Many patients report that they have goosebumps on their heads, but they don’t understand what they are. Therefore, they are often asked to explain the reason for the appearance of such a symptom and talk about how treatment can be carried out effectively and safely. In this article you can find out what goosebumps mean and what diseases manifest themselves in this way. Advice is also given on choosing a specialist and conducting treatment.
Let's start with the fact that goose bumps on the scalp are a sign of neurological or vascular problems. To make this clear, let’s talk about how the innervation and blood supply system works.
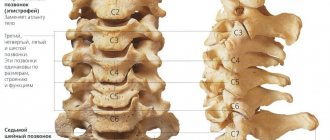
So, in the cervical spine there is a segment of the spinal cord of the same name. The radicular nerves extend from it. They branch and form plexuses, nerves. Some of them are responsible for the innervation of the scalp. Also, paired cranial nerves depart from the brain through the foramen ovale of the occipital bone. They also branch and are partially responsible for the innervation of the tissues of the head. In particular, the facial and trigeminal nerves are formed exclusively by the branches of the cranial pairs. Also, their branches are part of the nerve plexuses that innervate the hair follicles and small blood vessels. They provide tone to the posterior vertebral arteries.
Blood supply to the tissues of the head and brain is carried out by four arteries. Two posterior vertebrates and two carotid. They branch, giving rise to many arterioles, which pass into a network of capillaries. Each nerve ending in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer has its own capillary vessel.
When a capillary spasms, the blood supply process is disrupted and the nerve ending enters a state of ischemia. This may feel like numbness or crawling. Also, similar sensations occur in clusters (in a certain area of the scalp).
The lower the area of negative impact is located, the larger area of the head is subject to paresthesia, in which the patient feels that goosebumps are crawling on or under the skin. Therefore, an accurate description of the area of distribution of the clinical sign will allow the doctor to quickly make a diagnosis and develop an effective treatment regimen for the underlying disease.
Please note that the feeling of crawling sensations in some cases can be a physiological phenomenon. This may occur due to short-term compression of blood vessels or nerves by external factors. For example, if a person was in an uncomfortable static position for some time. Or if he was wearing a tight headdress. Similar sensations can occur after exposure to low temperatures. When hypothermia occurs, blood vessels in the epidermis and subcutaneous fat layer spasm. After the cessation of cold exposure, the vessels begin to restore their tone. Fresh capillary blood enters the tissues. And this may be accompanied by the effect of crawling goosebumps. If this is a physiological condition, then all unpleasant sensations disappear within 30 - 40 minutes.
If they continue for hours or do not stop at all, you need to see a doctor for help as soon as possible. It is necessary to visit a neurologist or vertebrologist. These doctors have the necessary medical qualifications to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
In Moscow, you can make a free appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. Experienced specialists work here. They will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective course of treatment. You will receive comprehensive individual recommendations regarding eliminating potential negative impact factors. This will help stop the destructive pathological process and allow the necessary treatment to be carried out more quickly.
Characteristics of the symptom
Goosebumps is a comparative description of a sensation that is similar to a slight tingling, tightening, or moving of the skin. In medical terminology, this phenomenon is called paresthesia. It arises as a response to irritating factors of an endogenous and exogenous nature.
Paresthesia can be either episodic or chronic, depending on the triggering agents.
The symptom is a type of sensory disorder and has several characteristic features.
The following properties of pathology are distinguished:
- wave contraction of the middle layer of skin (dermis), with changes in sensitivity;
- spontaneous occurrence of sensations, without a specific chronological periodicity;
- the duration of the episodes increases, depending on the worsening of the provoking factors.
As the symptoms increase, the goosebumps may spread to the cervical spine, upper and lower extremities, or enter a more severe phase, which is accompanied by numbness and soreness of the skin.
Features of the symptom
In some cases, paresthesia is of a reflex nature and is called the pilomotor reflex or piloerection. The condition occurs in response to a pronounced emotional outburst, which can be caused by the following emotions:
- joy;
- fear;
- sexual arousal and other feelings.
In addition to the causes of the emotional spectrum, pilomotor paresthesia can be triggered by a feeling of cold, a reaction to anti-stress toys, or unexpected sounds (grinding metal, creaking foam). The effect can also be caused by dosed physical activity and massage, even if a simple hand massager is used.
Piloerection is a rudimentary reflex and is not a sign of disease.
The origin of this reflex is the stimulation of peripheral nerve endings and is manifested in the contraction of smooth muscle of conical connective tissue fibers. As a result of the contraction of the hair follicles, the hairs rise and the “goose bumps” effect is observed. The mechanical movement of the skin is accompanied by the sensation of goosebumps running over the head.
Goosebumps on my feet
The symptom of goosebumps “running” down the leg is caused by various conditions. Let's look at the main ones.
Lumbar plexus neuropathy
It appears due to compression of the plexus by altered upper lumbar vertebrae, hematomas, abscesses, phlegmons, and tumors in this area.
Symptoms: pain and pins and needles - in the lower abdomen, in the pelvic area, on the thigh. They intensify when the extended leg is raised upward.
Varicose veins
The legs, especially when standing for a long time and at the end of the working day, itch, swell, and feel heaviness. Dilated veins and purple vascular networks are visually identified.
Restless legs syndrome
This is the name of a condition caused by various reasons, when a burning, tingling, feeling of bursting or squeezing is felt in the legs, due to which the lower limbs perform a frequent reflex movement of “throwing off”.
To clarify and eliminate the cause of such sensations, contact a therapist and neurologist.
Bernhardt-Roth disease
It manifests itself:
- goosebumps, burning, numbness, tingling in the area from the hip joint along the anterolateral surface of the thigh to the knee;
- pain and pins and needles intensify when walking, disappear if you sit or lie with your legs bent;
- if you touch the skin in this area, it will hurt, you will feel a feeling of heat, a prick;
- sensitivity here is increased;
- There may be both dry skin and increased sweating in this area.
After lumbar puncture
Injury to the nerve roots during lumbar puncture can lead to pain, loss of sensation in the legs, and weakness in their muscles.
Operations on the spinal cord, spinal nerves, spine
If the nerve roots were injured during the intervention, the following occurs:
- goosebumps in the legs;
- weakness of the leg muscles;
- decreased sensitivity in the legs.
Raynaud's disease
It manifests itself as pain and coldness of the fingers, then the fingers turn blue, which is accompanied by increased pain. Then the vascular spasm goes away, the fingers turn red, and the pain and goosebumps go away.
Femoral nerve neuropathy
It can be caused by a fracture of the pelvic bones with bleeding into the muscles surrounding this nerve. It may occur if the nerve was injured during puncture of the femoral artery, or if it was compressed by lymph nodes or a hematoma localized in the area of the inguinal fold.
Symptoms:
- pain – in the groin area;
- spreads to the lumbar region, to the thigh and lower leg along their anterior internal surface;
- Here goosebumps are detected and sensitivity is reduced;
- flexion-extension of the hip and knee may be performed in too small a volume;
- climbing stairs is especially difficult.
Clamping of the saphenous nerve
Pins and needles, pain and loss of sensitivity are determined along the inside of the leg from the knee to the big toe.
Rabies
The disease occurs as a result of the bite of an infected animal, which introduces the rabies virus into the wound. Pathology manifests itself as the appearance of goosebumps in the bitten leg. Subsequently, fear of light, water and sound develops.
Causes of pathology
Paresthesia is a consequence of the influence of external and internal negative factors acting on nerve tissue. These include:
- exogenous factors, in which unpleasant sensations arise from external mechanical influence on the scalp (impacts, prolonged compression);
- endogenous factors in which disruption of innervation is caused by somatic pathologies (diseases of internal organs and tissues) and mental illnesses.
As a result of changes occurring under the influence of these aggressive agents, the conductivity of the nerve fibers responsible for the innervation of the dermis is disrupted. Interruptions in impulses passing through the occipital, transverse, trigeminal and other nerves innervating the scalp lead to microspasms.
