- Causes of high blood pressure
- Idiopathic form of the disease
- Symptoms of intracranial pressure
- Manifestations of liquor-hypertensive syndrome in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of intracranial pressure
- Drug treatment
Intracranial pressure is otherwise called intracranial pressure.
An increase in intracranial pressure is called intracranial hypertension, which is characterized by a moderate or pronounced clinical picture. This pathology is also known under the names “cerebrospinal fluid hypertension syndrome”, “cerebrospinal fluid hypertension syndrome”. The term “cerebrospinal fluid” refers to cerebrospinal fluid. The disease can occur in an acute form and become chronic. Acute most often occurs against the background of traumatic brain injury (TBI), back injuries and infectious lesions of the brain. Chronically elevated intracranial pressure is observed in patients with brain tumors and cysts, and symptoms increase as the tumor enlarges. The pathology persists after severe surgical interventions, injuries to the spinal cord and brain, inflammatory processes that led to disturbances in liquorodynamics - the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Intracranial pressure is reduced mainly by medicinal methods; surgical intervention is used only in particularly difficult cases.
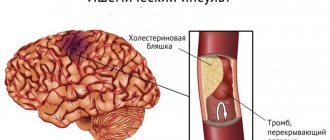
Causes of high blood pressure
The disease occurs in adults and children. Its causes can be congenital or acquired. They are conventionally divided into four groups:
- Volumetric formations.
This category includes brain tumors, cysts, abscesses, and vascular aneurysms. The tumor takes up space in the skull, compresses certain areas of the brain, and displaces its structures. This leads to a change in intracranial pressure. In young children, intracranial pressure higher than normal may be due to congenital developmental anomalies. Most often, specialists diagnose microcephaly or hydrocephalus. Trauma during childbirth, asphyxia, and oxygen starvation of the fetus can lead to pathology. At risk are babies born prematurely. - Edema.
Characteristic in the development of a number of diseases: encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis, ischemic stroke, as a result of head injury, intoxication, hypoxia. Edema can be local, that is, affecting individual areas of the brain, or diffuse.
- Increased blood supply inside the skull.
This pathology occurs with dyscirculatory encephalopathy and a number of other diseases. In this case, the blood flow increases or its outflow from the vessels supplying the brain becomes more difficult. Due to increased blood supply, blood pressure rises. - Disorders of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
In the human body, the brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which moves at a certain speed and affects brain tissue, thereby creating intracranial pressure. Part of the cerebrospinal fluid enters the blood, and the missing amount of fluid is produced to replace this volume. Thanks to this, constant pressure is achieved, which is considered normal. Infectious and inflammatory diseases, back and head injuries lead to various disorders of the secretion and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid becomes slow or its production is excessively activated. Liquorodynamic disorders can develop against the background of congenital anomalies in the structure of the spinal cord and brain. Intracranial dystension occurs, in which the pressure on the brain becomes uneven. Excessive accumulation of fluid in the cranium causes compression of individual areas and vessels, which leads to changes in intracranial pressure.
In addition to injuries and inflammation, disruption of the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid can cause treatment with potent drugs. At risk are patients who are forced to take hormonal drugs, antibiotics, and corticosteroids for a long time. Excessive amounts of vitamin A due to abuse of retinol preparations can lead to changes in intracranial pressure.
Intracranial venous hypertension: causes
Often a headache can be caused by a cold, lack of sleep, or overwork. It appears due to increased intracranial pressure. If headaches become permanent and severe, this is a signal to contact the Yusupov Hospital.
Benign intracranial hypertension is an increase in pressure inside the skull that is not associated with any pathological process in the body. Headaches occur due to taking certain medications or due to obesity.
In a healthy person, the volume of the brain consists of certain proportions of the volumes of its fluids and tissues - cerebrospinal fluid, blood and interstitial fluid. When the volume of one of these components increases, the blood pressure in the cranium increases.
If the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the skull is disrupted, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid increases and the pressure increases. An increase in the total volume of brain fluids leads to hemorrhages with the formation of hematomas.
The difference in fluid pressure can lead to displacement of brain structures relative to each other. This pathology leads to partial or complete disruption of the normal functioning of the nervous system.
With cerebral edema, an increase in the volume of brain structures occurs and intracranial hypertension is diagnosed.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure
You can suspect a problem based on the following signs:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- changes in blood pressure, pulse rate;
- decreased libido.
Headache is the main symptom of liquor-hypertensive syndrome. Patients note the dependence of pain on body position and time of day. For many people, headaches begin to hurt more severely in the evening and at night, when a person is in a lying or reclining position. In this case, the production of cerebrospinal fluid increases, and its outflow worsens, which increases compression.
There is a feeling of fullness, pressure from the inside, which is localized in the fronto-parietal areas. The patient complains of a feeling as if something is pressing on the eyes from the inside, and blurred vision occurs. This feeling intensifies when the eyeballs move. When examining the fundus, the doctor will note swelling of the optic nerve - one of the main signs of increased intracranial pressure.
Because of the headache, a person feels bouts of nausea, but after vomiting, the state of health does not improve. In severe cases, the disease is accompanied by fainting and confusion.
In the chronic form of the disease, the quality of life decreases significantly. The patient becomes emotionally labile, stress resistance and performance decrease. Many people feel worse when the weather changes, that is, they develop increased meteosensitivity. It manifests itself as headaches and dizziness, sleep disturbances, fluctuations in blood pressure, muscle and joint pain, and general malaise.
our treatment
Our center provides treatment aimed at eliminating the causes that lead to increased intracranial pressure.
We eliminate spasms of the neck muscles, realign displaced cervical vertebrae, and restore the normal outflow of venous blood and cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity.
Effective treatment methods have been developed for all age groups.
Children receive specialized treatment using a patented orthopedic product (Patent No. 2587960).
To eliminate ICP in adults after injuries to the skull and cervical spine, after head contusions and concussions, or in the presence of osteochondrosis, we use our own patented treatment method (Patent No. 2571234).
If necessary, osteopathic sessions are prescribed to restore correct biomechanics in the cervical spine.
Manifestations of liquor-hypertensive syndrome in children
In some cases, increased intracranial pressure in children does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms. This is due to the fact that the skull bones of newborns are softer, so hypertension is compensated.
With severe disturbances, it manifests itself as tearfulness and anxiety, sleep disturbance. The newborn refuses to feed and often spits up after feeding. A typical sign of increased intracranial pressure in a child is “protrusion” of the fontanelle. Compression of certain areas of the brain negatively affects the physical and intellectual development of children. In addition to behavioral disorders, disorders of vital functions and delayed psychophysical development are possible. In severe cases, the result of prolonged intracranial hypertension in a child is the formation of mental retardation.
Intracranial hypertension: diagnosis
Types of pathology diagnostics include:
- measuring intracranial pressure by inserting a needle into the fluid cavities of the skull or spinal canal with a pressure gauge attached to it.
- tracking the degree of blood filling and dilation of the veins of the eyeball. If the patient has red eyes, that is, the eye veins are abundantly filled with blood and are clearly visible, we can talk about increased intracranial pressure;
- ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography: the expansion of the fluid cavities of the brain is examined, as well as the degree of rarefaction of the edges of the ventricle;
- conducting an encephalogram.
Diagnostics
If there are signs of liquor-hypertensive syndrome, you should make an appointment with a neurologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a set of procedures:
- fundus examination;
- echoencephalography;
- X-ray of the skull;
- CT or MRI of the head
- Ultrasound of blood vessels supplying the brain;
- angiography.
In severe clinical cases, the doctor may prescribe a lumbar puncture, which helps determine accurate indicators of intracranial pressure.
The purpose of these procedures is primarily to identify the cause of hypertension. Based on the data obtained, the specialist determines a treatment regimen and prescribes additional diagnostics.
Which doctor should I contact?
If symptoms of liquor-hypertensive syndrome appear, you should contact a neurologist. An experienced specialist can be seen at the medical office by appointment. You can make an appointment by phone @. The doctor will see you at a time convenient for the patient.
The neurologist from the SmartMed clinic has many years of experience in treating noise in the head of various origins, including those caused by intracranial hypertension. To determine the cause of poor health, the doctor will conduct a visual examination.
The examination begins with a study of the patient's complaints and neurological testing. It is important for the doctor to know the person’s medical history, conditions of occurrence, frequency and intensity of noise in the head.
Increased VChP cannot be determined by external signs
The doctor must prescribe instrumental research methods:
- Spinal or lumbar puncture. Designed not only for studying cerebrospinal fluid, but also for measuring intracranial pressure. The procedure is invasive and involves inserting a puncture needle into the spinal canal and then connecting a pressure gauge.
- MRI of the head. Allows you to identify the causes and signs of intracranial hypertension: cerebral edema, vascular thrombosis, enlargement or narrowing of the cerebral ventricles, cysts, tumors, hematomas, hemorrhages. The study is the most informative and safe. In medical MRI of the head, it is carried out on a new ultra-precise Siemens Symphony 1.5 Tesla tomograph, thanks to which it is possible to obtain a highly accurate 3D image. The examination takes no more than 15 minutes, no special preparation is required.
- Ultrasound of the head. Used for children of the first year of life. The study is carried out through an open fontanel.
- Ultrasound of the vessels supplying the brain. Allows you to assess the condition of the arteries, as well as the direction, speed and intensity of blood flow in them, to identify the main vascular disorders that can cause high ICP and noise in the head.
- Electroencephalography. Designed to study the electrical activity of the brain, it allows you to identify areas of irritation of various brain structures.
Additionally, the neurologist may prescribe a consultation with an ophthalmologist. Papilledema, which can be detected during fundus examination, is a sure sign of increased ICP. If necessary, other highly specialized specialists are involved in the examination: a neurosurgeon, an oncologist.
Important! The reliability of the examination for intracranial pressure depends on the technical parameters of the diagnostic equipment and the qualifications of the diagnostician.
Treatment of intracranial pressure
Conservative and surgical methods are used to reduce intracranial pressure. The operation is performed if the cause of the disorder is a tumor, cyst, or congenital abnormality of the brain structure. Removing the tumor eliminates compression and normalizes blood pressure. To eliminate hydrocephalus, the cerebral shunt technique is used.
The operation can be performed planned or urgently. Emergency intervention is carried out in severe forms of the disease, when it can lead to dislocation syndrome. This is a dangerous complication in which cerebral structures are displaced due to compression. The cerebellar tonsils are wedged into the foramen magnum, and the brain stem is compressed. It includes important nerve centers responsible for respiratory function and heart function. Damage to these areas poses a threat to life.
Intracranial hypertension: treatment, drugs
Increased intracranial pressure can lead to a decrease in the patient’s intellectual abilities and disruptions in the normal functioning of internal organs. Therefore, this pathology requires immediate initiation of treatment aimed at reducing intracranial pressure.
Treatment can only be carried out if the causes of the pathology are correctly diagnosed. For example, if intracranial hypertension occurs due to the development of a tumor or hematoma of the brain, then surgical intervention is required. Removal of a hematoma or neoplasm leads to normalization of intracranial pressure.
When increased intracranial pressure is a consequence of inflammatory processes in the body (meningitis, encephalitis, etc.), then the only effective method of treatment is massive antibiotic therapy. In this case, antibacterial drugs can be injected into the subarachnoid space in combination with the extraction of part of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Therapy is aimed at reducing the release of cerebrospinal fluid while simultaneously increasing its absorption. For this purpose, patients are prescribed diuretics.
Quite often, treatment does not require taking any medications. A set of gymnastic exercises is developed for the patient, the implementation of which leads to a decrease in intracranial pressure. Adjustments are also made to the diet and a drinking regime is developed individually. Light manual therapy, acupuncture and physiotherapy have a beneficial effect. The effectiveness of non-drug treatment is observed within the first week from the start of therapy.
In case of postoperative, congenital cerebrospinal fluid block or other severe cases, surgical treatment is indicated. The most common type of surgical intervention is bypass surgery, that is, the insertion of a special tube with one end into the abdominal cavity or heart cavity, and the other into the cerebrospinal fluid space of the brain. Thus, excess cerebrospinal fluid is constantly removed from the skull, leading to a decrease in pressure.
When intracranial pressure increases at a very high rate and the patient’s life is threatened, urgent measures are required to save the patient. In this case, the patient is injected intravenously with a hyperosmolar solution, artificial ventilation is performed, the patient is put into a medically induced coma, and excess cerebrospinal fluid is removed by puncture.
The most aggressive treatment measure, which is resorted to in the most difficult cases, is decompressive craniotomy. At the time of the operation, a skull defect is created on one or both sides so that the brain does not rest against the bones of the skull.
Intracranial hypertension can be completely eliminated if the causes that caused it (tumor, poor blood flow, etc.) are eliminated.
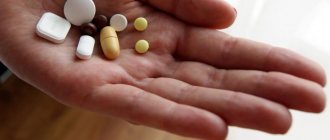
Drug treatment
In most cases, medications are selected for the patient to normalize intracranial pressure. These include:
- osmodiuretics;
- diuretics;
- potassium preparations;
- detoxifying agents;
- antiviral agents and antibiotics to eliminate the infectious and inflammatory process;
- vascular drugs;
- neurometabolic agents.
Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe magnesium sulfate for injection or piracetam for injection.
Attention! The selection of drug treatment for intracranial pressure is made by the doctor based on the diagnosis and after the diagnosis is made. To normalize the condition, it is important for the patient to reconsider his lifestyle, adjust his daily routine, and avoid psycho-emotional overload. Moderate physical activity is beneficial: walking, swimming.
Prognosis for liquor-hypertensive syndrome directly depends on the cause of its occurrence. With timely treatment of neuroinfections and liquorodynamic disorders, good dynamics and results can be achieved.
Preventative measures against the disease
For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to follow a number of rules:
- eliminate bad habits;
- avoid strong and prolonged stressful situations;
- minimize the risk of traumatic brain injuries when engaging in traumatic sports by using protective helmets;
- periodically undergo a course of massage of the cervical-collar area;
- prevent exacerbation of concomitant diseases such as hypertension, epilepsy, etc.;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- avoid excessive physical activity;
- provide a sufficient amount of potassium-rich foods in your daily diet;
- adhere to a rational daily routine;
- do gymnastics for the neck muscles;
- lead a healthy lifestyle.
These actions are aimed not only at preventing the development of the disease, but also at improving brain function in general. Preventive measures promote proper circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and blood, as a result of which the brain is more fully saturated with nutrients and oxygen.
It is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner; only with the help of adequate treatment can you get rid of the disease, prevent relapse and the development of serious complications that can be caused by intracranial pressure.
cost of treatment
The cost of treatment in our center is calculated individually, depending on the severity of the disease, its duration and the presence of complications.
Each patient is prescribed comprehensive sequential treatment in the form of a course of individually selected procedures.
In addition to the procedures, the treatment course includes a free follow-up appointment.
Initial and repeat appointments, as well as medications prescribed by a doctor, are paid separately. The cost of the initial appointment is 3,000 rubles.
A 10% discount is provided for a one-time payment for a treatment course.