Loss of speech during a stroke is a common complication of a dangerous disease that occurs in every third patient who has suffered an attack. This condition is called aphasia: the patient cannot express his thoughts, has difficulty speaking on simple topics, and cannot even name simple objects. You can often regain lost skills if you enroll in a rehabilitation center after a stroke and undergo recovery under the supervision of experienced doctors.
The prognosis largely depends on the severity of hemorrhage or ischemia, but even with a mild form of stroke, rehabilitation requires concentration on the part of the patient and supervision by a doctor. The doctor must identify aphasia and prescribe a rehabilitation program.
What is a stroke
The essence of a stroke is the cessation of blood supply and functioning of a part of the brain as a result of damage to a vessel.
The larger the affected area, the more severe the stroke. Necrosis of a portion of the brain substance is called an infarction [3]. There is a high risk of death in the first few hours, and then in the period up to 28 days after a vascular accident. The annual mortality rate from stroke in the Russian Federation is 374 cases per 100,000 [10]. In 2018, 35% of patients died in the acute period of stroke; by the end of the first year, this figure increases by 15%, and in general, in the first 5 years, the mortality rate of strokes is 44% [11]. The mortality rate from stroke was 92.9 per 100,000 population, and the hospital mortality rate was 19.1% [5].
Long-term disability is most likely for patients who have suffered a stroke. The prevalence of primary disability due to stroke in 2018 was 3.2 per 10 thousand population [2]. Of these, 31% need constant care, 20% have severe mobility limitations, and only 8% return to work [3]. The prevalence of recurrent strokes in 2014 was 0.79%, of which ischemic
strokes account for 87.5% [9].
Causes of stroke
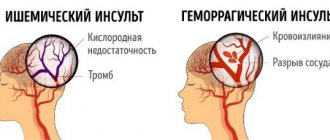
Depending on the cause of cerebrovascular accident, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes are distinguished.
Ischemic stroke occurs as a result of blockage of cerebral vessels by a blood clot, when gradually less and less blood flows to an area of the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke develops as a result of rupture of a vessel and hemorrhage in the brain tissue, as a result of which the blood supply to its area abruptly stops. Hemorrhage can be into the subarachnoid space (SAS) or directly into the cerebral substance (ICH). The ratio of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes is 4-5:1 [4].
Pathologically, a stroke can be cardioembolic, lacunar, atherothrombotic, or another, including unknown, etiology (TOAST classification) [10].
Predisposing factors:
- men from 45 to 59 years old;
- age 70 years and older (for both sexes) [4];
- arterial hypertension;
- atrial fibrillation;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- coagulopathy, thrombophilia, anemia;
- arteriovenous malformations;
- osteochondrosis with damage to the vertebral artery;
- brain tumors;
- dyslipoproteinemia;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- intermittent claudication;
- mechanical prostheses of heart valves and blood vessels;
- IHD, myocardial infarction less than 6 months before the stroke;
- other cardiac diseases;
- smoking, alcoholism;
- family history of stroke;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- stress [1, 3].
Types of speech disorders
Modern medicine knows two main types of speech disorders after a stroke: aphasia and dysarthria. In the first case, speech is impaired due to the death of neurons and their connections in the brain center that is responsible for speech. Aphasia can be complete or partial. Dysarthria occurs against the background of the fact that the centers in the brain responsible for the functioning of speech muscles have been damaged.
