Balance disorder, also called ataxia, is a dysfunction of motor coordination. It manifests itself in a person’s loss of control over the position in space of his body, as well as in violation of the accuracy of movements. In this case, as a rule, the strength of the limbs themselves is completely preserved or decreases slightly. Experts distinguish between static ataxia, that is, imbalance in a standing position, and dynamic ataxia, which is a lack of coordination during movements.
A balance disorder occurs when the interaction between the vestibular apparatus and the central nervous system, namely the spinal cord, the cortex of some areas of the brain and the cerebellum, is disrupted.
Causes
There can be several causes of ataxia, for example, external factors that cause an unbearable load on the vestibular apparatus - riding on a carousel or sailing on a yacht. The less trained a person is, the stronger the imbalance will manifest itself when exposed to irritating factors.
Internal causes are pathologies in the functioning of the central nervous system associated with organic lesions of both the spinal cord and the brain and vestibular apparatus. These dysfunctions can occur due to intoxication (food, alcohol, medication), trauma or hereditary diseases.
Depending on the nature of the balance disorder, various causes of its occurrence can be identified. The most common is vestibular ataxia, in which a balance disorder occurs as a result of damage to this organ, which is responsible for the perception of a person’s position in space and the direction of movement. The vestibular apparatus is part of the inner ear, and its signals are generated by the movement of the sensory hairs located in it. Receptors in the inner ear transmit two types of signals to the brain - those associated with the position of the body and those associated with its acceleration during movement. Disorders of this complex system, leading to vestibular ataxia, are most often associated with diseases of the inner ear.
Vestibular balance disorder is associated with damage to the inner ear, often of an infectious nature. Untreated otitis media can lead to subsequent complications - permanent hearing loss and the risk of inflammation of the meninges (meningitis). Vestibular ataxia can also be associated with life-threatening diseases - malignant brain tumors, stroke and encephalitis.
Links[edit]
- Sturnieks DL, St George R, Lord SR (2008). "Balance disorders in older people." Clinical Neurophysiology
.
38
(6):467–478. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucli.2008.09.001. PMID 19026966. - Smith PF, Zheng Y, Horii A, Darlington CL (2005). “Does damage to the vestibular system cause cognitive dysfunction in humans?” J Vestib Res
.
15
(1): 1–9. PMID 15908735. - Brandt T; Schautzer F; Hamilton D.A.; Bruning R; Markovich HJ; Kalla R; Darlington C; Smith P; Strupp M; and others. (November 2005). "Vestibular loss causes hippocampal atrophy and spatial memory impairment in humans". Brain
.
128
(11):2732–41. DOI: 10.1093/brain/awh617. PMID 16141283. - “Balance Symptoms, Causes, Treatment - What are the Symptoms of Balance Problems?” . MedicineNet. Retrieved March 2, 2014.
- Bhattacharya N; Baugh RF; Orvydas L; and others. (2008). "Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo" (PDF). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
.
139
(5 Suppl 4):S47–81.
DOI: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.08.022. PMID 18973840. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 26, 2011. Summary - AAO-HNS
(2008-11-01). - Fyfe T.D., Iverson DJ, Lempert T., Fuhrman J.M., Baloch R.W., Tusa R.J., Hine T.S., Herdman S., Morrow M.J., Gronseth G. “Practical parameter : Treatment modalities for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (evidence-based review)". Neurology
.
70
(22 (part 1 of 2)): 2067–2074. DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000313378.77444.ac. PMID 18505980. - "Van Der Berg et al. - 2015".
- Jump up
↑ Noll, D. R. (January 2013).
"Managing Falls and Balance in Older Adults". Journal of the American Osteopathic Association
.
113
(1):17–22. Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. - O'Sullivan, Susan; Schmitz, Thomas (August 2006). "8". In Susan O'Sullivan (ed.). Physical rehabilitation
.
5
. F.A. Davis Company. ISBN 978-0-8036-1247-1. - O'Sullivan, Susan; Schmitz, Thomas (August 2006). "13". In Susan O'Sullivan (ed.). Physical rehabilitation
.
5
. F.A. Davis Company. ISBN 978-0-8036-1247-1. - Gorak FB (2010). "Postural compensation for vestibular loss and implications for rehabilitation". Restaurant Neurol Neurosci
.
28
(1):57–68. DOI: 10.3233/RNN-2010-0515. PMC 2965039. PMID 20086283. - Alrwaily M, Whitney SL (2011). "Vestibular rehabilitation of elderly people with vertigo." Otolaryngology Clinics of North America
.
