Socialization factors are circumstances that encourage a person to take active action. There are only three of them - macrofactors (space, planet, country, society, state), mesofactors (ethnicity, type of settlement, media) and microfactors (family, peer groups, organizations). Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Macrofactors of socialization
Macro factors of socialization influence the socialization of all humanity or very large groups of people living in certain countries.
Macro factors include:
- Universe, or Space.
- Planet Earth.
- The entire human community.
- A country is a territory that has borders, distinguished from other territories by natural conditions and geographical location.
- Society is a set of social relations that have developed between people in a country, including in its structure the family, the state, age, social, professional and other groups.
- The state is a part of the political system of society that has power functions.
- Natural environment or geographical factor.
Are you an expert in this subject area? We invite you to become the author of the Directory Working Conditions
In the modern world, there are many problems that affect the living conditions of the individual and have an indirect or direct impact on the socialization of the individual:
- Environmental problems – environmental pollution.
- Demographic problems - growth or decline in the population of individual countries.
- Economic problems - economic crises, increasing gaps in the level of economic development of individual countries and continents.
- Military-political problems - the proliferation of nuclear weapons, the increase in the number of regional conflicts, political instability.
The socialization of an individual is influenced by the characteristics of the sex-role structure of society, predetermining ideas about the status of gender, sex-role expectations, and self-determination.
The state acts as:
- factor of socially controlled socialization: participation in the creation of educational and educational institutions (kindergartens, schools, colleges, institutes, institutions for children with poor health, etc.);
- factor regarding directed socialization: determination of the mandatory minimum education, length of service in the army, age of marriage, etc.);
- factor of spontaneous socialization: ideology, politics, social and economic practices characteristic of a given state form certain conditions for the life of its citizens.
Finished works on a similar topic
Course work Factors of personality socialization 410 ₽ Abstract Factors of personality socialization 270 ₽ Test work Factors of personality socialization 220 ₽
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Factors of socialization and personality formation
The term “socialization” in pedagogical science is usually understood as the formation of an individual into a part of the society in which he is located. In other words, we are talking about a person’s entry into society. Of course, at the first stage, the child’s social circle is very limited - peers, parents or teachers, then the person enters the student environment, and also, in addition to those people with whom he comes into contact at school, he communicates with other social groups. The factors of socialization and personality formation are varied and different options can be considered.
If we consider the ideal option (which is perceived as one of the goals of training and education), then a person should become a full member of society, treating other members with respect and interacting with them, making a worthy contribution to the life of this society. Moreover, the word “society” can be understood as a team at work, relatives, colleagues, friends, and even, ultimately, the whole country. All these are signs of successful socialization.
However, is socialization always successful? And does yesterday’s child, when becoming an adult, always transform into the personality that society would like to see? Modern research in pedagogy, sociology and psychology clearly indicates that this is not always the case. The fact is that there are special factors of socialization and personality formation, known to pedagogical science, and the success of a person’s socialization and the formation of his personality depends on the influence of such factors.
Factors of socialization: a view from the inside
Thus, domestic teachers conditionally divide factors of socialization and personal development
- Macro factors,
- Mesofactors,
- Microfactors.
Let's take a closer look at them.
- Macro factors (from the Greek word “macro” - “big”, “large”) are the most significant factors that influence the socialization of the inhabitants of a certain state, culture, state and sometimes even the entire population of the Earth. Such factors include, for example, the sphere of high technology, world culture and art, internationally recognized scientific achievements, and the environment.
- Mesofactors (from the Greek “meso” - “intermediate”, “average”) are those factors of socialization and personal development that create conditions for socialization on the basis of ethnicity and (or) ethnocultural affiliation, as well as on the basis of their place of residence: for example, such factors are characteristic of residents of a particular region - city, village or town. For example, the peoples of the Turkic world have one approach to family values, while the inhabitants of Scandinavian countries have a completely different one. At the same time, it is noteworthy that such factors do not in any way affect the moral self-awareness, level of education, culture and the degree of respect for universal human values of representatives of both nations.
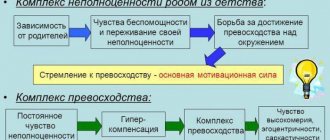
- Microfactors (from the Greek “micro” - “small”) are, perhaps, those factors of socialization and personality development that directly affect each individual or a small group of individuals. This is the marital status of parents and relatives, profession and related communication, peers, relatives, teachers, doctors. Later, members of the family created by young people are added to them (for example, a spouse and (or) children and grandchildren). These factors have a huge impact on the moral, cultural and professional development of the individual. It is for this reason that in Russia and in other developed countries there is an active fight against family troubles, an asocial lifestyle, unfavorable economic factors and everything that can lead to improper development of the personality of a child or young person, as well as the formation in him of a set of false moral guidelines and attitudes, which is fraught with extremely dire consequences, one of which is involvement in the asocial lifestyle that the child’s parents led in the family. The school plays a special role here as an institute of public education and medicine.
At the same time, it cannot be denied that every child from birth has certain genetic predispositions to a particular type of activity or lifestyle. Followers of this concept are called behaviorists (from the English word “behavior” - “behavior”). However, these same scientists do not assign a decisive role to the underlying natural factors. In particular, both representatives of behavior science and educational psychology believe that socialization factors and education built on their basis play a decisive role in the processes of socialization and personal development.
Mesofactors of socialization
Mesofactors of socialization are certain conditions for the socialization of groups of people united:
- national sign;
- type and location of settlement (town, village, city, region);
- belonging to the audience of one or another mass communication medium (computers, television, radio, cinema, etc.).
Ethnic characteristics that influence the method of socialization are divided into:
- vital, or vital (health, nutrition, methods of physical development);
- mental or spiritual.
Features of socialization, determined by the type and place of socialization:
- Significant social control over individual behavior, openness in communication in towns and villages.
- A wide choice of value systems, communication groups, lifestyle, significant opportunities for self-realization in the city.
- Main functions of mass media:
- Socio-psychological function: the need for connections with other people, satisfaction in receiving information that supports his ideas, values, views.
- Dissemination of knowledge in the field of science and culture.
- Social management and regulation, maintaining public relations.
Where does primary and secondary socialization of a person take place?
Forms of socialization
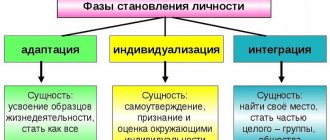
There is such a thing as primary and secondary socialization of a person.
- Primary socialization , as a rule, is also called childhood socialization. This process occurs unconsciously. It’s just that the child is influenced by various factors and with their help he already learns certain norms of behavior. At the same time, parents, educators and relatives act as assistants in this matter. The older a child gets, the more aware he becomes. As a result, after reaching a certain age, he may reject some norms of behavior and behave differently than others. Thus, he gets the right to choose his own line of behavior. At the same time, the very first place where the first social qualities are formed is the family.
- As for secondary socialization , this already occurs as the child grows up. In any case, he continues to assimilate social norms of behavior. And here secondary socialization begins, when you have to get used to different groups. For example, a child enters a university, where there is a different society and new norms of behavior. They have to conform. It is much more difficult when a person moves to another country, because in this case you have to change habits and accept new traditions, and this is quite difficult. Often people cannot cope without professional help.
Family functions in human socialization: features
Family and socialization
Human socialization begins with the family. It greatly affects the physical and mental qualities of the individual. The family is one of the main institutions of education. In particular, it lays down the future qualities of a person.
A family is a group of people united by kinship ties. It always has its own traditions and foundations. It is the main institution that forms the child’s life principles and moral principles.
Thus, the family promotes personality development, strengthens mental health, develops reliability and confidence in children, and also helps in self-realization and security. In addition, in the family, children learn to express their individuality.
The success of a child’s socialization depends on the structure of his family, that is, whether it is complete or not, and relatives can also raise the child. When the family is incomplete, there is a decrease in educational abilities. In particular, the child begins to experience a lack of emotions, or too many feelings are shown towards him. At the same time, in dysfunctional families, socialization is difficult and even disrupted. In this case, the basic family functions are ignored, and there are shortcomings in upbringing. This is where “difficult” children appear.
Socialization of people with disabilities: features
Socialization of a disabled child
Socialization of a person with a disability is a complex process in which he has to master accepted norms of behavior and stereotypes. The difficulty lies precisely in the person’s position, because a disabled person is a person who has certain physical or psychological disabilities. Accordingly, he requires special care. In addition, he requires support from the state and society as a whole.
Among other things, socialization presupposes the acquisition of certain skills and knowledge, as well as values that are quite difficult for people with disabilities to assimilate. Thus, among people with disabilities, one of the forms of socialization is continuous learning. With its help, a disabled person can participate in processes such as:
- Compensation for psychological defects. For example, a person has some mental problems that make him in some way different from others
- Formation of positive attitudes
- Development of other abilities that have been lost, for example, a person has lost the ability to walk due to an accident. Then we need to help him learn to walk again, if possible.
Learning is always about mastering behavior and environment. Often, when people with disabilities are treated differently from others, they become uncomfortable. In this case, the help of a psychologist is required, and training a person in such a way that he can interact with others and it will not be noticeable that he is not like that. In addition, adaptation and participation in public or social activities are important for people with disabilities.
Of course, the socialization of a disabled person has certain characteristics. In this case, everything depends on the pathology itself, for example, developmental delay or loss of some functions. In addition, gender and age are important, as well as initial position in society, family, state. There are people who are simply not noticed and no one cares about their socialization. It is much more difficult for them, because in addition to their peculiarity, they are isolated from society.
For example, disabled people with mental retardation can achieve independence, but for this they need to constantly work and memorize every action. Today there are even special trainings.
Disabled people aged 16-25 years, in addition to having disabilities, may experience difficulties communicating with peers. This makes the situation worse. However, in some cases, disability is the main obstacle, not even for the person himself, but for those around him. This can cause the person to withdraw or begin to behave antisocially. So training programs must necessarily take into account all the limitations of a disabled person.
Classification of agents of socialization by age
At different stages of socialization, the influence of certain agents on a person is noticeably different. Here are some examples:
- The main agents of socialization for a child 1-3 years old are his relatives, in particular his closest relatives, which include parents, grandparents, sisters and brothers. The feeling of attachment to people and the desire to trust them is formed in children precisely during this period of life;
- At the age of 3-8 years, the child has additional agents of socialization, for example, educators and teachers. At this stage, the process of mastering the individual with a list of very important cognitive and thinking skills occurs;
- At the age of 8-15 years , socialization is provided mainly by small social groups of peers, which children and adolescents join. The main task of these groups is to facilitate the process of a person’s transition to adulthood.
What is human socialization like: forms
It is important to know what forms a person’s socialization takes. In general, there are two main ones.
- Non-directional . Personality formation occurs spontaneously when a person is influenced by the immediate social environment. Then a person develops certain qualities. That is why it is spontaneous. In this case, the environment includes relatives, friends and colleagues.
- Directed . In this case, a special method of influence is provided, that is, people are specially attached to certain values and qualities that are important to society. In particular, this concerns education. From childhood, parents instill in their children a certain set of values and attitudes so that in the future they can develop a perception of the world that allows them to become part of society. In other words, parents prepare the child for life in society.
Forms of socialization may be related, but there may be no coordination. If there are contradictions, they can become an obstacle to a person’s socialization.