Child neurology: Problems originating from childhood
Various injuries in early childhood can have a great impact on the development of pathologies of various types in adulthood. Thus, a concussion can subsequently affect vision loss, and fractures can lead to joint deformation. And often, seemingly completely unrelated phenomena turn out to be links in one chain: for example, a childhood injury to the cervical spine may in the future become a harbinger of the manifestation of autonomic dysfunction in adulthood. Our questions about why such injuries lead to such consequences were answered by neurologist Valeria Olegovna Korotkevich and pediatric neurologists Ekaterina Aleksandrovna Zornina and Alexey Sergeevich Semenov.
Ekaterina Aleksandrovna, how can birth injuries affect the future health of the child?
Birth injuries are a fairly common problem, because childbirth is an extremely complex process in which many factors influence the child: its position, the mother’s narrow pelvis, obstetric manipulations and much more. All this directly affects the baby's spine. Even minimal deviations from the norm during childbirth can lead to significant complications in development. It is advisable to visit a neurologist three to four times during the first year of life and contact a neurologist in the future as needed. In this case, there is a chance to notice some deviations that parents may not see. After all, clinical pathologies of the nervous system are often detected before the age of 3-5 years. According to statistics, among all diseases of the nervous system in childhood, 50% of them are associated with birth injuries, 30% arise due to genetic reasons, and only 15% are acquired during the process of growth and individual development.
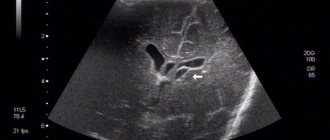
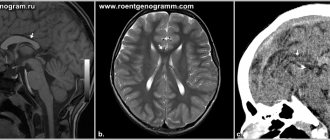
Today, the diagnostic method of neurosonography or ultrasound of the brain has become widespread. It allows you to safely and quickly obtain objective data on the state of the brain. As a screening procedure, this method is highly recommended to be done at a very early age, regardless of the indications. Ultrasound of the cervical spine and computed tomography, if required, are also used.
What injuries can be identified as the most dangerous?
There is a theory that cervical injury during childbirth and early life can subsequently lead to neurological diseases, hypoxic and ischemic lesions, which, in turn, when combined with other causes, can provide or enhance a predisposition to autonomic dysfunction. This is a complex of symptoms of disorders of various body functions, which are caused by a disorder of their nervous regulation. Therefore, we can talk about the consequences in a fairly wide range, because the manifestation of a particular pathology depends on the level of damage to the spine.
In newborns, the manifestation of this syndrome is often practically asymptomatic. But in the future, injuries can indirectly aggravate other pathologies. When it comes down to it, the most common one is minimal brain dysfunction. It usually manifests itself in preschool and early school age with impaired coordination, inability to concentrate, hyperactivity and emotionality, and headaches. I would like to note that if a child at this age cannot calm down or fall asleep for a long time, there is muscle hypertonicity or, on the contrary, he is too sluggish, has poor articulation or pronunciation problems - all this is a reason to visit a neurologist. Alexey Sergeevich, how is therapy for children when neurological pathologies are identified?
To begin with, a thorough examination is carried out. And since neurological diseases most often have a borderline nature with the psychological and pedagogical spheres, the approach and treatment itself are applied comprehensively. So, a psychologist or chiropractor can be involved, and the whole family should be involved in the correction process. Psychological, pedagogical and neuro-psychological therapy is used, and there is also medicinal treatment for individual indications, osteopathy and manual therapy. Of course, the younger the child, the greater the compensatory capabilities of his body, that is, the treatment is faster and easier.
But in any case, we must not forget about prevention. It is very important that parents understand that the rotational and adaptive mechanisms of the child’s body cannot be blocked. That is, you should not wrap your child up in the same way as in the first month of life; you need to take a rational approach to his physical and psychological development, giving him the opportunity to explore the world on his own in combination with reasonable restrictions and upbringing. Then neurological and other problems can often be avoided.
Valeria Olegovna, can childhood neck injuries make themselves felt in adulthood?
Of course, pathologies that are not detected in time can lead to the development of diseases, in particular to impaired blood supply. Indeed, as a result of injuries to the cervical spine, both birth and acquired, arteries can be damaged. Even a minimal disturbance in the relationship between the vertebrae in the neck leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain - both in childhood and adolescence, and in adulthood. This can manifest itself as headaches, dizziness, and loss of consciousness.
Is autonomic dysfunction a consequence of a cervical spine injury?
This cannot be said to be a direct relationship, but such injuries can indirectly affect the development of this syndrome. In any case, autonomic dysfunction (autonomic dysfunction syndrome) or, as it is also called, vegetative-vascular dystonia appears, first of all, as a result of the constitutional structure, genetic characteristics, stress and lifestyle, and is also provoked by injuries to the cervical spine. Taken together, spinal curvature, other diseases and injuries can cause this syndrome. Often, under the influence of physical activity, unprepared people develop vascular disorders, and to prevent this from happening, it is important to maintain a sports regime and move more.
