Borderline Personality Disorder (or BPD
) is a rather rare mental destruction, characteristic of only 2-3% of people around the world. The pathogenesis of this type of psychopathy is usually accompanied by the presence of a complex of unfavorable factors.
It is quite difficult to recognize this type of disease in everyday life. Often, it is confused with narcissism or simply the bad character of an individual, since the behavior of “border guards” can be characterized by an extreme degree of unpredictability and hysteria, as well as a tendency to manipulation. For example, they confess their love to their partner, and after a couple of hours they leave “forever”; they can sincerely sympathize with someone, and then hit. It is also very common for patients of this type to constantly violate the boundaries of other people, shifting their problems onto them and avoiding responsibility. Let's look at the symptoms of borderline in more detail.
Symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD)
The main symptomatic difference of this type of disorder is the patient’s prolonged abnormal behavior
.
While in many other psychopathy periods of instability alternate with remission, in the case of BPD the patient behaves destructively over a long period of time. The field of psychological anomalies includes such manifestations as:
- aggressive behavior leading to relationship problems,
- unstable emotional background and inadequate self-image,
- high anxiety,
- total fear of loneliness and permanent feeling of boredom,
- dichotomous thinking and changeable moods, dividing the world only into “black and white” (today I love, and tomorrow I hate).
Also among the main symptoms can be noted: sociopathy and fear of society, associated with low self-esteem and, as a consequence, separation anxiety (an individual experiences it when separated from home or loved ones). Often, patients exhibit reckless, irresponsible “risky” behavior, the extreme form of which can be self-harm or suicide attempt.
Types of spontaneous actions accompanying mental borderline personality disorders
Due to difficulties in self-identification, lack of personal opinion, and a tendency toward polarity, BPD sufferers are prone to spontaneous destructive behavior.
A panicky fear of loneliness and the lack of an inner core pushes them into connections with sociopathic personalities who are characterized by destructive behavior: gambling, theft, vandalism, promiscuous relationships, drug addiction. This also includes self-harm, which was mentioned above.
One of the reasons for such uncontrolled behavior is the problem of maintaining internal impulse. The level of impulsivity is so high that a person is unable to control it.
Anxiety
It happens that a child is susceptible to emotional “explosions” due to birth trauma. But often the cause is mistakes in raising a child, as a result of which the child constantly experiences a feeling of anxiety. Anxiety manifests itself in hyperactivity, difficulty concentrating, excessive impulsiveness, and emotional imbalance.
The cause of such violations can even be cartoons featuring magical, fantastic characters. Also, parents who want to somehow influence the child often use stories about a “strange uncle” or a “wolf” who will come and take the child away because of his disobedience.
Parents' conversations in a raised voice and frequent quarrels in the presence of children are also factors in the manifestation of anxiety and worry in the baby.
Pathogenesis of BPD
The pathogenesis of the disease lies in incorrect or incompletely formed intrapersonal awareness of oneself, in other words, “self-identification.” Borderlines have difficulty understanding how they relate to major areas of life. They have problems with the concept of their opinions, interests, hobbies and their character as well. This is where the more common definition of the disorder – “borderline” – came from. In this aspect, it means maneuvering on the line between psychopathy and a stable state. The word “borderline” in this particular case means a precarious state between the norm and deviation, as if a person lives on the border between “mental illness” (psychosis) and “mental health”. That is why the slang name for patients of this type is “borderliners” (from the English expression “border line”, which literally translates as “border”).
In classical psychiatry, borderline personality disorder is also classified as a type of ego-syntonic disorder. Ego-syntonicity implies that the patient does not evaluate his condition as painful, is not critical of it, and calmly accepts deviations in behavior, without considering that they harm him in any way. Moreover, the patient seems to “defend” his symptom, preventing his own healing due to the difficulty in identifying his own “I”.
What characterizes intellectual instability?
Unlike emotional lability, its intellectual subtype can be very useful in a person’s everyday life. For example, intellectual lability is characterized by the ability to quickly switch attention and instantly respond to surrounding circumstances. Also, a person with similar phenomena has the ability to quickly learn new skills and abilities. It is easier for them to learn and be in conditions that are not natural for them.
The higher a person’s intellectual lability, the more successful he is in life. His reaction is heightened, he can be trained, explores new opportunities, and is able to succumb to feelings of envy, motivating himself with this. And those who do not have the described type of lability are more susceptible to anger, a feeling of fatigue, irritability, and nervous disorders.
Therefore, passivity and stability of the intellect are a negative quality for a person.
Causes of BPD
The underlying causes of borderline disorder are not clearly defined at this time, however, like most other disorders, BPD is caused by a group of factors.
Hereditary (genetic determination), physiological (impaired brain function) and social factors (low resistance to stress and psychological traumatic factors).
Unfavorable social environment
According to statistics, groups of people exposed to an unfavorable social environment, for example in the family, are more often susceptible to the disease. This may include:
- difficult childhood
- abuse,
- tyranny
- physical or emotional violence in the family,
- early loss of parents.
It is worth noting that among women “borderline” is 3 times more common than among men.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
, as a variation of an unfavorable social factor, can act not only as a cause, but also as a concomitant separate disease that is in a pathogenetic relationship with the diagnosis in question.
Chronic childhood emotional trauma may contribute to the development of BPD, but in rare cases it is the sole cause. Personal qualities responsible for the ability to cope with a stressful situation in this aspect also play a big role. It is worth noting here that, according to statistics, trauma received in childhood (especially before the age of 10) is much more likely to lead to subsequent disorder than that received in adulthood. Scientists also note that situations not associated with direct violence, such as natural disasters or catastrophes, are less likely to lead to the development of post-traumatic syndrome.
Physiology
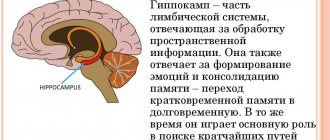
Another group of factors considers a possible cause of the development of the disease - disturbances in the functioning of neural brain connections, namely the destruction of the functioning of frontal-limbic neurons
Heredity
The third significant cause of BPD is genetic predisposition, which accounts for up to 40% of cases of this diagnosis. It is quite difficult to achieve clear indicators in this regard, however, according to European studies, BPD is ranked 3rd out of 10 in terms of genetic determinants among personality disorders. It is logical to note that deviations in the functioning of certain lobes of the brain can be inherited and lead to a number of psychological problems, the development of which is aggravated by social factors. Most studies show that borderline personality is most often inherited from the mother.
Drug treatment
The use of medications is necessary to relieve the main symptoms of the disease and associated disorders. When selecting medications, the following factors are taken into account:
- patient's age;
- risk of complications and adverse reactions;
- the likelihood of drug abuse and, accordingly, the formation of drug dependence.
Benzodiazepine and non-benzodiazepine tranquilizers, antidepressants, and hypnotics are indicated. They are prescribed for a short period to await the result of psychotherapy. After completing the main course of drug treatment, general strengthening vitamin complexes and herbal medicines are prescribed for a long period.
Borderline mental state in psychiatry and severity of personality disorders
In clinical psychiatry, three levels of mental disorder are traditionally distinguished:
- Neurotic
. This includes neuroses of various types, implying reversible temporary conditions that can be treated. - Psychopathic
level. In its plane lie personality disorders, which include character anomalies of various pathogenesis or painful changes in his traits, with which nothing can be done, since they relate to the personal structure of the individual. - And finally, the deepest damage to the psyche manifests itself at the psychotic
level. This includes manifestations such as delusions, hallucinations, and twilight consciousness.
In modern psychoanalysis, there are 4 levels of deviations. Between the state of psychosis and neurosis the “ borderline”
level", also called
borderline state
. A borderline state can mean both the disorder itself and a designation of the level of mental damage.
Autonomic instability
There is another type of negative lability. This is a disturbed vegetative system. This includes the factor of control over body movements, stability of the musculoskeletal system and all key organs. If you feel dizzy, lose control of yourself, notice tremors in your limbs or numbness, then you are likely to develop autonomic lability. The disorder is also manifested by erectile dysfunction, vaginal dryness, tachycardia and impaired sleep stability.
With all these manifestations, you should also consult a specialist.
How to Reliably Identify Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Borderline personality disorder is extremely difficult to diagnose and differentiate, as it has a high level of comorbidity, in other words, it is combined with a large number of concomitant disorders. For example, panic anxiety, eating disorder, bipolar affective disorder, attention deficit disorder, sociopathy, and so on. Due to the above, the patient has to undergo a lengthy diagnostic process and special tests.
Test for borderline personality disorder BPD
One of the fairly popular tools for identifying the presence of psychopathy are tests, which are essentially a personality questionnaire. The test used in modern clinical psychology to screen for strong signs of BPD was developed in 2012 by a group of scientists. In their work, the authors relied on the basic criteria for differentiating borderline disorder.
The questionnaire edited by them is a fairly effective tool for diagnostic verification and confirmation of symptoms. It is used both in psychiatric and general clinical settings, as well as in other practices that are not directly related to medicine.
The test itself consists of 20 questions and asks the test taker to answer only yes or no. For each answer, the system counts a certain number of points. The likelihood of diagnosing BPD appears if the respondent scores more than 25 points.
Principles of treatment
Therapy begins after confirmation of the diagnosis. To exclude an organic cause of the disorder, studies are indicated to assess the condition of the brain (presence of congenital or acquired organic lesions, hypoxia, etc.). Psycho-emotional status is assessed using various questionnaires, which are compiled taking into account age and gender characteristics.
Treatment for unstable psychopathy is usually carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization at the Leto specialized clinic is necessary for repeated suicide attempts, chemical dependency, and severe depression. But sometimes therapy in a hospital leads to a deterioration in the patient’s well-being, and in such cases the issue of transfer to a day hospital is considered.
Psychotherapy
The main goal of individual and group consultations with a psychologist is to correct the patient’s behavior and thinking and stabilize the emotional status. For this purpose, doctors practice the following techniques:
- psychoanalysis, especially if the cause of unstable psychopathy is associated with psychotrauma, problematic relationships with parents;
- dialectical behavioral therapy, which helps to cope with auto-aggression;
- psychodynamic approach: this is one of the types of psychoanalysis, but in this case the doctor works on correcting the so-called “transferences” - the unconscious transfer of previously experienced traumatic situations and conflicts to certain people in the present.
According to experts, not all people suffering from unstable psychopathy turn to doctors with this problem, attributing the symptoms of the disease to their character or reaction to troubles in the family or at work. We will help you cope with the disease! Don't ignore these personality and behavior changes! For a preliminary consultation and to make an appointment, call us on an anonymous 24-hour phone number 8(969)060-93-93.