44
(2):473–496. DOI: 10.1016/j.otc.2011.01.015. PMID 21474018. - National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders
- Cao, Chao; Cade, W. Todd; Li, Shengxu; McMillan, Jacqueline; Friedenreich, Christina; Yang, Lin (2021-03-11). "Association of balance function with all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US adults". JAMA Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery
. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0057. ISSN 2168-6181.
Symptoms
The main signs characteristic of balance disorders are:
- dizziness;
- nausea and/or vomiting;
- noise in ears;
- lack of coordination;
- loss of body balance.
The listed symptoms are usually noted by patients independently. Some other symptoms can only be determined by a doctor - for example, one of them is horizontal nystagmus - uncontrolled eye movements.
Other symptoms that indicate the patient needs to consult a specialist:
- asymmetrical impairment of coordination of limb movements;
- falling when losing balance on only one side;
- speech and facial expression disorders.
These symptoms may be a sign of acute stroke or malignant lesions of the central nervous system and require immediate medical attention.
Why do I constantly feel sweaty and hot at the same time?
Feeling drunk, dizzy
There are times when your health sharply deteriorates: it’s as if a wave is rolling through your body, it becomes hot, your head hurts and feels dizzy, your heartbeat begins to increase, weakness and sweating appear, and nausea is possible.
- Why do I constantly feel sweaty and hot at the same time?
- Causes of fever and sweating
- Increased sweating at night
- Hormonal disbalance
- Increased sweating as a symptom of disease
- Consequence of hereditary predisposition
- Symptom during pregnancy
- Other reasons
- What tests need to be taken?
- Recommendations and preventive measures
- What to do if you feel dizzy and sweaty
- Causes of the condition
- Diseases that are accompanied by dizziness and sweating
- Eliminating symptoms
- Prevention
- Recipes you need
- Cold sweat and weakness: what are the causes?
- What is dizziness and hyperhidrosis?
- What diseases might these symptoms indicate?
- Reasons why these symptoms may occur
- The concomitance of two symptoms as signs of illness
- Dizziness, sweating, nausea, weakness - what do the symptoms indicate?
- Why do these symptoms appear?
- Eliminating symptoms
- Cold sweat and nausea
- Nature of the symptom and mechanism of occurrence: weakness
- Appearance and etiology: nausea
- Sweat: a natural reaction or pathology
- Abnormal sweating with negative sensations
- Triad of three symptoms
- Why do dizziness, weakness, sweating and nausea occur?
- Causes of dizziness, nausea, weakness, sweating
- Diabetes
- Starvation, exhaustion
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia
- Pregnancy
- Infectious diseases
- Hyperthyroidism
- Traumatic brain injuries, strokes
- Intoxication, dehydration
- VIPoma
- Diagnosis and treatment
- Headache makes me sweat and feel nauseous
- Dizziness and sweating: signs of chronic diseases
- Diagnosis and determination of causes
- Illnesses with frequent sweating and dizziness
- Helpful information
- Why do I constantly feel sweaty and hot at the same time?
- Causes of fever and sweating
- Increased sweating at night
- Hormonal disbalance
- Increased sweating as a symptom of disease
- Consequence of hereditary predisposition
- Symptom during pregnancy
- Other reasons
- What tests need to be taken?
- Recommendations and preventive measures
- Dizziness, nausea and sweat #8212; What is this?
- Didn't find a solution to the problem? Ask your question now:
Such attacks may indicate the presence of serious illnesses, especially if they occur frequently
Therefore, it is important to be examined in time - before starting treatment, it is necessary to establish why the person is throwing up heat and sweat. Many women and men of all ages suffer from such symptoms.
Changes in health with fever and sweating are an alarming sign for health.
There are a number of reasons that can cause these symptoms. Among them:
- hormonal imbalance in women (for example, during menopause);
- pregnancy;
- IOP;
- feverish conditions (the patient breaks out in cold sweat);
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- hypertension;
- consequences of heart attack, stroke;
- heredity;
- stress, mental disorders;
- overwork.
People suffering from hypertension often complain to doctors: “I sweat a lot at night because of attacks.” Sweating at this time also worries those who have suffered a stroke or heart attack. Such symptoms are associated with the fact that patients’ blood pressure rises sharply, their heart rate increases, and anxiety and fear appear. During a stroke, in addition to profuse sweating, people often notice redness of the facial skin.
Hormonal disbalance
According to statistics, representatives of the fairer sex constantly experience fever during menopause or before the cessation of menstruation. Poor health is caused by a lack of estrogen. In addition, when the ovaries stop functioning, a woman suffers from insomnia, experiences weakness, becomes irritable, often has a headache, increased blood pressure, painful sensations during menstruation, and possible nausea. In girls, similar symptoms occur before menstruation and ovulation (second week before menstruation).
During pregnancy, the hormonal levels also change, menstruation stops, so from the very first weeks the expectant mother first feels hot, she may feel dizzy and have a headache, then she feels nauseous, cold sweat appears, and she becomes cold. There are other reasons for changes in hormonal levels. In particular, most endocrine diseases that are associated with an insufficient amount or excess of a certain hormone lead to similar pathological manifestations. People suffering from diabetes and thyroid diseases are especially susceptible to this.
Diagnostics
If dizziness and loss of balance bother you constantly, and not just when exposed to factors that irritate the vestibular apparatus, you should consult a doctor. The primary diagnosis is carried out by a therapist; depending on the identified symptoms, he prescribes further examinations and refers to a specialist - an otolaryngologist, neurologist or oncologist.
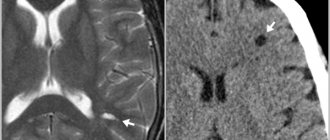
To accurately determine the causes of balance dysfunction, a general and biochemical study of the patient’s blood is prescribed to exclude the presence of an infectious lesion. At the same time, depending on the symptoms, radiography of the skull bones, electroencephalography, MRI of the brain, electromyography of the limbs and Doppler sonography of the brain are performed.
Which doctor treats balance disorders?
Balance disorders are treated by a neurologist. At the Kuntsevo Center, experienced specialists offer their services to patients who use new methods to eliminate ailments. To accurately determine the cause of the disease, a visual examination is carried out and the accompanying symptoms are clarified. The root causes of balance disorders can be both pathologies in the cervical spine and diseases of the brain.
To diagnose the disease, patients are prescribed electromyography, encephalography, MRI, and clinical and biochemical blood tests. The clinic approaches the treatment process comprehensively. The patient is recommended to undergo a general examination of the body and undergo a tomography of the spine. When concomitant ailments are identified, highly specialized specialists are involved in the work.
Treatment
Treatment of balance disorders is carried out depending on the etiology of the disease that led to symptoms of incoordination. Acute diseases such as stroke and encephalitis are treated only in a hospital setting. For a mild form of the disease that occurs when traveling on public transport, the doctor may recommend medications prescribed for seasickness.
For vestibular ataxia associated with inflammation of the inner ear, it is necessary to first eliminate the source of infection; for this purpose, antimicrobial drugs are used. In parallel, concomitant treatment is prescribed - non-steroidal (Otinum, Otipax) or corticosteroid (Sofradex, Polidexa) drugs to relieve swelling, immunostimulating agents (Laferobion, Vitaferon, Lyophilisate) and vitamin preparations.
For balance disorders that are not infectious in nature, a complex of drugs is prescribed:
- synthetic histamine analogue;
- nootropic drugs (Nootropil, Piracetam, Phenibut);
- antihypoxants and drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Actovegin, Vinpocetine, Cavinton);
- muscle relaxants, for example, Mydocalm;
- anticonvulsants;
- vitamin complexes.
In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapy is also used. It includes physical therapy, massage and electrical stimulation of the muscles of the limbs. These methods improve muscle tone and stimulate overall muscle function.
The reception is conducted by specialists
Important
In case of a sudden attack of dizziness:
- for several hours, remain calm, finding a convenient body position that is comfortable for you;
- take a sedative: growing anxiety will worsen your condition and prolong the attack;
- if the dizziness is very severe, accompanied by vomiting and other alarming symptoms (numbness of a part of the body, face, rise in blood pressure to high levels), call an ambulance.
No dizziness. Exercises for training the vestibular apparatus
Read more >>
Risk factors and prevention
Factors contributing to the development of heart and vascular diseases may include:
- Congenital heart defects.
- Hereditary diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Sedentary-lying lifestyle, low physical activity.
- Adverse habits such as alcohol and nicotine addiction, overeating and poor nutrition, lack of sleep.
- Stress loads.
- Colds and viral diseases suffered “on your feet”.
To prevent such heart pathologies, you should lead a correct lifestyle:
- Avoid alcohol abuse, smoking, drugs, drug addiction.
- Exercise.
- Watch your diet: it should be balanced.
- Sleep consistently 8 hours a day.
- Visit your doctor promptly if you experience dizziness with loss of coordination and other symptoms.
- Avoid stress and overwork.
- Spend a lot of time outdoors.