Medical information is reliable Checked by Eremin Alexey Valentinovich
The intense rhythm of life, constant stress, individual characteristics of response to certain circumstances. All this can provoke various pathologies. Borderline personality disorder is characterized by the individual's emotional instability, impulsiveness, anger for no reason, and other unpleasant manifestations. The patient himself, as well as those around him, suffer from them.
The disorder is persistent, manifests itself throughout life, and occurs at an early age. The diagnosis is established based on the history of events, the results of diagnostic techniques, and a personal conversation with the patient. The Clinic of Doctor Isaev provides treatment for borderline personality disorder. To normalize the patient's condition, traditional techniques and original methods of psychotherapy are used. Drug therapy and related techniques are prescribed to restore mental balance.
General information about the disease
Borderline personality disorder is a form of psychopathy that significantly impairs the quality of life. A person suffering from it cannot build long-term relationships with partners, he has no friends, and adaptation to new conditions is extremely difficult. Conflict situations are aggravated by a lack of self-control. The patient is unable to monitor his reactions and control his own impulses in behavior.
The disease is diagnosed in approximately 3% of patients with mental disorders, 10% of them die by suicide. The first symptoms of BPD appear in adolescence, and the trigger is not necessarily stress. The development of mental illness can occur gradually. At first, it often remains invisible to others.
The inner world of such patients is very poor; they often describe their state as empty, “de-energized,” devoid of energy and strength. Borderline personality disorder is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent worries over minor issues;
- emotional instability;
- impulsiveness in decision making;
- internal experiences;
- inability to master basic communication skills.
Frustrated attempts to realize oneself in the profession and society aggravate the situation. Against the background of constant dissatisfaction with oneself, depression develops. Drug and alcohol addiction occurs. First, with the help of third-party stimulants, such patients try to relieve internal pain. Unnoticed, they become involved, exhibiting extreme forms of alcoholism and drug addiction.
general information
Within the borderline spectrum, psychopathy, neurotic personality development, and reactive states are considered. The description of this group largely overlaps with the characteristics of borderline psychopathy, but does not fully correspond to it.
In various sources, the listed pathologies are found within the framework of the description of different clinical forms. This is explained by the extreme mobility of diseases, the multiplicity of etiofactors and pathogenetic mechanisms, and possible variations of symptoms. The main characteristics are:
- the presence of a fluid transition between normal and pathological functioning;
- mobility and blurred boundaries between different forms of pathologies included in this group;
- the possibility and likelihood of changing the relationship between a person and psychogenic factors or pathogenic environment.
Due to the ambiguity, flexibility and variability of disorders, borderline states are the subject of study not only in psychiatry, but also in psychology, sociology and jurisprudence. At the same time, due to the possible emergence of a psychopathological component, psychiatry still remains the leading area in this issue.
Causes of BPD
Borderline personality disorder develops due to exposure to a number of external factors that cannot be controlled by the person.
- Heredity.
If the parents had this diagnosis, then the chances of it being diagnosed to the child in adolescence are quite high. Women suffer from this disease more often than men.
- Character traits.
If a person has low self-esteem, he is a pessimist by nature, his psyche is not resistant to stressful situations, he has increased anxiety, and the risk of developing borderline disorder is high.
- All forms of violence.
If a child suffered from emotional, sexual or physical abuse as a child, he or she may develop this disorder later in life. This also includes separation from one of the parents or their physical loss.
- Lack of emotional contact with a significant person.
Lack of attention on the part of the parent, his emotional coldness, and a subconscious prohibition on expressing his feelings lead to mental disorders. A similar picture is observed if significant adults expressed excessive or contradictory demands on the child. Unfavorable living conditions form a maladaptive pattern of behavior that manifests itself at a late age.
- Excessive activity of the limbic system of the brain.
This pathology occurs as a result of emotional deprivation, being a secondary disorder.
Borderline mental state in psychiatry and severity of personality disorders
In clinical psychiatry, three levels of mental disorder are traditionally distinguished:
- Neurotic
. This includes neuroses of various types, implying reversible temporary conditions that can be treated. - Psychopathic
level. In its plane lie personality disorders, which include character anomalies of various pathogenesis or painful changes in his traits, with which nothing can be done, since they relate to the personal structure of the individual. - And finally, the deepest damage to the psyche manifests itself at the psychotic
level. This includes manifestations such as delusions, hallucinations, and twilight consciousness.
In modern psychoanalysis, there are 4 levels of deviations. Between the state of psychosis and neurosis the “ borderline”
level", also called
borderline state
. A borderline state can mean both the disorder itself and a designation of the level of mental damage.
Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder
Although the full clinical picture is formed around age 25, the first signs of BPD appear in early childhood. Such children demonstrate inadequate emotional reactions to the situation. They may be too strong, although the stimulus is quite weak. Constant anxiety, emotional instability, and decision-making under the influence of impulse are the main characteristics of a child who has borderline personality disorder.
Identity defect
The main symptom of the disease, which creates great problems for the socialization of the patient. The patient is partially aware of his situation and at some moments understands that he lacks his own emotions, desires and habits.
Inability to build stable relationships
A person with borderline personality disorder is very vulnerable and suffers from pain caused by other people. He knows that a new relationship is doomed to failure, but he subconsciously strives for it. A timely visit to a psychiatric clinic will give a good prognosis for recovery.
The incentive for such behavior is the inability to tolerate loneliness. This condition is very painful for such people. They spend a lot of time in places where they can meet someone. They agree to go anywhere, just not to be alone.
One of the main symptoms of borderline personality disorder is the inability to recognize one's emotions. This leads to difficulties in controlling the distance between a partner and oneself.
Such patients have only one way to compensate for unbearable pain and loneliness - a change in mood. They fall into unreasonable anger, and after a few minutes they turn to joy.
Feeling empty inside yourself
The person feels unwanted, and this condition is chronic. Periods of exacerbation and remission alternate with each other. Often during psychotherapy sessions, patients describe an emptiness in their soul that looks like a huge black hole. Everything that is dear to a person falls into it. Panic arises due to the inability to take control of this process.
If you don’t have your own emotions, their substitutes are often physical pain and random acquaintances. It is important for the patient to feel the adrenaline, which tones the body. People with this pathology often say that their soul hurts. On a physical level, these sensations manifest themselves in the form of tightness in the chest and abdomen.
- Tendency to self-destruction.
The behavior of a person with borderline personality disorder is almost always impulsive. This happens because he cannot stand his own experiences and doubts that those around him can also do this. By failing to cope with this situation, the patient tends to harm his psyche and physical body. These are not necessarily wounds or cuts on the skin; often self-aggression and self-destruction manifest themselves in the form of the following tendencies:
- eating large amounts of food so that the body loses its attractiveness;
- a large number of tattoos on the skin, a gloomy style in the form of symbols of evil and death predominates;
- alcoholism and drug addiction, which lead to personality degradation;
- unprotected sex is a risk factor for diseases such as HIV, STIs and hepatitis;
- non-compliance with traffic rules, increasing speed as a subconscious desire not to return from a trip by car (risk when crossing the road and other deviations from the norm).
Constant mood swings
Patients with this diagnosis get used to the fact that emotional highs are replaced by lows. In the morning they can wake up with very gloomy thoughts and desires, at lunchtime they can be the happiest in the world, and in the evening they can sit and stare at one point, not seeing any light in their inconsolable sadness.
Such mental metamorphoses greatly deplete the nervous system and affect all organs. This condition drags on for many years. The symptoms are very similar to other mental disorders, making diagnosis difficult.
- Lack of control over one's actions.
When the patient experiences intense anger, he may cause physical harm to others. Paranoid thoughts strengthen his belief that close people and friends are constantly plotting something and wishing him death. Constant mood swings provoke fights and crime. Often such patients end up in the dock; it is not always possible to suspect their inadequacy and refer them for treatment. Attacks can be made not only on people, but also on animals. The latter are weak and defenseless, and therefore cannot resist the patient’s aggression.
Common symptoms that may indicate mental problems in a loved one include:
- low self-esteem, lack of self-confidence;
- thoughts of suicide and attempts to implement them;
- the desire to be dependent and submissive;
- minor speech disorder;
- in any situation the patient blames only himself;
- lack of self-discipline and punctuality;
- resistance to change and the desire to maintain one’s status by any means necessary;
- confusion about life goals and one’s own feelings;
- inability to decide on sexual orientation;
- spontaneous spending of large sums of money;
- resistance to close contact and reduction of distance;
- casual sexual encounters and episodes;
- exacerbation of paranoid thoughts.
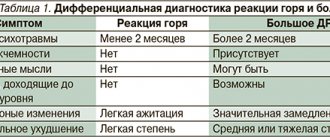
Symptoms
PS are represented by neurotic, neurosis-like, psychosomatic and mildly expressed affective symptoms. A variable multicomponent clinic may be revealed, representing a mosaic of neuroimmune, neurovisceral, neuroendocrine, autonomic and mental disorders.
The condition is often based on a feeling of psychophysical discomfort, in which mildly expressed somatic symptoms are incorrectly interpreted by the psyche or, on the contrary, psycho-emotional disorders are “reflected” in the body in the form of certain symptoms.
Characteristic signs are emotional lability, increased anxiety, strong feelings associated with uselessness, inferiority, inability to meet established requirements, fear of abandonment and rejection. An unfavorable emotional background becomes the basis for the development of depression, eating disorders and chemical dependencies. The risk of suicide increases.
Diagnosis of BPD
Diagnostics is the first and main stage before prescribing a course of therapy. The specialist takes the following steps step by step:
- a detailed survey of relatives, work colleagues and friends, which helps to establish the exact time when signs of borderline personality disorder first appeared;
- studying family history - it is important to make sure that close relatives do not have similar diseases;
- collecting maximum information about the patient’s life;
- conversation with the patient and observation of him from the outside in order to identify characteristic symptoms of mental pathology;
- conducting psychological testing to obtain a complete picture of the internal state of a mentally ill person.
How to get rid of it?
As you can see, the disease is characterized by serious symptoms and consequences; the natural question is: is borderline personality disorder treatable?
Let's look at which doctor treats borderline personality disorder and what methods are used.
When a person commits repeated inappropriate actions, and the problems arising in connection with this interfere with a comfortable life, he himself begins to understand that something is wrong. A person analyzes - is everything okay with me?
Some ignore it, others resign themselves, and still others begin to “calm down and heal their psyche.” In the latter case, one uses a search for similar situations described on the Internet and independently “prescribes” sedatives to oneself: from valerian and motherwort to serious medications. Based on symptoms, a person identifies himself as having a psychological personality disorder. Not all patients go to a doctor to confirm their diagnosis. Ignoring the problem only makes it worse.
If the patient’s borderline mental state is a threat to the life and health of other people, if the patient has a persistent personality disorder or neurosis, thoughts of suicide, loss of control and confusion, then he may be hospitalized.
Hospitalization and isolation of a patient with BPD do not show high effectiveness compared to the main method of treatment - long-term psychotherapy.
If a patient is diagnosed with borderline personality disorder, how to treat using psychotherapy methods is determined by a psychotherapist. Psychotherapy for borderline personality disorder is carried out using different methods.
Specific treatment for borderline disorders is lengthy and expensive. Treatment for BPD involves medication and psychotherapy.
The choice of drugs for the medicinal treatment of borderline disorders is selected by the doctor, taking into account individual characteristics.
The most effective medications for treating borderline personality disorder are:
- Antipsychotics are drugs that affect the central nervous system and correct the mental state: olanzapine, aripiprazole.
- Normotimics are stabilizing drugs that soften and inhibit the development of the disease: lamotrigine.
- Valproic acid is a drug to mitigate and prevent “peak” situations.
Drug treatment for BPD normalizes and harmonizes the psychological state and reduces the tendency to psychosis. At the same time, antidepressants, antipsychotics, benzodiazepines, and antipsychotics only temporarily alleviate the patient’s condition. Psychotherapy provides more lasting results for BPD. There are many techniques that help people with borderline disorders understand their problems and learn to build adaptive behavior patterns.
Psychotherapy for borderline personality disorder, some treatment methods:
| Schema therapy | The methodology works with the analysis of the image of perception of reality formed in childhood. Typically, distortions in perception that arise in the presence of facts of mistreatment, traumatic situations, and similar events manifest themselves throughout life. The task is to process the traumatic experience: the patient becomes aware of emotions and finds a way to react differently to situations similar to events from childhood. Different areas of psychotherapy are used - psychoanalysis, cognitive behavioral therapy, gestalt therapy. |
| Mentalization-based therapy | Problems in interpersonal relationships are corrected. The duration of treatment is up to one and a half years. A person is taught to comprehend his needs, emotions, actions and ultimate goals. Patients are also taught to understand how another person may feel. In various situations, what motives and meanings are inherent in the actions of other people. Therapeutic sessions are carried out individually or in small groups. |
| SET-UP | A method of communication associated with support, empathy, truth, understanding and persistence (American Acronym). The basis of the method is working with patients during periods of exacerbation of borderline disorders. Therapy is complicated by the fact that during crises, patients especially acutely feel melancholy, loneliness, and misunderstanding of others. |
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy | Based on the need to accept those suffering from borderline disorders as they are. The goal is to encourage patients to change and change their behavior. For this purpose, validation is carried out - communication between the patient and the doctor, where the doctor teaches ways to deal with stress, the basics of emotional stability, self-control and the ability to achieve set goals. The work is aimed at correcting impulsive behavior and self-regulation, and at developing crisis coping skills. The duration of therapeutic courses ranges from one year or more. |
| Art therapy | Treatment through creativity - music, dancing, creativity. During classes, patients learn to be aware of their feelings, accept themselves and remain in a harmonious state. |
To achieve a faster effect, group therapy can be prescribed along with psychoanalytic individual therapy. For this purpose, the patient is invited to a suitable group where other patients have a similar clinical picture. Additionally, the attending physician may prescribe family therapy. Family therapy is used only when the patient has a close connection with his family, and loved ones express their willingness to provide stable, calm treatment conditions.
