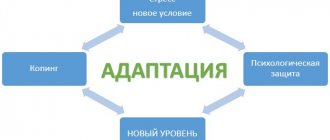
The ability to adapt to the conditions of the natural environment is called adaptation. It is a complex social and biological process. Dramatic changes occur in the functionality and systems of the human body. In some cases, it is necessary to change behavior and habits. Finding himself in new circumstances, a person adapts and adapts to the changed environment. Adaptation can occur at the molecular or biocentric level. The ability to adapt is influenced by various factors. Depending on the complexity of natural conditions, the period of adaptation of the organism changes.
Human adaptation to the environment: what relates to natural conditions
Each country has certain natural conditions. The African continent is fundamentally different from European countries. Asia is the complete opposite of the countries of South or North America. Existing natural conditions include:
- Features of the geographical location;
- Climatic conditions;
- The nature of inland waters;
- Type of soil and terrain;
- Vegetation;
- Representatives of the animal world.
The body undergoes two-way adaptation. He adapts to the environment on his own, while at the same time trying to make new conditions comfortable for his body. A person arranges a home, studies the population, and selects a suitable product. He can build a house that is familiar to him or purchase transport to move around a new area.
The process of adaptation of the body to weather and climatic conditions in a new area is called acclimatization. The main difference between acclimatization and adaptation is the absence of genetically fixed new properties in the body. This is a temporary process that occurs in the body forcibly and does not leave its mark on later life. After returning from a country where the weather conditions differed from the natural conditions at home, the acquired skills are gradually forgotten. The next time you travel to another continent, you will go through the acclimatization process again.
Factors driving the need for change
Any adaptation process is a response to environmental factors that lead to environmental change. Such factors are divided into biotic, abiotic and anthropogenic.
Biotic factors are the influence of living organisms on each other, when, for example, one species disappears, which serves as food for another.
Abiotic factors are changes in the surrounding inanimate nature, when the climate, soil composition, water supply, and solar activity cycles change. Physiological adaptations, examples of the influence of abiotic factors - equatorial fish that can breathe both in water and on land. They have adapted well to conditions where drying up of rivers is a common occurrence.
Anthropogenic factors are the influence of human activity that changes the environment.
What are complex natural conditions: human adaptation to climatic conditions
Difficult weather conditions are those that differ sharply from the standard climate. Let's look at a few examples:
- Southern countries with a hot climate. Body temperature turns out to be lower than air temperature. This condition is difficult for an unaccustomed body to tolerate. Heat transfer is complicated, metabolism changes, breathing and blood circulation are disrupted. The person becomes apathetic and feels constant fatigue. The higher the humidity in the air, the faster the body adapts. An unaccustomed person goes through the longest period of adaptation when he finds himself in a tropical forest area. There is no wind, high levels of humidity and heat can trigger heat cramps, exhaustion, and stroke. Water and salt regimes, suitable clothing, and room cooling help speed up adaptation.
- Mountain climate. The natural type of climate is characterized by a number of features. Low atmospheric pressure and temperature, intense solar radiation, high level of ionization. The mountain air is filled with oxygen. Hemoglobin increases in the body, the hematopoietic system is irritated, and the minute volume of the heart muscle increases. Hyperventilation occurs. Possible development of altitude sickness. It is extremely difficult for older people to endure the difficult natural conditions of a mountain climate. It will take at least a week to adapt.
- Subarctic and arctic climate. The development of light starvation, magnetic disturbance, and magnetic storms may predominate here. From a medical point of view, these natural conditions are the most difficult. It can take more than one year for a healthy body to fully acclimatize.
Resettlement of people. World population
The population of our planet is the total number of people living on Earth. At the beginning of the 19th century, the world population was 1 billion people (1804), 2 billion in 1927, and today, about 100 years later, it is already 7.79 billion people. This rapid growth can be attributed to the constant development of medicine and the improvement of people's living conditions. Currently, according to the calculations of demographers, the population grows by about 90 million people in one year, an average of 247 thousand people per day, but once at the dawn of humanity this was difficult to imagine: ancient people had a short life expectancy and difficult, harsh living conditions.
According to numerous archaeological finds, East Africa can be considered the cradle of humanity. The remains of skeletons and tools found here suggest that it was in this territory that the first people arose and the human race was born.
Having mastered Africa, people began to look for new places to live, moving first to Eurasia through the Arabian Peninsula, then some went to the Persian Gulf, some to Europe, some to India, and then to other continents, except Antarctica.
- Most likely, the straits between the continents in the distant past were not as deep as they are now. Some could be waded, but somewhere there was land instead of water - the level of the World Ocean began to rise only when the glaciers melted, the map of the world changed during times of global climate change.
At first, the Earth's population grew slowly - natural disasters, harsh conditions, diseases, wars, epidemics claimed many lives, fewer were born than died, and natural growth was negative.
- Natural increase (NI) = the number of births during a certain period in a certain territory minus the number of deaths during the same period, for example, in 1 year, divided by the population of the area. The resulting number is multiplied by 1000. The unit of measurement is ppm.