If the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted, not only goosebumps can be felt. Increased symptoms are accompanied by pain (the face and neck hurt), and the scalp becomes numb. Intense manifestation of paresthetic symptoms indicates an acute course of the underlying pathology.
Paresthesia in somatic diseases
The cause of the feeling of goosebumps running on the scalp is often diseases of the internal organs or tissues. The main diseases that can cause paresthesia of the skin are associated with the following factors:
- disruption of the innervation of nerve tissue;
- difficulty in peripheral and cerebral circulation.
Somatic causes of unpleasant sensations can be classified according to pathogenetic reactions and the mechanism of development of the root cause of symptoms.
Neurological pathologies
Degenerative or tumor processes (trigeminal neuralgia, cervical plexus neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, Bell's palsy, vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetic and alcoholic polyneuropathy) cause changes in the tissues and fibers of the central or peripheral nervous system. Demyelination, tissue compression or gradual destruction of trigeminal nerve cells and cervical plexus ganglion fibers occurs, which leads to disruption of nerve conduction in the skin and the appearance of goosebumps on the face, back of the head, neck and upper part of the head.
Inflammatory diseases of the spine
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine and adjacent tissues (osteochondrosis, arthrosis, spondylitis and other pathologies of the upper spine) are accompanied by the development of inflammatory processes within the fibers of smooth and skeletal muscles. Inflamed muscle tissue compresses blood vessels and nerve lines, which causes difficulty in the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses.
Cardiovascular diseases
Arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, stenosis, atrial fibrillation, ischemic stroke and other pathologies, which are characterized by thickening of the vascular walls and narrowing of their lumen, are accompanied by impaired cerebral circulation. Narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels leads to insufficient nutrition of the brain. Hypoxia and nutrient deficiency cause discirculatory encephalopathy (with gradual death of neurons). Focal damage to brain tissue is accompanied by various neurological symptoms, including paresthetic ones.
Paresthesia in mental disorders
Sensitivity disorders in patients with mental illness are observed quite often. The sensation of tingling and crawling is recorded in symptom complexes of such nervous disorders as:
- depression;
- schizophrenia;
- neurotic somatoform disorder (hypochondriacal, dysfunctional);
- anxiety disorders.
In most patients, the sensory disorder is hallucinogenic or imaginary and refers to perceptual disorders. This manifestation of symptoms is called sensopathy.
Sensopathy is characterized by a sensation of pins and needles not only on the surface of the body, but also under the skin.
The similarity of paresthesia and sensopathy makes diagnosis difficult only at the initial stage of symptoms. If the pathogenesis of a symptom is of physiological origin, then it is characterized by constant localization. The sensitive symptom can move and is determined in the arms, legs and other parts of the body, since it is a projection of the patient’s state of mind.
Additional factors
There are several other pathological causes that can cause paresthetic symptoms. The table shows some conditions that may be accompanied by a feeling of goosebumps.
| Pathology | Cause of symptom development |
| Respiratory diseases | When you have a cold, the sensitivity of the skin and body temperature increase, which contributes to an exacerbation of the pilomotor reflex. |
| Mechanical impact (non-traumatic) | Skin receptors are irritated, which provokes microspasm |
| Endocrine system disorders | Insufficient release of parathyroid hormone in the thyroid gland causes the development of hypoparathyroidism and hypocalcemia, which are characterized by the appearance of spastic conditions |
The feeling of crawling sensations, not associated with a violation of innervation, can be caused by pediculosis (lice), seborrheic dermatitis, follicular hyperkeratosis, a reaction to shampoo or hair styling and coloring products (the skin becomes covered with keratinized scales). An allergic reaction to medications may also be a factor in causing symptoms.
Visit doctor
With occasional goosebumps, there is no reason to worry. However, if you suspect the development of other diseases, you should still think about visiting a doctor. Therefore, you need to know what exactly may indicate serious illness. But no less important is the diagnosis itself, which includes several procedures.
