Any deviations in the behavior of newborns cause concern for parents. One of these alarming symptoms includes erratic, convulsive movements of different parts of the body. In medical parlance this is called “tremor”. Most often, immediately after birth, the baby's chin shakes when crying or during feeding. It is difficult for young parents to understand the nature of such phenomena and distinguish a pathological condition from a normal one.
Trembling and convulsions in infancy are not a deviation, but a normal physiological reaction to external stimuli. The symptoms go away over time, but there are cases when spontaneous twitching of the chin does not stop, but, on the contrary, becomes more frequent. In such situations, timely medical intervention is required.
Tremor
Tremor is a small shaking. It is usually one of the first symptoms to develop. Most often, one hand begins to tremble first. There may be specific finger movements, as if a person is rolling a pea. Gradually the tremor spreads to the other arm and legs. There may be a shaking of the head in a vertical or horizontal direction, such as nodding “yes-yes” or “no-no”. The eyelids and lower jaw may tremble separately. Very rarely, tremor covers the entire body.
Tremor is a small shaking. It is usually one of the first symptoms to develop. Most often, one hand begins to tremble first. There may be specific finger movements, as if a person is rolling a pea. Gradually the tremor spreads to the other arm and legs. There may be a shaking of the head in a vertical or horizontal direction, such as nodding “yes-yes” or “no-no”. The eyelids and lower jaw may tremble separately. Very rarely, tremor covers the entire body.
Parkinson's disease is characterized by tremors at rest. During movement, the trembling decreases, and during sleep it disappears altogether. But there are cases of intentional and postural tremor. Intentional is manifested by trembling, which occurs in the limb when it has already completed the movement it has begun. When you aim your finger at a target, at first everything is fine, but the closer you press, the more it trembles. Postural tremor occurs when it is necessary to maintain a static posture, such as holding your arms outstretched.
Trembling of the chin in a newborn is a physiological norm
Tremor caused by immaturity of the nervous system is considered a physiological norm. When a child cries and his chin trembles, it is enough to simply calm the baby. In newborns, such conditions are not treated. 3 months will pass and all phenomena will disappear. Don't worry if you notice your chin shaking while breastfeeding, bathing, or changing clothes. With any load on the nervous system, the baby begins to twitch. Trembling can be caused by:
- Overwork.
- Fright.
- Paradoxical (rapid eye movement) sleep.
- Hunger.
- Painful sensations.
- Uncomfortable air temperature.
- Bright lights and loud sounds.
- Sudden change in body position.
For obvious reasons, when the mother understands what is causing the trembling of the chin, there is no need to worry. If twitching is observed in other situations, occurs for no reason and in complete rest, the child should be examined by a doctor.
Muscle stiffness
Muscle stiffness and increased tone are also among the main symptoms of Parkinson's disease. This symptom even has its own term - plastic waxy flexibility. It is characterized by the fact that the limbs and body freeze in a given position. In this case, certain muscles suffer, and their stiffness leads to the formation of the so-called supplicant pose. The person slouches, his head leans forward, his arms are slightly bent at the elbow joints and pressed against the body, and his legs are bent at the hip and knee joints. If an outsider tries to straighten the patient’s limb, he will feel the kind of stepwise movements that are characteristic of gears in mechanisms. The phenomenon also got its name - the cogwheel symptom. Muscles lose the ability to return to their original position after performing an action. Therefore, patients may freeze in different positions for some time.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the nature of the underlying pathology, the symptom of which is trembling. Some conditions, such as neonatal tremor, go away on their own and do not require medical intervention; in other situations, specialized care is necessary. Usually the emphasis is on complex drug correction:
- Etiotropic.
It is possible to eliminate the infectious causes of trembling with antibacterial and antiviral drugs. To reduce the severity of hyperbilirubinemia in newborns, tinmesoporphyrin is used. Elimination of drug-induced parkinsonism is achieved by transferring the patient to atypical antipsychotics. - Pathogenetic.
In the treatment of hypoxic-ischemic disorders, vasoactive agents (vinpocetine, pentoxifylline), antihypoxants and antioxidants are used. In case of hydrocephalus, diuretics (furosemide, mannitol) can be used to reduce the production and improve the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid; for intracranial hemorrhages, hemostatic therapy is indicated. - Symptomatic.
Treatment of parkinsonian tremor is carried out with levodopa, dopamine receptor agonists (pramipexole). Neuroleptic tremors are treated with amantadine and anticholinergics (trihexyphenidyl). In cases of severe familial tremor, beta blockers (atenolol, sotalol) are used; in resistant cases, botulinum toxin injections are used.
The traditional method of treating kernicterus is phototherapy, if it is ineffective, exchange blood transfusion is practiced. The consequences of perinatal damage to the nervous system and cerebral palsy require complex neurorehabilitation - with physiotherapy (myostimulation, electrophoresis, reflexology), massage, exercise therapy. Special devices (orthoses) are used, and children are recommended to work with a speech therapist or psychologist.
Hypokinesia
Hypokinesia is a decrease in motor activity. General stiffness of movements is characteristic. In order to make any gesture, the patient must make an effort. Outwardly, it looks as if the movements are made after a pause, they are slow.
A person's gait changes. He moves in small mincing steps, with his feet parallel to each other. The arms do not move in time with the walking, but are pressed to the body. Facial expressions suffer. The face becomes motionless and impassive. The display of emotional reactions is delayed. Such people rarely even blink. The voice changes, it becomes monotonous and dull. If a person utters a long sentence or phrase, it fades towards the end.
How to treat tremors in babies
Only a doctor can decide how to treat chin tremor. When diagnosing neurological abnormalities, medications are used, but most often children are prescribed massage, swimming and gymnastics. All therapeutic actions are aimed at relaxing the nervous system. A specialist may recommend herbal infusions based on mint, lemon balm, chamomile and valerian. Using sedatives, you can do baths and wipes.
If the baby is not yet 2 years old, the reaction to medicinal herbs can be unpredictable. Do not rule out allergic and toxic reactions. The younger the child, the more serious the complications can be. Natural helpers are safe only when used correctly. The duration of treatment, administration and dosage should be controlled by a doctor.
Caution must also be observed when performing relaxing massages. If there is no experience and sufficient knowledge in this matter, it is better to entrust the procedure to a specialist.
With adequate therapy, the state of the nervous system can be easily restored and normalized. If no pathology is identified, parents can help the baby. Learn to understand what causes your baby’s dissatisfaction and, if possible, eliminate all irritants. Follow your daily routine and diet, walk and swim more, create a favorable, calm atmosphere at home. For a child, a permanent contract with his mother is very important. When a loved one is nearby, children feel protected. This has a positive effect on health and behavior.
Postural instability
Violation of postural fixation can occur in the early stages, for example, patients cannot hold their arms extended forward. But these are not such serious deviations that both patients and doctors pay attention to them. But closer to the later stages of the disease, serious problems begin. For example, there are difficulties with starting movement and stopping it, no matter how difficult it is to overcome the inertia of rest and movement. During movement, the body tilts along the course of inertia; in particular, when moving forward, it tilts and, as it were, moves ahead of the legs. This disrupts the center of gravity and leads to frequent falls and injuries.
Diagnostics
Tremor as a visual symptom is easy to identify during the initial examination. It is much more important to establish the cause of rhythmic chin tremor, since this affects the therapeutic strategy and prognosis. A neurologist can cope with this task using additional diagnostic methods. Taking into account the clinical situation, the following procedures may be prescribed:
- Lab tests.
Assuming the presence of an infectious factor, in the hemogram they pay attention to the leukocyte formula, ESR, perform serological tests, and PCR. The key role is played by the analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (clinical, biochemical, microbiological). Important biochemical blood parameters are bilirubin and glucose. A coagulogram is required. - Tomographic methods.
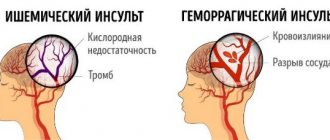
It is possible to confirm organic pathology of the central nervous system using CT and MRI of the brain. Computed tomography has an advantage in diagnosing TBI, hydrocephalus, and hematomas. Ischemic foci, diffuse processes, damage to the membranes and nerves are better visualized on MRI. The state of the dopaminergic system can be studied with single-photon emission tomography. - Neurosonography.
In pediatric practice, ultrasound scanning of the brain through the large fontanel is highly informative. Ultrasound scanning determines the expansion of the ventricular system, changes in the density of brain tissue, and the presence of pathological formations. Dopplerography examines blood flow in the arteries of the carotid and vertebrobasilar areas. - Electroencephalography.
Trembling hyperkinesis in children, simulating epileptic seizures, is an indication for an EEG. A study of the electrical activity of brain structures reveals foci of pathological impulses and helps predict the neuropsychic development of newborns. - Electromyography.
Electrophysiological parameters of tremor (frequency, amplitude, type) are determined by EMG. By the nature of the central oscillations, essential tremor can be differentiated from parkinsonian tremor. The technique is also useful for assessing neuromuscular conduction.
In many cases, an examination of the fundus is necessary; echo and rheoencephalography provide some information. When carrying out differential diagnosis, physiological conditions and dangerous pathologies requiring immediate help are first excluded. Tremor in children should be distinguished from convulsive seizures, absence seizures, myoclonus; at older ages, motor stereotypies must be taken into account.
Other symptoms of Parkinson's disease
In addition to movement disorders, Parkinson's disease may cause a lot of other symptoms, some of which lead to maladaptation and disability:
- Increased salivation.
- Mental disorders - depression, psychosis, dementia, insomnia, hallucinations. These manifestations can be associated with the disease itself, or occur as side effects from its treatment.
- A speech disorder associated with the impossibility of normal functioning of the muscles of the speech apparatus.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- Weight changes - from emaciation to obesity.
- Increased greasiness of skin and hair.
Without treatment, the symptoms of Parkinson's disease steadily progress, and within 15 years of the onset of the disease, about 90% of patients have disability. But modern methods of therapy (medical and surgical) make it possible to keep the situation under control, increase life expectancy and improve its quality in people with such problems.
General symptoms
The main symptoms of hyperkinesis include motor acts performed by patients against their will, the so-called violent ones. Patients themselves describe them as the result of an irresistible desire that they cannot resist.
The list of symptoms representing hyperkinesis includes:
- frequent blinking and squinting of the eyes (tics);
- convulsive tilting or turning of the head;
- tremor of various parts of the body, most often the limbs;
- myoclonus – sudden muscle twitching of the arms or neck;
- chorea - arrhythmic movements of facial expressions, involuntary sounds arising from rapid contractions of the muscles of the larynx;
- ballism - sudden rotation of the hip or shoulder;
- Blapharospasm is a pathological closure of the eyelids, as one of the signs of various diseases.
Forms of hyperkinesis can vary from intermittently frequent to constant. Some patients manage to control certain forms of hyperkinesis (for example, tics) by force of will, but after a while the attack of violent movements manifests itself again with even greater force.
How long does it take to cure trismus?
Typically, full muscle recovery can take one to three weeks, depending on the cause of the trismus. More time will be needed for fractures of the jaw, which must heal properly and subsequently develop.
To prevent trismus of the masticatory muscle, you must:
- do not cause diseases of teeth and gums;
- get vaccinated against rabies and tetanus (rabies and, as a result, lockjaw can be fatal);
- In case of blows or damage to the jaw, seek emergency help from dentistry;
- avoid stressful situations, nervous tension;
- when engaging in contact sports, wear special helmets and mouthguards for protection;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with a trusted dentist. These are the doctors who work in the 32 Dent network of clinics, where you will be happy to see you at any time. Contact us!
Causes of tremors in the hands and other parts of the body, tactics
Tremor is the involuntary shaking of body parts, which can be caused by a variety of reasons.
Tremor of the chin in newborns causes the same clinical concern as tremors of the limbs in the elderly. This phenomenon is manifested by rapid rhythmic movements of some part of the body caused by muscle contraction. This reduction, in turn, is provoked by a failure in the transmission of impulses along the nerve endings.
It is necessary to distinguish physiological tremor from pathological.
The physiological type of tremor can be provoked by transient conditions and does not indicate organic pathology on the part of any organs or systems. Most often, such tremor occurs against the background of:
- emotional stress is one of the common causes of hand tremors;
- anxiety - if it does not drag on over time and does not require specialized help;
- fatigue - for example, after too intense exercise in the gym;
- hypothermia.
In this article we will talk about pathological tremor - caused by diseases and pathological conditions.
Causes of jaw clenching during trismus
- inflammation of the masticatory muscles;
- inflammation of the gums;
- caries;
- abscess;
- inflammation of the periosteum of the lower jaw;
- jaw injuries (cracks, fractures, dislocations);
- dousing with cold water;
- animal or insect bites.
Trismus can also be a consequence of the following diseases:
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periostitis;
- neurosis;
- epilepsy;
- meningitis;
- hysteria;
- arthrosis of the jaw joint;
- cancerous tumors;
- convulsions;
- rabies;
- tetany;
- paralysis;
- tetanus;
- pulpitis in the acute stage, etc.
Hyperkinesis, or nervous tic
04.03.2020
Have you ever noticed in yourself or those around you an involuntary twitching of the upper eyelid, a wink of the eye , frequent lip curling or twitching, or wrinkling of the nose ? If it seems to you that the movements described above are nothing more than a bad habit, and you can get rid of it at any time, then you are mistaken. When such a phenomenon occurs, it is time to sound the alarm and take action.
What is a nervous tic?
This disease must be understood as involuntary muscle contraction caused by malfunctions of the brain responsible for coordination. Often, a tic is a temporary phenomenon that suddenly began and also disappeared unexpectedly. But there are many patients who suffer from symptoms for months and even years. In this case, there is no point in enduring discomfort. If the twitching does not go away within a few days, then you need to go to the doctor and take action.
Types of nervous tics
If you think that a nervous tic is manifested only by twitching of the eyes and lips, then you are mistaken. In medicine, there are 3 large groups of conditions:
- motor tics, the main symptom of which is, for example, twitching of the shoulders and fingers. This basically includes any uncontrolled movements of the limbs;
- facial tics, manifested by twitching of the eyelids , frequent blinking, wrinkling of the forehead and other uncontrolled muscle contractions in the facial ;
- vocal tics that make themselves known by uncontrolled pronunciation of any sounds . This may include grunting, clicking, smacking, or coughing.
Causes
In fact, there are quite a few of nervous tic And here you will need the advice of an attentive and experienced specialist who can reliably understand what caused the discomfort. The reasons may be as follows:
- heredity. It turns out that a nervous tic can be transmitted at the genetic level to children from parents and grandparents. Therefore, if you have had or currently have manifestations of tics in your family, then take this seriously and, if necessary, take action;
- internal imbalance. Have you been experiencing internal dissatisfaction with yourself and the way your life is going for a long time? Do you keep everything to yourself? Then don’t be surprised that sooner or later the body will malfunction and show its protest, for example, in the form of twitching of the lips or eyes . It’s not for nothing that psychologists talk about harmony with oneself and peace of mind;
- overwork or excessive stress. a nervous tic appears, there is a regular impact on sensitive receptors, which respond to you with uncontrollable winking of the eyes , clicking of the tongue, or, for example, twitching of the fingers;
- damage to the nervous system . Perhaps this is the most common cause of nervous tics . Here we are talking about problems of cerebral circulation, previous brain , head trauma, including birth;
- stress. And, of course, we cannot fail to mention stress and its consequences. One of them is a prolonged nervous tic .
Treatment
If the nervous tic was a one-time occurrence, then there is nothing to worry about. But if it appears with enviable regularity or does not go away for a long time, then it is imperative to go for a consultation with a neurologist , who will select the appropriate treatment and medications. As a rule, therapy does not always involve the use of sedatives. In the fight against tic, physiotherapy, psychotherapy , massage , soothing herbal cocktails, yoga, swimming, sauna, and various meditation techniques are popular.
Published in Neurology Premium Clinic
The main stages of trismus
- third - a person can open his mouth 10 mm, the most difficult stage;
- second - the patient can open his mouth 10-20 mm;
- first - the patient opens his mouth 30-40 mm, respectively.
In all cases, a person should immediately consult a doctor. You may need treatment in a hospital setting. In the process of clenching the jaw, there is a high probability of damage to the gums and chipped teeth. If help is not provided in time, oxygen starvation may occur.
Dental diagnosis of trismus involves:
- visual examination of the patient;
- to unclench the jaw, the dentist injects a drug that relaxes the muscles;
- To make the diagnosis more comfortable for the doctor and patient, an anesthetic drug is also administered;
- In addition to the dentist, you may need to consult a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist.