Hemiparesis is a neurological disorder in which there is a restriction of muscle movement on the right or left side of the body due to damage to the opposite hemisphere of the brain.
The condition is associated with damage to the cell bodies of cortical motor neurons and pathways in the brain or (in more rare cases) the spinal cord. As the pathological process progresses, a gradual decrease in sensory and motor functions is observed, which causes the development of muscle damage. Usually hemiparesis occurs on the side opposite to the damage, which is caused by the decussation of nerve fibers at the junction of the medulla oblongata and the spinal cord.
Types of paresis
Folk remedies
Photo: fitohome.ru
Paresis does not mean a complete loss of motor activity, so it is important to engage in therapeutic exercises and physical education for a long time, gradually increasing the load. A course of therapeutic exercises is selected by the attending physician and carried out in a medical institution
This is necessary so that each time the patient is under the supervision of a specially trained person who can assess the correctness of the exercise technique, as well as monitor the dynamics of treatment. In addition, it is important to exercise yourself and at home in order to improve and speed up the expected effect of treatment. A gradual increase in load should subsequently be complemented by movements with resistance. This will help in increasing muscle size and strength.
Therapeutic exercises should be combined with massage sessions, which improves tissue nutrition, promotes the formation of nerve impulses, and also prevents the development of muscle atrophy. You can sign up for a massage with a specialist, but given that this therapy is long-term, it is possible to teach massage techniques to relatives so that they can constantly practice at home.
For peripheral paresis, physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect. They help improve blood circulation, stimulate metabolic processes and trophism, and help restore lost function. In this case, physiotherapy is used:
- diadynamic currents;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy.
Currently, acupuncture (acupuncture) is gaining momentum. This is one of the methods of alternative medicine, which still has a lot of critical views from various specialists, however, despite this, the demand for this procedure is progressively growing.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Hemiparesis in children treatment
Regardless of the type of hemiparesis disease in children, in any case it is necessary to act immediately and eliminate its symptoms and causes. During treatment, constant monitoring of the baby is required so that timely and adequate correction of these deviations can be carried out.
To prevent severe disorders of the psyche, speech, movements and increase the chances of recovery, a course of treatment must begin immediately.
As soon as the exact diagnosis is known, special physical exercises for the baby and special medications will be prescribed.
Most often, physical therapy is prescribed, because without constant training and physical activity there will be practically no result. They prescribe, for example, pumping up the abs, jumping on one leg, special exercises to tighten the abdominal corset, and for small children, parents should do a special massage using the technology prescribed by the attending physician, and various stretches.
After discharge, treatment must continue at home. All doctor’s prescriptions must be strictly observed and carried out regularly! After all, only with proper use of medications and physical therapy can you not only get rid of the symptoms, but also soon completely “defeat” the disease, and a school-age child will be able to look normal, and in adolescence will completely overcome hemiparesis.
Description
Paresis is a decrease in muscle strength.
This condition is a consequence of various diseases and does not depend on belonging to a particular gender, so we can say that it occurs with equal frequency among both women and men. The age range is also different and depends on the cause of paresis. A decrease in muscle strength leads to a decrease in working capacity and the inability to cope independently in everyday life, therefore the development of paresis is a serious social problem and requires timely provision of medical care.
Based on the area of the body in which paresis occurs, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- monoparesis – symptoms appear on only one arm or leg;
- paraparesis – signs of paresis are present on both parts of the body, which are located symmetrically in relation to each other. With paresis of the arms it is called upper, with paresis of the legs - lower;
- hemiparesis – paresis affects one half of the body;
- tetraparesis - all limbs are affected.
Depending on the level of damage to the nervous system, there are two types of paresis:
- Central (damage is localized at the level of the brain and spinal cord);
- Peripheral (peripheral nerves are damaged).
The main causes of central paresis:
- stroke;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- spinal cord injuries;
- tumors of the brain and spinal cord;
- intervertebral hernia;
- multiple sclerosis;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS);
- cerebral palsy.
Among the causes of peripheral paresis are the following:
- radiculitis;
- demyelinating diseases of the nervous system;
- peripheral nerve injuries;
- compression of nerves, so-called “tunnel syndromes”;
- nerve damage due to connective tissue diseases and vasculitis;
- various poisonings, including alcohol.
