Get an MRI of your head and find out the cause of your concern within 60 minutes
Make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 120-55-67 or 24 hours a day using the registration form on the website
Sign up for an MRI
- Restrictions on the procedure: weight up to 120 kg, volume up to 140 cm;
- The procedure time is 20 minutes;
- Imprisonment time 20 minutes;
- There are no preparatory procedures;
- Application of constructing If necessary;
Indications
- skull injuries accompanied by bleeding, especially internal;
- head injuries with temporary loss of consciousness;
- post-stroke condition;
- brain tumors;
- diseases and abnormalities of the vascular system of the head;
- infectious diseases of the nervous system;
- pathologies at the base of the skull;
- sinusitis;
- epilepsy;
- multiple sclerosis;
- constant headache;
- eye diseases and hearing loss.
Contraindications
- presence of a pacemaker,
- ferromagnetic devices,
- metal implants,
- hemostatic clips on blood vessels.
In some cases, in order to create a more complete and accurate picture that will help identify the causes of the patient’s complaints, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the head using tomography.
In such cases, magnetic resonance imaging of the head is carried out simultaneously with the diagnosis of the cervical spine, blood vessels of the brain and neck, as well as MRI of the sella turcica, maxillary sinuses, eye orbits and internal auditory canals.
| Field of study | MRI prices without discount | Prices for MRI ON PROMOTION in Kurkino | Prices for MRI + online consultation with a doctor after MRI | ||||
| Equipment power | 1.5 Tesla | 1.5 Tesla | |||||
| Magnetic resonance imaging of the head | 4,500 rub. | 5 200 | |||||
| Pituitary gland | 5 100 | 4,500 rub. | — | ||||
| Orbit | 5 100 | 4,500 rub. | — | ||||
| Paranasal sinuses | 5 100 | 4,500 rub. | — | ||||
| 2 temporomandibular joints | 9 000 | 7,500 rub. | 8 000 | ||||
| Brain + trigeminal nerve for neurovascular conflict, slice thickness 1 mm | 9 500 | 7,500 rub. | 10 900 | ||||
| MRI of the internal auditory canal | 5 100 | 4,500 rub. | — | ||||
| High-resolution MRI - episyndrome | 11 000 | 9,000 rub. | — | ||||
| 1,600 rub. | ||
| Recording an MRI study on flash | 1 200 | 1,000 rub. |
| Photographs on film | 800 | 700 rub. |
| Archive forwarding | 400 | 300 rub. |
Book your MRI now!
Why is it better to do MRI here?
- Our specialists will make an accurate diagnosis in a short time
- Best prices in town!
- We have extensive experience in providing such services
- We take on the most complex and confusing cases
During a comprehensive examination, it is possible to obtain a more complete and accurate picture of the characteristics of the blood supply, as well as both structural and morphological changes in the areas under study. The totality of the data obtained helps the attending physician in correlating the identified changes with the symptoms found in the patient, which makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate therapy. Timely and properly selected treatment will help to significantly improve the prognosis and get rid of the disease in less time.
Contrasting The use of a contrast agent (based on gadolinium salts) allows you to delineate the boundaries of pathologies, tumors, and identify even the smallest metastases that cannot be seen with other types of diagnostics. The contrast agent is injected intravenously before the start of the diagnosis, carried through the bloodstream, it accumulates in places with pathologies that become clearly visible when exposed to a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. gadolinium-based drugs have no side effects and very rarely cause an allergic reaction. The cost of contrast is added to the total cost of the MRI.
Equipment for MRI MRI at the MRI Center clinic in Moscow is performed using modern high-tech equipment. Philips Achevia 1.5T tomographs are installed in all Moscow branches, supporting SENSE parallel scanning technology, which helps increase the speed of diagnostics by 16 times, and 4D visualization and display of tomograms in real time increases the accuracy and quality of the resulting images. Thanks to the technical parameters of this type of tomograph, a patient weighing up to 120 kg can undergo diagnostics in any of our branches in Moscow.
Magnetic resonance angiography of cerebral vessels
The use of vascular MRI (MR angiography) makes it possible to visualize brain vessels in a short time, without the use of contrast agents.
MR angiography (MRA) is used as a screening method in the initial examination of patients.
Vascular MRI allows:
- Obtain information about morphology;
- Determine the size of vascular malformations;
- Determine anatomical location;
- Assess the relationship between the AVM node and the feeding arteries;
- Assess the nature of venous drainage;
- Determine the sizes of medium, large and giant aneurysms;
- Distinguish between the dome, body, and neck of the aneurysm;
- Assess the cervical-body ratio;
- Detect the presence of an intraluminal thrombus by direct signs.
In difficult diagnostic cases, to differentiate a tumor or vascular malformation, it is additionally possible to administer a contrast agent to the patient. The cost of an MRI examination depends on the specifics of the diagnostics being performed, for example, additional examination of blood vessels. The cost of an MRI scan with contrast will be higher. A comprehensive MRI of the head can take up to 1 hour.
When is a comprehensive head diagnosis necessary?
Complex tomography can be prescribed to patients with frequent headaches of unknown etiology, dizziness or fainting, since in this case the cause of the ailment can be any of the above areas. An important factor is also that the price of MRI for a set of services is usually significantly lower than for sequential examination of each area.
In addition to the above indications, a full head examination may be prescribed if the following indications are present:
- head injuries;
- neurological diseases;
- problems with hearing, vision, smell;
- suspicion of cancer;
- decreased mental abilities;
- external hydrocephalus;
- feeling of numbness;
- noise in ears.
Indications for MRI of the brain are:
Emergency conditions:
- Traumatic brain injury (MRI is performed after computed tomography);
- Acute cerebrovascular accident of an ischemic or hemorrhagic nature (MRI is performed after computed tomography).
Routine MRI studies of the brain and blood vessels of the head:
- Suspicion of a tumor of the brain or its membranes, pituitary gland.
- Diagnosis of degenerative or demyelinating diseases.
- Diagnosis of focal inflammatory processes in the brain.
- Detection of arteriovenous cerebral aneurysms, stenoses of intracranial vessels, vascular malformations.
- Assessment of the condition of the liquor-conducting pathways and liquor-containing structures of the brain (cysts, hygromas, porencephaly).
- Detection of abnormalities in brain development.
- Assessment of the state of the brain after a cerebrovascular accident.
- Assessment of the state of the brain after traumatic brain injury.
- Evaluation of the results of surgical treatment of brain diseases.
- Detection of pituitary gland diseases.
In ophthalmology:
- volumetric lesions of the orbit;
- optic nerve atrophy.
In otorhinolaryngology:
- volumetric lesions of the paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx;
- exclusion of acoustic neuromas.
Contraindications
A comprehensive examination of the head using MRI is an absolutely safe and harmless procedure that has almost no contraindications. Limitations on diagnostics using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner are mainly associated only with the features of the device and the principle of its operation.
Thus, using MRI it is prohibited to examine patients:
- with a cochlear implant;
- with a neurostimulator;
- with an artificial heart valve or pacemaker;
- with metal plates, pins or surgical staples;
- with limb prostheses or joint replacements.
Also, persons under the influence of alcohol and patients whose maximum weight exceeds the technical limitations of the device are not allowed to undergo a comprehensive examination of the brain.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, diagnosis is prescribed only in cases where the benefits of the procedure outweigh the possible harm (studies have not been conducted on pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, so there is no data on the effect on the body).
If there is an allergic reaction to a contrast agent or renal failure, tomography is possible only after studying the results of a biochemical blood test.
Children, patients with claustrophobia, and people with increased nervousness may need to take a sedative before the diagnosis, as movement in the tomograph can spoil the result of the study.
For the same reason, patients with diseases that cause involuntary body movements (schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease) may be denied the study.
Patients experiencing pain may need local anesthesia or general anesthesia (depending on the condition) before the examination.
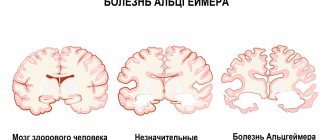
How does a psychiatrist diagnose dementia?
People change as they age, and some of these changes are part of natural aging. First of all, the doctor evaluates them. Signs of normal aging include the following cognitive changes:
- minor memory impairments about recent events (slight confusion in dates, details, sequence of events is acceptable);
- slower processing of new information and learning;
- longer completion of neuropsychological tests.
At the same time, an elderly person should normally be fully oriented in time and space, maintain criticality, clear thinking, the ability to speak, count, and determine his own personality.
At a preventive appointment, a psychiatrist assesses cognitive functions in several ways:
- Conversation. The doctor collects information about previous and existing diseases, other medical history data, assesses the preservation of memory and thinking, emotional manifestations, the degree of adaptation to living conditions, the level of independence, and the ability to self-care.
- Behavioral assessment. During the examination, the doctor assesses to what extent the elderly person interacts with him, how easy or difficult it is for him to answer questions, and how quickly he fulfills requests.
- Assessment using screening scales. During a conversation or survey, scales or questionnaires are filled out to assess mental status and the severity of cognitive impairment, if any.
- Assessment of additional factors. The results of the examination may be influenced by the fatigue or poor motivation of the elderly person, high or low level of education, health status (including hearing impairment, visual impairment, severe pain syndromes), the presence of disorders and impairments, and the use of certain medications (including sedatives, hypnotics, psychotropic, antitumor, antiparkinsonian and others).
If the results of the examination reveal disorders, it is necessary to differentiate between dementia and other age-related disorders. If cognitive function is impaired in old age, a neurological examination is necessary, especially in cases where there are obvious neurological symptoms. These include reflex disorders, their one-sided manifestation, walking disorders, reduced field of vision, and others.
The task of a psychiatrist when diagnosing dementia is to assess not only the current state of cognitive functions, but also the dynamics of the disease, how it progresses. This often allows us to judge the cause of the development of the syndrome.
Diagnostic criteria
Dementia is diagnosed if, as a result of an examination by a neurologist or psychiatrist, all of the following symptoms and conditions are identified:
- Cognitive or behavioral impairment that is so severe that it affects a person’s ability to work, perform normal activities, or take care of themselves.
- The identified symptoms are not associated with delirium or other mental disorders.
- Cognitive impairment increases over time, and the person’s condition gradually worsens.
In dementia, at least two disorders from the following list are identified:
- Inability to remember new information (the person constantly asks questions, forgets where he put his things, how to use them).
- Problems in solving complex problems, performing sequential actions, and reasoning.
- Speech disorders: mistakes, problems with formulating thoughts, choosing the right words. Difficulties can arise in both written and oral speech.
- Visual and spatial disorientation (a person does not understand where he is, gets lost in places familiar to him, does not recognize familiar people).
- Noticeable changes in behavior or personality traits.
If any of these symptoms appear, gerontological doctors recommend contacting a neurologist for diagnosis as soon as possible. Dementia is best treated at an early stage, and if the disease is caught early, its progression can be significantly slowed. Without treatment and rehabilitation, the disease quickly progresses and leads to the fact that a person loses independence, cannot take care of himself, he needs constant care, and his personality changes irreversibly.
- Preventative medical examination for the elderly
- Types of instrumental examinations
- Laboratory diagnostics: main types of tests
- Examination by a neurologist and psychiatrist for the diagnosis of dementia and Alzheimer's disease
What does a brain MRI show?
Having received 3D images of the brain in different projections, the doctor has the opportunity to examine each area in detail. This allows us to draw conclusions about:
- processes occurring in brain tissue;
- condition of blood vessels;
- the presence, location, shape and size of neoplasms, hematomas or blood clots;
- the presence, stage and localization of other brain pathologies.
Thanks to MRI, it is possible to visualize the brain in different projections, which significantly increases the information content of the examination
If the results are not accurate enough or additional visualization of a specific area is required, an MRI of the brain with contrast may be ordered. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to obtain a more accurate idea of the structure of brain tissue or pathological formation and to clarify its boundaries.