Aphasia
It is the most common cause of speech impairment. There are six variations of aphasia in total:
- Motor
. This form is divided into two more types of aphasia. With afferent aphasia, the patient cannot choose the articulatory posture that is needed in order to pronounce specific sounds. With efferent aphasia, speech is preserved at an instinctive level, but repetition is impaired. Victims have difficulty moving from one position to another. - Dynamic
. In this variant, patients experience problems with active utterance: the inability to correctly formulate a sentence because both external and internal speech are impaired. There are frequent cases of echopraxia - repetition - situations when the patient automatically begins to repeat words, phrases, facial expressions or gestures after the interlocutor. - Sensory
. It is divided into three types: cortical, subcortical and transcortical aphasia. In the first case, the patient lacks both understanding and pronunciation of sounds; in the second, the transmission of impulses from the parts of the brain responsible for the perception of sound information is distorted. In the third case, writing and visual function are impaired, but the patient is capable of perceiving light speech structures. - Sematic
. The victims do not fully understand the complex speech structures that are responsible for spatial relationships. Problems are often observed when completing tasks that contain complex syntactic formulations. Patients forget the names of the simplest household items - dishes, furniture, clothing, electrical appliances, and read slowly. Sometimes acalculia develops, a neuropsychological disease when a person loses the ability to count consistently. - Acoustic-mnestic
. With this aphasia, patients experience difficulties that are associated with the ability to retain information perceived auditorily in memory. During classes with a speech therapist, patients cannot repeat the simplest connections of several words, or understand the meaning of a sentence when it is pronounced at a fast pace or during a conversation with several interlocutors. - Total
. A distinctive feature of this type of aphasia is the complete absence of speech due to damage to a large number of areas of the brain. Total aphasia is subject to hard and long-term correction work from various specialists - from massage therapists to speech therapists.
Dysarthria
A type of speech disorder when a stroke victim has impaired functioning of the organs responsible for articulation (tongue, palate, lips). It is observed much less frequently than aphasia and develops, as a rule, with damage to various brain structures, in particular the cranial nerves involved in the work of speech muscles. Patients experience sluggish and uncertain speech, and difficulty pronouncing individual sounds or words.
Articulatory dyspraxia
Another type of speech impairment is the inability of a person to make consistent movements with the mouth, lips, and tongue - which is divided into two types: kinetic and kinesthetic.
In the first option, difficulties arise when sequentially changing sounds and syllables, skipping them, replacing one syllable or sound with another, and incorrect placement of stresses.
In the second option, disturbances occur in the articulatory structure: the brain experiences difficulty interacting with the muscles responsible for producing sounds.
The formation of motor skills is carried out through adequately coordinated actions. After a stroke, neuronal death can occur in areas of the brain with the premotor, profrontal and motor cortices, which can lead to dyspraxia.
The correction of dyspraxia is carried out by a speech therapist in collaboration with a neurologist and psychologist.
Signs of an incipient stroke
The onset of a hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- increased blood pressure;
- vomit;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- visual impairment;
- seizures [1].
The onset of ischemic stroke is gradual; within an hour, some of the following symptoms appear:
- facial asymmetry, numbness;
- difficulty speaking – incoherent, impaired understanding;
- double vision, visual disturbances;
- headache;
- numbness, limited mobility in the limbs, often on one side;
- dizziness, imbalance, staggering, staggering gait;
- confusion with disorientation, subsequently there may be loss of consciousness [3].
If one or more of these signs appear, you should:
- Sit the patient down, providing access to fresh air.
- Call emergency medical help immediately.
- If the patient is conscious and able to chew and swallow, give him one aspirin tablet.
The patient must be hospitalized in a neurological or neurosurgical department, where stroke treatment will be carried out. The sooner the patient is in the hospital, the more effective the therapy.
Speech therapy exercises to restore speech after a stroke at home
Let us now consider what methods a specialist can offer to restore a patient’s speech, and how they should be applied.
Articulation and breathing exercises
First, the person is asked to simply breathe, then, as he exhales, pronounce certain consonant sounds, one sound per exhalation. After this, while exhaling, all these sounds are pronounced in a row. There are no more than four of them. Sounds can be pronounced while exhaling, also with the chin raised.
Articulation gymnastics after a stroke
It includes exercises for the tongue, lips, voice, and facial muscles.
Exercises for the tongue and soft palate
- Stick your tongue out of your mouth and hold it there for a few seconds.
- Pull it down again and bend it up, hold it for a while.
- Pull it down and direct it first to the right corner of the mouth, then to the left.
- Move the tip of your tongue back and forth across the roof of your mouth.
- Direct your tongue to the right and left cheek.
- Click your tongue, first once, then twice, then three.
- Relax your tongue and, moving it back and forth, lightly bite with your teeth.
- Lick your lips first in one direction, then in the other.
Lip exercises
- Move your lips forward.
- Make a smile with your mouth closed.
- Bare your teeth and raise your upper lip, hold this for a couple of seconds.
