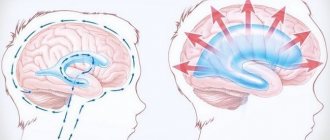
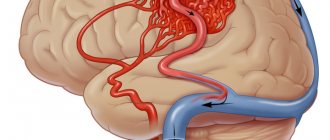
Brain compression
The clinical picture of brain compression depends on the etiology, localization of the compressive formation, its size and rate of increase, as well as on the compensatory abilities of the brain. Pathognomonic for most post-traumatic hematomas and hygromas is the presence of the so-called. “bright interval”, when the victim is conscious without showing signs of severe brain damage. The duration of the light interval can vary from minutes to 36-48 hours. Subarachnoid hemorrhage and the formation of a subdural hematoma can be accompanied by a clear interval lasting up to 6-7 days. In cases of severe brain damage (severe brain contusion, axonal damage), the lucid interval is usually absent.
Acute compression of the brain usually manifests itself with repeated vomiting, persistent intense headache and psychomotor agitation with sleep disturbance, sometimes delusional and/or hallucinatory syndromes. Later, the excitement turns into general inhibition, manifested by apathy, lethargy, and lethargy. There is a disturbance of consciousness that progresses from stupor to coma. Diffuse inhibition in the central nervous system is accompanied by respiratory and cardiovascular disorders, which are also caused by the resulting mass effect. The latter is a displacement of cerebral structures towards the foramen magnum, occurring due to increased intracranial pressure. The result is prolapse and infringement of the medulla oblongata in the foramen magnum with disruption of the centers located in it that regulate respiratory and cardiac activity.
There is a disorder in the breathing rhythm. Tachypnea (increased breathing) reaches 60 per minute, accompanied by noisy inhalation and exhalation, Cheyne-Stokes respiration is observed. Heart rate gradually decreases, bradycardia reaches 40 beats/min. and below, the blood flow rate drops significantly, and arterial hypertension is observed. Congestive pneumonia and pulmonary edema develop in the lungs. On auscultation, multiple moist rales are heard. The skin of the limbs and face becomes cyanotic. Body temperature rises to 40-41°C. Meningeal symptoms are detected. In the terminal stage, tachycardia and arterial hypotension appear. The pulse becomes thread-like, episodes of apnea (breath holding) appear, the duration of which increases.
In parallel, against the background of general cerebral symptoms, focal symptoms arise and worsen. They entirely depend on the topic of the pathological process. On the side of the lesion, drooping of the upper eyelid, diplopia, strabismus, mydriasis, central facial paresis (facial asymmetry, lagophthalmos, “sailing” cheek) are possible; on the opposite side (heterolateral) - paresis, paralysis, tendon hypo- or areflexia, hypoesthesia. Epileptic seizures, hormetonic convulsions (paroxysms of muscular hypertension), tetraparesis, coordination disorders, bulbar syndrome (dysarthria, swallowing disorders, dysphonia) may occur.
Characteristic symptoms
The fact that the pathological process has affected the brainstem can be understood in 95% of cases from examination data.
Focal neurological manifestations can be observed in the first hours of the disease and during the recovery period. The clinical picture of brainstem damage appears suddenly and develops at lightning speed, compared to other parts. The prognosis for recovery is usually worse. Signs of brain stem pathology are directly related to its purpose. It belongs to the nervous system and is its central part. Responsible for perspiration, heart function, body temperature, swallowing and chewing. Therefore, brainstem strokes are extremely dangerous, even fatal. The defeat of the department manifests itself sharply. The state of health quickly deteriorates, temperature fluctuations begin, nausea, vomiting, tachycardia, loss of consciousness, and coma often occurs.
In medicine, indicators for a disorder of this type are divided into two groups, depending on the form of the ailment, but there is a more general list suitable for all types:
- speech dysfunction;
- failure to regulate body temperature;
- poor coordination;
- muscle paralysis;
- change of voice after swallowing;
- change in pulmonary ventilation;
- inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- bradycardia or tachycardia;
- deterioration of vision of space;
- clouding of consciousness;
- poor sensitivity of the limbs;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma.
