The brain is the most complex structure of the human body. Many metabolic processes occur in it and when they are disrupted, various pathological processes develop, one of which is cerebral atherosclerosis or cerebral atherosclerosis.
This disease is assigned the ICD 10 code – 167.2. This dangerous disease of the cerebral artery belongs to the cerebrovascular type of disease and is characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, which results in a stroke, profound disability or death.
Symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis
Unfortunately, cerebral atherosclerosis may not manifest itself for years. Only regular examination and monitoring of blood sugar and lipid levels helps to recognize the impending danger in time and take effective measures.
Entrust your health to the professionals of the multifunctional center of the FMBA of Russia with extensive experience in the treatment of patients with vascular pathology, as well as prevention and subsequent recovery. Annual monitoring of your health will help you prevent vascular accidents in time and maintain a high quality of life for many years.
Below is Table 1 with the most common symptoms of cerebral atherosclerosis at different stages of the disease. It will help you recognize the first signs of pathology and promptly seek medical help.
| Stage | Patient complaints |
| First stage | Often : headache, tinnitus, memory loss (remembers the past well, but cannot remember new information. Often : asthenia - fatigue, weakness, inattention, general lethargy. Relief may occur after rest. Rarely : sleep disturbance, insomnia or daytime sleepiness. |
| Second stage | Disease progression . Anxiety, suspiciousness, mood swings, and a tendency toward depression appear. Memory loss: a person does not remember what happened today and stops thinking clearly and logically. Headache and tinnitus become constant. Speech: unclear, diction changes. Tremors of the limbs and head appear. Vision and hearing deteriorate. Coordination in space deteriorates: dizziness and unsteadiness of gait are bothersome. There may be a loss of sensitivity in one half of the body and the appearance of facial asymmetry. |
| Third stage (irreversible) | Dementia develops . The patient may behave like a child or become whiny and aggressive. Not interested in the world around him and the events in it. Not oriented in space and time. There is complete or partial memory loss. Needs constant care because he has lost self-care skills at home. |
Such complaints may indicate that the lumen of an important vessel in the brain is closed by more than 50%. Be attentive to your health!
Self-medication of cerebral atherosclerosis is not acceptable!
Even at the first stage! As we said above, the first symptoms of the disease appear already with a significant degree of vascular damage.
Entrust your health to specialists with many years of experience in the treatment of vascular accidents and subsequent neurorehabilitation. Start by seeing a neurologist and tell him about how you have been feeling over the past months.
A professional, sensitive attitude towards patients and attention to detail will allow us to recognize and prevent irreversible changes in the brain in time.
Possible risks associated with atherosclerosis
The most dangerous complication is a stroke. If at the same time the patient has poor eating habits, is overweight, moves little and is regularly exposed to stress, then with an 80% probability he will become disabled as a result, unable to care for himself. The mortality rate is also high.
Prevention
To prevent cerebral atherosclerosis, you need to avoid smoking, follow a diet, and keep yourself in good shape with moderate physical activity. It is very important to establish a psycho-emotional background, protect yourself from stress, and if this is not possible, then take courses of sedatives and amino acids, for example Glycine.
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price, rub.) | In installments* |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a cardiovascular surgeon, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1 750 | — |
| Program “Risk of atherosclerosis and ischemic heart disease, predisposition to dyslipidemia” | 19 000 | — |
* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments.
Diagnostics
A neurologist deals with cerebral atherosclerosis. His task is to collect anamnesis, as well as conduct a series of tests. Doctor:
- will ask you to look up (a sick person will not be able to fulfill the request);
- will check the reflexes (they will be either excessively high or low, and asymmetrically);
- will ask you to stretch your arms forward and look to see if there is any tremors in the fingers, or if the patient is losing balance;
- will ask you to touch your nose with the tip of your finger with your eyes closed (the patient will not be able to cope with this task).
This is only a small component for assessing the patient’s health. Therefore, more detailed examinations are required next:
- consultation with an ENT doctor, ophthalmologist and other specialists depending on the identified disorders;
- biochemical blood test for triglycerides and cholesterol (lipid spectrum);
- According to indications, instrumental examinations are carried out.
To assess the condition of cerebral vessels, the following is carried out:
- Ultrasound of the brain and neck using two-dimensional and transcranial duplex scanning technology;
- angiography of cerebral vessels;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- MRI of the brain in vascular mode;
- REG (radioencephalogram);
- CT computed tomography of the brain and blood vessels;
- EEG – electroencephalogram.
The diagnostic capabilities of our multifunctional center of the FMBA of Russia allow us to carry out not only these, but also any other examinations necessary for the patient using the most modern and accurate equipment. You will be able to get advice from related specialists on any clinical case, including suspected cerebral atherosclerosis.
Causes
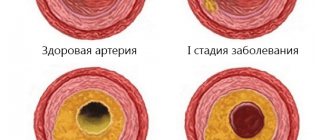
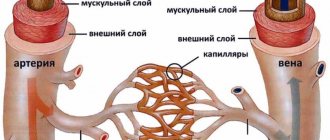
Cerebral atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries of the brain when cholesterol plaques form on their inner wall. As a result of this process, the lumen of the vessels narrows, up to complete blockage. The disease is characterized by widespread prevalence. Such atherosclerosis can develop as early as 30 years of age.
This pathology is characterized by a long asymptomatic course, and symptoms appear much later, usually after reaching 50 years of age. It is more common in males than in females. The development of vascular atherosclerosis occurs under the influence of a wide range of risk factors. One of the main ones is age.
The rapid progression and early manifestation of atherosclerosis is facilitated by:
- metabolic disease;
- diabetes;
- thyroid diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- obesity;
- abuse of fried and fatty foods;
- fiber deficiency;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- lack of physical activity.
The risk of developing cerebral atherosclerosis is increased by the presence of arterial hypertension in a patient. Often these 2 diseases develop simultaneously and provoke each other. In addition, vascular pathologies, in particular their damage, become favorable conditions for the formation of atherosclerotic plaque.
Damage to blood vessels is facilitated by frequent infections and chronic intoxication of the body, and frequently repeated psycho-emotional stress. Among the reasons, genetic predisposition plays a decisive role. The main role in the development of atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels belongs to disorders of fat metabolism and the accumulation of “dangerous” cholesterol in the blood.
As a result, the concentration of low-density cholesterol increases. It is this substance that is deposited on the inner surface of the arteries and blood vessels of the brain. In cerebral atherosclerosis, mainly arteries of large and medium caliber are affected.
First, a fatty spot forms, then it becomes “overgrown” with calcium salts and increases in size – the result is a cholesterol plaque. It narrows or blocks the lumen of the vessel. This, in turn, leads to a decrease in blood flow to the areas of the brain that feed them.
Thus, ischemia and hypoxia of the brain develop, resulting in the death of neurons. This pathological process is manifested by dyscirculatory encephalopathy: impaired cognitive functions, emotional disorders and motor disorders.
With severe metabolic disorders, cholesterol accumulates on the walls of blood vessels
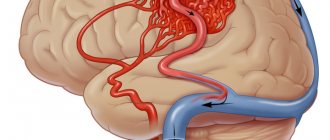
As the plaque grows, blood clots or blood clots may form. They can break off and enter small cerebral vessels, completely blocking their lumen. As a result, a person develops an ischemic stroke or begins to experience transient ischemic attacks.
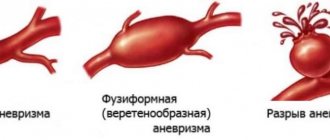
At the site of attachment of the cholesterol plaque, the elasticity of the arterial wall is lost over time. An increase in blood pressure in this vascular condition can lead to a hemorrhagic stroke.
Treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis
It is not only the neurologist who treats patients with atherosclerosis in our center. We treat the disease comprehensively with the involvement of doctors from different specialties. This approach makes the recovery process comfortable, gives better results and helps patients return to their normal lives sooner.
The basis for the treatment of cerebral atherosclerosis is the correct selection of nutrition. On the one hand, the diet combines a complete diet with individually designed physical activity. On the other hand, medications help compensate for the pathological process and reduce the harmful effects of the disease on the body.
Medicines used:
- diuretics;
- drugs that normalize lipid and blood sugar levels;
- vitamins;
- drugs to improve cerebral circulation;
- means for normalizing blood pressure and heart rate;
- thrombolytic agents, etc.
Treatment
The basis of treatment for this pathology is lifestyle adjustments. This means:
- lipid-restricted diet,
- rejection of bad habits,
- physical activity regimen,
- avoiding stress,
- treatment of chronic diseases.
The focus of drug therapy is the use of lipid-lowering drugs, antiplatelet, antihypertensive and antioxidant drugs, drugs to improve microcirculation and symptomatic therapy. Therapy, as a rule, takes a very long time and depends on the stage at which it was started.
In case of severe stenotic processes, surgical treatment is recommended for the patient. Most often, surgical intervention is performed on the internal carotid arteries. Source: E.A. Shirokov. Stenosing atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries: modern strategies for diagnosing and treating patients // Consilium Medicum, vol. 18, no. 9, 2021, pp. 37-42.
Treatment for this disease is aimed at ensuring that metabolic processes are restored, and harmful cholesterol no longer settles on the walls of blood vessels. At the same time, attention is also paid to restoring blood circulation and normalizing the nutrition of brain tissue.
Drug therapy
This is the most important part of the comprehensive treatment of atherosclerosis. Patients may be prescribed several groups of medications:
- Statins - reduce the size of cholesterol plaques, reduce the risk of narrowing of the main arteries of the brain, and stop the growth of plaques.
- Antiplatelet agents – reduce blood viscosity and prevent blood clots.
- Fibrates are similar in action to statins, but do not affect the size of plaques, but lower the triglyceride content in the blood.
- Means for restoring vascular function.
- Bile acid sequestrants prevent cholesterol from being absorbed from food.
- Nootropics and medications that improve metabolic processes in nervous tissue.
- Hypotensives that stabilize blood pressure and help prevent stroke.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes to improve the general condition of the body. They must contain vitamins A, C, group B and nicotinic acid.
Medicines are taken in long courses, and most of them are taken for life with periodic dosage adjustments.
Surgical treatment
Operation is a last resort, indications for it:
- narrowing of the lumen of the carotid artery by 70% or more;
- condition after a minor stroke;
- recurrent ischemic attacks.
Surgical options:
- bypass - the formation of a vessel bypassing the one affected by cholesterol deposits;
- endarterectomy - a procedure to remove cholesterol plaques along with a small amount of tissue that lines the vessel from the inside;
- stenting using endoscopic technology - an expanding structure impregnated with a composition that dissolves cholesterol is installed in the vessel.
Operations can be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. An anesthesiologist is consulted before the operation. The length of hospital stay varies depending on the technique, as do recommendations for the recovery period. SM-Clinic doctors inform patients in detail about all the nuances and are ready to answer any questions related to treatment at the initial consultation. Consultation on the operation is free of charge.
You can find out more about discounts on preoperative examinations by following the link.
Prevention
Below are a few useful habits that will help significantly reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis:
- to give up smoking;
- nutrition balanced in composition of nutrients;
- correction and maintenance of optimal body weight;
- annual preventive monitoring of lipid and blood sugar levels.
The diagnostic capabilities of our center allow us to establish a diagnosis quickly and accurately. Based on the results of the examination, you will be advised by experienced neurologists, whose knowledge has helped save hundreds of patients.
Also, individual health monitoring programs have been developed on the basis of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia.
- for men (under 40 years old, over 40 years old, standard);
- for women (under 40 years old, over 40 years old, standard based on age and optimal)
Don't put off taking care of your health. Call us or make an appointment to assess your risk of atherosclerosis and receive comprehensive recommendations.
Diet
Changing your diet is also a way to improve your well-being and is a great help for other treatment methods. Atherosclerosis very often progresses precisely against the background of poor nutrition and lifestyle, so it is necessary
- follow a certain diet:
- reduce consumption of red and fatty meats and meat in general;
- limit the consumption of confectionery products and baked goods;
- eat as few egg yolks as possible;
- limit solid vegetable fats – margarine – in the diet;
- completely eliminate alcohol, sausages, fast food, and canned food.
Recommended products include vegetables (fresh, pickled, dried), cereals (rice, buckwheat, barley, millet, oats, flax, etc.), dried, fresh and dried fruits, turkey and chicken fillets, river and sea fish.
You need to eat at least 5 times a day at the same time in small portions. It is necessary to avoid fried foods and prepare food using the methods of boiling, steaming, stewing, and baking.
Complications
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is dangerous due to the development of gangrene, muscle atrophy, and thromboembolism of blood vessels of vital organs in the event of plaque rupture.
Cardiac complications with damage to the coronary vessels include myocardial infarction, focal dystrophy of the heart muscle, myocardiosclerosis, and coronary sclerosis.
With obstruction of the mesenteric arteries, ischemic colitis and intestinal gangrene are possible, and secondary arterial hypertension is possible in the renal arteries. Cerebral consequences include hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attacks, and atherosclerotic dementia.
An aortic aneurysm poses a danger to the patient's life, the rupture of which in most cases is fatal.