- Puff out your cheeks and pump the air from side to side, rolling the air around your mouth.
- Relax your lips and blow through the gap in them.
Voice exercises
Speech gymnastics is performed for ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds separately, first long, then short, while exhaling. After this, as you exhale, we pronounce all the sounds in a row.
- We say the sound Y only articulatory, without sound, and feel the tension under the chin.
- We pronounce all the vowel sounds in a row, flowing into one another, alternately emphasizing different sounds.
- We pronounce consonant sounds, first unvoiced, separately, then one after another on one exhalation. After this, we pronounce voiced sounds in the same way. We add consonant sounds with vowels into certain syllables, while alternating paired unvoiced and voiced consonants.
All combinations of sounds, their permutations and combinations are determined by the speech therapist.
Tongue twister exercises after a stroke
First, we ask the patient to finish the tongue twister he knows, gradually increasing the number of words he says. If possible, we bring the exercise to perfection.
Exercises for facial muscles
- Raise your eyebrows, lower them, frown, relax.
- Open your mouth wide, try to stretch it, then relax it.
- Smile without opening your mouth.
- Inflate and deflate your cheeks.
- Pull your lips out as if for a kiss.
- Extend your tongue as far as possible in different directions from your mouth.
- Move your lower jaw carefully, first to the left, then to the right, then in a circle.
Speech therapy massage after stroke
After completing a set of exercises, it is necessary to apply a facial massage to each area of the face.
It is important that massage movements are selected only by a specialist. Some areas of the face will need to be relaxed, while others will need to be toned. If you approach this on your own, you can cause irreparable harm.
In addition to massaging the facial muscles directly, they massage the tongue, lips, inner surface of the cheeks, ears, scalp, and hands. All this relieves muscle stiffness and thus liberates speech.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke leads to various brain injuries, depending on the location of the lesion and the pathological type of cerebrovascular accident:
- disturbances of movement in the limbs: from restrictions (paresis) to complete paralysis. When the lesion is localized on the right, the left limbs suffer; with a left-sided lesion, right hemiparesis is formed; in some cases, movements in all limbs may stop (tetraparesis or double hemiparesis);
- sensory disturbances on one or both sides;
- speech disorders (dysarthria - poor articulation; aphasia - inability to pronounce and understand words, write and read);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements, “overshooting”, unsteadiness, imbalance, tremor);
- visual impairment: from blindness to double vision and gaze paresis;
- hearing impairment and dizziness;
- violation of mental functions (consciousness, thinking, attention, memory, will, behavior);
- paresis of the soft palate and pharynx, swallowing disorders;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- depression of respiration and vascular tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- patients complain of headaches, vomiting, hiccups, yawning, shoulder pain;
- consciousness is gradually depressed to the point of coma [1, 3].
Causes of death may include cerebral edema, pneumonia, heart failure, and recurrent stroke. In severe cases, “locked-in syndrome” may develop: the patient is conscious, but cannot move, swallow or speak [3].
A set of activities after the crisis
Despite the fact that each type of aphasia has its own exercises for restoring normal speech after a stroke, it should be remembered that all disorders are mixed in nature and require a systematic, special approach.
A set of special classes will help not only regain lost skills, but also improve a healthy person’s oratory abilities and diction.
- How to avoid stroke in women: prevention with drugs and folk remedies
During training, it is recommended to adhere to the recommendations of the speech therapist, which include:
- Pull the lip folds into a tube, hold for 3-5 seconds, then repeat (up to 10 approaches).
- Use the lower part of your jaw to grab the top of your lip, hold for 2-3 seconds, release (5-10 times).
- Similar to the previous exercise, only in reverse - pinch the lower part with your upper lip.
- Open your mouth slightly, stretch your neck forward, stick out your tongue (as far as possible), hold for a few seconds (5-10 repetitions).
- We take turns licking the upper and lower lip folds, from left to right, then vice versa (up to 10 approaches).
- Draw a tube with your tongue.
- Lick the lip folds in a circle.
- Close your mouth and reach your lower palate with your tongue.
- Clicking your tongue like a horse while running.
- Close your mouth, open your teeth, move your tongue in a circular motion between the labial folds and teeth.
- Try to smile, showing all your teeth, then repeat the movement with your jaw closed.
- Hiss like a snake, moving your tongue out of your mouth.
- Send a kiss while smacking your lips loudly.
- Use your tongue to reach your chin, after the tip of your nose.
Speech therapy exercises after stroke
Exercises for aphasia can be performed in different sequences 2-3 times a day, combining them with other activities to restore speech functions. Logically complete phrases with an assistant, learn tongue twisters, poems, counting rhymes, songs, listen to your favorite pieces of music.
In order for speech to be restored completely (as far as possible), it is necessary to approach the implementation of the recommendations of the speech therapist or the attending physician with all responsibility. There should be complete silence in the room during classes.
Consequences of a stroke
There are transient ischemic attack (less than a day), minor stroke (from 1 day to 3 weeks) and stroke with persistent residual effects. The consequences of a stroke are expressed mainly in motor and sensory disorders, the formation of muscle contractures (pronounced constant restriction of movements in the joints), speech and swallowing disorders. General symptoms may also remain, including confusion, disturbances in thinking, will, and emotional regulation. Complications can develop: from epilepsy to bedsores, encephalopathy and anxiety-depressive syndrome [1, 3].
Diagnosis of strokes
First of all, it is necessary to conduct a detailed neurological examination. Instrumental diagnostic studies and laboratory tests are also prescribed. In case of a stroke, in the first hours, an MRI or CT scan of the brain is performed, if necessary, CT or MR angiography, color Doppler mapping of blood flow, ECG or Holter monitoring, echocardiography as indicated, monitoring of blood pressure, saturation, assessment of the risk of developing bedsores, assessment of swallowing function [ 1, 3, 6].
Tests for stroke
- Complete clinical blood test, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Biochemical blood test with determination of C-reactive protein and homocysteine, glucose level, platelet count, activated partial thromboplastin time, INR.
- Interleukin 10.
- Extended coagulogram.
- Determination of acid-base status.
- General urine analysis.
To prepare for neurosurgical intervention, a blood test is additionally performed for hepatitis, syphilis, HIV, blood group and Rh factor determination.
Signs of speech impairment
The fact that the areas of the brain responsible for speech were damaged during a stroke is indicated by the behavior of the victim:
- The patient confuses words and sounds, stumbles, stutters;
- The construction of sentences is disrupted - instead of “I went to the street,” a person can say “I went to the street,” etc.;
- Frequent repetition of the same sounds or words;
- The patient does not understand well what is being said to him, forgets the names of objects;
- Consistent counting skills are impaired;
- Obscene words and expressions appeared.
The last factor often comes as a surprise, since after a stroke even cultured and well-mannered people can begin to swear. Experts say that this is due to the ancient origin of obscene language.
Stroke treatment
Treatment of stroke is regulated by relevant clinical guidelines and the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accident. In the first hours, thrombolytic therapy is carried out and subsequently - prevention of thrombus formation. For hemorrhagic stroke, neurosurgery may be performed. They normalize blood pressure, water-electrolyte balance, glucose levels in peripheral blood and urine, support the basic vital functions of the body and prevent complications. Drug therapy is also aimed at improving the affected functions of the nervous system [1, 3, 6].
Stroke rehabilitation
Stroke is a disease in which rehabilitation and care are of the utmost importance.
Recovery from a stroke begins in intensive care, from the moment vital functions are stabilized. A multidisciplinary rehabilitation team works with the patient, which includes a rehabilitation doctor, physical therapist or exercise therapy instructor, speech therapist, massage nurse, physiotherapist and physical therapy nurse, psychologist, occupational therapist, guard and rehabilitation nurse. Diagnosis is carried out using special scales that reflect the degree of dysfunction and limitations in the patient’s activity, the influence of environmental factors on the rehabilitation potential. The rehabilitation process continues throughout the entire period of hospitalization. At the second stage, patients with serious disabilities who are unable to move independently are sent to rehabilitation departments or specialized hospitals. Those who can walk independently or with support are rehabilitated in outpatient centers based in clinics and sanatoriums.
The rehabilitation process should not be interrupted, so classes must be continued at home. Of course, there are no high-tech robotic complexes or physiotherapeutic equipment at home, but exercise therapy, massage, and work with a psychologist, speech therapist and occupational therapist are possible. For this purpose, telemedicine technologies are used and visits to rehabilitation specialists are organized.
The individual rehabilitation program includes not only a referral for rehabilitation treatment, but also technical means of rehabilitation. However, usually relatives also have to devote significant physical and financial resources to achieve the best effect [7].
How to restore the ability to speak in an adult after losing it?
How long it takes for speech function to recover depends on how severely the brain was damaged.
Therefore, in some patients, the ability to speak is restored quite quickly (within a few weeks or months), while in others it takes years, and it is difficult to predict how long it will take. To restore patients who have suffered a stroke, the following types of rehabilitation are used:
- Drug therapy.
- Classes with a speech therapist.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage.
- Surgical intervention.
Medicines
During rehabilitation after a stroke, the doctor prescribes several groups of drugs to the patient that help reduce side effects, improve the condition and help the patient quickly return to their normal lifestyle:
- Muscle relaxants.
- Antidepressants.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Antiplatelet agents.
Muscle relaxants
On a note. In the third month after a stroke, the patient may develop muscle hypertonicity, which greatly slows down the rehabilitation process.
Then muscle relaxants are prescribed that can reduce excessive muscle tone. The best muscle relaxants for stroke:
- Sirdalud (cost in Moscow from 227, in St. Petersburg from 176).
- Tizalud (cost in Moscow from 160, in St. Petersburg from 125 rubles).
Antidepressant series drugs
Almost 80% of patients suffer from depression after a stroke, which slows down the recovery process. In this case, antidepressants are prescribed. The best antidepressants for stroke:
- Nortriptyline (cost in Moscow from 990, in St. Petersburg from 1,000 rubles).
- Paxil (cost in Moscow from 650, in St. Petersburg from 660 rubles).
Anticonvulsants
When seizures occur, anticonvulsants are prescribed, but they should be taken with caution, as this group of drugs can cause side effects. The best anticonvulsants for stroke:
- Finlepsin (cost in Moscow from 215, in St. Petersburg from 193 rubles).
- Convulex (cost in Moscow from 116, in St. Petersburg from 135 rubles).
Antiplatelet agents
If after a stroke the patient’s blood becomes more viscous, this slows down the recovery of brain tissue. In this case, the help of antiplatelet agents is required to prevent the formation of blood clots. The best antiplatelet drugs for stroke:
- Reopoliglyukin (cost in Moscow from 102, in St. Petersburg from 110 rubles).
- Clopidogrel (cost in Moscow from 226, in St. Petersburg from 205 rubles).
Important! Any medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician. Do not self-prescribe medications, otherwise this can only worsen the patient’s condition.
Medication alone does not provide much benefit, but it does help progress recovery when used with other types of therapy, such as speech therapy and physical therapy.
- How exactly does speech restoration proceed after a stroke?
Classes with a speech therapist
At the first lesson, the speech therapist draws up a plan for each patient individually. The following exercises are required:
- Reading tongue twisters.
- Drawing.
- Mimic and speech therapy massage.
If all the specialist’s recommendations are carefully followed, about 20-30% of patients with moderate and severe speech disorders begin to speak normally by the time they are discharged from the hospital. Classes can also be held at home. The exercise program must be combined with medications, physical therapy and other types of rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
This type of rehabilitation stimulates muscle recovery and helps to achieve better results from classes with a speech therapist and from taking medications.
- Magnetotherapy. This procedure stimulates all processes in the brain, and also improves the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. A rather painful method, but it is considered one of the most effective. The patient's condition improves after 2-3 weeks.
- Dorsanval. Prescribed for poor blood supply to the brain and limbs. After a whole course of procedures, which is at least 5-7 sessions that take place over 2-3 weeks, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Massage
Therapeutic massage for stroke significantly improves blood supply to the affected tissues, which increases the flow of oxygen and other nutrients to them. In addition, massage helps relieve muscle and psychological tension. A therapeutic massage course usually consists of 10 sessions , but can be adjusted individually for each patient.
Note! A massage course can only be conducted by a qualified specialist with a medical education.
