Is it easy for you to fit into a new team? Do you calmly get used to new living conditions or do you feel anxious? Are you afraid of change? If you answered “yes” to these questions, then you have weak adaptive abilities. This article is devoted to the socio-psychological adaptation of the individual; this information will be useful to you if changes terrify you.
In this article:
The concept of socio-psychological adaptationForms of psychological adaptationFeatures of the course of socio-psychological adaptationThe concept of personality maladjustmentTypes of maladjustment
Concept and tasks
A person is involved in social interaction from birth. At first, he is surrounded only by family members, who form the newborn’s primary understanding of the norms and methods of communication, and role models. Subjective experience becomes part of the personality. By the time the child comes out and actively interacts with society, he already has established skills and behavioral scenarios. When faced with society, a child adopts accepted values and norms of behavior, but introduces his own attitudes, transforming the existing way of life.
The process of mutual exchange and formation of attitudes between a person and society lasts a lifetime. With successful adaptation, the individual becomes a self-sufficient social unit.
History of discovery and study
Socio-psychological adaptation is a process that everyone goes through, regardless of where they live. It acts as a means of protecting the individual, reducing internal psychological stress that arises during contacts with other people. The development of defense mechanisms, as a rule, occurs after a traumatic encounter with society. A defensive reaction is formed in childhood; as one grows up, the types of defense improve and change.
If a person has fully mastered defense techniques and learned to choose the optimal style of behavior in a difficult situation, his adaptive potential increases. This leads to successful socio-psychological interaction.
If defense mechanisms are primitive, a person uses them unconsciously, and his ability to adapt is reduced. Primitive behavioral strategies relieve the feeling of discomfort, but make it impossible to assess the situation adequately. A person cannot take a place in a group and feels like an outsider.
Representatives of different schools studied the psychological phenomenon of adaptation and defense mechanisms. The structure of psychological defense was developed by psychoanalysts. By defense mechanism, Freud meant a set of techniques that protect the psyche from trauma that is inevitable when confronted with reality. He included these methods:
- negation;
- crowding out;
- substitution;
- isolation;
- projection;
- rationalization;
- inversion;
- regression.
Representatives of Gestalt psychology and humanistic psychology have created alternative classifications of defense methods. They differed in names, but described the same sets of mental functions.
Mechanisms of socio-psychological adaptation, based on defense mechanisms, lead the individual to a state of emotional comfort. The person feels calm, openly expresses his feelings, and is optimistic. If defense mechanisms are chosen incorrectly, their use causes psychological discomfort. A person experiences anxiety, fear, worry, depression. This condition disrupts normal activity, making it difficult to adequately respond to the surrounding reality.
Classification
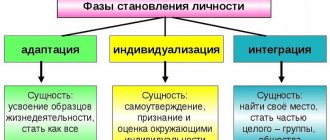
In the process of socialization, a person uses one of two types of adaptation: progressive or regressive. In the first case, the individual successfully takes a place in the team, in the second, adaptation becomes formal and incomplete.
If integration into society follows a regressive path, the individual does not accept social norms and requirements of society. An individual can perform them, but he does it forcedly. The contradiction that inevitably arises in such a situation causes great tension. If an individual does not have the opportunity to change the demands of society, tension provokes the development of psychological disorders. This leads to the inability to realize one's potential.
A person can achieve full socialization only with a progressive adaptation option. A person accepts the norms of the group, agrees with them and realizes himself in learning, work, creativity and other areas.
Types of maladjustment
There are three types of personality maladjustment:
- Temporary maladjustment;
- Sustained situational maladjustment;
- General stable maladjustment.
Temporary maladjustment is characterized by an imbalance between the individual and the environment, which generates adaptive activity of the individual. Stable situational maladaptation of a person is distinguished by the absence of adaptation mechanisms, the presence of desire, but the inability to adapt. General stable maladaptation is manifested by a state of permanent frustration, activating pathological mechanisms and leading to the development of neuroses and psychoses.
As you can see, maladaptation is the very condition that can harm the human psyche. If you have difficulties with social and mental adaptation, seek help.
Methods
If a person is diagnosed with problems with adaptation, you can try to compensate for them. Methods for improving social and psychological skills can be used at any age and with different abilities.
For children
At primary school age, children have problems adjusting to a new lifestyle. First-graders exhibit typical symptoms of maladjustment: sleep disorders, digestion disorders, and hysterical behavior. Parents should help their child cope with the assimilation of new norms of behavior. They should initiate the child’s rapprochement with peers and help establish relationships.
If a child is embarrassed by embarrassment, it is necessary to select activities for him that require teamwork. Outdoor games, in which each child will have his own role, will help him accept the need for interaction. In adolescence, extracurricular activities will help you adapt to society. Participation in clubs and sections will increase a teenager’s self-confidence, and he will feel freer in a team.
For adults
For people over 25 years of age, the problem of maladjustment is more acute. Without the opportunity to form normal relationships with the work team, a person is deprived of the opportunity to build a career. The main way to correct the problem is psychotherapeutic influence. To master interaction skills, a consultation with a psychologist is necessary. Together with a specialist, the individual will be able to study and apply scenarios for positive interaction with others.
Therapy is aimed at reducing anxiety and increasing self-esteem. The doctor’s task is to show the possibilities of normal self-actualization.
Disabled
The presence of a disability in an individual becomes a serious obstacle to establishing contacts with others. Even if a disabled person himself is interested in joining society, his environment may not have suitable conditions for this. In this case, you will need the help of others who can create these conditions.
It is better to begin entering society in the company of people with similar health problems. Once in a comfortable environment, a person becomes liberated and feels free. Receiving moral and psychological support, he learns to build complex types of group relationships. He will be able to successfully apply these scripts when interacting with people without disabilities.
Pathology and norm
The main task of socialization is to reveal personal potential. Its success and breadth depend on the level of personal development. The older an individual is, the easier adaptation is. Normal personality development occurs only in favorable conditions.
In conditions of totalitarianism, a person chooses destructive methods of socio-psychological adaptation:
- Masochism is the desire to transfer responsibility for one’s life to another person. A person prone to masochism is afraid of making decisions and being alone. Other people are a source of security for him.
- Sadism is the desire to subjugate people to your will, to use them as a resource. Sadists intimidate others and love to enjoy people's dependence on them.
- Destruction is the desire to socialize through the destruction of the existing social system. People prone to destruction feel powerless in front of existing institutions of power. They try to get rid of this by eliminating the external pressure of power, but at the same time they often have no idea what kind of social system they would like to create.
- Conformism is realization through dissolution in the crowd. A conformist person is afraid of being an outsider and strives to meet society's expectations. He does not notice manipulations and is prone to conservatism and thoughtless consumption.
The type of entry into society depends not only on the social system, but also on the immediate environment. If the family model is opposed to society, then the child will have difficulty finding his place. He risks becoming an outsider and not finding opportunities for implementation.
Controversy
This word perfectly characterizes the adaptation process. Why? Because on the one hand, a person must “merge” into society. But on the other hand, to separate yourself from it in order to remain yourself.
It is very difficult to maintain balance, since in our time, in the conditions of all-encompassing changes, it is disrupted. Due to fundamental changes in almost all spheres of life, the functions of socialization institutions have also become different.
Modern people often simply cannot keep up with such a rapid pace of events. Many cannot even understand what to focus on - life values change, and life goes on at such a rhythm that some are unable to stop and reflect on what they really exist for.
Diagnostics
Parents may notice problems with adaptation in a child at an early age. Children are normally interested in interacting with adults. Their level of mental development does not yet allow them to perceive themselves and other people as separate, equal individuals. The need for regular interaction is dictated by the fact that babies cannot survive without the help of adults. Children aged 5-6 months can manipulate their parents by crying.
If the problem was not diagnosed at an early age, it will manifest itself even more acutely when the child enters the children's group. Children with adaptation problems do not communicate with others. They play by themselves and do not respond to attempts to involve them in a common game. The reaction to the environment in children with maladjustment is manifested either by fear of society, or by aggression and negativism. The older the child gets, the more severe the symptoms become. At the age of 10–12 years, a child who is unable to interact with a group may become completely withdrawn into himself.
In adults, problems of maladaptation are manifested by the same symptoms: fear of people and general negativism. To protect the psyche from the destructive awareness of reality, an individual can unconsciously oppose himself to society. At the same time, he behaves as if it was he himself who refused to join society, and not the demands of the collective that turned out to be impossible for him to fulfill.
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 246853
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
Issues
The inability to fit into the standards of society and become part of it deprives a person of a normal life. This pathological condition has different causes:
- Dysfunctional family scenario. If the family has a negative attitude towards society and its norms, the child will perceive this behavior strategy as the only correct one. At the same time, he will not have the opportunity to instill his values in society.
- Marginal environment. The family scenario may be prosperous, but the environment puts more pressure on the individual than the immediate circle of friends. If a person acts according to the family scenario, he automatically loses the chance to enter society.
- Physiological features. Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, chronic diseases and other characteristics do not allow a person to be part of a group. Being forced into isolation, he does not have the opportunity to master behavioral scenarios in society.
- Psychological reasons. An obstacle to normal socialization is often the psychological characteristics of the individual. For example, autism spectrum disorders, which prevent a person from correctly reading the emotional reactions of other people and responding to them appropriately.
- Uncontrollable external causes. These include wars, natural disasters and other global causes, the destructive effects of which a person cannot control or cancel.
If the cause of socio-psychological maladjustment is identified in childhood, a person still has a chance to overcome the obstacle and compensate for it. In adults, therapy will take longer and require significant effort.
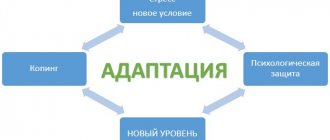
Mechanism of social adaptation
The mechanism of social adaptation is complex and lengthy. An individual is under the influence of powerful external factors, he is under pressure from public opinion, he may be condemned for provocative behavior or violation of the legal structure of society.
Studying social adaptation means exploring a person’s activity and independence as an important element of decision-making, getting acquainted with the characteristics of his activities and attitude to work, diagnosing the level of responsibility and the ability to foresee the consequences of his actions.
Signs of successful completion of the stages of this process are:
- The basis of human character is self-criticism;
- Demanding attitude towards yourself and others;
- Serious attitude to work, high-quality performance of one’s duties;
- Objective assessment of the results of your work;
- Developed reflection and a tendency to introspection of one’s achievements and failures.
Attention! At the initial stage of adaptation to life in society, a person strives to transform social reality and existing conditions, and ultimately transforms his attitudes and values.