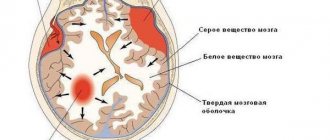
Depending on the type of disorder, dysfunction is manifested by high blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, headaches, weakness, malaise, and others. In some cases, impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and impaired venous circulation, due to birth injuries to the nervous system, can lead to the development of hypertension syndrome. It is a brain lesion resulting from increased intracranial pressure combined with an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. The syndrome has the following symptoms: blurred vision, convulsions, headaches, impaired consciousness, nausea and vomiting.
How are autonomic dysfunction and other neurological syndromes treated?
To get rid of autonomic dysfunction for adults, the Scandinavia clinic uses medicinal methods, acupuncture and reflexology, manual therapy, and homeopathy also helps many. Vegetative-vascular dystonia can cause serious endocrine diseases and cardiac disorders, so it is very important to consult a specialist, undergo an X-ray, MRI and ultrasound examination as directed.
For more information and to schedule a consultation, please call (812) 600-77-77
or by filling out the form on the website.
Through the Eyes of a Doctor: Child Neurology
Most people think that the rubber hammer that the neurologist waves helps him determine what is wrong with the patient. But in fact, the doctor receives a large amount of information simply by looking at the child. I suggest we talk about the visible signs that allow the doctor to suggest a diagnosis.
Important: the information below is for informational purposes only. Under no circumstances should you try to “diagnose” your child on your own, much less start unauthorized medication treatment. This can be very dangerous for your baby. The article is intended to help recognize alarming symptoms in order to seek qualified medical help in time.
Let's start from the top
Neurologists always pay close attention to head circumference. Approximate ideal figures are described in various tables, but most often doctors estimate “by eye”:
— children with unnaturally small heads for their age immediately arouse suspicion. The circumference should increase with age - this is an immutable law;
- worse when the head grows too quickly. Then the doctor may think about hydrocephalus - the accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the brain and the spaces around it;
— the shape of the head also provides a lot of information. There is a terrible disease - craniostenosis, in which the sutures of the skull close very early. Then the growth of the head stops and the shape changes greatly;
- sometimes, based on the enlarged parietal tubercles alone, one can suspect rickets and begin to examine the baby;
- an experienced doctor can see strabismus at first glance. It is not difficult to check it; it is enough to draw the child’s attention to the light source in front of him. With true strabismus, the reflection of the flashlight will not be in the center of the pupil;
- sometimes when crying, some children experience severe facial asymmetry. For example, the edge of the mouth does not go down. Most often, this is what underdevelopment of the depressor muscle looks like;
— it happens that a child is brought in for examination whose mouth is constantly open. In these cases, it is reasonable to visit not a neurologist, but an otolaryngologist, and rule out enlarged adenoids;
- even a quick glance allows you to assess muscle tone and the presence of torticollis. Let me remind you that babies up to three months have increased tone and tighten their arms and legs, then the tone evens out. Manifestations in the form of very low tone (prostrate child) or stiffness should make the doctor wary. Torticollis is usually clearly visible up to three months if it is associated with the usual position of the head. There is no need to worry about this; it is enough to place the child on his stomach more often and encourage him to turn his head in the unloved direction, for example, to interest him in something that is there.
Let's go lower
Looking for stains and seals is of utmost importance. Babies with large red-brown spots on the face or café-au-lait spots on the body should be seen by a neurologist.
Also, close attention should be paid to the lumbar region. Areas of intense hair growth, spots, hemangiomas (benign tumors from epithelial cells - editor's note), seals, deep depressions may indicate a possible anomaly in the development of the spine (spina bifida).
Sometimes parents pay attention to a sudden change in skin color. Sometimes it becomes marbled, sometimes the tips of the fingers turn blue. In most cases, such changes are normal and go away over time.
In the abdominal area, you can notice a protrusion of the navel, which upon careful examination turns out to be an umbilical hernia.
It is imperative to examine the child’s genitals. I know cases where parents only noticed six months later that the boy was missing one testicle in his scrotum.
Parents often worry about folds in the buttocks, associating their asymmetry with hip dysplasia. This sign cannot be taken seriously, because it is often found in children without orthopedic problems. And there are other reliable ways to confirm the diagnosis.
I always check all the listed features during the appointment. Of course, there are other signs that may indicate some kind of disease. But only a specialist will see them. Or, on the contrary, they are so obvious that anyone will notice them.
Be healthy and take care of the health of your loved ones!
Daniyar Zhuraev , pediatric neurologist.
Photo depositphotos.com The author's opinion may not coincide with the opinion of the editors.