Cardiophobia is manifested by an intense fear of death due to any cardiac pathology. Usually, those diagnosed with this disease do not actually suffer from any dangerous diseases or they have been found to have minor changes in the functioning of the heart with the recommendation of periodic monitoring in the future. But mental disorders provoke constant anxiety, and the slightest changes in heartbeat are perceived as pathology or even a sign of imminent death. People suffering from cardiophobia often spend almost half their lives in hospitals, trying to identify and treat a serious illness. But almost always experts do not find serious reasons for concern. The best solution in this situation is to contact a psychotherapist, who, based on the results of diagnostics and testing, will make the correct diagnosis and help get rid of cardiophobia. At the Leto mental health center you will find high-quality medical support and a quick recovery!
General information
Being one of the most common types of nosophobia (as the irrational fear of the appearance of incurable pathologies is called in psychiatry), cardiophobia seriously worsens a person’s life. According to statistics, almost every fifth patient in cardiac hospitals suffers from this disorder.
But among those who actually suffer from cardiovascular pathologies, there are also cases of cardiophobia. They are distinguished by an overly strong, hypertrophied emotional reaction that does not correspond to the real severity of the disease.
Anxiety-phobic spectrum disorders require an integrated approach:
- If cardiac pathology is diagnosed, therapy is prescribed by a cardiologist after a thorough examination. In parallel, a course of psychotherapy is required.
- In the case of a classic picture (without detection of health problems), treatment is carried out only by a specialist in the correction of mental disorders.
Pseudo-infarction cardiophobia
In this case, discomfort and pain in the heart are noted, which are accompanied by severe fear of a heart attack. Such patients are often prone to self-medication; often, without prior consultation and examination by a doctor, they take any medications (usually the well-known nitroglycerin, validol, valocordin, and sometimes, which is much more dangerous, potent drugs), which, naturally, do not bring relief.
For this form of cardiophobia, panic attacks are typical, accompanied by:
- focal hyperemia of the skin of the neck, chest and face;
- increased sweating;
- increased breathing and heart rate;
- shortness of breath, a feeling of suffocation, fear of approaching death.
As a rule, with the pseudo-infarction variant of the disorder, the patient knows all the symptoms of a heart attack by heart, so he constantly subconsciously looks for (and usually finds) them in himself.
Symptoms of a panic attack
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- muscle tremors, chills;
- tachycardia;
- dystonic or physiological tremor;
- hot flashes (instant sensations of heat);
- asphyxia (suffocation);
- dyspnea (difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air);
- irradiation of pain to the left side of the chest;
- nausea, urge to vomit;
- abdominal pain syndrome (stomach pain);
- sensation of a foreign body, coma in the throat;
- paresthesia (tingling in the limbs, feeling of numbness);
- lightheadedness, dizziness;
- stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea);
- dysbasia (gait disturbance);
- high blood pressure;
- impairment of vision and/or hearing;
- frequent urination.
- derealization (feeling of unreality, alienation, indistinctness of the surrounding reality);
- fear of schizophrenia, obsessive fear of going crazy, losing control over one’s actions;
- disorientation, confusion;
- depersonalization (the patient perceives his actions as if from the outside and feels that he cannot control them);
- interrupted sleep, insomnia (insomnia), nightmares;
- Thanatophobia (fear of death).
- more frequent repetition of attacks with the appearance of new symptoms;
- isolated attacks;
- the addition of depressive symptoms (sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, persistently depressed mood);
- constant fear for your health;
- refusal to perform habitual life rituals (patients stop traveling in public transport, going outside, and their performance sharply decreases).
What does a person experience during a panic attack?
- feeling of fear of varying strength;
- feeling of impending danger;
- fear of death;
- stiffness reaching the point of stupor (in some people);
- motor activity (in others);
- fear of committing an uncontrollable act;
- fear of going crazy;
- confusion of thoughts;
- unreality of what is happening;
- loss of orientation in personality, space and time.
