What's happened
All cystic defects consist of a cavity filled with liquid contents. A subependymal cyst in a newborn child is formed due to exposure to provoking factors.
Minor neoplasms are not dangerous to the health of the baby and are prone to spontaneous resorption. Large tumors, on the contrary, require constant monitoring by a specialist, as they can cause serious consequences, including death.
Subependymal cystic formations are considered common among newborns who were born with various problems. The defect is formed due to injuries to the walls of small blood vessels, after which a small outpouring of blood occurs. Special cells process blood, and the resulting cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Such minor neoplasms subside after a few months, do not cause neurological disorders, and therefore do not require drug therapy. However, this does not apply to extensive defects that threaten the child’s health.
Pseudocyst of the brain in newborns and adults
Cystic pseudocysts are cavity formations with liquid contents and a thin wall that limits the size of the structure.
The false cavity differs from the true analogue by its formation from the germinal matrix, which is clearly visible on MRI of the brain. Nosology refers to developmental anomalies. The most common location of a cystic cavity formation is between the head of the caudate nucleus, the optic thalamus, and the lateral angles of the lateral ventricles. In adults, the main cause of cystic cavities is brain infections (Toxoplasma, Cryptococcus).
Classification
Symptoms and selection of treatment depend on the characteristics of the subependymal cyst in the newborn. Depending on the size, formations are divided into small and large.
Dimensions for surgery to remove Baker's cyst of the knee joint
Not all patients require removal of a knee cyst.
The first include defects with a diameter of up to 3 cm. Most often, such cavities resolve on their own, do not threaten the child and do not require any medical intervention. However, it is better to carry out routine inspections periodically.
With large formations, the risk of developing serious complications increases significantly. To protect the baby from dangerous problems, the doctor is obliged to prescribe the correct treatment, including surgery.
Based on the tendency to increase, tumors can be enlarged or non-enlarged. The first type includes cystic formations that rapidly progress, compress the tissue structures of the gray matter, and disrupt the functioning of the brain. In this case, immediate surgical intervention is required.
Non-enlarging defects do not reach large sizes and the patient’s condition does not worsen. In such a situation, the prognosis is considered favorable.
Depending on the number of chambers, cysts are divided into single-chamber and multi-chamber neoplasms. The first type is not so dangerous and can be effectively treated.
Multi-chamber cavities cause symptoms similar to those of many diseases, so diagnosing this pathology is difficult. In addition, the second type is difficult to eliminate.
Cyst surgery on the coccyx
Surgery to remove a coccyx cyst is the most effective way to get rid of the disease.
It is equally important to differentiate the subependymal capsule from other cystic diseases of the brain in newborns. The development of an arachnoid cyst is affected by damage and infection. This disease progresses rapidly and requires immediate treatment.
Sometimes a vascular plexus cyst is also diagnosed. This defect is formed during the prenatal period if the expectant mother is infected with the herpes virus. the disease often goes away on its own.
Manifestations of subependymal cysts
Subependymal cystic cavities, detected by ultrasound, have clear contours, spherical or slit-like shape, their sizes range from a few millimeters to a centimeter or more. Sometimes cystic transformation resembles a honeycomb due to the multiplicity of lesions. Experts associate the different structures of cysts with their detection at different stages of pathological development, when some of the cavities are relatively fresh, while others are already undergoing the process of resorption and “healing.”
subependymal cyst on ultrasound
Subependymal cysts can be located symmetrically, only on the right or left, in the area of the middle sections or horns of the lateral ventricles. The stronger the hypoxia experienced, the greater the volume of brain tissue that will be damaged. If the baby has a hemorrhage, then a single cavity filled with clear cerebrospinal fluid may subsequently be detected.
During the first year of life, the subependymal cyst shows a tendency to decrease in size and even completely disappear, while it is possible to both maintain the normal size of the sections of the lateral ventricles and increase the volume of their bodies or anterior horns. In rare cases, it is possible to observe the growth of a cystic formation, which can provoke compression of surrounding tissues and disruption of liquor dynamics.
The symptoms of a subependymal cyst on the left or right are variable, they can be either absent or quite severe, which is determined by the size, number and location of the cavities, as well as their combination with other lesions of the brain tissue.