- Fertility (F)
- Mortality (C)
- Population (N)
The rate of natural population growth can be easily calculated using statistical data available from civil registry offices.
From time to time, countries around the world hold a population census, which makes it possible to find out the number of people living in the country, their age, gender, and what category they belong to - urban or rural residents.
The numerical growth of the population directly depends on the level at which the economy of a particular country is located, as well as on religion, traditions, and culture. For example, in Islamic countries, a large number of children in the family is encouraged.
In economically developed countries, where most people have a high quality of life, and they have the opportunity to eat well, get good housing, excellent education, modern, timely medical care at a high level and have time to travel and relax, 1-2 children are generally born , the number of childless families is increasing. The natural increase here is either very low, zero, or negative (that is, more people die than are born). The average life expectancy in developed countries ranges from 75 to 80 years or more, which leads to an increase in the overall average age of the country's people and the aging of the nation.
In many Asian and African countries, the birth rate is accompanied by the highest mortality rate in the world: famine, infections (low level of medicine), and war are often factors. Here, most people do not live to old age, and the average age in these countries hovers around 40 years. Such countries can be identified on a world map with an indicator of average life expectancy.
Source
There is such a thing as mechanical population growth. Unlike natural, it represents an increase in the number of inhabitants of a certain country due to migrants.
In the past, migrations were the result of climate change, wars, and the need to develop new lands. In the 21st century The main factor in resettlement was labor migration.
As for the sex ratio, it is now 1:1.018 in the world—there are slightly more men than women. According to 2021 data, the average age of the planet's inhabitants was 30 years.
Examples of human adaptation to climatic conditions
All people are dependent on climatic conditions. During life, the body gets used to a certain environment, so even in the hottest or frostiest countries, the population lives as usual. A few examples of how people adapt to harsh climates:
- Peoples living in countries with bright sunshine and hot climates are black or dark-skinned. Residents of cold regions have fair skin;
- Characteristic clothing helps protect the body from difficult weather conditions. Many of them become traditional - the national costume of the inhabitants of the north or the outfits of Africans;
- Flared nostrils in people with dark skin;
- Asian eye shape.
In any case, each person goes through a certain adaptation period, moving temporarily or for permanent residence to another region. Depending on the conditions, there are different adaptation methods:
- In the Arctic, special fur overalls are used to protect against the cold;
- In temperate climates, people build houses from wood to avoid cold winters and hot summers;
- In tropical regions with sandstorms, people wear long capes made of light fabrics. Nomads use goat skins to build housing;
- In areas with an equatorial climate, people live in huts built from branches and leaves. This protects from the scorching sun.
Phenomena of the human body
A person has a huge reserve of safety inherent in nature, which is used in everyday life only to a small extent. It manifests itself in extreme situations and is perceived as a miracle. In fact, the miracle lies within us. Example of adaptation: the ability of people to adapt to normal life after the removal of a significant part of their internal organs.
Natural innate immunity throughout life can be strengthened by a number of factors or, conversely, weakened due to an incorrect lifestyle. Unfortunately, addiction to bad habits is also a difference between humans and other living organisms.
Ghost insects
0
Camouflage is something that many fauna have excelled at. Some of the most talented pretenders are leaf insects, or stick insects: in the course of evolution, they have learned to merge with nature and remain motionless for a long time. Thanks to this, they are completely invisible against the background of leaves and branches. For their amazing camouflage, stick insects received another name: ghost insects. The largest insect on Earth was classified only in 2008: it is Chan's megastick insect, reaching a length of 35.7 cm with elongated limbs. You can find this “ghost” in Malaysia, in the state of Sabah.
0
Peoples of the world, diversity of countries
The peoples of the world, countries and their government structures are diverse.
We already know that there are three main human races on our planet.
These are large groups of people with different physical characteristics.
Each of these groups is characterized by a unity of origin, as well as formation in a certain area. Will races cease to exist in the future? The condition for the formation of a race is isolation. Now there is no doubt that, despite public rejection and misunderstanding of interracial marriages, in the future we will experience mixing of races and the formation of a hybrid population of people.
Every person on planet Earth belongs to some people (ethnic group).
Peoples may differ in one or multiple characteristics. Main differences:
- language;
- customs;
- traditions;
- culture;
- religion;
- appearance;
- housekeeping.
Each nation lives on its own territory and speaks its native language. Of course, there are exceptions to the rules: for example, the Gypsies do not have their own territory, and until the mid-20th century, the Jews did not have a certain territory either. There are peoples who speak the same language (for example, the Scots and the English).
- Some peoples living in Africa, the Far North and the forests of South America are very small in number - there are only a few hundred of them. They are in danger of extinction. Ethnographers study them, record songs and legends, language, traditions, because the diversity of ethnic groups and cultures is the wealth and heritage of humanity.
The number of peoples of the world is not constant - they appear, disappear, mix, adopting the languages and customs of other peoples.
Languages of the world
On average, the peoples of the world, according to scientists, speak 5,000 languages. Languages of similar origin are united into groups, which in turn form families.
