slightly or within the normal range: “upper” 120-139 mmHg, “lower” 80-89 mmHg. So a decrease of 5 mmHg. helps reduce the development of stroke by 30%.
Diet, exercise, and giving up bad habits are important in preventing a recurrent stroke.
The superiority of some groups of antihypertensive drugs over others has not been proven. When prescribing, the doctor has to take into account the individual characteristics of the patient, compatibility with other drugs, and minimizing side effects. At the same time, for patients after a stroke, it is important not only to reduce blood pressure, but also to stabilize it as much as possible, even if slightly above the target values. For this use:
- Amlodipine - long-acting calcium channel blockers;
- Perindopril, Diroton, Renitek - angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors;
- Lozap, Cozaar, Valsartan - sartans, angiotensin receptor blockers;
- Hypothiazide, Indap are diuretics.
Drugs that prevent blood clots
With various arrhythmias, the risk of thrombosis and stroke increases up to 4 times. Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents can be used to prevent these conditions:
- Warfarin;
- Thrombo ACC;
- Plavix;
- Chimes.
Taking this group of drugs is usually long-term, one might say lifelong.
Statins
They help not only fight atherosclerosis and high cholesterol levels, but also stabilize the surface of already formed plaques, reduce the level of inflammation in the vascular wall, which will also reduce the risk of thrombosis:
- Mertenil;
- Atoris;
- Basil.
Read more about statins in the article.
Motor rehabilitation
The return of motor skills should begin as early as possible. Various exercises are used for rehabilitation after a stroke at home. Some of them can be done while the patient is in a supine position. These include:
- raising and lowering, bending and straightening the joints of the legs and arms;
- rotation of the arms at the wrist and elbow joints;
- clenching and unclenching fists;
- foot movements.
If the patient cannot yet sit or roll over independently, it is necessary to periodically change the position of his body. An assistant helps the patient turn over by approaching him from the affected side and holding him by the healthy shoulder, knee or hip.
When the patient begins to sit down, a special device on the functional bed will help him with this, by which he will pull himself up. You can do the following exercises while sitting:
- throwing the head back, tilting the head, rotating;
- stretching and bending the body forward;
- arching in the back, retraction of the shoulder blades;
- rotation of the arms in the shoulder joints;
- alternate leg lifts.
If a person can stand, the list of recommended exercises expands - the patient can additionally perform rotations and arm swings, bending, arm extensions with an expander, and walking in place.
Sitting down, changing positions in bed, getting up and walking if the patient was initially in a supine position is possible only after the doctor’s permission.
To improve coordination of movements, you should move your eyes in different directions, throw small objects at the target, gradually increasing their volume and mass and moving the target away. As the patient's condition improves, swinging movements in large joints, turns and tilts of the body are added.
Puzzles, construction sets, modeling from plasticine, origami, making appliques or regular copybooks are perfect for training fine motor skills.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.
Restoring everyday skills
All everyday skills should be developed under the supervision of a loved one, an assistant who will control the patient’s movements and, if necessary, support and guide his hand.
Nutrition
To prevent spoons and forks from slipping out of the patient’s hand, you can wrap their handles with thin foam rubber. If paralysis/paresis affects the leading hand, then when eating, you should help the patient - support and guide his hand towards the mouth.
Using the tap and washing your face
A chair should be placed in front of the sink so that the patient can wash while sitting. He should open the tap with the affected hand and, if necessary, should be assisted by guiding his hand towards the tap. In this case, the patient should check the temperature of the water with a healthy hand with preserved sensitivity. Once a comfortable temperature has been established, the patient should attempt to wash the affected hand.
Combing
You should choose combs made from non-slip materials, or wrap the comb handle with thin foam rubber. If possible, you should try to comb your hair with the hand with impaired function.
Dressing
Clothes (jacket, shirt) should be loose, fastened with buttons. It is placed on the knees, between which the sleeve for the affected arm is lightly fixed. With the help of the healthy one, she gradually moves into the sleeve.
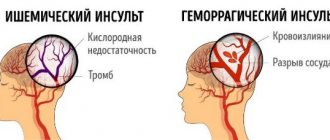
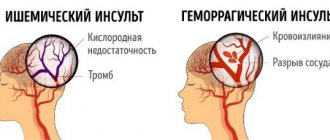
Briefly about the main thing - features of ischemia and hemorrhage
There are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic
. Leads to contraction of blood vessels in the head, which clogs their walls, causing hypoxia. - Hemorrhagic
. The process of bleeding into the brain, often fatal.
According to statistics, the ratio between the two species is 80% to 20% (Consilium Medicum No. 02 2000).
Ischemic stroke can develop at any age - in children, adolescents, middle-aged people and the elderly. The severity of the consequences is also individual, depending on the speed of decision-making after the attack, the correct diagnosis, and the prescribed treatment.
Hemorrhagic stroke can happen to a person of any age. It occurs suddenly and is accompanied by a serious condition of the patient, constant gag reflexes and severe headache. At the first signs, a person often loses consciousness.
Causes:
- sudden movements, change of position;
- food with a lot of fat and other harmful ingredients;
- bad habits - smoking, alcohol addiction, drug addiction;
- high water temperature during water procedures or outdoors;
- excessive physical or psychological load on the human body;
- cardiac arrhythmia;
- blood pressure problems.
Information about stroke - clickable
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear, you should be careful and prompt; minutes count. On average, 3-4 hours after the first signs appear, the condition of the blood vessels in the brain deteriorates, and the consequences may become irreversible. The first 3-4 hours are the most important in the fight against the disease.
If the signs and pain go away within 24 hours, the person most likely had a mini-stroke.
Symptoms of left-sided and right-sided strokes differ
Algorithm of actions when symptoms appear:
- Place the patient on a horizontal surface, holding his head at an angle of 30 degrees.
- If the victim feels sharp gag reflexes, you need to turn his head to the side.
- You should carefully monitor changes in blood pressure and pulse. It is recommended to measure them and monitor fluctuations.
- When emergency doctors appear, you should fully describe the picture of what happened. Tell what actions were taken before the doctors arrived.
Speech rehabilitation
To restore speech skills, the patient will need to consult a speech therapist, who will prescribe exercises for training facial muscles, language, as well as help and certain behavior from loved ones.
The patient's relatives should constantly communicate with him, while pronouncing words slowly and clearly, avoiding complex long sentences. The patient must first train the pronunciation of individual sounds, gradually moving on to syllables and words. Sometimes it is easier for a person to pronounce words in a sing-song manner than in the usual way.
Recommended exercises:
- stretch out your lips like a tube and “bar your teeth”;
- lick and lightly bite lips;
- stick your tongue out of your mouth, stroke your cheeks with your tongue, “click” your tongue;
- puff out one's cheeks;
- smile, trying to use both sides of the mouth symmetrically.
Help in the acute period
Which doctors are needed in the treatment of stroke depends on the period of the disease, but in any case, they must be experienced, highly qualified specialists who know how to properly provide assistance in this situation.
When diagnosing an ischemic stroke in a patient, the doctor’s goal is to restore blood supply with subsequent rehabilitation. This may require blood thinning medications or mechanical removal of the clot using a catheter. To remove atherosclerotic plaques, endarterectomy is performed, and to increase the diameter of blood vessels, plastic surgery with stenting is performed.
Memory training
Memory and intellectual function training occurs simultaneously with speech restoration. The patient should try to repeat the syllables, words, phrases spoken by the assistant, gradually increasing the interval between pronouncing the word and repetition.
Board games, composing stories based on pictures, solving crossword puzzles, and even simple conversations help restore thinking abilities. Near each item in the room you can put a card with its name. As cognitive functions are restored, the patient can read, watch films, and discuss their content.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine?
Folk remedies are not decisive in the recovery period. All medications are prescribed and discontinued by a doctor. Auxiliary traditional methods must be agreed with the doctor. They are used without limiting therapy and other recommendations.
You should not be fooled by advertisements that claim “the growth of new nerve cells.” This is a complete bluff. Scientists are indeed conducting experiments on the use of stem cells for patients with strokes, increasing the activity of the opposite hemisphere. And the effect of decoctions and herbal tinctures is based on lowering cholesterol and supporting the immune system.
These properties have:
- garlic-lemon tincture;
- various recipes from pine cones;
- onion ointment.
Psychological support
The patient’s relatives need to provide a positive environment at home, demonstrate their willingness to help, support the patient, and assure that his condition is temporary and changes for the better are inevitable. If the patient’s condition allows, he should be involved in feasible household chores, making him feel important and not removed from everyday worries.
A psychologist or psychotherapist will help you cope with panic attacks and depression. If the patient experiences acute conditions, aggression, or suicidal thoughts, the help of a psychiatrist and the prescription of medications may be required.
The duration of the recovery period depends on many factors: the extent of the damage, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases. In patients who have suffered a mild form of stroke, partial recovery requires 1-2 months, and complete recovery takes about 3 months. In severe forms with persistent impairments, partial restoration of lost functions occurs after at least six months, and the chance of returning all lost skills is minimal.
According to statistics, after the first year after a stroke, 60% of patients do not need outside help. 30% can return to their previous work. Help with complex tasks is required during this period by 20% of patients. 15% of those who have suffered a stroke remain dependent on outside help, 5% need constant care.
Dealing with the consequences
Treatment of muscle hypertonicity
Muscle spasticity occurs when attempting passive movement in a limb. The goal may not be to completely remove the spasm, since some patients use this muscle tension as an element of stability when moving. This poses a problem in bedridden patients, when spasms cause pain and interfere with rehabilitation and care.
Spasms in bedridden patients cause pain and interfere with rehabilitation
To locally eliminate spasms, neurotoxin preparations can be administered intramuscularly:
- Botox;
- Dysport;
- Xeomin.
Antispastic agents:
- Sirdalud (central acting muscle relaxant);
- Baklosan (central acting muscle relaxant);
- Mydocalm (central acting muscle relaxant);
- Relanium.
Reception begins with a minimum dose of the drug and gradually increases until the effect is achieved or until the first side effects occur. Treatment of these symptoms helps with physical therapy and prevents the development of joint contractures.
Correction of brain functions
Dementia may develop in about half of stroke survivors. The risk of dementia is highest during the first 6 months and can persist for several years.
Nootropic and neuroprotective drugs are used:
- Cerebrolysin, carried out in monthly courses of intramuscular injections 2-3 times a year;
- Piracetam, Nootropil, Lucetam;
- Phenotropil in courses up to 3 months.
As well as drugs from other groups that are actively used for various neurological problems: Memantine, Cavinton.
Treatment of post-stroke depression
2/3 of patients experience post-stroke depression of varying severity. The requirements for antidepressants combine a minimum of side effects, since there are usually many other comorbidities. A slight stimulating effect is also needed, since most patients develop asthenia. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may be suitable for this purpose:
- Paxil;
- Prozac;
- Fevarin.
The effect usually occurs within 2 weeks. It is necessary to discontinue medications gradually.
Post-stroke pain
Sensations similar to a burning sensation from ice water occur after damage to the areas of the brain responsible for pain sensitivity. For treatment, combinations of the above antidepressants with anticovulsants are used:
- Lyrics;
- Finlepsin;
- Tebantin.
Post-stroke pain occurs after damage to certain areas of the brain.
In addition to medications, transcranial electrical stimulation may be used.