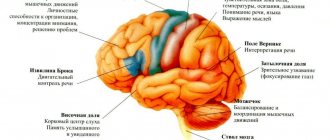
Organic damage to the central nervous system (CNS) is a diagnosis that indicates that the human brain is in an unstable state and is considered defective.
As a result of such lesions in the brain, degenerative disorders occur, destruction and death of brain cells or their necrosis. Organic damage is divided into several stages of development. The first stage is characteristic of most ordinary people, which is considered the norm. But the second and third require medical intervention.
Residual damage to the central nervous system is the same diagnosis, which shows that the disease appeared and persisted in a person during the perinatal period. Most often this affects infants.
From this we can draw an obvious conclusion. Residual organic damage to the central nervous system is a disorder of the brain or spinal cord that occurred while the child was still in the womb (at least 154 days from the date of conception) or within a week after his birth.
Mechanism of damage
One of all the “inconsistencies” of the disease is the fact that a disorder of this type belongs to neuropathology, but its symptoms may relate to other branches of medicine.
Due to an external factor, the mother experiences disruptions in the formation of the phenotype of cells that are responsible for the full list of functions of the central nervous system. As a result, fetal development is delayed. It is this process that can become the last link on the path to central nervous system disorders.
Regarding the spinal cord (this is also part of the central nervous system), corresponding lesions can appear as a result of incorrect obstetric care or inaccurate turns of the head when delivering the child.
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system
Infectious diseases of the central nervous system are among the most common neurological pathologies. CNS diseases caused by infection are very dangerous. They have a severe course, leave serious consequences and significant neurological deficits. Infectious diseases of the central nervous system can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungal diseases. Most often, diseases develop when meningococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, ECHO and Coxsackie enteroviruses, mumps, and candida enter the body. The entry gates for infection are the ENT organs; it is also transmitted by contact, hematogenous, lymphogenous, and perineural routes.
The infection can affect the nervous system as a primary disease or occur secondarily as a result of the development of an infectious process outside the central nervous system. Infectious diseases of the central nervous system include:
- meningitis,
- encephalitis,
- polio,
- syphilis of the nervous system,
- toxoplasmosis of the nervous system,
- neurological manifestations of HIV infection,
- parasitic diseases of the nervous system.
Causes and risk factors
The perinatal period can also be called a “fragile period”, because during this time literally any unfavorable factor can cause the development of defects in the central nervous system of the infant or fetus.
For example, medical practice has cases that show that organic damage to the central nervous system is caused by the following reasons:
- hereditary diseases that are characterized by chromosome pathology;
- diseases of the expectant mother;
- violation of the birth calendar (long and difficult labor, premature birth);
- development of pathology during pregnancy;
- poor nutrition, lack of vitamins;
- environmental factors;
- taking medications during pregnancy;
- stress of the mother during pregnancy;
- asphyxia during childbirth;
- uterine atony;
- infectious diseases (and during lactation);
- immaturity of a pregnant girl.
In addition, the development of pathological changes can be influenced by the use of various dietary supplements or sports nutrition. Their composition can have a detrimental effect on a person with certain characteristics of the body.
The main reasons for the development of organic lesions are:
— Brain damage during pregnancy or during childbirth — Open and closed head injuries — Meningitis, abscess, encephalitis, arachnoiditis and other infectious diseases. - Abuse of alcohol, drugs, nicotine. — Ischemic stroke, encephalopathy, hemorrhagic stroke and other vascular diseases of the brain. — Tumors — Multiple sclerosis — Parkinson’s disease — Alzheimer’s disease
The vast majority of cases of organic brain damage occur due to the fault of the patient himself. For example, damage can be caused by intoxication or improper treatment of infectious diseases.
Classification of CNS lesions
Perinatal damage to the central nervous system is divided into several types:
- Hypoxic-ischemic . Characterized by internal or postnatal lesions of the brain. Appears as a result of chronic asphyxia. Simply put, the main cause of such damage is oxygen deficiency in the fetal body (hypoxia).
