Doctors Cost
Price list Doctors clinic
Treatment of dizziness in elderly patients is a complex task, which can be accomplished by a team of experienced doctors at a multidisciplinary clinic equipped with modern equipment. This disease is a consequence of various changes in the body that occur when organs and systems are damaged. Therefore, the approach to the disease must be comprehensive.
For reference:
An elderly person in Russia is considered to be a man aged 61–75 years old and a woman aged 56–75 years old.
Vertigo syndrome
Dizziness, or vertigo (from the Latin “vertigo”), is a condition in which a person in a stable position notices the illusion of movement of objects around him. In young people, vertigo may be the only symptom; in older people, it is usually accompanied by other symptoms: hearing loss, ringing in the ears, nausea, vomiting, and weakness in the legs. The severity of vertigo varies significantly - from insignificant to catastrophic. Severe dizziness in an elderly person, if left untreated, can lead to complete disorientation, incoordination, falls and injuries, and panic disorders.
When should you see a doctor?
You should sound the alarm if dizziness becomes regular or prolonged. Get immediate help if you experience severe dizziness and unsteadiness along with the following symptoms:
- sudden headache;
- painful sensations in the chest area;
- labored breathing;
- numbness or weakness of the limbs;
- fainting;
- fast or intermittent heartbeat;
- slow or slurred speech;
- problems with coordination;
- continued vomiting;
- convulsions;
- sudden hearing loss;
- numbness or facial asymmetry.
Development mechanism
Several systems help a person navigate space and stay in balance:
- vestibulocochlear organ, visual and proprioceptive systems;
- Nerves connecting peripheral analyzers with brain structures;
- Central nervous system (CNS or brain and spinal cord).
If any of these systems fail, vertigo develops.
Systemic dizziness in the elderly. Causes and treatment
The condition is associated with damage to one or more systems, which is why it got its name. In people over 60 years of age, several systems are often affected simultaneously. The clinical picture and the recommended treatment regimen depend on the level of impairment.
There are peripheral and central vertigo.
Table 1. Some diseases accompanied by peripheral vertigo
| Diagnosis | Symptoms |
| Meniere's disease | Attacks are accompanied by hearing loss, nausea, tinnitus |
| Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) | Vertigo occurs when turning or tilting the head and lasts less than a minute. |
| Vestibular neuronitis | Severe rotational vertigo with loss of balance, vomiting, nausea. Often a complication of ARVI. |
| Perilymphatic fistula | Develops after injury, chronic otitis. An attack is provoked by changes in pressure and loud sounds. |
| Labyrinth infarction | Combined with tinnitus or one-sided deafness. |
Diagnostic methods
The Clinical Brain Institute has all the conditions for a full diagnosis of dizziness. The process is carried out by analyzing the work of the vestibular apparatus and the brain, after which the localization of the pathological process and its stage can be detected. During the initial examination, it is important to conduct a detailed interview with the patient and obtain a detailed description of the complaints. At this stage, it is possible to differentiate true dizziness from other conditions that are also often called by this term. Next, specialists will select an individual diagnostic scheme, which may include the following steps:
- examination of the spinal column (analysis of X-rays, CT or MRI) to identify osteochondrosis, vertebral displacements and other pathologies that cause impaired blood supply to parts of the brain;
- examination by a neurologist, which includes determination of nystagmus, various tests and assessment of the ability to coordinate movements;
- examination of the state of the brain using MRI or CT - carried out to exclude tumors and other diseases leading to demyelination of nerve fibers;
- electroencephalography is a way of assessing brain activity by capturing the signals it produces;
- study of the functioning of the vestibular apparatus - may include rotational tests, vestibulometry and other tests.
Instrumental techniques are prescribed after a general examination. Based on the data obtained, the doctor can determine what examinations need to be performed in order to conduct a differential diagnosis and exclude possible causes of dizziness. Thus, if Meniere's disease is suspected, patients are offered a test to detect low-frequency sound signals.
Central vertigo in the elderly: causes, treatment
Associated with brain dysfunction.
Vestibular migraine.
It is characterized by attacks of dizziness with migraine-type headaches lasting no more than a day.
Impaired blood supply to the central nervous system.
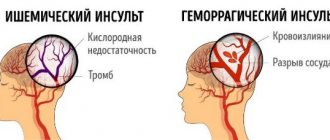
Cerebral ischemia is often caused by embolic or atherosclerotic vascular lesions. This is dangerous for the development of a stroke.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Associated with short-term (1 day) blockage or spasm of a blood vessel in the brain by a thrombus or embolus. With spontaneous restoration of the lumen, all symptoms disappear. Vertigo may be accompanied by nausea, numbness of one half of the face or body, weakness in the legs, and speech disorders.
Archer syndrome
caused by compression of the vertebral artery at the C1-2 level. When turning the head to the left or right, severe dizziness occurs.
Infarction or hemorrhage in the cerebellum.
Typical for elderly patients with high atherosclerotic risk, suffering from diabetes mellitus and hypertension. The disease begins acutely with dizziness, unsteady gait, and falling towards the affected side.
Multiple sclerosis.
Occurs when foci of demyelonization occur in the cerebellum. It is characterized by persistent vertigo that lasts for several weeks or longer.
The best drugs for dizziness with disorders of the vestibular apparatus
Violation of the vestibular apparatus also requires taking pills for nausea and dizziness. Their main task is to influence special histamine receptors that are located in the vessels of the inner ear. It can be taken once in case of long trips in transport, or as a course for maximum therapeutic effect. The top rating of 2021 presented 2 drugs in this category.
Dramamine
The active substance in the composition is dimenhydrinate, which inhibits the increased activity of the vestibular apparatus analyzer. As a result, taking the tablet suppresses nausea, the urge to vomit with all the ensuing consequences, and gives a moderate antiallergic effect. Most often, Dramamine is used to prevent motion sickness on airplanes, vehicles, and ships; for this, it is important to take the tablet an hour before travel. Doctors prescribe tablets for a course of treatment for Minière's syndrome, epilepsy, and other vestibular pathologies. Age limit: from 1 year of age; use in the first trimester of pregnancy is not recommended.
Advantages
- Performance;
- Prevention of motion sickness;
- One-time, course admission;
- Over-the-counter sale;
- Minimum restrictions;
- Children allowed;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws
- Possible side effects;
- Causes drowsiness.
The tablets not only calm the vestibular apparatus, but relieve muscle tone in all internal organs and prevent motion sickness in any type of transport. The advantages include quick help within 15 minutes, minimal restrictions, and price. The weaknesses of this treatment are drowsiness and the presence of side effects.
Relanium
A modern second-generation anxiolytic drug belonging to the group of tranquilizers. Most often prescribed by doctors for muscle spasms, nervous strains, anxiety disorders, as well as in various cases of damage to the cervical spine. The active component in the composition is diazepam, which enhances the effect of the inhibitory neurotransmitter, on which the transmission of nerve impulses directly depends. Widely used in medicine as a muscle relaxant, hypnotic, and sedative. There are no age restrictions; Relanium is prohibited for use during pregnancy and lactation. Available in the form of an injection solution.
Advantages
- Removing mental and nervous excitement;
- High efficiency;
- Emergency help;
- Sedative, hypnotic effect;
- Children allowed;
- Relieving cramps;
- Inexpensive.
Flaws
- May be addictive;
- Sale by prescription.
In medical practice, Relanium is used in emergency cases when it is necessary to quickly relieve attacks of nervous and mental agitation. Course treatment is also practiced, but strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Among the advantages, reviews emphasize speed, high efficiency, calming and hypnotic results. The disadvantage is considered to be sale only under a prescription, the risks of developing addiction.
Non-systemic dizziness in the elderly. Treatment
It is also called imaginary or false vertigo, since there is no characteristic damage to anatomical structures. However, it bothers up to 20% of patients over the age of 50 years.
Pre-fainting state.
Lasts a few seconds before fainting occurs. Caused by a sudden disruption of the blood supply to the brain caused by a spasm or another reason. Symptoms go away if you immediately sit or lie down.
Orthostatic vertigo.
Appears during a sharp transition from a horizontal to a vertical position, when getting up from a chair after eating. Caused by changes in blood pressure and cerebral ischemia.
Persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPVD)
, which was previously called psychogenic. Patients experience a feeling of excessive lightness or fog in the head, swaying, and non-rotational vertigo. It can last several months with periodic fluctuations in the severity of symptoms. It usually intensifies when being in crowded places, transport, watching TV or flashing pictures on a computer monitor, in enclosed spaces.
Disembarkation syndrome.
The illusion of continuing to travel on a train, on a ship, or riding a carousel, although physically the person is on a stable, flat surface.
Providing assistance at home
If dizziness bothers you regularly, you need to contact a neurologist who will find out the cause of the problem and help eliminate it. Before visiting a doctor, you can try to get rid of dizziness during sleep using several traditional medicine methods. These include:
- light massage of the neck and scalp;
- performing regular breathing exercises for two minutes (to do this, place a hand on your stomach and begin breathing slowly through your mouth, while you need to inflate your stomach as much as possible when you inhale and draw it in when you exhale);
- pressing the center of the forehead with your fingertips for several seconds (about ten);
- ventilation of the apartment;
- getting rid of tight clothes (they should be unbuttoned or removed);
- Avoid sudden body movements, including sudden turns of the head. You need to take a vertical position carefully, without rushing.
Changing your lifestyle can significantly improve the patient’s condition and even cure dizziness. That is why experts advise normalizing your diet, following a daily routine (it is very important to distinguish between rest and sleep time), taking active walks in the fresh air for at least an hour every day, and conducting therapeutic exercises.
These measures have a therapeutic effect for any pathologies that provoke dizziness. Their regular adherence will help a person prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the symptoms of vertigo.
If, despite following all the advice of a specialist, the head continues to feel dizzy, leading to further deterioration of the patient’s condition, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance.