Diagnosis of the inflammatory process
How easy it is to recover from the disease will depend on the timeliness and correctness of complex therapy.
The incubation period of the disease is 1-3 weeks. Basic diagnostic methods:
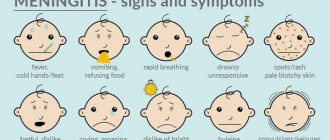
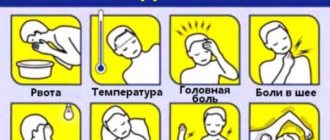
- The presence of muscle rigidity in the occipital region, a feverish state, attacks of unbearable headaches are symptoms of meningitis.
- A set of studies to determine the form of the disease.
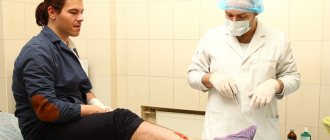
- Puncture of cerebrospinal fluid (protein level, sugar level, culture).
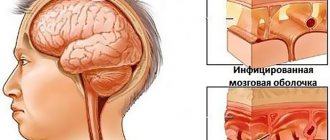
Non-infectious meningeal infection is diagnosed when the level of leukocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid is elevated, but the disease is not complicated by other pathogens. If a cystic formation in the brain is suspected, the patient is prescribed a CT or MRI.
Analysis determining the level of protein, sugar and culture
Treatment
Because acute bacterial meningitis can cause permanent brain damage, nerve damage, or death within hours, treatment should begin as quickly as possible without waiting for the results of diagnostic tests.
Mild meningitis with minor symptoms is usually caused by viruses and, with symptomatic treatment, goes away on its own within 7-10 days. For moderate and severe meningitis, the patient is hospitalized and antibiotics are prescribed. The drugs of choice at the first stage are penicillins and cephalosporins. If the results of the study reveal a bacteria resistant to the antibiotic, the drug is changed. If a herpes simplex virus is detected, an antiviral drug is prescribed. For other viruses, etiological (that is, directly affecting the pathogen) treatment has not been developed.
The antibiotic is discontinued when:
- clinical recovery;
- normalization of general blood count and cerebrospinal fluid indicators7.
In addition to antibiotics, the patient also receives corticosteroids (dexamethasone) to reduce cerebral edema and intracranial pressure, infusion and symptomatic therapy.
Prevention
There are two methods of prevention: following doctor's recommendations and vaccination. General tips:
- Eat healthy and balanced.
- Take vitamins (especially during an epidemic of infectious diseases).
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Use local antiviral agents during acute respiratory infections epidemic.
- Treat inflammatory pathologies in a timely manner.
- If the first signs of infection appear, consult a doctor immediately.
For purulent or viral meningitis, doctors use the meningococcal vaccine (during an epidemic), vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae B.
Is it possible to get a secondary infection and what are the ways of transmitting the virus?
Note! You cannot become infected with secondary meningitis, which is the result of other diseases, traumatic brain injuries, or taking certain medications.
Primary meningitis, which is the result of viral and bacterial infections, can be transmitted in the following ways:
- Hematogenous (through the blood) - viruses and bacteria penetrate through blood vessels from the initial source of infection. In this way, infection with enterovirus, pneumococcal and meningococcal, tuberculous meningitis can occur.
- Transplacental - infection of a child in the womb from the mother. Most often, infection with the meningococcal type occurs this way.
- Fecal-oral – infection occurs due to lack of hygiene, dirty hands, living together and using common hygiene items with an infected person. Adenoviral, enteroviral meningitis and lymphocytic choriomeningitis are transmitted in this way.
- Airborne is the most common method of infection. Occurs due to the release of infections, viruses and bacteria during talking, sneezing and coughing of a sick person. Enterovirus, tuberculosis, meningococcal, adenovirus and meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae are transmitted in this way.
Who is at risk?
A key factor contributing to the onset of meningitis is a weak immune system. It is the body’s defense against various infections. Human immunity becomes weak due to:
- previously suffered infectious diseases (respiratory, pneumonia, pharyngitis, influenza, sore throat),
- chronic pathologies, especially syphilis, HIV, tuberculosis, liver cirrhosis, severe stress,
- vitamin deficiency and strict diets,
- head and back injuries,
- total hypothermia of the body,
- alcohol and drug abuse,
- long-term use of tablets with non-compliance with recommendations.
All this can cause infection in a person, as the body becomes weak.
Prevention: what to do to avoid catching the disease during an epidemic?
To date, several types of vaccines have been developed that can prevent infection by certain viruses and bacteria. First of all, such vaccination is recommended for children and those who travel to areas where outbreaks of the disease have been recorded.
It is always necessary to observe basic hygiene rules - use a separate towel, toothbrush, and wash your hands frequently. If there is a person with meningitis in the house, he should be isolated as much as possible from healthy family members. Close contact with the patient should be limited.
Advice! To prevent the spread of epidemics, it is necessary to frequently ventilate rooms where large numbers of people gather (schools, barracks, large offices) and carry out systematic wet cleaning there.
- Where to treat arthrosis of the knee joints in Chelyabinsk?
Tuberculous form of meningitis
You can become infected with the tuberculosis form only if there are bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in the body. If tuberculosis has not been completely cured, the risk of developing a secondary meningitis infection increases. Using contaminated water, eating poorly processed food, and contacting the blood of a carrier of tuberculosis bacteria are possible ways of transmitting meningitis.
Rodent excrement is also dangerous. The open form of tuberculosis is contagious and is easily transmitted by air and droplets or through household objects.
Types of meningeal infection
There are primary and secondary forms of pathology. The first type is an independent disease, transmitted from a sick person to other people. The secondary form is a complication of other diseases, in most cases it is not dangerous to others.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the syndrome occurs:
- Bacterial.
- Viral.
- Parasitic.
- Fungal.
- Non-infectious.
It is impossible to determine exactly why meningitis develops. There are a huge number of irritating factors. In case of primary infection, the cause of the inflammatory process will be the penetration of a foreign agent into the human body: bacteria, viruses, for which the shells of the “gray matter” are the optimal habitat.
Types of infection
Bacterial meningeal infection
Patients suffering from this form of pathology are contagious. The infection is transmitted by airborne droplets. Compared to the viral form of the disease, the bacterial type of the disease does not pose a serious threat to a healthy person - the risk of infection is not so great.
Some healthy people have microbes in the nasopharynx - they are carriers of meningococcal infection. But they themselves cannot get sick.
Main risk groups:
- age – according to statistics, children get sick more often than adults;
- working in a large team - bacteria spread in entire groups;
- weak immune system – the body cannot resist infection;
- profession – people interact with pathogens that provoke the development of the disease;
- trips abroad (especially to Asian and African countries).
It is possible to become infected with bacterial meningitis from a patient, but only if one of the risk factors is present. Timely treatment of the inflammatory process is the key to a quick recovery.
Meningeal viral infection
The aseptic type of illness is a contagious pathology that can be caused by various viruses. Namely:
- Adenoviruses.
- Enteroviruses.
- Herpes virus.
- The causative agent of such a disease as mumps.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the viral form can be transmitted in various ways. How you can get meningitis:
- Where to treat arthrosis in Samara?
- aerosol or airborne method;
- in direct contact with a carrier of infection;
- by water (the peak of the disease may occur at the height of the swimming season);
- by transmission through insects;
- vertically (from mother to unborn child).
Not only adults, but also children can become infected with this form of meningitis. People with weak immune systems are more likely to get the disease and it is more severe. When in contact with an infected person, healthy people can pick up the infection, but only get the flu.
Virus infection occurs when the immune system is weakened
Parasitic meningeal infection
The inflammatory process of the membranes of the “gray matter” can be caused by Naegleria Fowler, a parasite. Routes of infection:
- Polluted swimming pools.
- Lakes and rivers.
- Geothermal (hot) springs.
- Water heaters.
First, bacteria enter the human body through the nasopharynx, then into the brain. Whether parasitic meningitis is contagious or not depends on the frequency of contact with the carrier and the state of immunity.
Gray matter is affected
Fungal meningeal form
This type of inflammatory process is one of the rarest, but anyone with a weak immune system can become infected. The inflammatory process is triggered by a cryptococcal infection that lives in African countries. It penetrates into the blood plasma and then into the brain, causing disease.
Primary risk factors:
- people with HIV infection;
- long-term treatment with medications that suppress the immune system as a result of taking hormones;
- chemotherapy treatment.
Fungal meningitis is contagious - yes, if it is a consequence of fungal pathology. That is, you can contact a sick person without fear. But treatment of the disease must be started in a timely manner to prevent the development of serious consequences for the patient.
Non-infectious form of meningitis
With this disease, as with a fungal infection, infection is impossible. Provoking factors are:
- Oncological pathologies.
- TBI of varying severity.
- Brain surgeries.
- Taking certain medications.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Regardless of the form of the disease, it is dangerous for people. You should maintain personal hygiene, wash your hands, disinfect contaminated surfaces - all this will help protect yourself and prevent the development of meningitis.
- Treatment of diseases of the joints and spine
Any form of the disease is dangerous for people.
Causes of the disease
The main causes of meningitis in children, symptoms and signs, lie in various infectious pathogens. The types of disease differ from each other depending on the sources:
- Bacterial. Often the disease is provoked by microbes, in particular, we are talking about staphylococcus, streptococcus, meningococcus, and E. coli.
- Viral. People suffering from meningitis often have herpes, mumps, and influenza viruses.
- Candida. Occurs due to candida and critococci.
- Simple microbes. These include amoebas and toxoplasma.
In a separate group, diseases of a combined form appear. In this situation, the disease appears due to several different pathogens.