- Traumatic . This is a type of injury that occurs to a newborn during childbirth.
- Hypoxic-traumatic . This is a combination of oxygen deficiency with injury to the spinal cord and cervical spine.
- Hypoxic-hemorrhagic . Such damage is characterized by trauma during childbirth, accompanied by a failure of blood circulation in the brain with subsequent hemorrhages.
Our help
Specialists from the Department of Developmental Neurobiology of the Research Institute of Pediatrics and Health Protection of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences work on the basis of the CDC:
- Diagnosis, observation and treatment are carried out by experienced neurologists, candidates of medical sciences with 20 years of experience working with this problem. Our specialists are the authors of the book “Modern neurobiological aspects of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system”, published by the publishing house of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
- Defectologists and clinical psychologists are involved in the diagnosis, who help clarify the presence of developmental disorders. Development assessment is carried out using unified development tables.
- If necessary, children can receive specialized therapeutic, correctional, developmental classes with early development specialists, aimed at stimulating sensory, visual, auditory, tactile, and coordination functions.
- There is the possibility of comprehensive monitoring of children with perinatal damage to the central nervous system with the involvement of qualified specialists, candidates of medical sciences.
- Accompaniment by an experienced pediatrician who will answer all questions about care, nutrition, prevention of rickets and ARVI, and hardening.
- Vaccine prevention department: consultation with a vaccinologist-immunologist in order to draw up an individual vaccination calendar and direct vaccination under his supervision.
- Involvement of any other pediatric specialists, including orthopedists and ophthalmologists.
Symptoms depending on severity
In children, residual organic damage is difficult to see with the naked eye, but an experienced neurologist, already at the first examination of the baby, will be able to determine the external signs of the disease.
Often this is an involuntary trembling of the chin and arms, a restless state of the baby, a syndrome of tone disorders (lack of tension in the skeletal muscles).
And, if the damage is severe, it can manifest itself as neurological symptoms:
- paralysis of any limb;
- disturbance of eye movements;
- reflex failures;
- loss of vision.
In some cases, symptoms can only be noticed after undergoing certain diagnostic procedures. This feature is called the silent course of the disease.
General symptoms of residual organic damage to the central nervous system:
- unreasonable fatigue;
- irritability;
- aggression;
- mental instability;
- changeable mood;
- decreased intellectual abilities;
- constant mental anxiety;
- inhibition of actions;
- pronounced absent-mindedness.
In addition, the patient is characterized by symptoms of mental infantilism, brain dysfunction and personality disorders. As the disease progresses, the set of symptoms can be replenished with new pathologies, which, if left untreated, can lead to disability and, in the worst case, death.
Clinical manifestations of CNS PP
- Nervous system excitability syndrome: excessive and multiple movements, tremor of the chin, tongue, limbs, regurgitation, sleep disturbances (excessive wakefulness), spontaneous Moro reflex (spreading of arms in a supine position)
- Nervous system depression syndrome: decreased spontaneous motor activity, short-term wakefulness, excessive sleep, weakness of the sucking reflex, insufficient emotional response when interacting with the child.
- Autonomic-visceral dysfunction syndrome: thermoregulation disorders, transient cyanosis, disturbances in heart rate and respiratory rhythm, marbling of the skin, hypothermia of the extremities, vegetative-vascular spots on the skin, regurgitation, vomiting, unstable stool.
- Intracranial hypertension syndrome, hydrocephalic syndrome: excessive growth of head circumference, bulging of the fontanelle, throwing the head back, loud monotonous crying (brain scream), throwing the head back up to the arching of the body (opisthotonus), persistent vomiting and regurgitation not associated with food intake, increased sensitivity to sound stimuli (hyperesthesia), spontaneous bulging of the eyes (Graefe syndrome), difficulty falling asleep (wants to sleep, but cannot fall asleep), short-term and superficial sleep, excitability.
- Convulsive syndrome: various sudden and repeated contractions of the eyelids, facial muscles, abduction of the eyes, paroxysmal chewing, swallowing, sucking, protruding the tongue, swimming movements of the arms, pedaling, tonic tension of the trunk or limbs, single or group twitching of the muscles of the limbs, accompanied by convulsive eye movements or “stopping” the gaze, apnea.
- Dysregulation of muscle tone (muscle dystonia) increased, decreased, mixed muscle tone in the limbs, range of motion in the joints, spontaneous posture in sleep and wakefulness, position of the hands and feet, support during verticalization, position of the head during traction (pulling) by the handles.
Necessary set of measures
It is no secret that diseases of this degree of danger are difficult to cure using single methods. And even more so, to eliminate residual organic damage to the central nervous system, it is even more necessary to prescribe complex treatment. Even with a combination of several therapy methods, the recovery process will take quite a long time.
To select the correct complex, you must strictly consult your doctor. Typically, the prescribed therapy includes the following set of measures.
Treatment with various medications:
- sedatives;
- psychotropic drugs;
- nootropics;
- antipsychotics;
- vitamins and minerals to improve brain function.
External correction (treatment with external stimulation):
- massage;
- treatment with special loads (kinesitherapy);
- physiotherapy (laser therapy, myostimulation, electrophoresis, etc.);
- reflexology and acupuncture.
Neurocorrection methods
Neurocorrection is a psychological technique that is used to restore impaired and lost functions of the brain.
If there are speech defects or neuropsychic disorders, specialists involve a psychologist or speech therapist in treatment. And in case of manifestation of dementia, it is recommended to seek help from teachers of educational institutions.
In addition, the patient is registered with a neurologist. He must undergo regular examination by the doctor who is treating him. The doctor may prescribe new medications and other therapeutic measures as the need arises. Depending on the severity of the disease, the patient may require constant monitoring by family and friends.
We emphasize that treatment of residual organic damage to the central nervous system during the period of acute manifestation is carried out only in a hospital setting, and only under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Remember! Timely treatment of organic damage to the central nervous system can stop the development of complications, reduce the consequences of the disease, eliminate symptoms and completely rehabilitate the human nervous system.
Treatment of organic pathology and mental disorders
First of all, the cause of organic pathology should be established. Treatment tactics will depend on this.
In case of infectious pathology, antibiotics sensitive to the pathogen should be prescribed. For viral infections - antiviral drugs and immunostimulants. For hemorrhagic strokes, surgical removal of the hematoma is indicated, and for ischemic strokes, decongestant, vascular, nootropic, and anticoagulant therapy is indicated. For Parkinson's disease, specific therapy is prescribed - levodopa-containing drugs, amantadine, etc.
Correction of mental disorders can be medicinal and non-medicinal. The best effect is shown by a combination of both methods. Drug therapy includes the prescription of nootropic (piracetam) and cerebroprotective (citicoline) drugs, as well as tranquilizers (lorazepam, tofisopam) and antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine). To correct sleep disturbances, hypnotics (bromizoval, phenobarbital) are used.
Psychotherapy plays an important role in treatment. Hypnosis, auto-training, Gestalt therapy, psychoanalysis, and art therapy have proven themselves well. This is especially important when treating children due to possible side effects of drug therapy.
Rehabilitation is all in the hands of the mother and doctors
Rehabilitation measures for this disease, as well as for its treatment, should be prescribed by the attending physician. They are aimed at eliminating existing complications in accordance with the patient’s age.
For remaining movement disorders, physical methods are usually prescribed. First of all, it is recommended to do therapeutic exercises, the main idea of which will be aimed at “revitalizing” the affected areas. Additionally, physical therapy relieves swelling of nerve tissue and restores muscle tone.
Mental development delays are eliminated with the help of special drugs that have a nootropic effect. In addition to the pills, they also conduct classes with a speech therapist.
Anticonvulsants are used to reduce the activity of epilepsy. The dosage and the drug itself must be prescribed by the attending physician.
Increased intracranial pressure should be eliminated by constant monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid. Pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed that increase and accelerate its outflow.
It is very important to eradicate the disease at the first alarm bells. This will enable the person to lead a normal life in the future.
How is PCNSL treated?
To restore the basic functions of the central nervous system, as well as to reduce the manifestation of neurological symptoms, the baby is prescribed a whole range of medications. Treatment can include, for example, nootropic drugs that can restore trophic processes in the brain - piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Cortexin, pantocalcin, solcoseryl and many others. In order to stimulate general reactivity, a newborn child is given a course of therapeutic massage, special gymnastics, and, if necessary, a set of physiotherapeutic procedures (for example, electrophoresis and microcurrents).
If parents detect at least one of the signs of central nervous system damage, they should immediately consult a doctor. Do not forget that the development of each child is an individual process. Such individual characteristics of a newborn child in each specific case play an important role in the process of restoring the functions of higher nervous activity.
Complications, consequences and prognosis
According to the experience of doctors, organic damage to the central nervous system in children can cause the following consequences:
- mental development disorders;
- speech defects;
- delayed speech development;
- lack of self-control;
- hysterical attacks;
- disruption of the normal development of the brain;
- post-traumatic stress disorder;
- epilepsy attacks;
- vegetative-visceral syndrome;
- neurotic disorders;
- neurasthenia.
In children, quite often such disorders affect adaptation to environmental conditions, manifestations of hyperactivity or, on the contrary, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Today, the diagnosis of “residual organic damage to the central nervous system” is made quite often. For this reason, doctors are trying to improve their diagnostic and treatment abilities.
The exact characteristics and features of a certain type of lesion make it possible to calculate the further development of the disease and prevent it. In the best case, suspicion of the disease can be completely removed.
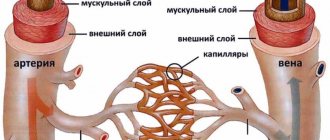
Vascular diseases of the central nervous system
Poor circulation in the brain provokes the development of vascular diseases of the central nervous system. These pathologies are extremely dangerous because in most cases they lead to disability. Also, vascular diseases of the central nervous system have a high mortality rate. Brain damage occurs as a result of ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, transient ischemic attacks, and spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhages. The causes of such pathologies are:
- aneurysms,
- thromboembolism,
- vascular atherosclerosis,
- hypertonic disease,
- acute toxic damage to the walls of blood vessels,
- chronic degenerative diseases of the walls of blood vessels.
The trigger for the development of strokes can be severe stress, seizures, alcohol intoxication, and sudden changes in body temperature. Vascular disease of the central nervous system most often occurs spontaneously and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures must be comprehensive. Drug therapy is complemented by lifestyle correction. It is necessary to normalize the daily routine, alternating work and rest, sufficient time in the fresh air, and moderate physical activity. Physiotherapy and sanatorium-resort treatment are recommended, and sometimes psychotherapy is indicated. Medicines are prescribed taking into account the existing symptoms:
- cephalalgia: analgesics and NSAIDs;
- migraine: medications from the triptan group;
- dizziness: betaserc;
- insomnia, psychoemotional disorders: adaptogens, sleeping pills, antidepressants;
- intracranial hypertension: diuretics.
How to treat RE is determined individually. Patients are prescribed nootropics and nerometabolites. Children, along with symptomatic therapy, are given classes with a psychologist and a defectologist. The most important role is played by the participation of parents who support the baby and regularly work with him.
The forecast for the future is quite favorable. In most cases, with adequate complex therapy, it is possible to achieve the disappearance or significant reduction of symptoms. Patients lead normal lives: they study various professions, work, and build families. In severe cases, residual effects may persist, mainly headaches and autonomic disorders.
To make an appointment, just call tel. 8(969)060-93-93.