Cerebral palsy, popularly known as cerebral palsy, is not a separate disease, it is a whole complex of various abnormalities and pathologies. Scientists have proven that the disease is most often not transmitted genetically, however, a certain amount of heredity is still present. Some potential parents, having studied the statistics of morbidity in children, are afraid to plan offspring. After all, who knows what causes such pathology in children. We will try to cover the causes of cerebral palsy in children as clearly as possible and give readers information on what to do if a child is diagnosed with such a disease.
Most often, cerebral palsy occurs due to disruption of the brain, due to the destruction of its cells due to exposure to certain negative factors on the body. In addition, various injuries, including prenatal and postpartum, can provoke the development of the disease. Most children with cerebral palsy are born underweight.
The disease can occur before childbirth, after childbirth, and directly during childbirth. Cerebral palsy is chronic and does not progress. Many parents may notice a significant deterioration in the child's condition, but in fact the disease does not develop.
The fact is that as a child gets older, his brain constantly develops and grows, and some previously hidden pathologies begin to manifest themselves more clearly. This does not mean that the child is getting worse, just that the disease, passing through all stages of its development, acquires new symptoms. Such false progression can cause various secondary pathologies, such as stroke, anesthesia, epilepsy.
Important! Cerebral palsy is not a contagious disease and is not inherited. High-quality rehabilitation helps the child settle into society, significantly improve the condition of the body and quality of life.
Reasons for the development of cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy develops in a child in the womb, during childbirth, or in the first weeks of a child's life. Most often, the cause is various injuries, abnormal development of the fetus or death of brain cells. Let's consider the main reasons that provoke the development of a pathological condition in children.
- The main impetus for the development of cerebral palsy is hypoxia; it is this disease that negatively affects those areas of the brain that are responsible for movement, coordination and balance. As a result of the development of such a process, the child cannot move normally, his muscle tone decreases or is lost, and paralysis is formed.
- Often, cerebral palsy occurs due to a pathological condition of pregnancy , for example, premature placental abruption or late toxicosis.
- The development of cerebral palsy can be influenced by various infections (herpes, syphilis, rubella).
- , such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, cause great harm to the fetus
- If a woman suffers a serious injury during pregnancy , this can also affect the health of the baby.
Hyperkinetic form
Risk factors for the hyperkinetic type of cerebral palsy disorders include hemolytic disease complicated by jaundice, early delivery, maternal infectious diseases, and low birth weight.
Symptoms of this type of cerebral palsy manifest themselves in delayed development of motor activity. The child experiences retardation in movements, abnormalities in the spine, and incorrect positioning of the legs. Mental development usually does not suffer, the child develops well intellectually and successfully adapts to life in society. This type of cerebral palsy disorder is diagnosed in 20-25% of patients.
The first characteristic signs of pathology in children
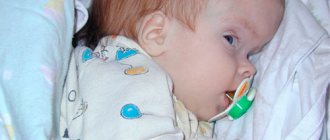
Sometimes the first signs of cerebral palsy can be noticed immediately after the baby is born, and sometimes months pass before parents begin to sound the alarm. The main symptom of cerebral palsy is impaired motor function. The sooner parents recognize the disease and begin rehabilitation, the more active the child will lead a life in the future.
Children with cerebral palsy, much later than healthy children, begin to hold their heads up, speak, crawl and walk independently. In this case, the muscles can be either in a very relaxed state, or, conversely, in excessive tension. Often the limbs of babies may be in the wrong position, the child is bothered by seizures, they appear already in infancy or at a later age.
Cerebral palsy - symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of cerebral palsy are usually difficult to miss, and they manifest themselves not only in motor function. Often the child’s speech and visual function are impaired. Children cannot normally navigate in space, begin to perceive the world around them differently, and mental disorders and dementia may develop. Sometimes problems arise with the urinary system and stomach.
The most difficult time to notice cerebral palsy is in the first months of a baby’s life. You should definitely show your child to a doctor if the following symptoms :
- a newborn baby does not blink at a loud sound;
- by 4 months the baby does not move his head when he hears the mother’s voice or other sounds;
- after 6-7 months from birth, the child cannot sit independently;
- when the baby is one year old, he does all actions with one hand, does not speak, does not walk;
- convulsions and strabismus appeared;
- The child’s movements are either very slow or, on the contrary, excessively abrupt.
Clinical picture
Spastic diplegia is found in children under 6 months of age. The development of the motor system in patients lags behind; they learn to walk by the age of 3-4 years. When trying to stand on the floor, the legs cross and the child rests on the front of the foot. When trying to walk with the help of another person, the patient makes “dancing” movements, the body turns towards the leading leg, the knees rub against each other. Asymmetric paresis is often observed. A child with such a disease does not like to communicate with healthy people; they feel better in the company of children with similar diagnoses.
The disease also has the following symptoms:
- tetraparesis - limb dysfunction;
- hypertonicity;
- muscle spasticity of the legs;
- delayed mental, mental and speech development;
- paralysis;
- pronunciation problems;
- hearing impairment;
- strabismus, blurred vision;
- facial paresis.
Mental development is less impaired than in other types of cerebral palsy. Oligophrenia is diagnosed in 20-25% of cases; its severity does not move beyond debility.
Forms of cerebral palsy and diagnosis
Depending on the degree of brain damage, symptoms and forms of the disease may vary. Sometimes cerebral palsy manifests itself mildly, but sometimes the pathology can cause serious harm to the body.
There are the following forms of the disease:
- Hemiparetic - only one hemisphere of the brain is affected, and only one side of the body does not function well. The most common paralysis of the right side of the body with this form of pathology. Among all cases of cerebral palsy, this form is more common than others. The disease affects the cortical parts of the brain.
- Hyperkinetic – the disease manifests itself in the form of sudden and uncontrolled movements. Occurs in approximately 25% of all cases of the disease. It differs significantly from all other forms by the presence of hyperkinesis (involuntary muscle contractions, and, consequently, movements). The peculiarity of the hyperkinetic form is a strong violation of muscle tone with a slight disturbance in the mental development of the baby.
- Atonic-astatic - in this situation the cerebellum suffers, causing the child to lose a sense of orientation and balance. The difference between this form is not an increase in muscle tone, but, on the contrary, its decrease. The child’s movements are preserved, but poorly coordinated, which prevents him from walking or standing independently. The child’s speech is impaired to one degree or another, sometimes words are almost impossible to understand. In half of all cases of the atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy, debility or imbecility is noted.
- Spastic diplegia – the part of the brain that is responsible for movement is affected, causing partial or complete paralysis of the limbs, mainly the lower ones, while the upper ones retain mobility. Increased muscle tone. Due to damage to the nerves in the brain, the child develops strabismus. The nasolabial folds are smoothed, and the tongue, as a rule, is deviated to one side, and, consequently, speech is impaired. The child’s psyche suffers, but not as much as in other forms of the disease.
- Double hemiplegia – the child cannot walk or sit, hold his head up, or stand on his own. This form of cerebral palsy is considered the most severe. On the part of the child’s mental development, there are such deviations as debility, imbecility, and idiocy.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
There are no special measures or procedures for identifying cerebral palsy. The specialist makes a diagnosis based on the main symptoms and signs of cerebral palsy. If a child cannot move fully, is delayed in development, or has impaired muscle tone, he is referred to a neurologist for more detailed observation and research.
Using electrophysiological methods, it is possible to determine whether a child really has cerebral palsy, or whether pathological processes are associated with hereditary neuralgic diseases. An MRI can help determine how much of the brain is affected and which areas are affected.
Double hemiplegia Spastic tetraplegia
One of the most severe forms of cerebral palsy, which is a consequence of brain damage due to intrauterine chronic fetal hypoxia. The cerebral hemispheres or the entire brain are affected. Spastic quadriplegia (quadriparesis, since both the upper and lower limbs are equally severely affected) is diagnosed clinically. Characteristic deformation of the trunk and limbs. In almost half of the cases, movement disorders are accompanied by strabismus, atrophy of the optic nerves, and hearing impairment. pseudobulbar syndrome, epileptic seizures are observed. Such patients subsequently cannot learn to sit, stand and walk; hand defects and lack of motivation exclude self-care and work activity. On the mental side, severe debility, imbecility, and idiocy are noted.
Features of children with cerebral palsy
The main difficulty that arises in children with cerebral palsy is the performance of complex movements, which is why a person cannot move properly, take care of himself in everyday life, and socialize in society.
The child begins to lag behind in development. He cannot study for a long time, studying is very difficult for him, and it is very difficult to concentrate on one thing. Due to slowness, exact sciences are difficult for children; sometimes children can hardly add even simple numbers in their minds.
Even if a child has good intelligence, due to disorders in the brain, he cannot quickly absorb information, unlike his peers. Children with cerebral palsy often have speech disorders. This is due to low tone of the muscles that are responsible for producing sounds.
Sometimes sick children can be overly shy, they do not show initiative in learning and playing, have difficulty finding a common language with other children, do not want to make contact with them, do not want to develop and overcome their illness.
Treatment of cerebral palsy and principles of rehabilitation
No matter how sad it may sound, it is almost impossible to completely cure cerebral palsy in a child. During treatment, it is important to restore motor function as much as possible. A child must learn to care for himself, live in society, communicate with other people, study and live a full life.
Treatment should be aimed at eliminating the causes that led to its development. In addition, it is necessary to treat concomitant diseases that complicate the child’s condition. It is necessary to constantly engage in physical therapy with the child, attend various procedures, and develop intellectual abilities.
There is no universal technique that would help everyone get rid of cerebral palsy. Good results can be achieved if you act comprehensively:
- taking medications to normalize muscle tone, eliminate cramps and spasms;
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- orthopedic correction;
- the use of special suits, exercise equipment and walkers.
Rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy should consist of therapeutic exercises, massage, light labor, manual procedures and hardening. The child must eat properly and receive sufficient amounts of vitamins and minerals. The child's immunity must be strong.
You can play active games with your child, thereby stimulating him to be mobile. Swimming, training for balance and spatial orientation have a good effect. The baby must be constantly monitored by specialists and follow the program that the doctor will develop individually.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of many diseases that can be detected during intratubal development. The images show any structural changes in organs and tissues, which can be used to make an accurate diagnosis.
In diagnosing cerebral palsy, ultrasound is informative only in cases of large damage to brain tissue. Minor pathological areas are difficult to identify using this method.
Working with children with cerebral palsy
Features of treatment for cerebral palsy include daily work with the child. You can work with your baby at home, visit medical institutions and special centers. During the rehabilitation process, it is necessary to do everything possible so that the child’s muscles do not strain, but become stronger.
The child must learn to be resilient and cope with a heavy load. The most important thing is that the baby himself wants to be cured. Children with such diagnoses should not be socially isolated. On the contrary, the baby should communicate with friends, try to move and develop in all directions.
In the treatment of a child, it is necessary to involve as many doctors as possible, such as an orthopedist, surgeon, neurologist, psychologist. You definitely need to work with a speech therapist and physical therapy trainer. If possible, you should visit special centers for the treatment of cerebral palsy as often as possible.
Treatment of spastic diplegia
There is no specific therapy. A complex of drug treatment and rehabilitation is needed. The goal is to prevent complications and adapt to living conditions. Vascular drugs, neurometabolites, muscle relaxants, nootropics and botulinum toxin are prescribed.
Rehabilitation therapy includes:
- Exercise therapy - carried out daily by a doctor or parents;
- massage - improves muscle blood supply, relaxes muscles;
- classes with a speech therapist - correction of dysarthria and speech therapy massage;
- psychocorrection - for oligophrenia.
Massage and exercise therapy
Physical therapy should consist of a set of procedures that are aimed at:
- muscle strengthening;
- elimination of spasm and tension;
- increase in range of motion;
- developing endurance;
- formation of correct walking;
- strengthening the whole body.
As for massage, it is better to have it performed by a professional massage therapist. After the session, all the child’s muscles relax, pain, tension and fatigue decrease, and it is much easier for the child to move.
Gradually, parents learn everything themselves. Over time, you can begin to do massage and light exercises at home. It is not at all necessary to have certain massage skills to simply massage the skin and relieve fatigue and tension.
The most important thing in treating cerebral palsy is movement. Don't forget about proper nutrition, a balanced diet, walks in the fresh air, and taking vitamins. The child’s body must be strong and healthy in order to fight the disease every day.
Types of disease and severity
In medicine, various stages of the hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy are distinguished, but the severity of the manifestations of the disease differs in the severity of symptoms. The mild form involves minor impairment in patients, since the musculoskeletal system is minimally affected. With moderate and severe degrees, it is no longer possible to do without constant parental care.
Also, the dyskinetic form of cerebral palsy, in accordance with its clinical manifestations, is classified into two subtypes: dystonic and choreathetous. In the first case, the general muscle tone experiences sudden abnormal shifts that have the nature of spasms (this is a spastic-hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy). The choreatous subtype is manifested mainly by hyperkinesis, the tone is unstable, most often reduced.