We continue a series of publications devoted to neurosurgical diseases. The project was prepared jointly with the MBOO for helping children with neurosurgical diseases “He Needs You.” We want these “terrible” diagnoses not to put pressure on parents and not to take away their hope. In our publications, the best specialists and experienced parents will talk about ways to cure and overcome, give recommendations and show that life can go on with any, even such complex, diseases.
The rate of surgery for indications such as brain cysts has increased not because morbidity has increased. An increasing number of X-rays have revealed, often quite accidentally, cysts in the brain. Or other pathologies described by specialists as cysts, but which are not cysts. And the risk minimized during such operations and their good financing have led to the fact that cysts are operated on when necessary and when, to put it mildly, it is inappropriate.
So, let’s figure out what a cyst is, how to distinguish it from a fake cyst, and which particular cyst requires surgical treatment, together with Dmitry Yuryevich Zinenko , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Head of the Department of Neurosurgery at the Scientific Research Clinical Institute of Pediatrics named after Yu.E. Veltishchev.
"Scary" names
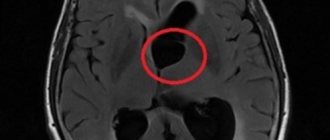
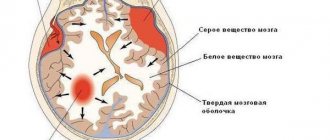
What is a cyst? A cyst (its other name is “cerebrospinal fluid cyst”) is a cavity filled with liquid, having a capsule that isolates it from other liquor-containing spaces.
with a retrocerebellar cyst consult a neurosurgeon . And although this phrase frightens and even makes parents panic, it must be said that with these words radiologists describe a variant of the norm. Most often, this is not a cyst at all (that is, not an isolated cavity filled with fluid), and it does not require surgical treatment.
Children under two years of age diagnosed with a retrocerebellar cyst should be shown to a neurosurgeon to avoid the development of hydrocephalus.
Another normal variant is a pineal gland cyst . Perhaps the most common incidental finding on MRI. Does not require surgical treatment.
An epidermoid or dermoid cyst is not a true cyst. It is filled not with liquid, but with skin appendages - follicles, sebaceous glands, hair, cartilage tissue, etc. In its structure, it is more similar to a tumor and requires the same treatment as for a tumor - removal.
A porencephalic cyst usually occurs in the place where part of the brain has died as a result of hypoxia or hemorrhage; this place is filled with fluid. In itself, such a cyst does not interfere with development and does not require mandatory surgical treatment.
Pseudocyst - looks like a cyst, but is not a cyst, a cavity that is not limited by anything, it has communication with other parts of the skull. Does not require surgical treatment.
a cyst of the transparent septum is a normal variant, but if it is large in size, it can lead to impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid, which requires surgical treatment.
For children in whom the cerebrospinal fluid cyst rapidly enlarges, causes increased intracranial pressure, neurological symptoms or seizures, surgical treatment is indicated.
If your child has a photo taken and a cyst is found, don’t panic! Having received a description of the x-ray image, first of all, pay attention to the conclusion. If the report says: “There are no pathological abnormalities,” most likely you will not need any surgical intervention. Even if you see the word “cyst” somewhere, most likely the radiologist needed it to describe a normal condition. Just in case, check with him whether you need a consultation with a neurosurgeon.
Clinical picture
A cyst in the head in children in the early stages of formation does not show signs. Unpleasant symptoms occur when the formation begins to put pressure on neighboring brain structures.
The clinical picture depends on where the formation is located. In cases where it affects the occipital region, vision deteriorates. Nebula and double vision are noted.
When the cerebellum is damaged, dizziness and loss of coordination of movement are observed. When the cyst is located in the pituitary gland, the body's hormonal levels are disrupted, which negatively affects the physical development of the baby.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Common signs of a cyst in the head include frequent regurgitation, constant restlessness, sleep disturbances, nausea and vomiting.
When is a consultation with a neurosurgeon necessary?