Hemorrhages occur suddenly, and the speed of assistance plays a big role. As soon as the severity of symptoms becomes obvious to others, you need to immediately call an ambulance. Most often, loss of consciousness or complete paralysis occurs. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of breathing.
Dizziness and loss of coordination
The harbinger is a feeling of pain in the skull or dizziness, accompanied by deterioration in coordination of movements and loss of balance.
This is often the earliest symptom of a pathological process in the trunk. Due to a persistent feeling of dizziness and pain in the back of the head, it is difficult for a person to stand on his feet and maintain balance. In such cases, the patient may suddenly fall or be forced to take a horizontal position. Coordination of movements suffers: the patient may not understand the position of body parts, an unsteady gait develops, hand movements are uneven and slow, and handwriting changes. All manifestations have a similar picture, but there are signs that are more noticeable than others or appear earlier. Unfortunately, a symptom such as dizziness will not allow you to accurately determine the cause of its occurrence, but will help you prepare for all possible outcomes. If the patient exhibits the described signal, place him in a lying or sitting position and wait for improvement. If none are noted, call a team of medical workers.
Make an appointment
Movement disorders
A brainstem stroke causes motor problems that become noticeable in the period following the stroke.
It occurs due to damage to the area of the brain responsible for cognitive activity. At the initial stage, programmatic decay manifests itself, which is expressed in changes in gait, frequent motor errors and focusing increased attention on arbitrary objects. Morphological damage in the nervous tissue of the trunk leads to impaired motor activity. This defect can progress and provoke structural disintegration of the statolocomotor system, which leads to disorganization of dynamic control of movement. At the final stage of development, the basic characteristics of the central generator of the step rhythm are affected. In this case, the patient experiences asymmetry in movements of both legs and arms, as well as freezing in place while walking. In other cases, while consciousness is preserved, a person is struck by paralysis of one half of the body (hemiparesis) or spreads to all limbs (tetraparesis). The prognosis for the restoration of motor functions is more favorable in the first 2-3 months of the disease.
Swallowing disorders - dysphagia
This is a severe manifestation of an acute disorder of cerebral blood supply.
It is observed in 65% of patients with brain stem stroke. When the nerve center is damaged, vital parameters, for example, the swallowing of saliva, are significantly affected. These tasks involve a significant number of muscles that can fail due to illness. Imperfect swallowing is called dysphagia. The danger of this complication is associated with a high risk of developing respiratory disorders and aspiration pneumonia. Most of these patients require tube feeding. The prognosis is usually unfavorable. In approximately 85% of cases, the ability to swallow is restored on its own within 2-3 weeks after the incident. Rarely does this defect remain for the rest of one's life. In this case, complications will follow:
- poor nutrition will lead to a deterioration in overall health;
- constant inflammation of the lungs due to unwanted microorganisms entering the respiratory tract;
- suffocation.
Timely treatment will allow you to get rid of all possible consequences and recover. To do this, it is recommended to contact a speech therapist, he will determine the severity and prescribe appropriate complex therapy.
Speech disorders - dysarthria
The cause of this disorder is a violation of the motor functions of the muscles of the tongue, facial muscles, and pharynx.
It is observed in approximately 30% of cases and manifests itself in changes in sound pronunciation, timbre, and intonation. Speech is distorted, losing intelligibility and articulation. In severe cases, speaking skills are completely lost. Dysfunction is accompanied by paralysis of the facial muscles located on the face and responsible for the ability to speak. This phenomenon is medically called dysarthria. The ability to communicate is lost due to disturbances in the brain stem. Associated symptoms are as follows:
- poor facial mobility;
- distorted, unintelligible speech;
- uneven speed of pronunciation;
- stops in the middle of a phrase;
- lack of emotional coloring.
To restore speech functions, the supervision of a speech therapist is required. Based on clinical information about the patient, he will select a personal plan of classes and exercises, after which he will begin rehabilitation. It is worth noting that the speed of recovery directly depends on the moment you contact a specialist.
Eye symptoms
If the part where the oculomotor center is located is damaged, the patient loses the ability to control the movements of one or both eyeballs.
This is reflected in the inability to fixate on an object, double vision, strabismus, outward deviation of the eyes and drooping eyelids. Sometimes fields of vision may disappear. Vision plays one of the main roles in the perception of surrounding information. It allows you to distinguish colors, objects and significantly affects the quality of life. Damage to critical areas leads to deterioration of visual perception. The described disadvantage can be determined by the following characteristics:
- black spots before the eyes;
- difficulty concentrating on one object;
- impossibility of recognition.
A problem with seeing the environment can haunt the patient throughout his life and cause disability, but it is not uncommon for him to be restored through medical practice.
Alternating syndrome - paralysis and distorted face
This symptom complex occurs as a result of dysfunction of the cranial nerves on the side of the lesion and conduction disorders on the opposite side of the body. Due to paralysis of the facial muscles, the patient on the affected side experiences sagging skin, drooping of the corner of the mouth and upper eyelid. In this case, the upper and lower limbs from the opposite area of the body remain immobilized. Paralysis or distortion of the face is one of the main symptoms of the disease. This has a significant impact on the ability to speak, causing dysarthria or dysphagia. To confirm, ask the victim to smile. If asymmetry is observed, then specialists should be called immediately.
Disorders of breathing, heartbeat and thermoregulation
Damage to the respiratory, vasomotor centers and thermoregulation center in a large percentage of cases ends in death.
Impaired respiratory function during a trunk stroke manifests itself in the form of severe shortness of breath or complete loss of the ability to breathe independently. Such patients are completely dependent on a ventilator. In other cases, when the center is not completely affected, the period of wakefulness may be accompanied by spontaneous breathing, but during sleep periods of apnea are observed. A change in the functioning of the cardiovascular system is expressed in an increase in heart rate, which is then replaced by bradycardia and a drop in blood pressure. Arrhythmias and fibrillations may develop. Taking traditional antiarrhythmic drugs in such cases is ineffective. Unstable thermoregulation is observed in rarer cases and is characteristic of the most severe degree of the disease. It manifests itself in the form of a sharp and persistent increase in body temperature to 39ᵒC and above, and cannot be corrected with medication.
In other cases, critically low temperatures may occur. Both options have a disappointing prognosis for recovery.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
A patient with suspected cerebral compression should be assessed and treated as soon as possible. In Israel, it takes about three days to make a diagnosis and develop a treatment program.
- Day 1
- Day 2
- Day 3
Immediately after admission to the medical center, the patient is sent for a consultation with a leading neurologist.
The doctor conducts a thorough neurological examination and clarifies the nature of the symptoms. If it is impossible to talk with the patient, the neurologist interviews the relatives accompanying him or the people who were present at the incident that caused the injury. If there is a traumatic brain injury, the patient is examined by a traumatologist. During the consultation, the doctor prescribes the most necessary types of diagnostic examinations. Carrying out the examinations specified in the list of appointments:
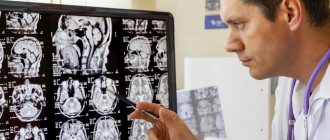
— computed tomography (CT) of the brain is the main method for diagnosing pathology; in addition to standard technology, multislice CT (has a shorter duration) and perfusion CT (designed to determine the activity of cerebral blood flow) are used;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain - provides the most complete information about the degree of displacement of brain tissues and structures, the presence of foci of ischemia, and signs of contusion;
- laboratory blood tests.
The data obtained is submitted for consideration to a medical council, which includes a neurosurgeon, neurologist and highly specialized specialists. After analyzing the information, doctors collectively establish a diagnosis and prescribe therapy.
Advantages of treatment in Israel
- High level of qualification of specialists.
- Availability of modern high-precision equipment.
- Treatment using modern methods.
- Fast diagnostics.
- Loyal prices.
With timely and adequate treatment by highly qualified specialists, it is possible to improve the prognosis and achieve maximum restoration of impaired brain functions. Don’t waste precious time, contact an Israeli clinic as soon as possible and start treatment under the guidance of the best doctors in the world.
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(0 votes, average: 5 out of 5)