Preventive recommendations
The development of left-sided paresis can be prevented by directing forces to the primary disease, which can lead to spastic changes in muscle and joint structures. We can only name preventive measures common to all diseases, namely:
- Maintaining proper nutrition. By following a balanced diet, you can prevent atherosclerotic changes that increase the risk of stroke - the cause of hemiparesis. It is recommended to limit foods rich in cholesterol and animal fats. The diet includes vegetables and fruits, cereals, vegetable oil. Eating sea fish is beneficial because it contains unsaturated fatty acids that prevent damage to blood vessels.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle. In this case, you can prevent obesity, weight gain, and arterial hypertension - serious risk factors. In addition, systematic exercise helps improve blood properties, reduce the risk of blood clots and stroke.
- Elimination of bad habits. Ischemic stroke and its consequence – hemiparesis – can be prevented by eliminating smoking, which causes vasoconstriction and increases the risk of developing atherosclerotic changes.
- Elimination of stressful situations. There is no need to be nervous or depressed, because this does not have the best effect on the state of the central nervous system. If you cannot solve the problem on your own, you need to consult a psychologist.
It is important to monitor your heart health and control your blood sugar levels. And, of course, if alarming symptoms are detected, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment for hemiparesis.
Reasons for development and classification
Hemiparesis is not a separate disease, but a symptom of another primary pathological process. This condition is characterized by partial paralysis, weakening of the strength of muscle tissue on one side of the body. The second half of the body is healthy.
Left-sided paresis occurs if the upper motor neurons and their axons are affected. In most cases, the functioning of motor neurons is also disrupted. Often the diagnosis is cerebral rather than spinal. In other words, the primary pathological process is a disruption of the central nervous system and brain.
To determine the severity of pathological changes, it is necessary to study the symptoms characteristic of focal lesions of the cerebral cortex. These are impaired speech, difficulties with movement, impaired coordination and perception. In addition, epileptic syndrome often occurs, the sensitivity of the skin is lost, and cognitive disorders develop.
In some individual brain lesions, ipsilateral disturbances in the functioning of the nerves located in the brain are combined with contralateral paresis. With concomitant anomalies in the structure of the head, the pathology develops more rapidly. In this case, postictal hemiparesis occurs.
The main reasons for the development of left-sided (as well as right-sided) paresis in an adult and a child are congenital or acquired diseases. These include:
- formation of a tumor-like neoplasm in the brain stem;
- the presence of intracerebral or epidural injuries;
- subdural hygroma of traumatic origin;
- history of stroke or heart attack;
- development of acute ischemia;
- the presence of intracerebral hemorrhage caused by thrombosis of the carotid artery;
- presence of parenchymal hemorrhage;
- the development of Farah's disease, which occurs with the formation of stone-like deposits in the brain area;
- development of multiple sclerosis;
- frequent hysterical attacks (in both women and men);
- the presence of hemiplegic migraine of a spontaneous or genetically determined nature;
- development of Brown-Sicart syndrome, characterized by the formation of a spinal tumor localized in the cervical area;
- the presence of syphilitic gumma - a soft tumor-like formation in the tissues.
When left-sided hemiparesis appears in childhood, the cause is often a congenital brain anomaly that arose during the prenatal period. The sources of the condition also include complications that arose during delivery, for example, compression of nerve fibers.
The first clinical manifestations of left-sided hemiparesis in a child can be detected within 2-3 months after birth. The final diagnosis can be made after 1 - 1.5 years, when the child makes his first movements. In severe cases, due to hemiparesis, a person’s mental ability and speech are impaired. In addition, damage to the left hemisphere of the brain causes mental disorder. This can be explained by the localization in this department of the maximum number of nerve centers responsible for mental function.
Classification
There are several types of hemiparesis, which have their own reasons for their development. One of these is spastic, which occurs in most cases and is characterized by damage to central motor neurons. Among the causes:
- development of transient ischemic attack;
- history of stroke;
- the presence of a tumor formation, an abscess in the brain;
- an inflammatory process with an infectious or non-infectious etiology;
- development of multiple sclerosis;
- history of brain injury.