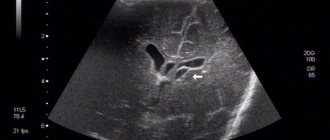
Newborns today are almost universally examined using neurosonography (ultrasound examination of the brain). During this test, infants often have some type of cyst. If the cyst is large, specialists will likely recommend an MRI. If not, they will watch. A rapidly enlarging cyst, or a cyst causing epileptic seizures or other neurological symptoms, requires consultation with a neurosurgeon.
If, at the age of several months, a previously healthy child shows signs of increased intracranial pressure and a cyst is detected during examination, surgical treatment is necessary.
When an older child is examined for a traumatic brain injury and a cyst is accidentally found, we are NOT talking about surgical treatment.
If an examination is prescribed due to speech delay or developmental delay, then the cyst found is a reason to consult with a surgeon to understand whether this cyst is associated with these symptoms.
When a school-age child is examined due to the appearance of severe headaches, the cyst found should be discussed with a neurosurgeon. Perhaps surgery will help eliminate the cause of these pains.
If a child who practices martial arts or boxing undergoes a mandatory MRI (young athletes are required to undergo examinations before competitions), during which a cyst is accidentally discovered, it is necessary to obtain advice from a neurosurgeon about the possibility of practicing these sports. A cyst without additional symptoms in older children is usually not life-threatening. But it has contraindications for engaging in traumatic contact sports, primarily martial arts and boxing, and to a lesser extent football and hockey. This cyst does not require surgical treatment.
Can it develop into cancer?
A brain cyst is a benign formation that does not always require removal. But in the absence of therapy, certain consequences may occur in some cases.
The most dangerous complication is the likelihood of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor. A similar process is observed under the influence of certain factors. These include exposure to chemicals, trauma to the skull, and genetic predisposition.
The transformation of a cyst into a cancerous tumor is established in rare cases. But, despite this, it requires careful diagnosis, constant medical supervision and therapy.
Treatment methods for liquor cysts
The most common indications for surgical treatment of a cyst: it grows too quickly, causes seizures, causes neurological deficits, the cyst interferes with the child’s development.
The main, safest and most effective method for treating cerebrospinal fluid cysts today is fenestration. That is, dissection of the walls of the cyst for communication between the cyst and other cerebrospinal fluid spaces, where this accumulated fluid is normally located.
It is possible to install a stent (catheter) connecting the cavity of the cyst and the ventricles. It happens that the operation turns out to be ineffective and forces you to use another method of treatment - bypass surgery.
Shunt surgery (today practically not used as a primary method of treatment), although it allows you to quickly reduce the size of the cyst, but creates a lifelong dependence on the shunt system. If this method can be avoided, neurosurgeons try to avoid it.
However, when treating young children (up to two years old), as well as when treating cysts that were complicated by hemorrhage, shunt operations are inevitable.
In general, surgeries to treat cysts have a low risk of complications in the hands of experienced doctors. This operation involves hospitalization for only three to four days and several subsequent consultations with a surgeon. Deviations from this rule occur only in 10% of cases.
Most often, in such a situation, endoscopic surgery is used, but in some cases, an open microsurgical approach is more correct. An uninitiated person will not see the difference after the operation; the size of access to the brain cavity will be the same. In this case, it is not so important for the patient which instrument is used to perform this operation. It is important to make the patient feel better.
Forecast
If a cyst is detected in the head of a newborn, the prognosis in case of timely treatment is favorable. Typically, neoplasms are established in the early stages of development. Severe consequences after surgery are observed in rare cases.
Often, a cyst that affects brain structures does not require therapy. In this case, specialists use a wait-and-see approach.
A person can live their whole life with a diagnosed cystic neoplasm. It has virtually no effect on life expectancy.
An unfavorable prognosis is established in cases where the cyst transforms into a malignant tumor. Life expectancy in this case depends on the stage of its development at which treatment was carried out and the characteristics of the course of the pathology.
Possible complications
If treatment is refused or the intermediate velum cyst is not detected in a timely manner, complications may arise. The deterioration concerns:
- disturbances mental state;
- delays ;
- paralysis of some limbs or the entire body as a whole;
- damage to the tactile, speech, and auditory functions of the body.
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
When deciding on radical treatment of a cystic formation, it is necessary to take into account factors such as the patient’s age, the size of the tumor, and its type.
However, even if the operation was successful, the risk still remains.
