Causes
In general, the origins of any type of ischemia are similar. Risk factors include previous history of:
- atherosclerosis of the large arteries of the brain;
- diabetes;
- compaction of the vessels of the extremities;
- hemicrania;
- atrial fibrillation;
- purulent-septic diseases;
- brain vasculitis;
- arterial hypertension and so on.
A stroke can develop against the background of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, in particular heart defects.
The occurrence of a blood clot can be provoked by pathologies in the composition of the blood, that is, its increased viscosity.
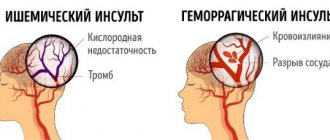
Atherothrombotic ischemic stroke in the left MCA region occurs due to the formation of a blood clot and blockage of the vessel.
This type of disease occurs against the background of coronary heart disease or arterial hypertension.
A completely healthy woman can develop a stroke due to frequent use of contraceptives.
Excessive smoking or drinking alcohol also depresses the condition of blood vessels. The result is a massive ischemic stroke.
Symptoms
The main symptoms by which you can determine the beginning of the process of brain damage:
- Decreased sensitivity of the limbs. Often there is a strong tingling sensation, accompanied by poor health, numbness in the arm or leg.
- Unnatural position of the corners of the mouth, the face seems skewed, the lower eyelid most often droops on one side.
- Loss of control over oneself, orientation in space.
- Decreased vision, unfocused gaze.
- Pain in the head, often increasing, dizziness.
- Severe vomiting, convulsions.
- Noticeable impairment of speech function.
It is important to notice stroke symptoms within three to six hours of their onset. If you seek help in a timely manner, you can avoid the development of irreversible changes in the brain.
A person can independently diagnose a stroke on the left side of the brain based on the following signs:
- How long do people live after a stroke, how do the consequences and age affect life expectancy?
- nausea and vomiting;
- numbness of the limbs;
- blurred vision;
- disorientation .
The presence of even two signs is a reason to consult a doctor.
If you notice a person's lack of coordination or speech, you should ask him to smile. In this case, it immediately becomes clear that a stroke has occurred - the corners of the lips will rise unevenly. Another way to diagnose a pathological condition before doctors arrive is to ask the person to stick out his tongue. The tip of the tongue will be directed to the side. Also, the patient will not be able to raise his arms up.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
If at least one problem is detected, you need to call an ambulance.
All symptoms that can be detected with ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere are divided into three groups:
- General signs. Symptoms occur when the meninges become inflamed and when blood pressure increases. With the development of left-sided hemisphere damage, there are practically no indicators by which one can immediately understand that pathology has arisen. If the stroke is extensive and the necrosis comes into contact with the meninges, then the signs become more noticeable, especially impaired consciousness, vomiting and nausea, and headache.
- Vegetative symptoms, expressed in heartbeat disturbances, pressure fluctuations. Skin color changes. At the same time, a person often begins to feel the fear of death and tries to fight it.
- Signs of the neurological picture of the disease, which appear depending on the size of the inflammatory focus and its location. Paralysis of the limbs, impaired sensitivity, loss of memory, vision, and hearing occurs.
All these signs can be detected immediately after the development of a stroke. Other symptoms often appear during the recovery stage.
Consequences of left-sided ischemic stroke
A patient who has suffered a stroke in the right hemisphere has a distorted image of his body, he does not feel motor disturbances and, therefore, does not strive for recovery. Such indifference makes rehabilitation difficult and requires referral to qualified specialists.
At the Yusupov Hospital, highly qualified doctors will select and implement an effective rehabilitation program after left-sided ischemic stroke. The program includes activities aimed at restoring the motor system and psycho-emotional state of the patient. Rehabilitation is based on classical and latest recovery techniques. Patients undergo massage, mechanotherapy, electrical stimulation, kinesthetics, diet and herbal therapy.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital combines the advanced achievements of rehabilitation medicine and a homely atmosphere, thanks to which patients feel the care and attention of medical personnel and receive the necessary assistance from highly qualified specialists.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosing a stroke on the left side begins with a few simple steps:
- Ask the patient to smile or stick out their tongue.
- Raise both hands up.
- Say any phrase, say your name or date.
During a stroke, a person's face will be distorted and movements will be limited or completely impossible. Speech is usually slurred and consciousness is confused.
- Periods of stroke: main stages, critical moments, recovery, prognosis
Further diagnostic measures are carried out by a neurologist in the hospital. He usually prescribes a number of procedures:
- general blood test and biochemistry;
- studying the composition of urine;
- study of coagulation;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- electrocardiogram.
Blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and temperature are also constantly measured.
Based on the results of the examination, a plan for further action is drawn up.
Therapy begins even before the doctor arrives. What should be done?
- Place the patient so that his head is at an angle of at least 30° above the surface of the bed. To do this, you need to place pillows under his head and shoulders.
- Open the windows to ensure air flow.
- Unfasten your clothes and remove your belt.
- Measure the pressure.
If the patient begins to vomit, you need to turn his head so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory tract.