The second form of hemiparesis is flaccid, caused by damage to peripheral motor neurons. Among the causes:
- toxic brain poisoning;
- taking certain medications (in this case, hemiparesis is a side effect of therapy);
- autoimmune neuropathy;
- myasthenia gravis;
- inflammatory myopathy.
The third form of hemiparesis is coexisting, combining spastic and flaccid paresis. Among the causes:
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis;
- transverse inflammatory process, another pathological condition in the spinal cord.
Only a doctor can determine the form of pathology based on the diagnostic measures performed.
Unilateral paralysis with decreased and increased muscle tone
Skeletal muscle paresis is a general neurological syndrome manifested in muscle weakness of one or more limbs (from mild to complete inability to perform movements). Areas of the body driven by weak muscles also suffer. Pathogenesis is associated with damage to the descending pathways connecting the nuclei of motor neurons in the cerebral cortex (CB) with the anterior horns of the spinal cord (SC) and peripheral nerves. A complete lack of movement for the same reason is called paralysis or plegia.
Paresis of both limbs on one side (right or left) is called left-sided or right-sided hemiparesis.
Symptoms
The following symptoms can help identify a right-sided stroke:
- the occurrence of headaches and a feeling of numbness in the left side of the body;
- paralysis of the left upper or lower limb. In this regard, when the patient tries to stretch both arms forward, a situation is observed where the left hand lags behind the right;
- patient complaints of dizziness, nausea and weakness;
- left-sided facial paralysis;
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- decreased visual and hearing ability on the left side;
- the patient’s ability to independently rely exclusively on the right leg;
- impaired logical thinking;
- limb spasms;
- at some point, a patient with right hemisphere damage may be found unconscious;
- with this condition, patients report disturbed sleep, a state of exhaustion and a poor emotional state.
In a situation where a stroke has developed in an elderly patient, a coma is likely to occur, which will last no more than a day. If a person does not regain consciousness within the specified time, then the likelihood of acquiring disability increases at a tremendous rate every day.
Treatment
The primary task of the doctor is to timely identify the syndrome, as well as the causes of its occurrence. This is especially true for young children. After all, the sooner a correct diagnosis is made, the higher the chance of a full recovery.
The treatment of paresis of all types must be approached systematically. Depending on the severity of the disease, the rehabilitation course should contain:
- Therapeutic exercise.
- Massage.
- Swimming.
- Physiotherapy.
- Drug treatment.
Exercise therapy
Therapeutic exercise is prescribed in parallel with massage. Depending on the severity of the disease and the affected area, the exercise therapy instructor prescribes an individual set of exercises for each patient. Initially, the training takes place under the strict supervision of a specialist, then independently at home.
The complex for patients with cerebral palsy should consist of the following exercises:
- Passive exercises for the affected limb, performed with the help of an instructor.
- Vigorous exercises performed with the help of an instructor and a healthy limb.
- Simple, vigorous exercises for healthy parts of the body.
- Exercises aimed at improving coordination in the movements of the affected limbs.
- Exercises to relax muscles and reduce hypertension.
- Walking.
- Breathing exercises.
- Exercises to develop fine motor skills.
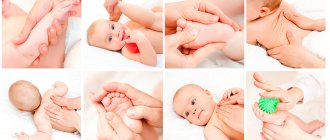
Massage, swimming
For cerebral palsy and hemiparesis, it is usually prescribed. This treatment relieves muscle spasms and improves blood circulation in them. The massage technique for each patient is selected individually, depending on the severity of the disease.
Swimming helps to: improve the coordination and rhythm of movements, trains the vestibular apparatus and cardiovascular system, relieves stress on the spine, and also has a positive effect on blood circulation in the body.
Physiotherapy, drug treatment
Physiotherapeutic procedures include electrophoresis, mineral and pine baths, Charcot's underwater shower, paraffin-ozokerite and mud applications to the affected parts of the body. Drug treatment is prescribed only in particularly severe cases. It is selected individually for each patient. The following medications are used to treat cerebral palsy:
- Sibazon.
- Piracetam.