There may be cases of relapses, especially if the formation in the brain was not completely removed, but only the cystic fluid was removed. In this case, the same symptoms are observed, which are characteristic of the third stage, when the cyst is increased in size.
Symptoms
The presence of small cysts in most cases goes unnoticed due to their asymptomatic development. Despite their stable condition and lack of growth, they must be monitored and supervised by specialists at all times.
If the cystic growth reaches a large size, compression of the surrounding tissue occurs, which causes the appearance of characteristic symptoms. Such conditions are often accompanied by:
- headaches that occur with a certain frequency or are constant;
- decreased auditory and visual function, as well as sense of smell;
- drowsiness or insomnia;
- violation of coordination ;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- convulsions and sudden loss of consciousness;
- frequent regurgitation or vomiting;
- numbness and tremor of the limbs;
- pulsation in the fontanel;
- epileptic seizures.
If the location of the cystic neoplasm becomes the pituitary gland, then disturbances in the endocrine system and sexual development of the baby are possible.
Diagnostics
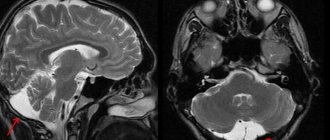
Diagnostics are carried out using methods that allow one to find the exact location of the formation and identify its structure. A complete examination of this type can only be carried out using MRI.
Complications after removal of a dental cyst
Compliance with the rules and recommendations during the rehabilitation period after removal of a dental cyst helps prevent the development of a number of complications.
Also, for diagnosis and subsequent diagnosis and treatment plan, the following methods are used:
- examination of the heart and cardiovascular system;
- checking the patency and blood flow of cerebral vessels;
- checking for the possibility of infectious infection by parasitic worms;
- identifying blood cholesterol
Not all additional methods may be needed - it depends on what stage the cyst is at.
Consequences of choroid plexus cysts
Complicated cystic formations cause specific manifestations:
- Hypertonicity of newborns;
- Neurological symptoms due to compression of brain structures;
- Epilepsy (muscle cramps);
- Slight loss of vision and hearing.
Magnetic resonance imaging will need to distinguish a true vascular cyst from a pseudocyst. The latter type is a variant of the physiological development of the brain, but the anatomical structure when examined by ultrasound resembles a cavity. Magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate study (informativeness is about 96%). The three-dimensional modeling mode will allow you to correctly verify the nosology.
Edwards syndrome can be detected by ultrasound by identifying abnormalities of the limbs and changes in internal organs. Additional diagnostic tests:
- Determination of the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin;
- Blood chemistry;
- Analysis of amniotic fluid.
A special risk group is women aged 32 years and older with hormonal disorders.
Causes
A cyst is a vesicle with liquid exudate filled with cerebrospinal fluid that appears in the embryonic stage.
The anomaly is formed due to the fact that the leaf-shaped folds of the membrane of the brain in the unborn grow together with each other, which should not happen in a normal state. The anomaly forms between the structures of the brain, the arachnoid, and the medulla.
All cysts are divided into two types:
- primary, which appear in utero;
- secondary, which are negative consequences of diseases.
Dimensions for surgery to remove Baker's cyst of the knee joint
Not all patients require removal of a knee cyst.
There may be several reasons why a child has a cyst of the pars intermedius of the brain. Among them are:
- congenital brain abnormalities and genetic defects;
- inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord or brain, resulting from operations or just like that;
- pathologies of various types of connective tissue development;
- impaired blood circulation in the brain resulting from injuries or bruises;
- viral diseases affecting the meninges.
Typically, a cyst is formed in utero, and factors such as illness, injury, inflammation, and viral diseases are only stimuli for tumor growth.
Prevention
First of all, preventive measures are carried out in relation to the expectant mother. As a rule, she is sent for genetic analysis, which will identify possible risks of the formation of a cystic formation in the baby’s brain.
It is extremely important when carrying a child, as well as during the perinatal period, to prevent traumatic situations and the development of inflammatory and infectious processes.
If such conditions cannot be avoided, you should immediately seek medical help.
Parents should pay special attention to the health of their newborn child. At the first symptoms of abnormalities in the body, you should immediately visit a specialist. Only timely diagnostic measures will make it possible to correctly diagnose and carry out the necessary therapy.