Physical symptoms of a panic attack
The main reason for their appearance is the release of biologically active substances (norepinephrine and adrenaline) into the blood in large quantities. Mediators have a stimulating effect on the nervous, respiratory systems, heart and blood vessels.
- Rapid breathing and heart rate.
- Shortness of breath, lack of air.
- Chills.
- Dry mouth.
- Increased sweating.
- Weakness, body numbness, dizziness.
- Diarrhea.
- Involuntary urination.
- Vomit.
The most pronounced physical symptoms are in anxiety, which develops due to pathology of organs and systems.
Neurotic type
Clinical manifestations are variable and vague. The patient describes his condition vaguely, there are no specific signs, only a general feeling of discomfort in the chest area. Neurotic cardiophobia is caused by:
- prolonged stress;
- severe fatigue;
- anxiety and neuroses combined with excessive suspiciousness;
- neurological disorders;
- psychotrauma.
Often the disorder develops due to an incorrect or inaccurately formulated diagnosis. Some doctors, when talking with a patient, use a variety of complex medical terms to describe even minor cardiovascular disorders. Many patients misinterpret them and perceive them as a “danger signal.”
Main features
The following symptoms are common to all forms of the disorder:
- panic fear and at the same time anxious anticipation of a heart attack;
- restriction of physical activity (including outdoor recreation, some hobbies and even sexual relations) for fear of worsening well-being;
- reluctance to remain alone, to go out unaccompanied, and the person argues that in the event of an attack there will be no one to even call an ambulance;
- the desire to “shift” one’s affairs onto loved ones with complaints of weakness and helplessness;
- constant study of medical literature, increased interest in the topic of cardiac diseases.
Such symptoms negatively affect all areas of a person’s life, so it is important to seek professional help and support as soon as possible.
help yourself
At the moment when you are overtaken by an attack, it is very difficult to control yourself. But you can try to pull yourself together and help yourself get rid of it quickly:
- Go out into the fresh air or open the windows, unbutton tight clothes. Pour cool water over your face.
- It is important to switch to breathing. Try to breathe deeply, slowly and fully. To increase the level of carbon dioxide in the blood, breathe into a bag or cupped palms (imitate the position of breathing into them, trying to warm them up).
- Try to think about something positive or talk to someone. Try counting to 100 or count passing cars or trees if fear catches you in transport or on the street. All this helps to shift attention away from anxious feelings. If the cause of alarm is a certain place, hurry to leave it.
- To stabilize your body, place your hands on a stable surface or press your feet into the floor. This position will give you a feeling of confidence and control.
- Keep telling yourself that this will all end now. The anxiety that arises will not harm you, it is simply a figment of your imagination.
If you witness an attack on someone, you can help the person cope with the problem. The main thing: do not panic yourself! You must be calm. And with your calmness set an example for him.
Talk to him, hug him on the shoulder or squeeze his hand. Show me how to breathe correctly. If conditions permit, give the person water or warm tea.
The main thing is not to get confused in this situation. Remember, your behavior can significantly alleviate the panicker’s condition.
How is the examination carried out?
To make a diagnosis, various methods of neuropsychological questioning are used. But even after confirmation of cardiophobia, it is necessary to exclude the presence of cardiovascular pathologies. For this purpose they prescribe:
- a cardiogram (ECG), during which the regularity and frequency of heart contractions are assessed;
- 24-hour monitoring of blood pressure and pulse;
- echocardiography, which helps to examine in detail the condition of the heart and its valves and assess its functionality;
- stress test to assess the functional activity of the myocardium during physical activity.
Additionally, a clinical and biochemical blood test and lipid profile are shown.
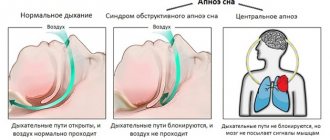
Why do extrasystoles occur during VSD?