Small cysts or a single small cavity may not manifest themselves in any way, not change the baby’s development and not cause any concern. In most cases this is what happens. Concerned parents can read a variety of information, usually from Internet resources, in which the symptoms will include both visual and motor disturbances, however, the small cavities located under the ependyma (lining) of the ventricles are unlikely to somehow affect the corresponding brain structures, therefore, such judgments should be treated critically, without panicking and trusting only the opinion of a pediatric neurologist.
With large, multiple or growing subependymal cysts that appear against the background of large hematomas, dysfunction of the corresponding parts of the nervous tissue with neurological symptoms is possible, but such events develop extremely rarely and are usually based on a combined lesion of the central nervous system. Possible signs of trouble are:
- Sleep disorders, causeless crying, anxiety;
- Anxiety, hyperexcitability of the baby or, conversely, lethargy and lethargy;
- Tendency to muscle hypertonicity, in severe cases - hypotension and hyporeflexia;
- Poor weight gain, weak sucking reflex;
- Visual and hearing impairments;
- Tremor of arms, legs, chin;
- Severe and frequent regurgitation;
- Pulsation and bulging of the fontanel due to intracranial hypertension;
- Convulsive syndrome.
These symptoms can be expressed to varying degrees. As cysts are reabsorbed, they often weaken and even disappear by the end of the first year of life, but in severe cases, delays in mental and motor development, stunted growth of the child, and problems with speech and learning become noticeable.
A subependymal cyst, which appears against the background of leukomalacia of the periventricular nervous tissue, can have cerebral palsy, convulsive syndrome, and mental retardation as the most severe consequences.
Problems with child development are most often recorded with brain damage combined with other signs of a generalized infection. In these cases, malformations of other organs, viral pneumonia and even sepsis are often diagnosed after childbirth.
The prognosis when subependymal cysts are detected is often uncertain, which is why doctors do not rush to premature conclusions. Both normal brain development and serious neurological deficits with combined pathology are possible. Children often exhibit polymorphic symptoms, ranging from severe depression of the central nervous system to hyperexcitability.
In some cases, normally developing infants exhibit some signs of immaturity of the nervous system in the form of transient and short-term tremor of the chin or limbs, restlessness, and regurgitation. It is difficult to associate these symptoms with small subependymal cysts, but children are under the close attention of specialists.
Causes
Cystic pathology occurs due to the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Hypoxia. This condition occurs with anemia, diabetes, problems with the kidneys, heart, lungs, and smoking.
- Birth injuries. Head injuries during childbirth significantly increase the likelihood of developing the disease. This often happens if the birth canal is narrow, the fetal head is too large, or the pelvis is deformed.
- Toxicosis.
- Lack of microelements and vitamins. Deficiency occurs if the expectant mother is hungry or malnourished.
- Anemia. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood leads to a lack of oxygen, developmental delays, and vulnerability to infectious pathologies.
- Hemolytic disease. Due to different Rhesus levels in the mother and fetus, the immune system attacks the embryo. This condition requires immediate medical attention, as it threatens the child’s life.
- Infections. Even a common cold can seriously harm the fetus.
Complications after removal of a dental cyst
Compliance with the rules and recommendations during the rehabilitation period after removal of a dental cyst helps prevent the development of a number of complications.
Multiple pregnancies significantly increase the risk of complications. In addition, in this case, children are often born with low birth weight.
Excessive or deficient amount of amniotic fluid also affects the child’s health. Polyhydramnios leads to brain pathologies, and a lack of fluid leads to a lack of protection for the embryo from external factors.
General information about pathology
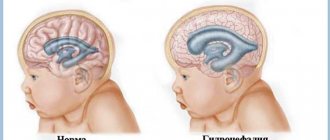
A cyst is a fluid-filled cavity located in the substance of the brain or its membranes. When the pathology is small in size, it has a subclinical course and is diagnosed accidentally during a neuroimaging examination of the head. Since the intracranial space has limited dimensions, with a significant increase in the volume of the formation, intracranial hypertension develops.
The size of the cavity with liquid is largely determined by the compensatory capabilities of the formation and its localization. Due to the pliability of the skull bones in children at an early age, the cyst may not manifest itself for a long time.
The formation can be found in people of different ages, both in infants and in elderly patients. Even if the fluid cavity is congenital, it can make itself felt only by the age of 30-50.
According to generally accepted practice, treatment is prescribed only in the case of a pronounced clinical picture and when complications develop. If the cavity with fluid is frozen or slowly progressing and its volumes are insignificant, a wait-and-see approach is chosen, which involves regular monitoring of the patient.
Clinical picture
Subependymal cystic formations affect both the left and right hemispheres of the gray matter. Most often, the ventricles filled with cerebrospinal fluid are affected.
Clinical manifestations depend on the location, size and rate of growth of the cyst. Different parts of the brain perform specific functions, so compression of them leads to specific symptoms.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Damage to the occipital zone leads to deterioration of visual acuity, up to complete blindness. When the temporal region is affected, hearing is impaired. A tumor of the cerebellum causes deterioration in motor coordination.
When the pituitary gland is damaged, developmental delays occur, and sometimes the child suffers from dwarfism. If the pathogenic process affects the frontal part, then speech formation is disrupted.
In addition to the signs described above, the baby may experience general symptoms such as worsening sleep, anxiety, weight loss, pathological muscle tone, and frequent crying for no reason.
A newborn child with a subependymal cyst often refuses to drink breast milk, spits up heavily, moves excessively, periodically loses consciousness, and suffers from attacks of epilepsy and tremors in the limbs.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing subependymal cysts is ultrasound neurosonography. This procedure allows you to achieve an accurate result. Moreover, the manipulation is absolutely safe and painless for the child.
Ultrasound examination of the brain is prescribed for infants whose fontanelles have not yet ossified. The planned procedure should be carried out when the baby is one month old. However, if there are pathologies during pregnancy or after a difficult birth, manipulation is prescribed earlier.
Additional methods are sometimes used to clarify the diagnosis. Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging allows you to accurately study the characteristics and location of the tumor. Due to exposure to radiation, CT scans are done no more than twice a year.
Diagnostic measures
A neurologist may suspect the presence of an intracranial formation of significant size based on the patient’s neurological status and clinical symptoms. In this case, the patient is sent for examination to an ophthalmologist and otolaryngologist to check vision and hearing. Specialists perform ophthalmoscopy, audiometry, perimetry and visometry. With severe hydrocephalus, ophthalmoscopy reveals congested optic discs.
By referring the patient for echo-encephalography, it is possible to diagnose increased intracranial pressure. If the patient experiences epileptic paroxysms, he is additionally sent for electroencephalography.
It is extremely important to differentiate a cavity with fluid from a tumor, abscess and hematoma. It is not possible to do this on the basis of collected clinical data alone. Therefore, to make a clear diagnosis, neurologists use neuroimaging diagnostic methods.
By performing an ultrasound examination, it is possible to diagnose certain types of congenital cysts even at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. After birth, until the baby's large fontanelle closes, neurosonography is performed to make the correct diagnosis. In adulthood, to visualize a brain cyst, the patient is sent to a magnetic resonance or computed tomography scan of the head.
MRI and CT are performed with contrast in order to differentiate a cyst from a tumor. A cavity with liquid is not able to accumulate a contrast agent, unlike a tumor.
After diagnosis, constant monitoring of the patient with a cystic formation is important. During regular examinations, the doctor monitors the volume of the cyst over time.
If the cyst is a consequence of a stroke, additional vascular examinations are carried out: ultrasound, MRI and CT of vessels, duplex scanning.
Treatment
The basis of therapy is the elimination of the factor that provoked the development of a subependymal cyst in a newborn. Most often it is necessary to treat hypoxia. The treatment process occurs in several stages.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Immediately after birth, in the presence of hypoxia, resuscitation procedures are immediately performed to prevent the development of formation. To do this, the trachea, oropharynx and nasopharynx are cleared of fluid, and artificial respiration is used.
After this, the baby’s condition is monitored by a neurologist for three days, who selects treatment tactics. Special medications are prescribed, courses of therapeutic massage and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to improve the condition and eliminate the lack of oxygen.
If the cyst was diagnosed in childhood, then drugs are used to normalize metabolic processes in the gray matter, and vitamin complexes. In case of rapid increase and large size, surgery is performed.
Using an endoscope, the cavity is cleared of liquid contents. Sometimes open manipulation of the brain is required.
Complications
If diagnosis is delayed, the cystic neoplasm will progress, grow and compress the surrounding tissue structures. Focal manifestations will become more pronounced as the defect increases, and the child’s visual acuity will significantly decrease.
Laser removal of dental cyst
Laser treatment of dental cysts is an innovative method in the fight against a disease that requires immediate therapeutic measures.
Often, a subependymal cyst causes an increase in intracranial pressure, as a result of which the newborn will begin to suffer from severe headaches, apathy, constant weakness, fatigue, dizziness, nausea with vomiting, and diplopia. Frequent loss of consciousness will also accompany an infant with this disease.
In the absence of timely treatment, extensive formation disrupts the development of the skull bones, causing physical and mental development to deteriorate. In advanced situations, the pathology leads to death. Sometimes cystic defects cause stroke.
Types of brain cysts and their symptoms
Arachnoid - occurs in almost 4% of the population. A cavity with fluid can be congenital or acquired. In the latter case, it develops in response to traumatic brain injury. The formation is localized on the surface of the brain in its membranes. The cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
In most cases, an arachnoid cyst does not make itself felt for quite a long time and is discovered by chance. Severe symptoms appear only if a large amount of fluid accumulates in the cavity. In this case, cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the cells lining the cavity.
With a sharp increase in the volume of the cavity with liquid, it can rupture and, as a result, die.
Colloid cysts are recorded in 15-20% of all cases of formations inside the ventricles of the brain. Most often it is localized above the foramen of Monroe in the anterior region of the 3rd ventricle. Less common in the area of the transparent cerebral septum in the 4th ventricle.
The liquid filling the cavity of the colloid cyst has high viscosity. Patients experience symptoms of hydrocephalus and, with a certain position of the head, a paroxysmal increase in cephalgia is noted.
In rare cases, memory loss, behavioral disorders and weakness in the limbs occur.
Pineal cyst of the pineal gland - according to statistics, 10% of patients have formations of this type that are small in size and do not make themselves felt. Cystic formations are localized in the epiphysis of the brain, in most cases they are no more than 1 cm in size. Otherwise, symptoms appear. When it grows, it can block the entrance to the “plumbing” of the brain and block the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, causing occlusive hydrocephalus.
Epidermoid or dermoid is a formation that is an anomaly of intrauterine development. In this case, the cells of the baby's future skin and its appendages remain inside the brain. Accordingly, in addition to liquid, elements of the ectoderm are present, namely sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
After the birth of a child, such a cyst quickly increases in size. The only possible treatment is surgical removal of the formation.
Choroid plexus cyst - forms regardless of the person’s age. In this case, the space between the plexus vessels is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Symptoms are rarely present, sometimes accompanied by epileptic seizures and symptoms of intracranial hypertension.
With a congenital choroid plexus cyst, the formation is diagnosed at the 20th week of intrauterine development using ultrasound. By the 28th week, such formations resolve.
Forecast
The prognosis of a subependymal cyst in a newborn is influenced by the size of the pathological cavity, location, timeliness of diagnosis and rate of increase. Minor neoplasms that do not increase in diameter do not cause serious consequences, so the prognosis in such situations is favorable.
Large formations that constantly grow threaten not only the health of the baby, but also his life. Sometimes even timely surgical intervention is not able to eliminate the problems that have arisen, as a result of which the child becomes disabled.
Therefore, it is important to detect a tumor at an early stage, when the defect does not compress neighboring tissues.
Prevention
To protect against subependymal cystic cavity, hypoxia must be prevented. To do this, a pregnant woman must eat properly and nutritiously in order to saturate her body and fetus with a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals.
It is equally important to quit smoking and drinking alcohol. Any infectious pathology, even a cold, must be treated in a timely manner and only under the supervision of a specialist. Expectant mothers also need to avoid contact with various toxic substances.
If all these recommendations are followed, the risk of a pathological defect in a newborn is significant. In addition, such prevention will help avoid other complications during pregnancy.
Subependymal cysts in infants are a widespread formation. Small formations usually resolve on their own and do not cause any abnormalities, while large neoplasms are dangerous with serious neurological consequences and even death.
Therefore, before giving birth, preventive recommendations should be carefully followed, and if the child has a disease, do not delay treatment.