Already in the hospital, the doctor will decide how to proceed. Treatment of ischemic stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain has several goals:
- normalize blood pressure;
- improve the functioning of the heart and respiratory system;
- reduce body temperature to normal;
- prevent or remove cerebral edema;
- restore normal blood circulation;
- improve metabolic processes;
- protect the patient from the development of complications;
- eliminate the manifestations of the disease.
Sometimes there is a need for specific therapy, the purpose of which is to destroy blood clots.
Treatment begins with taking medications:
- Question: Childbirth after a stroke. Is it possible to give birth after a stroke?
Fibrinolytics. If taken within the first 3 hours after a stroke, the risk of complete paralysis is minimized.
Anticoagulants. There are direct and indirect actions. Appointed in 2 weeks.
Antiplatelet agents. These are drugs that prevent the formation of new blood clots.
Vasoactive agents. Strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation. They have an antispasmodic effect.
Antihypertensive drugs. These include ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists. Reduce blood pressure.
Neuroprotectors. They improve blood circulation in the brain and normalize its functioning.
Massages, physiotherapeutic procedures, and therapeutic exercises are also indicated.
If necessary, the doctor may decide to perform surgery. It is needed if a focus of ischemia is found during the examination. The surgeon expands the damaged vessel or replaces part of it with an implant.
It will take a long time to treat a stroke. After the patient leaves the hospital, a long recovery period will begin. It often takes years.
Complications and prognosis after left hemisphere stroke
Left-sided stroke, according to statistics, occurs in more than half of all cases. It's easier to detect. However, it has more serious complications and a poor prognosis for life. Usually complications affect the right half of the body, but sometimes they develop on the left.
The consequences of an ischemic stroke on the left side imply disruption of the activity of almost all internal organs.
Speech impairment and decreased vision
The most serious problems are characterized by the acute form of stroke. It is possible to solve them, but almost always the speech remains incoherent, slow and meaningless. It is difficult for a person to formulate a thought and express it in a long phrase. It can be expressed in several meaningless words that cannot be combined into a single whole. At the same time, the patient spends much more time on the formation of thoughts than before.
Interestingly, speech disorders occur more often in right-handed people. Left-handers do not encounter them so often.
In addition to speech problems, visual impairments include:
- blurry image;
- decrease in field and clarity of vision;
- increase in eye pressure.
It is difficult for the victim to concentrate his gaze on one object.
- Pain after a stroke: how to relieve it
Articulation disorders and paralysis
One of the consequences of a stroke on the left side is impairment of fine motor skills. Due to a temporary or permanent feeling of numbness in the right arm and leg, it is difficult for the patient to perform even the simplest actions. Sometimes the ability to move can be completely lost.
Paralysis also affects the muscles of the face, as a result of which the so-called false smile rests on it. Facial features become asymmetrical.
Limitations also apply to articulation. The patient can no longer control the process of sound formation. Therefore, his speech is slurred and incoherent.
Decrease and loss of memory
Memory impairments can be partial or complete:
- With partial amnesia, the patient remembers only fragments of his life.
- Complete amnesia is characterized by an absolute absence of memories of life before the stroke. The patient does not remember anything about himself, and also does not recognize his family and friends.
Deterioration of speech memory is often observed. The patient not only forgets what the conversation was about a couple of minutes ago, but also cannot remember the person with whom he is talking. It is also difficult for him to understand what kind of objects are around. He does not know how to perform basic tasks, such as washing his face or brushing his teeth.
Decreased learning functions are another complication of left-sided stroke. Brain activity is reduced to a minimum. A person is not able to solve even the simplest logical problems. If he still has this ability, it takes a lot of time to think about it.
Mental disorders
Complications of this type include apathy and unmotivated aggression. In the first case, a person does not want to do anything, does not see the meaning of life and is not interested in anything. In the second, there are frequent changes in mood, manifested in sudden movements.
After the patient realizes what happened, he becomes withdrawn and unsure of himself. Social degradation is progressing. The desire to communicate with other people disappears. A person lives in his own closed world, where he does not allow even his closest ones. Such complications can develop in both older and younger patients.
- Why can a stroke occur with diabetes?
Causes
- Hypertension or the appearance of a hypertensive crisis.
- Chronic forms of vasculitis.
- Consequences of long-term use of anticoagulants or other drugs that thin the blood.
- Poisoning with toxic chemicals.
- Diseases associated with insufficient blood clotting, for example, hemophilia, thrombocytopathy.
- Violation of the integrity of the vascular wall.
- Consequences of strong physical exertion.
- Consequences of traumatic brain injury.
In ischemic pathologies, the causes are:
- Atherosclerotic lesion of the vascular wall.
- The manifestation of varicose veins of the lower extremities, which is complicated by the formation of blood clots.
- Blood clots formed in the atria due to abnormal heart rhythms, for example, the result of atrial fibrillation.
- Excess body weight.
- Increased blood clotting.
- Abrupt increase in blood pressure.
- Having bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol, or overeating foods with high calorie content and excess cholesterol.