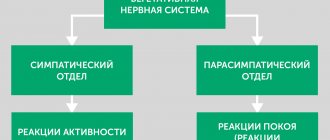
Cardiac “dancing” in vegetative-vascular dystonia can occur when both parts of the autonomic nervous system are disrupted.
If the sympathetic department fails, extrasystoles appear after physical exertion. They are poorly controlled by sedatives, and may even intensify after taking them.
If the functioning of the parasympathetic system is disrupted, in addition to cardiac symptoms, digestive disorders are of concern: epigastric pain, diarrhea, bloating. A cup of coffee or sweet tea or a brisk walk will help relieve such an attack.
If the cause is psychological, treatment measures are directed in the other direction.
Most often, dystonics are bothered by two types of extrasystole:
- Ventricular. Usually makes itself felt in the first half of the day. It is caused by disturbances in mental balance, for example, great joy or grief. It also appears when the weather changes or when drinking strong drinks. Other provoking factors include magnesium and calcium deficiency, osteochondrosis. It all starts with an intense beat in the heart area, followed by a pause. The patient becomes covered in cold, sticky sweat and develops a feeling of fear. Despair sets in, he cannot choose a comfortable position for himself, becomes numb or begins to fuss. The violence of his heart leads him into an uncontrollable state, causing him a lot of suffering.
- Supraventricular. The most common type of arrhythmia in VSD. The causes of this condition coincide with those of the ventricular form. In addition, dystonics who are addicted to antiarrhythmic and diuretic drugs are at risk. Patients claim that the condition worsens when lying down. It is this sign that indicates that the cardiac failure is functional in nature.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
How to get rid of the disorder
In most cases, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis, however, in cases of pronounced anxious affect, hospitalization in our hospital is possible, where the patient will be provided with maximum comfort and round-the-clock supervision by qualified medical personnel.
The basis of treatment is always rational and behavioral psychotherapy; group classes, various relaxation techniques, and strengthening self-control have proven themselves well. To relieve the somatic manifestations of the disease, sedatives, anxiolytics, and multivitamin complexes are used.
Under no circumstances should you ignore the signs of cardiophobia, since sooner or later constant exposure to stress and tension will cause very real cardiovascular disorders. We will help you get rid of anxiety and emotional discomfort! To make an appointment, call 8(969)060-93-93 .
Panic attacks and symptoms
Quite often, panic disorder is disguised as other diseases, which makes it difficult to quickly diagnose the disease. Patients experience the same sensations that appear in real neurological, cardiovascular and other serious pathologies.
A person who has recently experienced panic disorder, as a rule, does not know about it, so he often turns to doctors of various specializations for help. The patient is prescribed various examinations of the body, and in the end it turns out that he has no pathologies of internal organs, but despite this, the symptoms of a non-existent disease continue, even intensifying over time. In this case, we can talk about the presence of a panic attack or panic disorder.
Signs of a panic attack
The signs of this disease in most cases have a pronounced physical characteristic; the symptoms are similar to a heart attack, so many patients suspect heart pathology. However, even strong vegetative manifestations in this case are a consequence of dysfunctions of the nervous system and brain.
The main symptoms of a panic attack are anxiety attacks, which are accompanied by autonomic disorders (rapid heartbeat, chills, sweating). With an increase in the level of anxiety, the physiological parameters of the body, which are situational in nature, are often disrupted.
The severity of anxiety varies from a state of internal tension to pronounced panic and fear of death. The average duration of an attack is 15-30 minutes. Anxiety reaches its maximum in the first 5-10 minutes and goes away as suddenly as it started.
Sometimes a panic attack develops against the background of situations that are uncomfortable for a person: being in a crowd or in a confined space.
For some people, attacks occur several times a day, for others - 1-2 times a month. Panic attacks often occur during the daytime. At night, anxiety attacks are more likely to bother strong-willed people who control their feelings while awake.