Main language families:
- Altai;
- Afro-Asian;
- Austronesian;
- Dravidian
- Indo-European language family;
- Niger-Congo;
- Sino-Tibetan (Sino-Tibetan);
- Non-Austronesian languages of New Guinea.
The largest family is Indo-European, its languages are spoken by half of the world's population.
Language groups of the Indo-European family
And the most common language of this family is Hindi. It is spoken by about 600 million people in India and Pakistan. English is widely spoken and is currently the language of 500 million people. The popularity of English was led to by the colonization of North America and Australia in the 17th-19th centuries by English-speaking Europeans. Descendants of Spanish and Portuguese settlers now live in the countries of South and Central America, so these languages are spoken not only in Europe, but also in Latin America.
- The Russian language belongs to the Indo-European family of languages, its Slavic group, the East Slavic subgroup, which also includes Ukrainian and Belarusian.
The largest people in the world (the Chinese) speak Chinese. This language belongs to the Sino-Tibetan family.
Diversity of countries of the world and their populations
There are more than 200 countries on the planet, and their number changes, because a state can disintegrate, such as the USSR, or unite (Germany). Countries differ in size, population, form of government and government.
- A unitary state is a single state characterized by the absence of independence among administrative-territorial units. For example, Singapore, Poland, Mongolia, Japan, etc.
- A federation is a union state, its parts are state entities with limited state independence. For example, Russia, Belgium, Brazil, USA, etc.
- A confederation is a temporary association of states created to achieve certain goals: economic, cultural and others. For example, in the past the confederation was: USA, Germany, Switzerland. Then the confederation is transformed into a federation or breaks up into unitary states.
Countries also have different forms of government.
- Monarchy - in this form of government, the highest state power belongs to the sole head of state.
- Republic - in this form of government, the highest authorities are elected by the people.
Currently, there are only 30 states in the world with a monarchical form of government, most monarchies are constitutional, which means the power of the head of state is limited by the Constitution, laws are adopted by parliament, affairs are conducted by the prime minister and government. Such countries include Great Britain, Japan, Spain. But there are also absolute monarchies, where the power of the monarch is unlimited. An example of such a country is Brunei.
Countries can be single-national, that is, in them the majority of the inhabitants belong to one ethnic group that speaks the same language. For example, Poland and the Czech Republic. There are multinational ones, such as Russia. In some countries, several foreign languages are fixed. For example, in Canada - English and French, in Switzerland - German, Italian, French, Swiss Romansh.
Countries constantly agree among themselves on cooperation of various types and create international associations:
- military (NATO);
- economic (EU);
- political (EU);
- trade (WTO).
Increased giraffeiness
0
Living in the arid savannas of Africa and feeding on thorny bushes caused the gerenuk antelope to grow a long neck and legs, which is why it received the name “giraffe gazelle”, although it has nothing to do with giraffes. The entire structure of this graceful animal speaks about the way it feeds: a hard tongue and insensitive elongated lips allow it to grasp thorny branches, elongated limbs, a thin slender neck and a movable hip joint with an articulated joint make it possible to stand on its hind legs and reach branches at great heights . The legs of the giraffe gazelle are so thin that they can easily break in an accident.
0
Freeze or die!
0
Not all animals flee in a moment of danger. There are also special cunning creatures: they have learned to pretend to be dead so that predators mistake them for carrion. Thus, a wounded or very frightened opossum is capable of masterfully imitating death. He doesn't just fall and lie motionless - his eyes glaze over, foam flows from his mouth, and his anal glands emit a foul-smelling secretion. Having sniffed the body of an imaginary dead person, predators, as a rule, leave. They say that the possum gets so used to the image that it remains motionless even if it is touched with a foot or moved to another place. Only after some time will he come to his senses and run away. The pig-nosed snake from the colubrid family has the same talent for “dying”: when threatened, it turns its belly up and freezes.
Fangs instead of horns
0
Crested deer living in southern China have figured out how to compensate for the small antlers that are completely invisible due to the crest. They supplemented the arsenal of weapons used in battle with male competitors with long fangs - these processes up to 2.5 cm long protrude from the mouth, which is why the animals received the nickname “saber-toothed”. Chinese crested deer have other interesting features: alarmed animals make barking sounds, and when they sense a real threat, they notify other relatives by raising their white tail high.
0
Fish with antifreeze
0
For more than half a century, scientists have been trying to unravel the secret of the Antarctic toothfish (Dissostichus mawsoni) that does not freeze, which lives near the South Pole. The blood of most fish freezes at -0.9 °C, but this Antarctic endemic manages to survive at temperatures of around -1.8 °C and below. It turned out that during the course of evolution, toothfish learned to produce a special “antifreeze protein” that prevents the blood from congealing. Scientists only recently learned how exactly it works; the study was conducted at the request of the Volkswagen automaker. Using terahertz spectroscopy, scientists from the Ruhr University saw that water molecules, which usually perform a “disco dance” in the blood of toothfish, forming and breaking chemical bonds, slow down when the already known “antifreeze protein” appears, and this, in turn, prevents the formation of ice crystals in the blood of fish. The automaker hopes to use this discovery to create an effective antifreeze for cars.