Surgery
A method such as surgery is resorted to in extreme cases, when other methods do not improve the patient’s condition and cannot restore lost speech. To restore speech, a neurosurgical operation is performed, which creates additional connections between healthy tissues and vessels in the speech area of the brain, without affecting the damaged areas.
Prevention of strokes
Hereditary predisposition to stroke, the presence of cardiac diseases, pathology of blood vessels and blood composition, age over 40 years, obesity and diabetes require a number of preventive measures:
- Maintaining normal blood pressure, taking antihypertensive drugs as prescribed by a doctor, monitoring blood pressure.
- Maintaining a normal level of physical activity, exercise, walking 30-40 minutes a day (for example, walking the dog).
- Conducting preventive examinations, including a standard set of laboratory parameters. During a preventive examination, the following tests are additionally required: gene diagnosis of CADASIL syndrome using the PCR method, plasma factors of the blood coagulation system, antibodies to prothrombin of the IgG and IgM classes to determine the risk of thrombosis, determination of polymorphisms associated with the risk of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, lipid disorders exchange, in order to identify a predisposition to diseases that increase the risk of stroke, von Willebrand factor (a glycoprotein that ensures the formation of blood clots), complex laboratory tests for preclinical diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases are offered (“ELI-ANKOR-Test-12”, “Cardiorisk”).
- Avoiding chronic and acute stress, maintaining mental hygiene.
- Normalization of weight (BMI <25 kg/m2).
- Healthy eating (for example, Mediterranean diet, limiting salt to 5 5 g/day).
- Quitting smoking and taking psychoactive substances.
- Treatment of diseases that are a risk factor for stroke [8, 11].
Bibliography
- Hemorrhagic stroke in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021. Developers: Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: (access date 08/18/2020).
- Efremova M.D. Stroke as an urgent socio-psychological problem / M.D. Efremova – electronic text//Skif. Questions of student science.- 2021 - No. 2(24) URB: (date of access 08/17/2021) Access mode: Cyberleninka electronic library system. — Text: electronic.
- Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in adults: clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2021 developers: All-Russian Society of Neurologists, National Association against Stroke, Association of Neurosurgeons of Russia, Association of Neuroanesthesiologists and Neuroreanimatologists, Union of Rehabilitologists of Russia. - Electronic text. - URB: ( access date 08/18/2020).
- Machinsky P.A. Comparative characteristics of incidence rates of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in Russia / P.A. Machinsky, N.A. Plotnikova, V.E. Ulyankin [and others] – Direct text.// News of higher educational institutions. Volga region. Medical Sciences.- 2021.- “2(50)-P.112 – 132 DOI 10.21685/2072-3032-2019-2-11.
- Monitoring the implementation of the federal project “Combating Cardiovascular Diseases” - Presentation Department of Organization of Medical Care and Sanatorium Affairs of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation URB: (date of access 08/17/2021).
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2012 N 928n “On approval of the Procedure for providing medical care to patients with acute cerebrovascular accidents.” — URB: (access date 08/17/2021) Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 31, 2021 No. 788n “On approval of the Procedure for organizing medical rehabilitation of adults.” – URB: (date of access 08.17.2021).- Access mode: Electronic library system “Garant”. — Text: electronic.
- Prevention of cerebrovascular accidents: textbook. manual / Compiled by: L.B. Novikova, A.P. Akopyan. – Ufa: Publishing house of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education BSMU of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 2015.-58 p.
- Stakhovskaya L.V. Analysis of epidemiological indicators of recurrent strokes in the regions of the Russian Federation (based on the results of the territorial-population register 2009-2014) / L.V. Stakhovskaya, O.A. Klochikhina, M.D., Bogatyreva, etc.]. CONSILIUM MEDICUM, 2021, vol. 5, no. 9, p. 8-11.
- Shamalov N. A. Analysis of the dynamics of the main types of stroke and pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke / N. A Shamalov, L. V Stakhovskaya, O. A Klochikhina [and others]. Direct text. // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after. S.S. Korsakov. Special issues. 2019;119(3-2):5-10. doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20191190325.
- 1RRE Electronic edition. Updated daily Stroke Day is celebrated on October 29, 2021 URB: (accessed 08/17/2021).
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist