Drugs are a modern problem for the entire society. Due to poor information awareness of people, it is growing every day. Many are convinced that just one drug try will not change anything in their life. To become addicted, you need to use drugs for a very long time. And also the idea that everyone can recognize a disease in themselves and quickly get rid of it on their own.
This is the catch of drug addiction. Addiction occurs after the first use and there is no need to create other beliefs for yourself. You always want to make pleasure last long. But the high doesn’t last forever, it needs to be extended. This is how psychological and physical dependence occurs.
There is no stereotypical pattern for the onset of drug addiction. But experts distinguish three stages of drug addiction.
Definition of drug addiction and addiction
According to the definition of the World Health Organization (hereinafter referred to as WHO), since 1957, drug addiction has been defined as a state of periodic or chronic intoxication, which is provoked by the cyclic use of drugs of natural or synthetic origin.
Among the signs that characterize drug addiction are the following:
- An uncontrollable desire and obsessive desire to continue to use drugs and obtain them by any means;
- Loss of quantitative control of consumption, increase in consumed doses (development of tolerance);
- Development of symptoms of mental and physical dependence on the action (effect) of drugs;
- Dangerous consequences of drug addiction both for the drug addict himself and for society.
Since 1964, the WHO also introduced the concept of drug addiction : addiction can be both mental and physical (somatic) in nature. Based on the definition, the main types of drug addiction are usually:
- Opium addiction;
- Stimulant addiction;
- Dependence on tranquilizers;
- Cannabinoid addiction;
- Hallucinogenic addiction;
- Dependence on volatile solvents;
- Alcohol addiction;
- Nicotine addiction.
Up
When did drug addiction start?
The first cases of drug addiction appeared at the beginning of the 19th century
, when opium and hashish were first brought to Europe.
These substances were first used as painkillers. But by the beginning of the 20th century, in certain circles of society - mainly bohemians - opium and hashish addiction became a serious problem. The second coming of fashion for drug use occurred in the 60s of the 20th century
with the advent of informal youth movements. Drugs then became a symbol of freedom and self-expression. It was from that time that the number of drug addicts around the world began to grow rapidly. According to the chief narcologist of the Russian Ministry of Health and Social Development, Evgeniy Bryun, the growth of drug addiction in the territory of the former Soviet Union began around 1982, when a drug supply channel from Afghanistan opened. And since then, the number of drug addicts has only grown.
Reasons for drug use
The attraction to drugs initially precedes the development of drug addiction and in some cases manifests itself in the form of a simple interest in the opportunity to escape from the harsh realities of everyday life and become intoxicated. At the same time, the reasons for drug use can be different circumstances - from physiological discomfort (illness, pain, insomnia) to difficult or complex responsibilities.
As a rule, the initial factors for drug use are typically “internal” reasons: constant interpersonal troubles and confrontations of an ambivalent nature, from which you want to escape or drown out with drugs, then loneliness, depression and a complete loss of the meaning of life. Thanks to drugs, you can temporarily achieve a feeling of illusory emotional comfort, elevating your mood without really improving the situation or changing circumstances. Discomfort and intolerance from such “muffled” situations are de-actualized for some time but do not go away. Later it becomes even heavier. There is an uncontrollable desire for constant and periodic drug use (addiction), even greater dependence and inability to live without drugs. There is always an obvious self-destructive pattern in the addict's behavior. In this regard, drug addiction is secretly called prolonged suicide , and drug intoxication, euphoria and being “high” are the beginning of the end. Some drug addicts die as suicides, others expose themselves to complete physical or social destruction. At the same time, all suicidal fantasies, like the act of suicide itself, act as a tool for escaping from terrible reality, in the hope that after death all suffering will end.
Up
What is a buzz?
A high is a state of joyful intoxication, euphoria. It is usually triggered by changes in the neurochemical balance in the brain. A number of substances replace the so-called happiness hormones - the effect can be compared with the joy that we experience naturally. But at the same time, the psyche’s own resources are depleted with each episode of use. An increase in the number of receptors affected by dopamine leads to the need to increase the dose of the substance.
The high or state of drug intoxication can vary. Each substance acts specifically. Many substances relieve physical pain, but also lead to loss of self-control. A person loses his sense of reality, it may seem to him that he is floating through the air. Some drugs consist of the activation of all processes, the appearance of a surge of strength and vigor, others, on the contrary, give a feeling of bliss and calm satisfaction.
Factors in the development of drug addiction
Drug addiction and addiction arise under the general influence of such factors as the actualization of difficulties and conflicts with a tendency to protect against them and avoid them, personality changes that increase, perhaps, on the basis of a hereditarily determined personality structure.
The addictive behavior of a drug addict in its essence always has a neurotic character . From a psychodynamic point of view, drug addiction is considered as a replacement for an inferior sex life (according to Freud) or as an aggression on the oral level of development, which was not completed in a normal, natural way. With drug addiction on the side of the satisfying object, there is a failure to exclude oral needs. From a biographical point of view, bad habits are certainly present in childhood. From early childhood, the child was not taught the need to control her desires, and her tolerance to frustration (a special emotional state that occurs when a person is faced with any problems) is inferior. At the same time, excessive maternal control and guardianship may be a consequence of overcompensation of the desire to get rid of the child.
Attraction to psychoactive substances, in particular to drugs, is a unique form of drug addiction and its prototype regarding self-destructive tendencies. The harmful effects of drugs on the body are added to the habitual drug craving, as part of the neurotic-destructive process. Therefore, such attraction is defined as a disease of a mental or physiological (somatic) nature. When studying and considering drug addiction as a disease, knowledge in the field of the etiology of neuroses, psychopharmacology, as well as the toxicology of organic brain lesions or symptomatic psychoses is always used.
Narcotic drugs include drugs and drugs that change the state (usually reducing activity rather than stimulating), cause euphoria (pleasant feeling, bliss) or change the ability to sense and experience. When a person has received a pleasant sensation at least once, he will certainly try to get it again. However, other signs and effects of narcotic drugs and medications may differ from each other. Pharmacological agents that do not cause any narcotic effects (for example, antipsychotics and antidepressants) do not belong to the category of drugs.
Up
Why does a person start using drugs?
An attempt to normalize the emotional state. Addiction is based on a psychological problem. Often a person is not aware of it. Chemical doping quickly solves the problem of internal dissatisfaction and chronic discomfort.
Curiosity. Teenagers try illegal substances to experience an unusual state. 10% of people in Russia have taken drugs at least once, and in St. Petersburg this figure reaches 30%. Not every person becomes addicted after a single dose. But many types of drugs cause intense cravings after the first dose.
The influence of the environment. If friends or relatives are addicts, the likelihood of using is very high. Man is a social being. He adapts to the environment and adopts the behavior patterns of others. Therefore, to prevent drug addiction, as well as during treatment, it is necessary to isolate the patient from other addicts.
Mechanism of drug addiction development
In order to understand how drug addiction develops, one cannot ignore the diagnosis of the state of drug intoxication: “...enrichment, which makes it possible to experience life, then joining the flow of life, then pleasure in possibilities, which cannot be known in all its greatness and infinity ..." (Gebsattel), while a fundamentally sober person who lives and respects the established order, in the eyes of the one who seeks intoxication, is doomed to a miserable, impoverished existence and shackled by primitive principles that do not allow him to deviate from the right path, leaving a meager number of opportunities for the disclosure and fullness of sensations.
Expansion of consciousness and enrichment of life are the main arguments used to defend the use of drugs and their euphoric effect; this state for a normal person in a sober state is at least indifferent, if not burdensome. These arguments are difficult to criticize using purely pharmacological or psychotherapeutic arguments. Even though drug intoxication can give a person many positive feelings and experiences, it always carries with it a great risk for real life. Drug addiction entails the loss of free will, and the loss of health forces a person to resort to the services of narcologists.
Substance abuse in some cases can begin under the influence of trivial circumstances:
- performance of public duties (constant alcoholic feasts);
- trials and boasting among teenagers (first attempts at smoking or taking a drug);
- accidental use of medications found in parents' easily accessible first aid kits.
Insomnia is overcome by using drugs with a sedative effect, and in case of painful sensations, large doses of painkillers are recklessly prescribed, nervousness is usually treated with tranquilizers, and in the postoperative period, opiates are used for too long or in large doses. However, often the causes of drug addiction are difficult life situations, conflicts and neurotic crises.
Repeated use of drugs certainly leads to addiction , which is expressed in psychophysical processes: addiction is both a mental and physiological process. Mental addiction is the start of drug-addictive behavior ; Narcotization (the process of drug use) leads to addiction when a certain ritual associated with taking narcotic drugs develops. When the process of drug taking becomes systematic, the mechanism of chronic abuse is triggered.
At the same time, physical dependence caused by objective pharmacological processes is added to the general picture of the early development of drug addiction. Against this background, dispositional addiction stands out, in which the induction of enzymes entails an increase in tolerance, and then clinical addiction, the essence of which lies in a decrease in the reaction of target organs affected by drugs. As a result, drug addicts constantly increase their doses of the drug. Thus, finally plunging into the stage of dependence.
The development of mental dependence is caused by the inability to stop drug use. Changing habitual behavior immediately gives rise to fear and uncertainty. After all, the habits established by a drug addict are very difficult to overcome. An uncontrollable attraction to drug addiction prevails here.
Physical dependence manifests itself in the occurrence of drug withdrawal symptoms at the first attempt to stop or at least reduce use. Such significant psychophysical disturbances force the addict to take drugs more and more. Therefore, drug addiction should be understood as a dangerous and progressive process, from which it is almost impossible to get out of it on your own.
Since the addictive potential of individual types of drugs differs significantly, it determines the difference between addiction and abuse without dependence.
Since the drug, as a rule, affects the functioning of the central nervous system, it directly provokes mental disorders (in particular, a decrease in criticism and motivation), which significantly complicates all therapeutic actions of doctors at this stage of the disease. Hence the need for prevention in the early stages of drug addiction development arises.
In addition to the above, it should be mentioned that sometimes the use of narcotic substances is combined with the use of a significant amount of medications with psychopharmacological effects, which several times exceed the permissible therapeutic doses. This phenomenon is defined as a phenomenon called “toptolerantity” (“TT”).
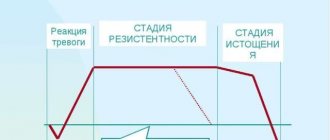
There are many different theories that try to explain the progressive development of drug addiction. Even the most popular and most recent of these theories have a number of significant shortcomings. However, based on numerous studies in the field of addiction, it can be assumed that the development of drug dependence syndrome associated with the use of psychoactive substances (drugs) in most people occurs during 3 main stages of drug addiction development:
- Stage of mental attraction to a drug;
- Drug addiction stage - syndrome of physical dependence on drugs;
- Stage of development of somatic disorders (pathologies).
Up
Benefits of inpatient drug addiction treatment
Treatment of drug addiction in a hospital setting has many advantages:
- The patient is in the hospital under the constant supervision of narcologists and medical personnel, which guarantees prompt provision of medical care.
- Favorable living conditions, comfortable rooms.
- Inability to purchase drugs and interrupt treatment
- Individual approach to treatment
- Guaranteed 100% anonymity
- Free psychotherapy during hospital stay
- Modern equipment and effective medications
Affordable prices, special offers and discounts About drug addiction and the levels of its formation, about drug and psychotherapeutic treatment of drug addiction, about the stages of opioid addiction will be discussed later in this section.
The first stage of drug addiction is mental dependence on drugs
Mental craving for drugs is manifested, first of all, by the emergence of a syndrome of mental dependence and a gradual decrease in the strength of its action with periodic use.
Mental dependence is a conscious or subconscious need to use drugs as a means of relieving mental stress or achieving a psychologically comfortable state.
In narcology, there are two types of mental dependence on drugs:
- Positive type - the drug is used with the aim of achieving objectively pleasant sensations (high, vigor, burst of energy, good mood);
- Negative type - anesthesia is necessary to relieve negative feelings (bad mood or well-being);
Refusal to use a drug or the inability to take it due to any circumstances is accompanied by changes in mood, as well as the manifestation of depressive-dysphoric conditions. The desire to use a narcotic substance becomes persistent and obsessive.
The positive type of drug addiction manifests itself exclusively at the first stage of drug addiction development.
The first stage of drug addiction is also commonly called neurosthenic , since in addition to sleep and mood disorders characteristic of asthenia, excessive irritability, nervousness, fatigue, distracted attention, hypertension (increased AT), and mild other mental and body disorders are observed.
In addition, the initial stage of drug addiction, as well as the entire period of its development, is characterized by an increase in tolerance, the body’s tolerance to constantly increasing doses of drugs . That is why drug addicts with each use, in order to achieve the desired “high,” are forced to constantly increase the amount of drug administered.
Up
Interest is the first stage of drug addiction
Interest and curiosity are the first emotions that an addict experiences in relation to a drug. This is why young people and teenagers often become victims of drug addiction.
Interest can be called not only curiosity regarding the immediate effect of use. Many people try the substance for company or under the influence of persuasion from older and more experienced comrades, they strive to keep up with the team.
In adulthood, people approach the start of use somewhat more consciously. Interest can stimulate the need to cheer up or cope with impressive workloads. Very often, people who occupy a leadership position or manage an entire enterprise begin to use drugs - they seek to relieve excess psychological stress or set themselves tasks that are mentally unbearable, as a result of which they need stimulants.
The results obtained can satisfy and act as an incentive to use more and more - this is how addiction is formed.
The second stage of drug addiction is physical dependence on drugs.
A characteristic sign of the development of the second stage of drug addiction is the development of physical dependence on drugs . Physical dependence should be understood as an adaptive state that manifests itself in intense physical disorders. With physical dependence, the drug addict’s body adapts to the constant use of drugs , which seem to “grow” into the natural metabolism of the human body. Refusal from further drug use at the early stage of drug addiction certainly leads to various painful physiological disorders, which are collectively called a manifestation of drug withdrawal syndrome.
Up
Treatment prices:
| Sign up for a free and anonymous consultation with a narcologist | 0 ₽ |
| Initial consultation with a narcologist | for free |
| Consultation with a psychologist in person or Skype | 3 000 ₽ |
| Psychiatrist consultation | 5 000 ₽ |
| Psychodiagnostics / pathological diagnostics | 7 500 ₽ |
| Narcopsychotherapy | 50 000 ₽ |
| Consultation with a psychologist and selection of a treatment and rehabilitation program for an addict | for free |
| Intervention session | 12 000 ₽ |
| Social rehabilitation of alcohol addicts | for free |
| Outpatient rehabilitation in Moscow | 33 000 ₽ |
| Standard rehabilitation program | 40 000 ₽ |
| Intensive rehabilitation program | 80 000 ₽ |
| Premium rehabilitation program | 120 000 ₽ |
| Medical and social rehabilitation (21 days) | 150 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation Spain, Bulgaria | 200 000 ₽ |
| VIP rehabilitation program | 350 000 ₽ |
| Online addiction rehabilitation course | 28 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation of age-related alcohol addicts | 50 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation of drug addicts | 60 000 ₽ |
| Adolescent social-psychological-pedagogical rehabilitation | 70 000 ₽ |
| Psychotherapy | 5 000 ₽ |
| Family psychotherapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Support groups for loved ones of addicts | for free |
| Webinars for relatives of addicts | for free |
| School for codependents | 3 000 ₽ |
| Transfer support | negotiable |
| Motivation for treatment | 6 000 ₽ |
| Escort to the clinic | 6 000 ₽ |
| Testing (urine/blood/hair) | specify |
Expand
Still have questions? Call us!
8
Free consultation and appointment
Withdrawal syndrome in drug addiction
Withdrawal syndrome in drug addiction is a complex of psychopathological, autonomic, neurological and somatic disorders, the main characteristics of which (duration of development, features of the course) completely depend on the type of drugs used, the frequency, quantity and intensity of anesthesia, as well as the psycho-physical individual characteristics of the body.
Withdrawal syndrome in drug addiction is characterized by the following clinical and psychopathological manifestations and symptoms:
- Loss of functions . This phenomenon is usually observed in the form of symptoms of severe muscle weakness after sleep in drug addicts who abuse sleeping pills or tranquilizers (especially with Noxiron addiction, when the addict has difficulty getting up, sitting down or getting dressed). Before the compensatory process is activated to the required extent, the unidirectional function takes on all excessive loads, thus causing tachycardia.
- Compensation for missing functions . The methods of such compensation are extremely varied. Firstly, due to the fact that any function-process includes several interconnected areas of work, each of which is capable of taking on the main emphasis of the load. Secondly, drugs that are similar in their effects can interfere with the implementation of a particular function in different ways and in different areas. Therefore, the ways of compensation for certain forms of drug addiction may be different. All these moments of compensation should give different expressions of symptoms when diagnosing pathology.
- Loss of functions due to drug addiction provokes the development of functional tandem disorders . Not only the next function is disrupted, but also the related, reflex function. This connection between these disorders is explained by animal disorders that manifest themselves during drug withdrawal, as well as in the symptom complex that characterizes the so-called mental stress - nervousness, insomnia, emotional shift.
- The emergence of protective symptoms as a consequence of hyperfunction. The role of these symptoms differs from the compensatory functions of other disorders, which are aimed at restoring performance. As a rule, such symptoms include anorexia: any attempt by a drug addict to eat food causes not only local dyspeptic symptoms, but also a deterioration in general well-being.
In addition, drug withdrawal syndrome is represented by the manifestation of certain stress symptoms. Their main difference from other disorders is their non-specificity, the absence of a direct investigative connection with the general symptoms that develop.
The clinical picture of any type of drug addiction indicates the symptomatic nature of withdrawal states in advanced forms of this disease. In addition, all symptomatic signs of drug addiction, namely: mydriasis (wide pupils), feeling of a cold, drowsiness, tremors of the limbs, dyspeptic symptoms (heartburn, belching, a feeling of pressure or fullness in the abdomen, rumbling, diarrhea, etc.), hypertensive syndrome, anorexia (hyperglycemia), loss of sleep, restlessness, anxiety and depressive moods.
Up
"12 Steps" - drug rehabilitation
The most effective way to consolidate remission after detoxification is a rehabilitation course in a specialized rehabilitation center. The Twelve Steps program is recognized as the most successful drug rehabilitation program. It was developed back in the late 30s of the last century by people who were previously dependent on drugs or alcohol. It is popular all over the world because it solves the main problem of drug addiction treatment: a complete spiritual reorientation of the drug addict, a gradual return or re-acquisition of life values characteristic of healthy people. In this program, the focus of recovery efforts is on the person suffering from the disease, rather than on the factor causing the addiction.
The program's steps provide a gradual, evolutionary approach to addiction recovery. They are organized in a certain order: from the most important, main, basic, towards further changes that a person motivated to recover goes through and integrates into the process of his life.
The addict gradually not only changes his attitude towards a dangerous substance, but also revises all ideas about his own behavior, his relationships with other people, his self-esteem and self-concept, his value system, and gets rid of ineffective options for psychological defenses.
In fact, the 12 Steps program, originally a therapy program, became a drug rehabilitation program, and later became a spiritual basis for life.
As a rule, the main rehabilitation program is complemented by intensive work with psychologists, psychotherapists and consultants, both in individual and group formats. An important factor in a drug rehabilitation center is the isolation of the addict from his previous contacts. Rehabilitation is built on the basis of the 12 Steps program, and in order to start it, no sacrifices are required, except for the ardent desire to break away from drugs and the willingness to put in long, difficult and not always pleasant mental work for this.
The third stage of drug addiction is the development of somatic pathology
Drug use at this stage no longer causes pleasant euphoric sensations. Drug use is carried out only for the purpose of relieving painful symptoms of drug withdrawal. Now, in addition to mental defects in the form of negative emotional-volitional disorders (apathy, general weakness, asthenia and anergy), somatic defects are also developing in the form of degeneration of the heart muscles, parenchymal organs, atrophic changes in the genital organs, changes in the functioning of the central nervous system (impaired ultrastructure of nerve endings, especially neurons of the cerebral cortex) .
The severe and difficult course of drug addiction is distinguished by certain changes in the nuclear apparatus of nerve cells. Often, general exhaustion is observed. There is also no deterioration in memory or mental ability. There is no dementia, as in general, and no mental degradation either. Fatal outcomes from drug addiction at the third stage are observed extremely rarely, more often from total depletion of the heart muscle (from nephropathy in combination with infection).
Until recently, the description of the nature of mental disorders in drug addiction was limited only to a description of the symptoms of euphoric disorders. However, recent clinical observations and studies make it possible to assert that mental disorders are not limited only to emotional disorders, because euphoria in this case manifests itself in the form of several sensations. This is not only an increase in the emotional background, but also some mental and physical sensations, due to which a positive effect is achieved.
Each drug in its action exhibits its own completely individual positive pharmacological effect. However, the general features of emotional experiences during drug intoxication are represented by their protopathy and depth, which correlates with the level of consciousness. Therefore, the pharmacological effects of all drugs are always presented in the form of not only emotional changes, but also in the form of disturbances of perception, changes in ways of thinking and disturbances of consciousness.
Up
Free consultation with a narcologist by phone
+7 (495) 120-16-76call!
Cocaine addiction
Cocaine is an expensive, naturally occurring drug. It is diluted with dangerous mixtures, baking soda. Also other substances. It is distributed somewhat less frequently than other drugs. Causes a group of symptoms. It is used intranasally. It is inhaled (“sniffed”). Systematic drug use can be detected by several symptoms:
- Pupil dilation.
- Behavioral disorders. Excessive self-confidence, inadequacy.
- Traces of powder on hands, nose, clothes.
- Runny nose. Increased secretion of mucus from the nose.
- Psychomotor agitation.
- Red sclera of the eyes.
Cocaine does not become addictive immediately, but after several doses.
Opioid addiction
Opioids - methadone, desomorphine, heroin and others are extremely hard drugs. Great difficulties arise with the treatment of such a pathological process. Recovery is carried out strictly in the clinic. Heroin addiction can be identified by several symptoms:
- Injection marks on the arms or legs.
- Paleness of the body.
- Increased morbidity.
- Irritability.
- After systematic use, the pupils narrow.
- The patient becomes aggressive and weak.
- Coldness of the body.
Opioid addiction develops from the first dose and quickly leads to death from overdose and complications.
Perception disorders during drug intoxication
Perception disorders during drug intoxication manifest themselves in three forms. Impaired consciousness during intoxication is defined as: increased perception (with the use of stimulants), selectivity (with opium addiction), decreased perception (with the abuse of sleeping pills and tranquilizers). These disorders correlate with a state of active attention.
It is important to note that during intoxication, the connection between attention and fixation of impressions is disrupted . Even with the use of certain stimulants, when logically there should be good memorization, amnesia is often observed for events that occurred during the period of drug intoxication. Later, a person can say that he heard and saw everything very clearly, but he definitely cannot tell any of this. In this way dissociation of mental functions ; this state is always accompanied by words like: “as if this was not happening to me.” In addition to these quantitative disorders, malignant disorders necessarily occur, such as impaired psychosensory perception, productivity, and even hallucinations.
Changes in the perception of what is happening and the external environment occur : the shape of objects, color saturation, distances from objects, it may seem that the immovable is moving (approaching or moving away). Metaphorpsia (distorted perception of the shape, color and size of objects) is less Violation of sensory synthesis manifests itself in a feeling of derealization (a disturbance of perception in which the surrounding world is perceived as unreal).
Interoreception is also disrupted , which ensures the body’s adaptive reactions to changes in the conditions of the internal environment: from elementary sensations of temperature, the weight of one’s body in space, in one’s own body, the feeling of the absence of certain limbs or the presence of “extra” ones. At the third stage of drug addiction, autotopagnosia also occurs (ignoring half of the body, but mainly failure to recognize its individual parts). At the same time, the description of what is happening by the drug addict himself takes on a fantastic coloring: the drug addict sees his brain and the processes that occur in it. When the corresponding analyzer is irritated, the likelihood of spontaneous or reflex hallucinations is very high. Also characteristic is the presence of visual hallucinations called pareidolia, visual illusions that are formed on the basis of real-life objects. The skin also feels imaginary blows or touches. Such an “abundance” of these experiences is so complete and “inspired” for the drug addict that at these moments he is afraid to even change his position, so as not to “spoil” or “scare off” them. With all this, others observe a certain pseudo-stupor from the side.
The difference between other disorders in drug addicts and perceptual disorders lies in the presence of prevailing symptoms: visual, auditory, tactile (sensation of touch and movement on the skin), propriosensitive (devices (receptors) of muscles, tendons and joints) analyzers. At the same time, taste and auditory analyzers rarely appear.
The “suggestivity” (directed mental impact) of these experiences is also characteristic: the addict can “order” himself what to see or hear. This suggestiveness is often associated with a state of consciousness; with several types of drug addiction, it acquires a collective character or under the influence of external stimuli. As the intoxication deepens, the ability to control one's thoughts and feelings decreases.
Up
The role of the family system in the formation of drug addiction
For a child, a family is a certain given, which at a certain stage of his development is the “Universe”, a certain model for building relationships with the world. The child tries and experiences different forms of behavior and emotional response, striving to understand the world, establish himself in it and adapt to the environment that is most significant for him. He tries and performs essentially different actions, in their selection focusing only on the reaction of a close adult, until he discovers the version of his response that he most approves of, which he will further hone and improve. Parental beliefs, emotional reactions and ways of relating to the world, patterns of behavior in it actually program the child’s psyche, since most of them are taken seriously by the child in infancy, without criticism. This makes sense of the almost unlimited influence of a parent on the formation of the basic emotional and behavioral structure of a growing, maturing person, which is created and established very early, and, as a rule, remains practically unchanged in the future. The behavior of loved ones during the first years of a child’s life and the feelings that it formed acquire a certain autonomy and determine the basic attitude of this child to the world and ways of communicating with him throughout his entire future life.
If the love, respect and care of adults are replaced by the desire for unlimited power over a loved one, if parents love not the child, but the image of what they imagine him to be (always obedient, “the best”, “always successful”, etc.) . If they try with all their might to squeeze the child into part of their script, manipulating the child to achieve their goals, to satisfy their needs and desires, then a very important moment in growing up and becoming a person is inhibited. Thus, parents do not allow the child to be himself; they either interrupt the child’s attempts to find his own behavior, overprotecting him (overprotection), or destroying his trust in his own ability to rely on himself in understanding the world (ignoring, lack of sufficient support).
The child is deprived of his individuality, devalues himself as a person and accumulates the baggage of repressed unsatisfied needs.
In this situation, a young man is unable to make up his mind, separate himself from the crowd and understand what he personally needs; all his actions aimed at achieving balance and establishing himself in life will be chaotic and unpredictable. A person’s ability to adequately, flexibly, positively and quickly (as an adult) adapt to changing conditions of existence is not properly formed, since he only has a limited set of rigid parental stereotypes of communicating with the world, which have long been inappropriate to the current situations. In this sense, a person remains mentally immature and infantile (with increased suggestibility, inability to delay receiving pleasure, to take into account the consequences of his actions, subject to a sense of “herddom”, with inadequate self-esteem, insufficient forecast and reflection, disproportionate claims, unrealistic optimism about future events, instability of interests, underdevelopment of conscience and envy). And then complexes will inevitably arise, often unconscious psychological conflicts, psychosomatic illnesses, neuroses, and after some time, one of the immature, infantile ways to solve them is drug addiction. Drug intoxication quickly and effectively “gets rid” of all internal problems, a person easily becomes “happy” for a short time, the environment of drug addicts “accepts”, approves of the person, no matter what he is, you just need to regularly perform simple actions - take the drug.
All other factors are biological (pathology of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother, severe chronic childhood diseases, concussions, etc.); microsocial (being raised by one parent, only child in the family, addiction or mental illness in close relatives, domestic violence); macrosocial (socio-economic crises, availability and prevalence of drugs) - play only a trigger role, contributing to the onset of manifestation of a person’s underlying problem through drug addiction.
Thinking disorders in drug addicts
Changes in the thinking of a drug addict occur in different ways and depend on the type and amount of a single dose of the drug that is used. The most characteristic and obvious feature of these changes is catastrophic thinking (the influence of emotional factors and ambivalent (that is, contradictory) tendencies (feelings, desires, fears) on a person’s mental activity. In a simplified sense, this means thinking through the prism of emotions). There seems to be a shift in emotional and intellectual proportions in the plane of mental activity. The emotional mood determines a set of sensations and reasoning, their intellectual processing and conclusions. In addition, the drug addict’s ability to actively manage attention suddenly disappears . Defective perception is intertwined with impaired thinking. Lighthouse ideas arise , which, due to the short duration of the state, do not have time to acquire a completed form.
Disorders of awareness cannot be explained only by emotional barriers, but also by disturbances in concentration, an objective decrease in the quality of thinking, since it is always possible to establish the level of disorder of consciousness, which is considered as a drop in the activity of higher levels of the psyche.
When intoxicated by hallucinogens, thinking is directed to a plane that lies outside the boundaries of reality. These fantastic thoughts may have an underlying thought disorder. And this fantasy is explained by the fact that disorders of active attention contribute to the free uncontrolled flow of imagination and their interweaving. The natural, normal train of thought is disrupted , which is confirmed by the pace of language broadcasting . Sometimes the rate of speaking may decrease , and perseverations appear (obsessive repetition of the same movements, images, thoughts).
Up
Drug addiction in adolescents
Drug addiction in adolescents develops according to a simplified pattern, leading to more disastrous consequences.
1-2 doses of a drug can cause serious addiction, personality degradation and irreversible physical consequences, all of which can eliminate a child from society.
Adolescent drug addiction occurs due to the interaction of social, psychological and biological aspects.
Main features:
- Strong personality changes
- Pronounced negative effect on internal organs
- Rapid onset of addiction
Doctors make a diagnosis based on examination, interviewing the patient and talking with relatives, and test results.
The signs of teenage drug addiction are generally the same as in adults.
Treatment requires an integrated approach, eliminating physical and psychological cravings.
About drug addiction prevention
There are several types of drug addiction prevention:
- Primary. The goal is to prevent the consumption of substances by a person who has no experience of drug addiction.
- Secondary. The point is to not allow the previously accepting person to relapse.
The essence of prevention consists of a group of measures:
- Explaining the dangers of drug addiction.
- The right social environment.
- Preventive conversations.
- Work, study, constant employment.
- Psychotherapy.
UBOD in Moscow from 50,000 rubles, help for addicts and relatives!
FREE specialist consultation
+7 (495) 120-16-76
| Request a call |
Amphetamine addiction
Amphetamine and its derivatives are dangerous synthetic drugs. They do not cause addiction immediately, but after some time. 1-3 months or more. Mental addiction occurs almost immediately. After 2-3 doses, which makes it difficult to give up the substance.
Amphetamine has a disinhibiting effect and “accelerates” the brain. Hence the typical signs of its consumption.
- Cheerfulness.
- Increased physical and mental activity.
- Talkativeness, reaching the point of talkativeness.
- A surge of strength.
- Hallucinations.
- Increased motor activity.
- Rave.
- Loss of appetite.
- Insomnia.
Amphetamine addiction is difficult to treat. But recovery is still possible.
Emergency detoxification from amphetamine
FAST INEXPENSIVE ANONYMOUS
+7 (495) 120-16-76 call!
Cannabinoid addiction
Cannabinoids are mistakenly considered recreational drugs. This includes marijuana as the main substance. The main problem is that addiction develops gradually. It draws the patient deeper and deeper into its network. It is necessary to start treatment as early as possible. The main manifestations of the pathological process:
- Redness of the sclera of the eyes.
- Cough.
- Drowsiness.
- Panic attacks.
- Increased appetite.
In addition, mental disorders occur.
Salt addiction
Salts are extremely dangerous. They are no less destructive than opioids. They also provoke addiction after the first couple of doses. In this case, death mainly occurs from failure of internal organs. For example, from heart failure. The salt type of addiction provokes several symptoms:
- Hallucinations.
- Sharp weight loss.
- Insomnia.
- Behavioral disorders.
Treatment for this type of drug addiction is carried out strictly in a hospital setting.
Spice addiction
The main types of drug addiction are crowned by addiction to spice. Synthetic cannabinoids with approximately the same effect. Distributed as smoking mixtures. The manifestations of systematic use are approximately the same:
- Nausea.
- Vomit.
- Thirst.
- Cough.
- Hoarseness of voice.
Treatment options for this type of drug addiction include detoxification, coding, and psychotherapy.
Let's remove the remaining spice from the body
anonymous-fast-effective