- Neuromidin.
- Seduxen.
- Cerebrolysin.
- Baklosan.
- Baclofen.
- Pantogam
Alternative treatment and PET therapy
For patients with hemiparesis, doctors recommend. They should only be carried out under the guidance of an experienced master. Since ancient times, yoga has been considered one of the best therapeutic exercises. With regular exercise, the body muscles relax and stretch, and the muscle corset strengthens.
Dolphin and hippotherapy are indicated for children diagnosed with cerebral palsy. When communicating with a dolphin, the child’s reflexes begin to become more active and improve, the central nervous system calms down, and tactile and speech skills are practiced. Another advantage of dolphin therapy is the effect of hydromassage, which trains muscles and joints. Your emotional state improves, feelings of fear disappear, and self-confidence appears.
During horse riding classes, due to the specific movement of the horse, patients develop correct posture and train the vestibular apparatus, muscles and ligaments. In addition to full-fledged treatment, which is officially recognized by classical medicine, the child receives a lot of positive emotions from communicating with animals.
In medicine, cerebral palsy is considered an incurable disease, but by choosing the right tactics, you can achieve good results and live a full life.
Hemiparesis is a weakening of the muscles of one half of the body, while the other half remains in normal condition. The development of this pathology is caused by damage to the upper neurons and axons of the brain. And the degree of severity is determined by the existing symptoms.
Possible complications
The consequences of a stroke are sometimes quite serious and even irreversible. This:
- loss of appreciation of cause-and-effect relationships and the ability to think logically;
- lethargy, difficulty perceiving reality;
- complete loss of speech function;
- immobility leading to the formation of bedsores and the development of pneumonia;
- helplessness provokes the development of isolation and depression.
Timely treatment can minimize the development of severe complications of the disease and prevent the possibility of death.
It should be remembered that recovery from paralysis caused by a stroke is a long process. It may last not a month, not a year, but even several years. However, strict adherence to medical recommendations, giving up bad habits, following a diet and reasonable physical activity give a chance for complete rehabilitation.
Medicines
Photo: plastichno.com
In the treatment of paresis, neuroprotectors are used - drugs that help protect nerve fibers. For this purpose, B vitamins (B1, B6, B12) are prescribed, which are either used individually or in combination. An example of such a combination drug is Milgamma. This drug is able to restore metabolism inside cells, which helps slow down the process of destruction of myelin (the sheath of the nerve fiber), and also affects myelin regeneration. It is recommended to prescribe in 2 stages. At the first stage, an injection form of the drug is used, at the second, a transition to tablets is made.
Vinpocetine is used to improve cerebral circulation. Its effect is achieved by dilating cerebral vessels. In addition, the drug has antiplatelet and antihypoxic effects. Some experts consider this drug to be outdated and ineffective, but, nevertheless, it is still used to this day.
For neuroinfection, antibiotics are used if there is a bacterial etiology of the disease. The choice of antibacterial drug is made based on an analysis of the sensitivity of the microorganism that causes the infection to certain groups of antibiotics. Often, treatment begins before the test results are obtained, and broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. For example, cephalosporins may be prescribed.
It is important to understand that such a phenomenon as paresis can be a manifestation of various diseases, therefore the treatment is carried out by a qualified doctor who is able to select the necessary treatment taking into account each individual case
What is hemiparesis
Hemiparesis is a weakening of the muscles of one half of the body, while the other half remains in normal condition. The development of this pathology is caused by damage to the upper neurons and axons of the brain. And the degree of severity is determined by the existing symptoms.
Symptoms
Hemiparesis, like any other pathological condition, has its own signs and symptoms, but they may differ from person to person, and it all depends on what exactly caused the pathological condition, the age of the patient and his general condition. The main symptoms include:
- Prolonged headache.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lack of appetite.
- Fatigue.
- Joint pain.
- Strong weight loss.
In addition, hemiparesis is classified into left-sided and right-sided. Left-sided is a form of cerebral palsy. In this case, weakening of the muscles on the left side of the body, and in some cases even complete paralysis, is diagnosed. In this case, on the affected leg the tone of the muscles that are responsible for extension predominates, and on the affected arm the tone of the muscles that are responsible for flexion predominates.
Right-sided hemiparesis most often develops in adults, and the motor activity of the right half of the body is affected. If such a condition develops completely suddenly, then the main reasons can be considered:
- Stroke.
- A brain tumor.
- Brain injury.
- Encephalitis.
- Migraine.
- Diabetic encephalopathy.
- Multiple sclerosis.
Sometimes this condition can develop quite slowly, for example over several days or weeks. This indicates a pathological process in the brain, and the main reasons may be:
- Slow growing tumors.
- Atrophy of the cerebral cortex.
- Head abscess.
- Radiation myelopathy.
Sometimes a lesion can occur against the background of some kind of mental illness or stress. In this case, we need to talk about pseudoparesis, which, after eliminating the factor that caused it, completely disappears.
Diagnostics and therapy
The first thing to do is to examine the affected limb, assess the range of motion on the affected side and determine the cause of the pathology. If necessary, for spastic hemiparesis, a number of additional studies can be performed, for example, CT or MRI. Diagnostic procedures such as electromyography may also help.
The first thing that needs to be done is to establish the cause of incomplete paresis of one half of the body, and then begin treatment. If a pathology has developed in a child, then you need to act as soon as possible, since the further course of the disease and recovery will depend on this.
Sometimes the cause of hemiparesis in children is abnormalities of the spine, brain or limbs themselves. It can also be pinched nerves, their complete atrophy, or disruption of normal brain function. Therefore, treatment will depend on identifying the causes.
In mild cases, treatment begins with an individually selected course of exercise therapy. Treatment should also include:
- Swimming.
- Massage.
- Hippotherapy.
- Reflexology.
- Fitball exercises.
- Hardening.
- Pouring.
- Sharko's shower.
And only in severe cases can drugs from the group of muscle relaxants be prescribed, which is especially common with cerebral palsy.
After discharge from the hospital, treatment must be continued at home, and not a single lesson should be missed. And only with daily training can you really achieve excellent results and completely get rid of the disease.
Drug therapy
As a rule, you can cope with the manifestations of the disease with the help of exercise therapy without resorting to the use of drugs, but in some cases only drug therapy can help.
For example, treatment of left-sided hemiparesis is the use of medications such as:
- Baklosan.
- Baclofen.
- Mydocalm.
- Neuromidin.
- Pantogam.
- Piracetam.
- Seduxen.
- Sibazon.
- Cerebrolysin.
Also in treatment you can use medications that contain vitamins, especially those belonging to group B and vitamin E.
Diagnosis
A number of tests are used to detect hemiparesis. Barre's test - a paretic leg raised upward in a lying patient gradually lowers, while the healthy leg is held in its given position. Mingazzini test - the paretic arm extended forward is lowered, while the healthy one is held at a horizontal level. Garkin's test - the patient bends the forearm and vertically raises the hand with the fingers wide apart; on the paretic side, the first finger in the metacarpal joint slowly moves in the adduction position and bends slightly. Hoffmann's sign - the patient holds his hands palms down, and the tip of the middle finger is in contact with the examiner's fingers; in response to a sharp push of the middle finger, all fingers of the paretic hand flex. Venderovich's symptom - weakness of adduction of the fifth and fourth fingers - is an early sign of pyramidal insufficiency. The nature of the patol, the process that caused G., is recognized with the help of special wedges and studies.
Differential diagnosis
Pyramidal G. differs from cerebellar in the absence of cerebellar symptoms and muscle hypertension. In multiple sclerosis, pyramidal G. (paresis) with muscle hypotonia is observed as a result of combined damage to the pyramidal system and the cerebellum. With severe hemiparkinsonism in paralyzed limbs, plastic hypertension is observed with the cogwheel symptom and postural reflexes of Westphal and Thévenard-Foix. Pyramidal G. differs from hysterical (functional) by the presence of patols, reflexes, and Wernicke-Mann gait.
Features of symptoms in right-sided stroke
In this form of stroke, the lesion is localized in the right half of the brain, the bodies of the central motor neurons or their processes forming the pyramidal tract are destroyed. The cause of the lesion may be hemorrhage or an obstruction to blood flow. As a result, an area of necrosis appears, compromising the integrity of the nerve pathways. Impulse transmission is seriously affected or becomes impossible.
After a stroke that affects the right hemisphere of the brain, speech disorders never occur, since the centers that control this function are located on the left. And this has a drawback, because there is a high probability of late diagnosis of stroke (after all, speech disorders are usually the first and most noticeable symptoms).
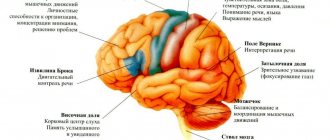
Areas of specialization of the left and right hemispheres of the brain
Damage to the right side of the brain is accompanied by the development of movement disorders and loss of sensitivity on the left side of the body. The left arm and/or leg are affected. The facial muscles on the left side of the face are often affected. Clinically, this is manifested by drooping of the corner of the mouth on the left. It should also be noted that the indicated party is unable to participate in facial expressions.
The right hemisphere is responsible for imaginative thinking, creativity, intuition, and the ability to solve several problems at the same time; regulates emotions and imagination. Therefore, after a stroke, symptoms such as absent-mindedness, depression, anxiety, unmotivated aggression, and inappropriate behavior occur (for this reason, by the way, treatment should not be done without the involvement of a psychotherapist). Right-sided stroke is also characterized by hearing impairment and loss of visual fields.
After a stroke in the right hemisphere, movement disorders occur on the left side.
Differences in the consequences of apoplexy in the right hemisphere
As has long been known, the consequences of stroke pathology of the brain are directly dependent on in which part of the brain the focus of pathological tissue damage is located and how extensive this focus is. As we have written more than once, the areas of the brain that are responsible for controlling certain motor, speech or other functions always control strictly opposite sides of the human body.
Note that the consequences of stroke pathology of the brain with the location of foci of damage to brain tissue on the right side (with damage to part or the entire right hemisphere) will be reflected exclusively on the left side of the victim’s body - this is, first of all, paralysis of the left limbs, the left side of the face and body .
Actually, in this case, we are more interested in the specific consequences of stroke pathology that affects part of the right hemisphere of the human brain.
Features of a right-hemisphere brain stroke
The main feature of stroke pathology of the brain, with damage to part of the right hemisphere, is the difficulty of diagnosing it at first (minutes and even hours), when a lot can depend on the correctness of the diagnosis. When we say a lot, we are talking about the favorable course of the disease, the final degree of damage to brain tissue, and what the consequences of such an emergency as a right-sided stroke may be.
The difficulty in diagnosing stroke pathology of the right hemisphere lies in the fact that this brain region is responsible for:
Damage to brain tissue
- For human orientation in space.
- For the emotional background.
- Perception of music, singing.
- For our fantasies or dreams.
- Sensitivity and empathy.
In this case, the speech center can be located in the right hemisphere only in left-handed patients. As a result, speech disorders, by which it is easiest to recognize the onset of stroke pathology, are absent in case of a right-sided brain stroke (in a right-handed person) and, often, the time during which it would be possible to quickly help the victim is lost, and the brain cells themselves die, in which case , already irrevocable.
Features of the consequences
Most often, victims of stroke pathology, the lesion of which is located in the right half of the brain (damage to the right hemisphere), experience some weakness (paresis or paralysis) on the left side of the body. The general nature of such weakness (whether it is permanent paralysis or not) depends on the severity of the cerebral stroke, on its extent.
Paralysis, in this case, can range from relatively minor muscle weakness in the limbs (a condition of left-sided hemiparesis) and end with complete paralysis (the so-called left-sided hemiplegia - complete loss of motor functions) on the left side of the body. With such a pathology, both hemiparesis and hemiplegia can spread not only to one limb; such weakness can affect the arm, leg, muscles of the face or torso on the left side.
Loss of motor function on the left side
In case of a brain stroke, with the localization of the lesion in the right hemisphere, with the subsequent development of left-sided paralysis, the victims can often experience a significant underestimation or even complete denial of the resulting motor defects. For example, such patients often claim that they are able to move an already paralyzed limb completely freely. When asked by others to raise their hands up, such patients boldly answer: “Here you go,” however, only the healthy right hand rises.
In addition, the consequences of a brain stroke of this right-sided type can manifest itself in strange sensations in already paralyzed limbs. Some say that their paralyzed arm is covered with hair, others claim that there is a stick tied to their arm - but this does not mean that the victims are developing some kind of mental disorder, they can indeed feel such oddities. In addition to motor disorders on the left side of the body, the consequences of a right-sided brain stroke can also manifest themselves in disorders of other functions. Such violations will be presented more clearly in the table:
Diagnostics
The main method for identifying left-sided hemiparesis was and remains a clinical examination by a specialist, including:
- careful collection of complaints and medical history;
- objective examination of the patient;
- assessment of muscle strength (in comparison with the opposite side and the strength of the researcher);
- conducting a muscle resistance test;
- Barre test (determining the time of holding a limb in weight).
To assess muscle strength and the degree of paresis, a special scale is used, where the range of movements in a particular muscle group is assessed in points from 0 to 5.
Diagnosis of congenital hemiparesis in children requires the earliest possible examination by a neurologist of small patients at risk. In order to clarify the diagnosis, dynamic monitoring and prevent possible complications, an ultrasound scan of the brain is prescribed.
To assess the risk of cerebrovascular disorders in children on mechanical ventilation, a spectroscopic study is performed.
Sources
- Prokopenko Semyon Vladimirovich, Ondar Vera Semenovna, Abroskina Maria Vasilievna Central hemiparesis syndrome and imbalance. 2012. Bulletin of Regenerative Medicine;
- Artemyeva S. B., Lobov M. A. Congenital hemiparesis in the work of a general practitioner. 2004. Almanac of Clinical Medicine;
- Kovalenko Alexander Pavlovich, Rodionov A.S., Kremlev D.I., Averkiev D.V., Lobzin V.Yu., et al. Restoration of walking in patients with spastic hemiparesis: new opportunities. 2021. Neurology, neuropsychiatry, psychosomatics.
Diagnostics
Accurate diagnosis is carried out in a clinical setting and includes:
- Taking anamnesis and visual examination of the patient;
- CBC and biochemical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- ECG;
- CT or MRI of the brain, cervical spine, spinal cord;
- EEG;
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels;
- Electroencephalography;
- CSF analysis;
- Cerebrospinal fluid analysis;
- The muscle strength of both sides of the body is compared;
- Muscle resistance test;
- Barre test - holding hands in weight;
- For children, in addition to early examination by a neurologist, ultrasound of the brain is used.
Since left-sided hemiparesis is a consequence of the underlying disease, then, first of all, it is necessary to treat it
But, at the same time, it is equally important to devote time to symptomatic therapy against hemiparesis
Mainly, in the treatment of children, emphasis is placed on:
- Classes with a speech therapist for the treatment of speech dysfunction;
- Classes with a defectologist for developmental delays;
- Treatment of episyndrome;
- Drug therapy.
In addition to this, it can help a lot:
- Gymnastics;
- Therapeutic baths and mud;
- Use of orthopedic beds, orthopedic shoes;
- Surgical intervention, if necessary;
- Holidays at resorts.
In adults
To treat hemiparesis, drug treatment is used primarily to improve neuromuscular conduction. Muscle relaxants to relieve tone, medications to improve blood circulation, anticonvulsants.
In addition, adults can also be prescribed:
- Orthopedic treatment: shoes, splints;
- Physical therapy and gymnastics;
- Massage.
- cold and hot shower;
- water gymnastics.
Exercise therapy and a set of exercises
A therapeutic set of exercises shows good results in the treatment of left-sided hemiparesis. You can practice both in specialized centers and at home. The main thing is that the classes are constant, or better yet, daily.
Exercise sets are usually developed individually for each patient. You can give an example of such a system of exercises as:
- Pulling the chin to the chest;
- Tilt of head to shoulders;
- Rotational movements of the hands;
- Raising your arms to shoulder level;
- Rotational movements of the feet;
- Raising on toes;
- Flexion and extension of the legs in a lying position;
- Raising your legs while lying down.
We invite you to visually familiarize yourself with an interesting video on the topic: