What to do if your legs are swollen?
In order to reduce swelling, it is necessary to reduce physical activity on the lower extremities; ice can be applied to the swollen area. If the vein valves are insufficient, leg bandaging is performed. It is recommended to place a pillow under your feet while sleeping to enhance venous return to the heart. For heart failure, medications are prescribed.
If you find swelling in your legs, contact a cardiologist at the FIRST NEUROLOGY clinic. In our work we use modern diagnostic and treatment methods
Treatment
Treatment of leg swelling is carried out comprehensively; therapy includes taking medications, regular massage, and moderate exercises involving the limb. Only in combination these methods will help get rid of swelling and prevent complications.
Massage
Massage is an additional method of recovery after a stroke. Massage stimulates the functioning of blood vessels, accelerates blood flow, relaxes muscles, restores their strength, and relieves swelling.
Massage is prescribed in the first month of recovery. The course is long, at least 14-30 days, depending on existing complications, type of stroke, etc.
Important! In case of cerebral infarction without complications, massage is performed 2-3 days after the crisis; in case of hemorrhage - after 6-7 days.
Time of implementation : immediately after sleep, in the morning or before therapeutic exercises.
Duration – from 10 minutes, time gradually increases to 30 minutes.
Frequency day .
The entire course and number of sessions are prescribed by the doctor.
Carrying out conditions – air temperature not less than 20 ᵒС; Only the massaged part is exposed, the patient is covered with a blanket; massage is performed before meals or 2 hours after meals; after the massage – rest for 15 minutes.
Massage movements are directed from the foot to the knee, then to the inguinal lymph nodes. To quickly relieve swelling (to narrow blood vessels), massage is done with ice cubes, which include a decoction of oak bark and eucalyptus.
Additional remedies: cool gauze compresses (wrapped around the leg) are applied at night.
Gymnastics
Gymnastics is a prerequisite for relieving leg swelling.
To return the vessels to their previous state and normalize blood flow, feasible physical activity is necessary.
Time : in the morning after the massage.
Duration – at least 20 minutes.
Frequency – at least 2 times a day.
If possible, it is advisable to visit the pool and gym.
In the afternoon, exercise can be replaced by a walk. Fresh air, nature, positive emotions contribute to recovery.
For paralyzed limbs, passive gymnastics is performed.
Medicines
Attention! All medications are prescribed only by a doctor; self-medication is dangerous for the patient’s life.
In the initial stages, medications that thin the blood and prevent blood clotting (heparin, warfarin) are most often prescribed.
Diuretics - furosemide, torasemide, etc. can be used intravenously, intramuscularly and in tablets. Daily dose – from 10 mg. Negative consequences may occur - arrhythmia, exacerbation of heart disease.
For varicose veins, venotonics are added (detralex, phlebodia, etc.). For bedridden patients, an elastic bandage and special underwear are used.
Don’t forget about folk remedies - decoctions, baths, tinctures effectively relieve swelling:
- Carrot, cucumber, lemon juice are diuretics (drink 3 times a day before meals);
- To increase overall tone and quickly relieve swelling, it is recommended to mix the yolk with 3 grams of milkweed (use 2-3 times a day);
- Tincture of mint or flax relieves swelling after 3-4 days;
- Baths of mustard, sea salt and mint tone muscles and increase blood flow (every day before bed for 6 days).
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Romanova Tatyana Alexandrovna
Pediatric neurologist. Experience: 24 years.
Temina Lyudmila Borisovna
Pediatric neurologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 46 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
About the disease
Stroke – translated means “strike, attack”, “paralysis” – an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. The disease develops suddenly (from a few minutes to 1-2 days), manifests itself against the background of overexertion.
Reference. The first descriptions of the disease were made by Hippocrates back in 460 BC.
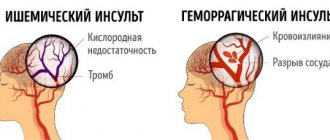
There are three types of disease:
- Ischemic stroke (up to 75–85% of cases), affects people over 60 years of age;
- Hemorrhagic stroke (up to 20%) occurs in people with hypertension aged 40–60 years;
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (up to 5%) – rupture of an aneurysm, brain injury.
Important! Every 1-2 minutes, someone in Russia develops a stroke. Up to 80% of stroke survivors become disabled, 20–30% of them require constant care.
Read also
Alzheimer's disease
47,000,000 people suffer from dementia in the world.
Doctors call Alzheimer's disease the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease accompanied by... Read more
Chronic cerebral ischemia
One of the most common diagnoses at an appointment with a neurologist for patients in the older age group is chronic cerebral circulatory failure, discirculatory encephalopathy. According to…
More details
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is? Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to classification...
More details
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms. This disease is diagnosed at different times...
More details
Swelling after a stroke: symptoms, consequences and treatment methods
One of the common consequences of a stroke is the appearance of swelling. Its most dangerous type is cerebral edema, but swelling of the extremities also carries certain health risks and significantly slows down rehabilitation. In our article we will look at the causes and types of swelling after a stroke, and also talk about the treatment of these complications.
********
There are two types of swelling that occurs as a result of a stroke - cerebral edema and swelling of the extremities. These two conditions have different etiologies and also have different effects on the body and recovery after a vascular accident.
Brain swelling
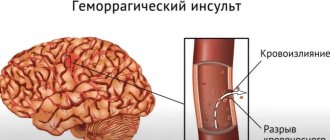
Due to hemorrhage in the brain, nerve cells in the affected areas die. A hematoma occurs, which compresses the brain tissue. This is how a hemorrhagic stroke occurs - a pathology that is most often accompanied by cerebral edema.
The larger the hematoma, the faster the swelling develops. It can lead to displacement of parts of the brain, which can be fatal. As a rule, swelling appears on the 4th day after a stroke, and it is important to begin specific therapy in the first 24 hours after its identification.
There are two types of cerebral edema:
- Cytotoxic when brain tissue cells accumulate water.
- Occurring against the background of impaired outflow of blood and other fluids (interstitial, intercellular) when capillaries are damaged.
How to treat cerebral edema
Symptoms of cerebral edema vary depending on various factors:
- location of the stroke focus;
- volume of damaged brain tissue;
- degree of nerve cell atrophy;
- age and condition of the patient.
Clinical manifestations also differ - from weakness and dizziness to severe headache, fainting, coma. Therefore, it is necessary to diagnose the condition of the brain tissue in order to understand the degree of threat to the life and health of the patient.
Treatment for cerebral edema includes:
- surgical decompression - an operation to eliminate compression of the brain in the middle cerebral artery;
- constant supply of a breathing mixture saturated with oxygen;
- osmotherapy - intravenous administration of diuretics (normotonic and high molecular weight solutions).
The patient must lie in a certain position for better outflow of venous blood (the upper body is raised at an angle of 30°). Pain relief is also indicated if swelling of the brain causes severe headaches.
Edema of the lower extremities
Another consequence of a stroke is swelling of the arms and legs. It can occur both on paretic limbs and on those that are not injured.
The swelling is aggravated by the fact that the patient lies almost constantly in the first days after a stroke. Stagnation of fluids in immobile limbs can slow down rehabilitation after a stroke, which means the affected arm or leg will not be able to fully function.
Causes of swelling of the hands and feet
The most obvious reason for the appearance of edema in paralyzed limbs after a stroke is impaired blood circulation and lymph movement. But there are others:
- Deep vein thrombosis. It most often occurs with ischemic stroke, which is directly related to increased thrombus formation and high blood clotting.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. They can appear both before and after a stroke. Such edema has a characteristic localization - swelling is noticeable not only on the arms and legs, but also on the back (sacral region), in the lower abdomen. They are denser; when pressed with a finger, a mark remains for a long time.
- Renal dysfunction. Against the background of a stroke, many chronic pathologies become aggravated. And if earlier malfunctions in the functioning of the kidneys could be asymptomatic, then in conditions of immobility, renal swelling can remind itself. It manifests itself in the form of pastiness in the limbs and on the face.
- Vena cava syndrome. In this case, not only the paretic limb swells, but also the face, neck, chest area and even the tongue. At the same time, the patient may experience headaches, speech problems, and nosebleeds.
- Compression of the subclavian veins . Occurs due to prolonged physical inactivity. Swelling develops gradually and does not cause discomfort. But the danger of this condition is that it directly affects the blood circulation of the upper body. The head, neck and face acquire a characteristic puffiness and bluish tint. In difficult cases, thrombosis of the subclavian vein is possible, which can result in the closure of the lumen of the vessel.
- Stagnation of lymph, diseases of the lymphatic system. It mainly affects the lower extremities and occurs due to their prolonged immobilization. When lymph stagnates, body temperature rises, muscle weakness appears, and the affected leg acquires a reddish tint. When palpated, this swelling causes pain.
- Cardiomyopathy . One of the common complications of stroke. May also cause swelling of the arms and legs.
The severity of swelling after a stroke depends on how deeply a particular part of the body is paralyzed. There may be either slight swelling with motor impairment of the limbs, or a severely swollen arm or leg with complete paralysis. In this case, the area of edema covers almost the entire limb.
How to treat swelling of the limbs after a stroke
Proper care of the patient is important - limbs affected by paralysis must be constantly developed and their position changed. The leg or arm should be placed completely on the surface of the bed, not hanging down. From time to time you can place a cushion or pillow under it.
Exercises aimed at restoring blood circulation in the limb will also be useful. On the recommendation of a rehabilitation specialist, massage and special restorative gymnastics are performed.
You can raise your arms and legs alternately, squeeze a ball, or hold an object in your hand. Moreover, it is necessary to involve not only the affected side, but also the healthy one.
Drug treatment of edema in the extremities involves taking antiplatelet agents - drugs that restore vascular patency. Diuretics are also prescribed to remove excess fluid from the body.
******
The development of cerebral edema is a condition that directly affects the survival of post-stroke patients. However, with swelling of the limbs, not everything is so simple - it can provoke an irreversible trophic disorder and complicate rehabilitation. As a result, a person may never recover from a stroke.
In both cases, timely diagnosis and complex therapy are extremely important. With successful treatment, the negative impact of swelling on the body can be reduced to a minimum.
Prevention
In order not to worsen the patient’s condition and prevent complications, immediately after a stroke you should take into account the necessary rules and recommendations:
- Fluid intake (in any form) is no more than 1 liter per day. The patient's urine should be excreted in the same volume;
- Diet (allowable amount of salt – 1.5 g per day);
- every 2 hours , at night - every 5 hours;
- It is unacceptable for limbs to hang from the bed (it is better to raise your legs and place them on a thick pillow);
- Massage and exercises should be performed regularly (even simple movements help restore blood circulation);
- In a sitting position, the back should rest on a backrest or support , pillows are placed under the arms, the position of the hands is palms down, fingers extended.
Useful video on the topic: