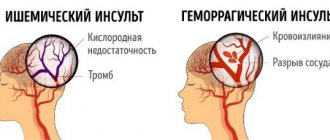
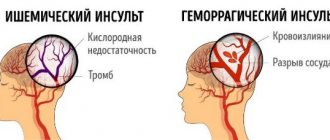
A stroke is an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain and, as a consequence, its focal damage. It entails irreversible consequences for the body; it can disrupt clarity of consciousness, the functioning of internal organs, cause paralysis, and more. To restore the body, as well as for effective rehabilitation, the patient needs to change the usual approach to household things, observe a special regime, and follow certain nutritional rules after a stroke. Often this all becomes the responsibility of family and friends.
Diabetics after stroke
Stroke and diabetes are closely related.
Diabetic patients are 2.5 times more likely to have a cerebral hemorrhage than healthy people. Moreover, in 90% of cases in diabetics it is an ischemic stroke. In such patients, disturbances in the water-salt balance lead to coarsening of the vessel walls, their narrowing; after a stroke, the recovery process is slowed down, since vascular atherosclerosis slows down the supply of oxygen needed by the brain.
Diet is a forced but necessary measure for recovery. Extremely important:
- completely eliminate salt;
- take potassium to strengthen the walls of blood vessels;
- drink plenty of liquids (water, compotes, weak tea);
- avoid foods with high cholesterol levels;
- eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Direct cause-and-effect relationship – stroke develops against the background of diabetes, and not vice versa.
Conclusion: Diet plays a huge role in maintaining a healthy state.
The first signs of a microstroke
The very first sign of a microstroke is numbness of the extremities for a short time (many patients attribute it to “numbness” of the leg or arm). Also, the first, that is, appearing earlier than others, signs of a microstroke include:
- Short painless blindness in one eye (as if a shadow had crept into the field of vision for 20-30 seconds);
- Temporary and sudden numbness of the face (the person will not be able to smile);
- Loss of the ability to speak coherently (sounds and words are confused, sometimes it is impossible to utter a word at all);
- A sharp headache (like a flash) - does not go away even if you take any medications;
- Short-term disturbances in coordination of movements are possible (objects fall from hands, the patient simply cannot lift them for some time);
- The skin becomes pale;
- Weakness appears throughout the body (a person suddenly wants to sit down or lie down);
- Sweating increases sharply for no apparent reason.
The essence of diet after a stroke
Diet Table 10 according to Pevzner after a stroke is aimed at optimizing the restoration of health and preventing relapse. It is both a therapeutic and preventive measure, which is based on proper nutrition.
Diet Table 10 according to Pevzner - basic rules:
An innovative drug for losing weight by 30-40 kg! Removes even age-related fat without chemicals, liposuction, diets or physical exercise. Exercises
- Question: Childbirth after a stroke. Is it possible to give birth after a stroke?
- Food should be varied. The diet should be rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber and all the necessary nutrients for normal life.
- Meals should be fractional. You should eat at least 4 times a day, but in small portions.
- The last meal of the Table 10 diet after a stroke should be light and at least 3 hours before bedtime.
- In the Table 10 diet, restrictions are imposed on fats of animal origin (reduced by at least half), salt (no more than 5 grams per day), sugar (no more than 50 grams per day).
- The amount of food consumed per day should not exceed 2 kilograms according to the Table 10 diet according to Pevzner after a stroke.
- You should drink about 1 liter of still water every day.
Permitted and prohibited products
Diet after a stroke - allowed foods:
- Veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey (boiled or baked on the Table 10 diet);
- Vegetarian soups;
- Low-fat varieties of fish (boiled or baked);
- Low-fat dairy and fermented milk products (butter no more than 20 grams per day);
- Eggs (no more than 1 egg per day, unlimited amounts of protein);
- Cereals and cereals (unpolished rice, buckwheat, oats, millet);
- Bread made from wholemeal flour (rye, whole grain);
- Crackers, savory cookies;
- Pasta (in limited quantities);
- Potatoes (boiled, baked, occasionally stewed);
- Cabbage, carrots, beets, eggplants, zucchini, cucumbers, tomatoes;
- Onions, garlic, horseradish, herbs;
- Apricots, bananas, dried apricots, citrus fruits;
- Berries and dried fruits;
- Jelly, puddings, marmalade;
- Unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks, jelly;
- Weak tea, decoctions of herbs and berries.
Diet after a stroke - prohibited foods:
- Pork, smoked and fried meat;
- Poultry skin;
- All types of sausages, especially salami on the Table 10 diet;
- Fatty fish;
- Smoked and fried fish;
- Fatty dairy and fermented milk products (cream, sour cream, condensed milk);
- Rich and fresh baked goods;
- Semolina;
- Legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- Fried potatoes and chips;
- Rutabagas, turnips, radishes;
- Sorrel and spinach;
- Mushrooms;
- Grape;
- Desserts and sweets (ice cream, chocolate, candies);
- Rich broths;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Sweet fruit drinks, juices and nectars;
- Freshly squeezed vegetable and fruit juices;
- Strong coffee and tea.
Treatment of microstroke
Treatment is aimed at normalizing blood supply and metabolism, preventing relapses and preventing stroke. In case of hemodynamically significant occlusion of large arteries, surgical treatment by angiosurgeons is possible. Patients with a ministroke are usually prescribed:
- Drugs aimed at restoring blood microcirculation in blood vessels;
- Drugs that dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow;
- Agents that prevent platelet accumulation;
- Drugs that improve brain activity;
- Vitamins.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient visits:
- Exercise therapy (to restore motor activity);
- Massage sessions (to stimulate motor activity in the limbs);
He also follows a diet (without fatty, spicy and salty foods) and does special breathing exercises (to ensure that sufficient volume enters the body).
But if the patient delays diagnosis and treatment, complications may arise. In this case, with a microstroke, the doctor prescribes the following groups of drugs responsible for restoring the body:
- improving blood microcirculation;
- improving metabolic processes in blood vessels;
- dilating vessels;
- preventing the formation of blood clots;
- stimulating brain activity;
- vitamins (to strengthen the immune system and improve brain activity).
Authorized Products
The patient's nutritional diet is limited as follows:
- Vegetarian dishes. Basically, these are soups prepared with potatoes, cabbage, carrots and other vegetables. You are allowed to add cereal to the soup. The soup can be milk or fruit; cold beetroot soup is recommended for consumption. The soup is seasoned with non-acidic sour cream and herbs. If your doctor allows it, you can cook soup with meat broth, but only several months after the stroke.
- Boiled poultry meat. It should be lean, low-calorie chicken or turkey. Fillet boiled in unsalted water is best. Meat contains a large amount of proteins and is very healthy.
- Lean meats. You can eat beef, veal and rabbit. Before cooking, cut off fat and tendons, anything that increases cholesterol levels and calories. The meat must be boiled.
- Low-fat fermented milk products. The fat content of milk and cottage cheese should not exceed 10%. Cottage cheese is mixed with cereals, carrots and fruits. Cheese can be eaten only in limited quantities and only low-fat varieties;
- Chicken eggs. The eggs are boiled soft-boiled, the omelet is steamed. You can only eat 1 egg per day.
In addition, patients are allowed the following products:
- Diet for hypertension - table No. 10 with a menu for every day. Proper nutrition and products for high blood pressure
- pasta;
- cereal;
- biscuits and soft biscuits;
- all types of vegetables;
- vegetable caviar;
- jellied fish;
- dried fruits, as well as fresh fruits and berries;
- compote, jelly, jam;
- green tea;
- still water;
- cocoa;
- honey.
All dishes should be consumed in limited quantities in accordance with the individual regimen developed by the doctor. Food must be prepared independently; it is not advisable for the patient to eat semi-finished products, again due to the calorie content and high cholesterol content.
Diagnosis of microstroke
Despite the fact that this disease, compared to traditional stroke, is relatively harmless, it still needs to be diagnosed and treated. Although a microstroke occurs and passes quickly, it still causes some harm to the body and in half of the cases ends in a stroke or heart attack. That's why diagnosing the disease is so important. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following examinations:
- ECG and ultrasound of the heart;
- Vascular examination;
- An echocardiogram determines any abnormalities in the heart;
- Blood test for platelet count, clotting time, sugar, etc.
- CT can detect a blood clot and determine its nature.
- REG (rheographic method for studying the vascular system of the brain) and ultrasound examination (ultrasound examination) with functional tests (for example, with turns and tilts of the head) - these methods are necessary for examining the arteries of the spine.
- MRI will allow you to detect the location of the blood clot with high accuracy.
It may be necessary to involve other specialists. For example, an ophthalmologist determines the visual field and conducts an examination of the fundus.
What not to eat
To exclude the development of severe consequences, the diet for a microstroke should be the same as for a patient who has suffered an acute cerebral infarction. Nutrition rules imply the exclusion of certain foods from the diet. After a stroke the following are prohibited:
- vegetables with coarse fibers - broccoli, legumes;
- fatty meat, fish;
- alcohol;
- sausage;
- beef kidneys, liver;
- canned food;
- cooking fat;
- cream;
- fatty cottage cheese;
- radish;
- radish;
- pasta;
- mustard;
- mushrooms;
- sorrel;
- chocolate;
- grape;
- bananas;
- mayonnaise;
- raisin;
- ice cream.
To prevent a person from gaining weight and increasing cholesterol levels after a stroke, it is prohibited to consume the following foods and drinks:
- rich broths - fish, mushroom, meat;
- products made from puff pastry;
- soups with legumes;
- smoked products - meat, fish;
- dishes including peas, beans;
- sauerkraut;
- semolina porridge;
- strong tea;
- cream cakes;
- coffee;
- baked goods made from white flour;
- cocoa.
Articles on the topic
- Coma after a stroke in a person
- Surgery for cerebral stroke - in what cases and to whom is it prescribed, contraindications for the procedure
- Sanatorium after stroke - review of the best centers for preventive and rehabilitative therapy with prices
Selected tips
We offer small culinary tricks to prevent negative emotions in the patient.
- To make food with limited salt tasty, you can add crushed garlic, parsley, dill, and seaweed.
- If the patient cannot swallow solid food, it is necessary to prepare everything in the form of purees or purchase high-quality baby food in jars at the store.
- A blender will help grind the vegetables into a mass. But you should make sure that the resulting dish is warm.
- For constipation, the menu should include a decoction of figs, dried apricots, and prunes, and drink it on an empty stomach. Be sure to give kefir in the evening.
- Legumes are very healthy; they contain folic acid, which activates the B group of vitamins. If the patient has difficulties with daily bowel movements, they should not be cooked.
Nutritionists do not advise deciding on your own the issue of adding immunostimulants (ginseng, aloe) to a patient’s drinks. They are contraindicated for hypertension. You should consult your doctor.
Prepared on the basis of flaxseed oil with cumin extract, it has valuable qualities
Motor rehabilitation
Passive gymnastics. Motor rehabilitation of patients who have suffered a stroke is an integral and one of the most important components of the recovery process. The basic method of motor rehabilitation is physical therapy, which begins as soon as the patient’s condition allows. The objectives of physical therapy include restoration (full or partial) of range of motion, strength and dexterity in the affected limbs, balance function, and self-care skills.
In the early period, immediately after a cerebrovascular accident occurs, passive gymnastics is performed. It allows not only to normalize the tone of the limbs, but also to prevent the formation of bedsores. Passive gymnastics is performed by exercise therapy specialists together with the patient’s relatives.
When performing gymnastics, passive movements of paretic limbs are performed at a slow pace, carefully, slowly, while trying not to cause pain or increase muscle tone. Such gymnastics is first performed on the healthy side and then on the sore side. It is important to start proximally, in isolation at each joint. In this case, 8–10 movements are performed in each joint.
Active gymnastics. The next stage of recovery is the beginning of active gymnastics, which begins with simple movements of the limbs and becomes more complex as the patient becomes more active. The patient is taught to sit up in bed, maintain balance and stand up, then walk, first accompanied or with support, and then independently.
Great importance is given to motor rehabilitation in the affected upper limb, in particular the restoration of fine motor skills, which is the key to full social and everyday readaptation. The patient learns simple self-care skills, in particular eating, personal hygiene, using the toilet and bathroom, as well as dressing independently, in stages.
The duration of the various stages of motor recovery depends, first of all, on the extent of the area of brain damage. An important part of rehabilitation, both motor and psychological, is the early involvement of patients in household work and the preparation of able-bodied patients to go to work.
Massotherapy
Along with physical therapy, positioning of the lying patient and therapeutic massage are important for the recovery of the patient. The purpose of these therapeutic measures is to prevent the development of muscle contractures and maintain normal joint function, prevent bedsores and pulmonary complications, primarily congestive (hypostatic) pneumonia. When conducting massage sessions, certain principles must be observed:
- the extensor muscles are usually massaged on the arm,
- on the leg - the flexor muscles of the leg and the dorsum of the foot.
Massage is carried out throughout the entire recovery period.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, acupressure, cryotherapy, and water procedures are widely used as additional methods that speed up the rehabilitation process.
An example of a one-day home menu for a patient
In the morning, breakfast after hygiene procedures:
- liquid low-fat cottage cheese diluted with milk;
- toast brushed with honey;
- green tea with mint.
After 1.5–2 hours - banana.
For lunch:
- vegetable broth soup seasoned with buckwheat;
- steam cutlet with grated carrot and cabbage salad;
- freshly squeezed fruit juice or grated apple.
For afternoon snack: chicory drink with dry cookies.
For dinner:
- steamed fish with mashed potatoes;
- prune compote.
Shortly before bed: a glass of yogurt or kefir.
Since many people get confused when it comes to preparing boiled dishes, we provide dietary recipes.
Porridge with pumpkin
You can cook it from rice or millet cereals to taste, or mix them in half.
Peel the pumpkin, cut into cubes, add water (2-3 cups) and cook for 10 minutes.
Add washed millet or rice (to remove gluten, it is better to first soak them in water for 2 hours) and cook for another 15 minutes, stirring.
Once ready, wrap the pan tightly with a warm cloth and leave the porridge to simmer.
Add a teaspoon of butter to a plate. You can replace it with honey.
Basic requirements for organizing a patient’s nutrition
The patient's nutrition in the hospital depends on the severity of his condition. If the patient is in a coma, then the necessary components are administered intravenously using special solutions. Another option is a custom table. Liquid products (milk, eggs, pureed soup) are prescribed, which are injected into Zhanna's stomach with a syringe through a nasal catheter.
When the patient regains consciousness, his ability to eat on his own, hold a spoon, and swallow food becomes more clear. If the motor function of the right or left hand is lost, they begin to gradually teach him to control the other, help him master previously familiar movements, and literally feed him from a spoon and a drinking cup.
You should continue to master the skills at home. Do not rush, scold the patient or despair. This greatly affects the desire to recover.
Take care of convenient, unbreakable dishes for eating and drinking, napkins, a towel, and a tray
Meals should be divided into 4-5 feedings. Portions for nutrition after a stroke should be kept small. All dishes should be heated, but not served very hot or cold.