A stroke is a signal to change your life, restore and maintain health. “Consider this your second chance,” says Alexander Atyashev, a neurologist at the Medicare clinic. How to recover from a stroke and what can relatives do to bring maximum benefit to the patient during the rehabilitation period?
Alexander Atyashev.
To minimize the consequences of an ischemic stroke, there is only the first 4.5 hours
— Alexander, what happens in the body during a stroke and why are its consequences so serious?
— A stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation when the blood supply to any part of the brain is cut off. The blood supply is disrupted - and damage or death of brain cells occurs, and this leads to disruption of any body function - speech, movement of the limbs, mental abilities, attention, memory, etc.
— Why is cerebral circulation disrupted?
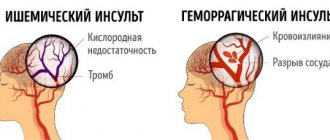
- A stroke occurs either due to a blockage of a blood vessel that supplies the brain (ischemic stroke) or when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures (hemorrhagic stroke).
Blockage of the vessel can be caused by the formation of atherosclerotic plaques (fatty deposits) or a blood clot that enters the bloodstream and causes a blockage of the artery.
Vessel rupture during a hemorrhagic stroke usually occurs in the softened artery wall: blood leaks out and accumulates, which leads to compression of brain tissue and cell damage. In both cases, as a result of a lack of oxygen, some brain cells at the site of the stroke die, and some are damaged.
Within minutes, the person loses the ability to reason, speak, or move their arms or legs.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
- What symptoms indicate a stroke?
— There is a simple test that will help relatives recognize a stroke. You need to ask him to do only three actions: smile, raise both hands and say his name. If the corner of the mouth droops when smiling, if a person cannot raise his arms because one of them is weak, and if he pronounces his name unintelligibly, call an ambulance immediately.
Remember: in case of an ischemic stroke, to effectively remove a blockage of a vessel (thrombus), there is only 4.5 hours until the cells of the damaged area are completely dead.
Signs of a stroke may also include:
- sudden numbness of the face, arms, legs, weakness in the limbs,
- sudden loss of consciousness, loss of ability to speak, difficulty speaking, loss of ability to understand the meaning of someone else’s words,
- sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes,
- sudden disturbance in gait, dizziness, loss of balance,
- sudden severe headache of unknown cause,
- sudden nausea, pain in the face or limbs, general weakness (more often in women).
— Why is it so important to seek medical help in the first hours after a stroke?
— A stroke is an emergency. Medical care is most effective only in the first 3-5 hours: this is the so-called therapeutic window, during which treatment can restore damaged brain cells and minimize the consequences of a stroke. If you do not seek help in time, the cells will die irrevocably, and further treatment will be aimed only at adapting to life, taking into account the existing disorders.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
— How is a microstroke different from a regular stroke? Is it just as dangerous and also requires treatment?
— A microstroke, or transient ischemic attack (TIA), is a temporary disruption of the blood supply to part of the brain, that is, a harbinger of a stroke. During a TIA, a person may experience some or all of the symptoms described above.
The peculiarity of a micro-stroke is that these symptoms are usually mild and pass quickly - the next morning a person can feel great.
But take them seriously - be sure to call an ambulance! Your health and life depend on it.
What affects life expectancy after an attack?
When considering the question of how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, several factors should be highlighted on which the patient’s life expectancy often depends:
- diameter of brain tissue damage. With extensive hemorrhage or ischemia, patients require immediate hospitalization. In a hospital setting, resuscitation measures are carried out, including artificial ventilation of the lungs, maintaining the vital activity of the heart and blood vessels. If the diameter of the affected area is large, such patients, as a rule, do not survive;
- Complications affect a person’s quality of life and its duration. With paralysis, the patient is forced to spend all his time in a horizontal position, without movement. This entails bedsores, pneumonia and many other diseases that shorten life;
- Age plays a big role. The consequences of a stroke in old age are more significant, and the risk of developing severe consequences increases over the years. After 50–60 years, the chances of recovery become less and less. Younger patients are able to overcome the disease and return to normal life faster;
- competent organization of space. This is another factor that plays an important role. After an attack, many people experience dizziness and fainting, which often causes falls and broken bones. The patient’s place of residence must be safe and equipped with special handrails;
- decreased mobility after a stroke leads to blood stagnation and blood clots. This causes repeated attacks.
If a person who has suffered a stroke is at a young age, follows all the rules of rehabilitation, eats right, and engages in physical exercise, he can live quite a long time. The situation is different for the older generation. Unfortunately, the disease causes many irreversible changes, which can be very difficult to overcome, which significantly reduces life expectancy.
Rehabilitation begins on the first day
— When can you start rehabilitation after a stroke?
- After completion of treatment of the acute phase, that is, in fact, on the first day after the stroke. Even if the patient is still lying down, he can and should move - turn his head, move his arms and legs, try to sit up.
Even with bedridden patients, you can and should do passive exercises.
The rehabilitation program begins in the hospital and continues at home (or in a sanatorium, medical center). Every day after a stroke is work on the road to recovery.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
— What should be the first step in the recovery process?
— First of all, you need to work on correct body positioning: this facilitates the restoration of motor abilities, prevents muscle injuries, contractures, and reduces pain. Main principles of positioning:
- maintain the maximum possible symmetry of key points (shoulders, shoulder blades, pelvis), keep the head, shoulders, hips in the correct position.
- golden melt - the patient lies on either side, but not on the back.
- do not ignore the immobile part of the body. The bedside table is placed on the affected side so that when moving, for example, behind a mug, the patient reaches across the affected side and uses it. Learn to use your weak hand - for support, support, opening a door, turning on a light. It is important to develop a strong habit of using your weak hand as much as possible.
— Does the patient need physical therapy?
- Necessarily. Exercise therapy is necessary to restore movement skills and prepare for the moment when you can move more fully. As a result of regular exercises, shortened muscles of the hand, forearm, and back of the legs will be stretched, weakened arm muscles will be activated, the amplitude of movements will increase, and balance while sitting and standing will improve. If the patient has speech impairment, articulation exercises are necessary (for the tongue, lips, lower jaw muscles, facial muscles). Vestibular gymnastics is needed to restore coordination of movements, exercises for rehabilitation for movement disorders. Having mastered these exercises under the guidance of a doctor, you can do them at home - first with the help of relatives, then on your own. The main thing is regularity: 5-6 times a week, 30-40 minutes a day.
Advice to the patient’s relatives: treat his complaints wisely and do not allow him to succumb to laziness and despondency.
A patient in this state is most often inclined to lie down, but your task is to insist that he moves. Adequately assess his condition, and if he can get to the toilet on his own, do not place the dry closet near the bed. If the patient is able to feed himself, do not spoon feed him.
Medicine divides disorders due to stroke into three groups:
- In terms of motor skills - paresis, paralysis, contracture.
- In speech - speech recognition, comparison of concepts and corresponding words when areas of the brain responsible for understanding are damaged.
- Cognitive and emotional-volitional - memory loss, attention disorder, cognitive and intellectual activity, depression.
In Russia, 48% of stroke survivors lose mobility, 18% lose the ability to speak, and only 20% recover without becoming disabled. These figures are caused by the lack of timely rehabilitation started by the patient’s relatives, the insufficient number of rehabilitation centers, and the low quality of rehabilitation measures for victims.
The following factors give hope for complete rehabilitation:
- preservation of the patient's intelligence;
- restorative procedures immediately after the end of the acute period;
- individual recovery programs;
- the patient’s activity in restorative procedures.
Early initiation of rehabilitation procedures gives a high chance of the victim returning to normal life.
Relearn to speak, eat, understand and remember
— How should you prepare a home for a patient after a stroke? And what additional equipment will he need?
— While the patient is regaining the daily skills necessary to independently care for himself, while he has difficulty moving, it is necessary to ensure that he can move safely. For this:
- remove carpets and wires on the floor to prevent the patient from tripping. Make sure all paths the patient uses are clear and well lit.
- equip the bed with rails so he can sit down
- in the bathroom, attach special vertical railings that the patient can hold on to,
Special devices - a toilet chair, a bath seat - will make the patient’s life easier at home.
- install a seat in the bathtub or shower so that the patient can wash while sitting,
- raise the height of the toilet using a bedside chair,
- when the patient learns to walk, buy him a walker, and later a cane.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
— After a stroke, people often have speech impairments. Can it be restored?
— Yes, articulation gymnastics, which I mentioned above, as well as classes with a speech therapist, help restore speech functions, but the main thing is communication with loved ones, that is, daily speech practice. Speech disorders can be of two types - aphasia (the patient has difficulty understanding words and expressing his thoughts) and dysarthria (there is understanding, but pronunciation and fluency and clarity of speech are impaired). General rules:
- Ask questions that the patient can answer “yes” or “no.”
- speak slowly and clearly, give the patient time to respond, do not speak for him.
- be patient and consistent. With regular exercise, improvement will definitely come over time.
— What should a person be fed after a stroke?
- Patients with stroke often have a problem with impaired swallowing - dysphagia, and there is a risk of obstruction of the esophagus and aspiration (penetration of foreign bodies into the lungs). It can cause suffocation, infectious diseases, and pneumonia. Such patients need to be fed, strictly following the recommendations: only in a sitting position with support under their back, turning to the healthy side at the time of swallowing, only with a small amount of food.
Semi-hard foods are best tolerated - casserole, thick yogurt, pureed vegetables and fruits, watery porridge.
Give solid and liquid foods at different times. Eliminate from your diet foods that often cause choking - bread, cookies, nuts, etc.
— What other disorders does a stroke lead to?
— During a stroke, areas of the brain that are responsible for the processes of learning, understanding, and communication can be damaged. Memory deterioration and problems with perception are often observed: a person does not realize that the functions of his body are impaired, he does not recognize familiar objects or people, he may ignore some part of the body. Over time, with proper therapy, lost skills will be restored, but this is a slow process.
At home, you can and should exercise your memory and attention: ask the patient about what he did/saw yesterday, look at a family album, solve riddles, remember similar objects by shape, color, etc.
Another important point is the patient’s mood. A person experiences despondency, emptiness and hopelessness due to the fact that he cannot fulfill his previous social functions (work, take care of his family), a feeling of humiliation due to lost basic skills, and may refuse to communicate. Sudden mood swings, aggression, anger, laughter and tears for no reason are possible.
In such cases, the patient may need treatment with antidepressants, and relatives may need to be calm and refrain from criticism.
Both the patient and his family need to remember that all of these are consequences of a stroke, which will go away as they recover.
about possible contraindications, consult a specialist
Symptoms of any type of stroke:
- muscle weakness;
- lack of sensitivity in some areas of the body;
- lack of coordination of movements;
- speech disorder;
- a sharp deterioration in visual acuity, double vision, narrowing of the field of view;
- difficulty swallowing.
Extensive brain damage in severe cases of the disease can lead to loss of consciousness and coma. Common symptoms include changes in body temperature and a sudden and severe increase or decrease in blood pressure.
An ischemic stroke typically occurs during sleep, closer to the morning, while a hemorrhagic stroke occurs during physical or emotional stress.
Signs of a stroke
Move!
— How to choose the right physical activity after a stroke?
— It is necessary to move regardless of the degree of impairment after a stroke, with any degree of limitation.
If the functions of your legs and arms are not impaired, get up and start moving as quickly as possible! Do physical therapy, take the stairs instead of the elevator, walk down the street, garden, play with your grandchildren. Any activity that you enjoy is fine—just make a commitment to move every day.
If there is weakness in the limbs, but they work, you can walk, including on a treadmill, it is useful to swim, do gymnastics in the pool, yoga, and dancing.
Even if the patient is in bed or in a wheelchair, he can also move - do strength exercises, stretching exercises.
— Can a person always return to normal life after a stroke?
“It depends on the volume of damaged cells, what part of the brain is affected and whether medical assistance was provided on time. With due persistence, patience, and the help of doctors and relatives, lost functions are restored.
In my practice, there were patients who returned to work even after several strokes.
Both the patient and his family need to understand that recovery is a long and complex process; one should not expect instant results and fall into despair when they do not exist. There will be good days when you make huge strides, and bad days when you seem to have slipped back to where you started. Don’t strive to embrace the immensity, don’t rush things, but divide your goals into:
- the nearest ones - which can be tracked and measured. For example, if the patient was lying down in the first days, the immediate goal would be to sit up in bed and eat on his own. Holding a mug, getting up and walking to the door of the room, doing hygiene procedures - all these are also immediate goals.
- distant - what you want to achieve in 6 months or more. Return to work, sports, hobbies - it is better to discuss all these goals with your doctor to understand what degree of functional restoration you can expect.
A set of measures to restore memory and intelligence in older people after a stroke
It is better to begin rehabilitation of mental abilities while patients are in the hospital, after the general condition after the stroke has stabilized. But the brain of older people should not be subjected to excessive overload.
Restoration of memory functions is accompanied by preliminary drug therapy aimed at maintaining stroke-damaged nerve cells. Elderly people are administered the appropriate drugs (Actovegin, Thiocetam, Piracetam, Cavinton, Cortexin) intravenously, or they take them in tablet form. The therapeutic effect of the use of drugs appears slowly, over 3–6 months. The course of medication is repeated after 2–3 months.
When restoring memory, the following rehabilitation actions are carried out:
- Train your memorization ability: listen and repeat numbers, words, short poems. First, you need to achieve short-term memorization - when the patient can repeat information immediately after listening to it. Then the memorization period should be increased - for example, the patient will independently pronounce the numbers when asked to count.
- Look at photographs and videos, while remembering and pronouncing the names of all the objects depicted.
- Play boardgames.
We recommend
“Diabetes mellitus in older people: features of diagnosis and treatment” Read more
Reducing the risk of recurrence
Unfortunately, 25-30% of strokes recur. There are no exact statistics for the Russian Federation; data from the domestic stroke registry indicate the real frequency is 5-6 times higher than recorded. The reason for this phenomenon is that the absence of CT results in 10 percent or more errors.
To prevent a recurrence of a stroke, it is necessary to: control blood pressure, the maximum acceptable is 140/90, without a sharp decrease. Follow a low-salt diet.
Normalize “bad” cholesterol and blood lipid composition. In addition to the medications prescribed by your doctor, it is advisable to add soluble dietary fiber (rice, oat bran) to your diet.
Take medications to prevent blood clots. Take acetylsalicylic acid prophylactically; for a blood clot in the heart with arrhythmia, use stronger medications to control blood clotting.
What is the problem with strokes?
Stroke, described in ancient times by Hippocrates, was called apoplexy until the 19th century. Often the disease ends in the death of the patient, and even with modern developments in medicine, patients are at risk of losing their ability to work with disability.
Stroke statistics
The main consequences of a stroke:
- loss of speech function, completely or partially;
- impairment of motor activity to complete paralysis;
- mental disorder - dementia, depression;
- memory impairment or loss;
- uncoordination of movements.
First aid to a patient—relieving an acute condition—takes place in a clinical setting, but in almost all cases long-term rehabilitation is needed. Sanatorium-resort treatment helps with this, as it is the most effective.