When to visit a doctor
Many people choose to turn a blind eye to minor sensations, which is why they face serious complications. It is very important to promptly notice changes in your body and go to the hospital. You should go to the doctor under the following conditions:
- Symptoms are episodic and last for more than an hour.
- Pain in the head, dizziness, and increased blood pressure appear.
- During an attack, problems with vision, speech or hearing occur.
- It becomes difficult to turn your head.
- The skin changes with each attack.
Even one point is enough to make an appointment now. It is better to get examined and make sure there are no diseases than to risk your health.
Adults should be very attentive to their children. If your child complains of a crawling sensation in his head, you should take him to the doctor. This is especially true in cases where the child’s behavior has changed dramatically.
Diagnostics
The first doctor a patient visits should be a neurologist. It is he who will prescribe all the necessary examinations, and also refer you to other specialists, if necessary.
What procedures will you need to undergo:
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- CT, MRI of the brain;
- ENMG;
- ECG, ECHO ECG;
- EEG;
- RVG;
- Ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound.
After all the studies have been completed, the doctor will make a final diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. In some cases, constant monitoring of the patient may be required, for which he will be admitted to the hospital.
Features of symptoms in women
If goosebumps appear on the head in women, the reason may lie in the hormonal changes in the body that occur during menopause. Symptoms of paresthesia can occur at any stage of the menopause, but they are more pronounced in the premenopausal and menopausal phases, when hormonal surges are most active.
Provoking factors that cause sensitivity disorders in women include vitamin deficiency. The feeling of goosebumps occurs when there is a lack of elements such as:
- vitamins A, D, E, C and B vitamins (cyanocobalamin, folic acid);
- trace elements zinc, copper, iodine.
If the content of useful substances in the body is low, especially during pregnancy, dry skin, dizziness, general weakness and sensitivity disorders of the skin may occur.
Reviews about the treatment of trichotillomania
Reviews about the treatment of trichotillomania at the Salvation psychiatric clinic are only positive. Real professionals with extensive experience work here who can cope with even the most complex problem. They will find a caring approach to each patient and will make their stay at the center more pleasant and comfortable. Doctors work not only with the patient, but also with his relatives, which allows them to eliminate the cause of the disease.
The center is located away from the noisy city in an ecologically clean area. This allows patients to enjoy nature and walk around the center.
The center itself has all the necessary equipment and medications for the treatment of many psychological diseases.
A clear advantage of the center is good living conditions. The buildings have been renovated, all rooms are equipped with everything necessary.
Treatment at the center is carried out anonymously, which will not negatively affect the patient’s reputation. After completion of treatment, the center’s workers will help the person socialize and even get a job.
Significance in diagnosis
Symptoms, accompanied by a feeling of goosebumps running in the head, have important diagnostic significance. Such manifestations mean that a pathological process is occurring in the body, which may be a consequence of the following factors:
- disruption of the innervation of the neck, head and brain;
- problems with blood circulation;
- hormonal disorders;
- consequences of mechanical damage.
Paresthesia is also of differential importance in the diagnosis of mental disorders.
The benefit of goosebumps is the possibility of early diagnosis. Making a diagnosis at an early stage allows you to avoid the development of acute life-threatening conditions (vascular obliteration, stroke). Since paresthetic effects appear in the first stages of the pathological process, timely treatment helps prevent chronic disease.
Goosebumps on the tongue
This is typical for:
- rubbing with dentures;
- changes in bite resulting from the removal of one or several teeth;
- galvanization, when an electric current occurs due to the fact that the crowns are made of different metals;
- getting filling material into the canal;
- hypovitaminosis B12;
- damage to the sensory fiber of the glossopharyngeal nerve;
- inflammation of the arachnoid membrane of the brain;
- peptic ulcer of the upper digestive system;
- diseases of the ENT organs: sinusitis, rhinitis.
What tests and examinations can be prescribed?
If the symptoms of goosebumps and loss of skin sensitivity recur, you should consult a doctor. A medical institution usually has all the necessary diagnostic equipment for a complete examination of the brain and the body as a whole.
A series of examinations prescribed by a doctor will be able to identify the symptom of which disease is numbness of the scalp. Examination of the head for numbness :
A complete blood count will indicate the presence of anemia or Addison-Biermer disease.- Examination of the condition of the spinal column using an X-ray machine will determine whether there is clamping of the nerve endings between the intervertebral discs.
- Ultrasound will give a complete picture of blood supply disorders in the carotid and vertebrobasilar arteries.
If there are injuries, additional consultation with a traumatologist or surgeon is necessary. And if there is numbness in the lower jaw, it is impossible to do without a dentist.
Diagnostic measures
A multifaceted examination of the patient’s condition will help the doctor determine the location of the source of the problem and its cause. In addition to visual diagnosis and analysis, a differential study is added, which allows one to completely determine the cause and extent of the lesion.
Set of research procedures:
- start with a general blood test , which allows us to identify a lack of vitamin B12 in the body and the presence of iron deficiency anemia;
- instrumental studies such as radiography and spiral computed tomography will make it possible to assess the condition of the brain, skull, spine and identify pathologies if they are present;
- Electroneuromyography will help find the damaged nerve ;
- Doppler ultrasound makes it possible to assess the condition of blood vessels and help diagnose diseases of the cardiovascular system;
If after these studies and tests the picture remains not completely clear, the doctor will prescribe additional procedures based on the patient’s condition.
When should you contact a specialist?
Urgent medical attention may be needed if factors are present:
- Attacks of numbness are often repeated.
Body temperature has increased.- There is an acute headache.
- There is a lack of coordination of movements and dizziness.
- Loss of hearing or vision.
- Blood pressure surges.
- Numbness of the tip of the tongue, lips and fingers.
- The duration of this skin condition can be up to two hours or more.
If you have such symptoms, you cannot hesitate. Stroke most often manifests itself exactly like this. Emergency medical care can save a person's life.
Treatment is prescribed after a complete examination. Based on the tests received and the results of the study, the doctor can make a diagnosis, talk about the progress of treatment and offer options for combating the disease.
Why is this happening?
Numbness of the scalp - what is it? Definitely not a disease, but a symptom of some changes in the body.
The causes of numbness and “pins and needles” can be:
pinched nerve endings;- neoplasms in the brain;
- spinal injuries;
- vegetative-vascular disorders;
- infections affecting the central nervous system;
- poisoning with poisons and toxins;
- vascular system disorder;
- prolonged exposure to a stressful situation;
- uncomfortable body position;
- staying in one position for a long time;
- severe hypothermia;
- incorrect position of the wisdom tooth;
- side effect of drug therapy.
As you can see, the reasons why the head goes numb can be different. From harmless, static poses to cancer.
If you experience a feeling of numbness in the head more and more often, then it is worth observing the body as a whole. It is possible that additional symptoms will appear that will tell the doctor what caused the numbness.
Numbness is often accompanied by a slight burning sensation, which you can learn about here.
Hair masks.
The following combinations of components will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the hair:
1. Kefir + 2 tbsp. spoons of mango pulp + yolk.
2. Honey + olive oil + yolk
3. Grapeseed oil (castor, burdock) + liquid honey
4. Mayonnaise + egg + olive
5. Castor oil + cognac
6. Lemon juice + rosemary and olive oil
7. Mustard + honey
8. Gelatin + clay
First aid
If your head is numb not because of a disease, but only because of an external factor, then getting rid of these sensations will not be difficult. You just need to change your position and calm down.
If the provoking factor is cold, you should dress warmly, and you can also apply an alcohol compress. But just don't overdo it. If the sensitivity of the skin is reduced, careless actions can cause a burn. The first aid is to try to improve blood circulation . This must be done both at the location of the numbness and in an attempt to improve blood circulation throughout the body.
- It is necessary to massage the entire scalp, especially the area with reduced sensitivity.
- Drink hot tea with ginger.
- Take a comfortable, relaxed position.
- Calm down and relieve anxiety with the help of calm music, good thoughts, meditation.