Issues discussed in the material:
- What are the stages of dementia development?
- What drugs are used at the initial, moderate and severe stages of the disease
- What anti-dementia drugs are best for older people after a stroke?
- What drugs for dementia can be bought without a prescription?
Among the serious illnesses that beset people after 65 years of age, it is senile dementia - a disease that creates serious problems for an elderly person and his loved ones. The patient's memory, behavior, and speech undergo changes that he is not even aware of. Is it possible to alleviate a person’s condition, what medications for dementia in the elderly can help? This is exactly what will be discussed further.
Drugs for the treatment of moderate dementia in the elderly
When the disease passes into the second stage, the list of independent actions of the patient is reduced to performing simple everyday manipulations. At this stage, another group of drugs is prescribed.
- Cerebrolysin.
We recommend
“How to communicate with elderly parents so that everyone is comfortable” Read more
The drug contains low molecular weight peptides combined with amino acids, which has a positive effect on brain function. Namely: it protects neurons from depressing factors and stimulates intercellular metabolism. As a result, memory and attention improve, and the patient’s thinking is activated. The course of treatment is usually from 4 to 6 weeks. The method of administering the drug is intravenously using a dropper. This remedy has a prolonged effect: accumulating in the body, it creates a long-term therapeutic effect.
- Actovegin.
Designed to improve oxygen supply to brain cells and increase the activity of intracellular metabolism. It is used intravenously through a dropper for two weeks, then in tablets. During and after treatment, cognitive functions stabilize and psycho-emotional symptoms of dementia weaken.
- Akatinol Memantine.
Helps normalize metabolism and improve the transmission of brain impulses, restore memory, concentrate attention, and accelerate the thinking process. As a result of taking the drug, the patient’s skills in practical actions in everyday life and self-care are restored. Minor side effects do not interfere with the treatment of dementia and its manifestations:
- Alzheimer's diseases.
- Parkinson's disease.
- Loss of memories.
- Low level of concentration.
- Rivastigmine (Alcenorm)
Serves to reduce the breakdown of acetylcholine, establishing connections between neurons by accumulating in the gray matter of the brain and hippocampus. At the same time, the rate of formation of amyloid plaques, which destroy neurons, decreases. As a result, memory improves and quality of life increases.
Types of disease, causes of occurrence and development
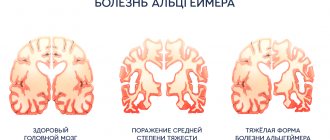
Dementia is classified primarily by the area of the brain affected.
- Cortical. Covers mainly the cells of the cerebral cortex. This type of dementia occurs from alcoholism and Alzheimer's syndrome.
- Subcortical. Covers subcortical neurons and structures. Characteristic of supranuclear palsy and parkinsonism.
- Cortical-subcortical. The disease affects both the cortex and the white matter of the subcortex. Can be caused by corticobasal degeneration, as well as diseases of the heart and blood vessels. It is especially common in hypertensive patients and atherosclerotic patients.
Dementia is also classified according to its causes.
- Primary (atrophic). The exact cause has not yet been determined. It is only known that with age, more and more neurons in the cortex and subcortex degenerate.
- Secondary. Most often caused by cardiovascular diseases and other ailments that are not directly related to brain function.
- Mixed. Natural atrophy can be aggravated by problems with the heart and blood vessels.
In addition, the development of dementia may be influenced by:
- traumatic brain injuries;
- severe poisoning and viral diseases;
- lack of vital vitamins;
- liver and kidney failure;
- problems with the immune system;
- alcohol, drugs, hormonal overdose.
A low level of intellectual development also negatively affects the state of the brain and can accelerate the development of dementia. The more a person works intellectually, learns new things, communicates with others, the lower the risk of getting sick.
Drugs for severe dementia in older people
A severe degree of the disease is characterized by general personality degradation. The patient no longer recognizes relatives and friends, cannot eat or care for himself. He is haunted by delirium and fear of aggression from other people.
At this stage, the attending physician prescribes Halopiredol or new generation analog drugs: Olanzapine, Risperidone. At the same time, he continues to take previously prescribed medications: antidepressants, sedatives and to improve memory.
- Risperidone.
We recommend
“Examination of an elderly person - which doctors need to be seen regularly” More
Indications for use are dementia of the schizophrenic type: the appearance of psychosis, delusions and hallucinations in the patient. Taking the drug extinguishes outbreaks of aggression and irritability, reduces hostility and suspicion, feelings of anxiety, detachment or guilt, and relieves depression. A person begins to think and communicate adequately, and speech returns to him. Contraindications include Parkinson's disease and epilepsy.
- Olanzapine.
This drug is prescribed today instead of Halopiredol. In addition to being effective against hallucinations, it also relieves depression, anxiety, tension and other mental disorders. Indicated for dementia of the schizophrenic type. According to the study, Olanzapine is superior to Halopiredol in improving cognitive function and restoring mental disorders. Relapses during treatment with Olanzapine occur much less frequently. The drug should be taken for speech disorders, decreased social activity, acute manic attacks, schizophrenia, and dementia.
The medicine increases the risk of developing diabetes, hypertension, weight gain, cancer, cholelithiasis, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Therefore, it is contraindicated for people prone to these pathologies.
- Exelon patch.
The use of this remedy is convenient for the patient, as it does not require special skills. The patch serves to ensure constant delivery of the drug Rivastigmine through the skin. You just need to stick the patch on an area of the body where there is no close contact with clothing, at the same time every day. This will ensure that a strictly defined amount of the active substance enters the blood. The patient can take water procedures and swim in the pool. Only visiting the sauna or bathhouse is not allowed.
We recommend
“Centers for pensioners: what they are and how to get there” Read more
Drugs for the treatment of vascular dementia in the elderly
A group of medications - antipsychotics and vascular drugs - are used specifically for this diagnosis. If the course of the disease is accompanied by psychopathy, feelings of anxiety and restlessness, fears and delirium, as well as Alzheimer's disease, the patient will need medications Propazine, Aminazine, Tizercin, Etaperazine, Melleril, Moditen. Let's talk about some of them in more detail.
- Propazin.
Has a sedative (calming) and hypnotic effect. Reduces anxiety, symptoms of depression and phobias. Does not cause tremors and shuffling steps. However, it does not eliminate delirium and visions.
- Tizercin (Levomepromazine).
Relieves anxiety more effectively than Aminazine. Eliminates delirium. In small doses it acts as a sleeping pill.
A big problem for older people is the functioning of blood vessels. The arteries of the brain must have good patency. To rid them of atherosclerotic plaques, expand the lumen and reduce spasms, special drugs have been developed. Medicines, calcium antagonists, remove spasms of the arteries, while the tension in the veins almost does not drop. The blood supply with oxygen is normalized, which is delivered to the brain without obstacles. The second generation of drugs is now in use and work is underway on the third.
Second generation of this group:
- Isradipin (Lomir).
- Anipamin, Gallopamil, Falipamin.
- Felodipine (Plendil), Amlodipine (Norvax).
- Clentiazem.
Positive properties of these drugs in comparison with other drugs:
- prolonged action;
- act selectively;
- have a minimum of side effects.
An alternative to these drugs can be herbal medicines: periwinkle, ginkgo biloba, vitamins B and P and nicotinic acid derivatives. But before taking these medications, which have virtually no contraindications, you need to consult a doctor. Only a specialist will be able to draw up a treatment plan taking into account the condition of the body and the existing pathology.
We recommend
“Boarding home for the elderly: how to place an elderly relative there” Read more
Possible complications
Each medication is prescribed by a doctor only after identifying all contraindications and assessing possible side effects.
For example, antidepressants and some NMDA antagonists can provoke the appearance of hallucinations, obsessive thoughts, and delusions. Many tranquilizers aggravate the condition, turning the patient into a withdrawn and apathetic person, so it is better to use Quetiapine for dementia, which has almost no side effects and is easily tolerated by patients.
The well-known medicine Phenazepam can cause drowsiness, depression, progression of memory impairment, motor dysfunction, and involuntary relaxation of the sphincters.
For dementia, it is better to replace amitriptyline with another antidepressant, although it is often used, it has a number of contraindications, often causes complications, and an overdose is sometimes fatal.
Drugs for dementia in the elderly after stroke
If a person has insufficient blood flow chronically, then dementia develops slowly. But in the case of a stroke, dementia can occur suddenly and immediately. The danger is precisely bleeding in the part of the brain that is responsible for mental function. There may be isolated signs of deterioration in brain function, but this will not be dementia. But when the disorders form a whole complex, we need to talk about mental degradation due to a stroke.
Symptoms of post-stroke dementia:
- persistent memory impairment;
- uncertain, unsteady gait;
- the presence of obvious signs of neuralgia;
- loss of counting ability;
- difficulty speaking and reading;
- inadequate thinking;
- difficulty in analysis;
- depression;
- a person is lost as a person;
- inability to use knowledge.
In such a situation, it is necessary to use medications of different groups:
- psychostimulants - trigger the protective functions of the central nervous system (caffeine, Mesocarb);
- nootropics - activate the brain, improve memory (Piracetam, Oxycytam);
- glutamic acid, Cavinton - improve metabolism and blood supply to the brain;
- Arbiflex, Curantil - improve cerebral circulation;
- complex of vitamins;
- Mezapam, Phenazepam - drown out fear and melancholy.
Anti-anxiety and sleeping pills for older people with dementia
Patients with senile dementia often suffer from insomnia, delirium, visions, hypochondria, and aggression occurs against a background of anxiety. We must try to improve the condition of such patients through treatment. After all, these symptoms deepen the development of dementia.
- Sonapax (Thioridazine).
This drug can serve as both a neuroleptic, an antidepressant and a tranquilizer. Plus it is used as a sedative, hypnotic and anti-manic agent. But this is not the whole list of what Sonapax can do. His arsenal includes the fight against phobias, anxiety, and aggressive states. They treat depression, as well as various types of dementia: vascular, Alzheimer's and combined. This medicine is used to relieve motor agitation and sleep disorders.
- Phenazepam.
This drug is not recommended for frequent use. The exception is an acute condition, and even then it is a one-time appointment. During the entire course of treatment, a deterioration in well-being and progression of dementia are observed.
- Phenibut.
This is a more effective medicine. Positive properties:
- improves impulse connections between brain cells;
- reduces vascular tone;
- normalizes the process of brain metabolism;
- improves blood circulation and oxygen saturation of neurons;
- removes anxiety and fear;
- reduces tension;
- promotes normal, timely sleep;
- restores memories;
- speeds up the reaction;
- normalizes coordination of movements;
- returns adequate speech;
- increases mental and physical performance with long-term use.
The main recommendation: strictly adhere to all doctor’s prescriptions. This applies to dosage, course duration and the medications themselves.
We recommend
“Lonely older people: how to help them” Read more
Dementia drugs for older people without prescriptions
If loved ones have an idea of the real condition of a person with dementia and know how to help him without going to the doctor, some medications can be purchased in pharmacies without a prescription.
- Melaxen.
Neuroleptic, used as an excipient. Acts as an anticonvulsant and sedative, fights delusions and hallucinations, and is recommended as a sleeping pill. There are also contraindications for use: myeloma, leukemia, autoimmune diseases, kidney disorders, as well as hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Analogues are Circadin and Vita-melatonin.
- Donormil.
Another drug that is widely used for dementia, as it has a hypnotic and sedative effect. The release form is tablets, which eliminates difficulties in dosage and use. If the dosage is incorrect, side effects may occur.
This drug should not be taken if you have urinary tract diseases, congenital galactosemia, closed-angle glaucoma, or hypersensitivity to substances in its composition.
Reviews from elderly patients about this drug for dementia show that they are satisfied with the actions of the medication. It also has analogues: Bromcamphor, Alora, Adonis-Brom.
- Afobazol.
It is a selective anxiolytic that can improve cognitive function. Recommended for dementia and asthenia. The drug is notable for the fact that it has very few contraindications. The only prohibition on taking it is individual hypersensitivity to its composition. Positive qualities include the prolonged duration of its action. Analogs are Adaptol, Tranquilar, Mebical.
More information about medications and treatment
All medications prescribed by a doctor must be taken on time, even skipping them once is strictly prohibited. Patients with moderate and severe dementia require constant care and monitoring of medications taken, which is most often carried out by relatives and loved ones.
If allergic reactions or side effects are detected, you should contact your doctor to discontinue inappropriate medications for dementia and replace them with analogues.
It is important to keep patients physically fit: walking, doing simple exercises, doing exercises. This helps to avoid muscle atrophy, improve overall well-being, and in combination with the drug Actovegin for dementia, even increase the saturation of brain cells with oxygen.
Important! Physical exercises should be done under the supervision of a physiotherapist, as overwork, overload, and sprains are possible.
Various vitamins and dietary supplements also help in stopping the progression of the disease. There are also traditional medicine methods that cannot provide a good result, but are suitable for relieving some symptoms of the disease. For example, herbal teas can replace sedatives for dementia in the early stages and help you sleep.