Cognitive behavioral therapy for borderline personality disorder (CBT) works by changing thoughts and ways of responding.
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is becoming popular for the treatment of borderline disorders. In DBT, work with the patient is aimed at ensuring that he does not change his thoughts, but understands that there is a variety of points of view for a situation that he considers hopeless.
When diagnosed with borderline personality disorder, clinical recommendations help develop skills in order to reduce the level of intensity and emotionality of the reaction in difficult situations. For example, instead of injuring oneself during peak moments, the patient is taught to act by lowering the temperature (washing with ice water or squeezing an ice cube with force in one’s hand). During attacks, patients are advised to tense and relax their body muscles alternately.
Treatment of borderline disorder in Moscow
Therapy for this disease is based on a combination of conservative methods and the latest techniques with medications. All patients require courses of psychotherapy, as well as the use of medications with a specific spectrum of action. Cognitive behavioral therapy has proven itself well, helping to restore the adaptive potential of the psyche.
The specialist works in the following areas:
- rethinking the patient’s lifestyle;
- a detailed discussion of his problems, aspirations, desires;
- developing skills to control one’s behavior and spontaneously arising emotions;
- formation of protective mechanisms that will help in time to get rid of stress and anxiety;
- developing skills of constructive communication with other people.
Consultations can be individual or group. Communication with a psychologist in a confidential environment helps to relax, understand and acknowledge your condition. The second option involves the participation of friends, relatives, and other significant persons in the program. The specialist teaches all participants how to avoid conflict situations. Individual indicators of the course of the disease include the use of drugs from the following groups:
- antidepressants;
- neuroleptics;
- tranquilizers.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Complications without treatment
Timely contact with a specialist in a psychiatric department improves the prognosis of recovery. Ignoring the clinical manifestations of the disease leads to its aggravation and acquisition of a chronic form.
Among the negative consequences are:
- lack of opportunity to build personal and business relationships with partners;
- constant thoughts of suicide, which will sooner or later be realized;
- chronic depression, lack of interest in the outside world;
- social isolation, secluded lifestyle;
- lack of desire to leave the house.
Borderline personality disorder develops in childhood. It is very important to take some preventive measures to prevent the manifestation of the disease. Among them are:
- visiting a specialist in critical situations (divorce of parents or death of a loved one);
- allowing the child to express his own emotions, even if they are negative;
- exclusion of physical, emotional, sexual violence;
- providing conditions for full communication with significant adults;
- creating an atmosphere in which it is comfortable to live and study;
- building a trusting relationship in which the child can freely share his problems.
The duration of therapy is determined by several factors:
- features of relationships with loved ones;
- age;
- the primary source of the disease;
- willingness to undergo long-term therapy;
- level of personal, professional, social development.
Reasons for development
Specialists in various fields differ significantly in their views on the causes of PS. At the same time, most researchers agree on the polyetiology and complexity of the mechanisms of their development. The presence of certain similarities between PS and PTSD has been confirmed. Issues of environmental influence, hereditary predisposition, and brain damage in the prenatal period remain insufficiently studied.
Social factors are important: the characteristics of the patient’s relationships with other members of the parental family, social groups (in kindergarten, school). Within the framework of psychological factors, temperament, personality characteristics, developed response patterns and ways of coping with stressful situations are considered.
Questions and answers
Can borderline disorder be treated at home?
No. Such mental disorders are treated in a hospital setting. The patient can cause physical harm to the life and health of others, as well as to himself. Therefore, he needs hospitalization.
Is it possible to get rid of BPD using folk remedies?
No, using questionable drugs will only worsen the situation. Any medications are used after prior consultation with a doctor.
Impact of injuries
According to statistics, there is a clear correlation between childhood trauma and the development of PS in adulthood. Possible causes include sexual, physical and emotional abuse, neglect of the child's needs, lack of necessary protection, and insufficient health care. The history also often reveals the emotional detachment or changeable attitude of the parent.
The lack of a secure attachment and a feeling of insecurity cause difficulties in relationships with oneself and other people, sometimes - problems with identity of varying degrees of severity. All of the above causes insufficient formation of internal supports and, as a result, a decrease in resistance to various stress factors.
How does BPD manifest and how to get rid of it?
Often, “borderline personalities” have several symptoms of mental illness. From time to time, one of them comes to the fore - anorexia, depression or alcohol addiction.
A person comes to a psychiatrist with this problem, and in the course of eliminating it, the therapist discovers BPD. How does the disease manifest itself and how to deal with it?
Borderline Personality Disorder: Pexels
Symptoms of Borderline Disorder
Patients with BPD are difficult for the average person to understand, and the patients themselves are not always aware of their diagnosis. According to Doctor of Psychology A. Merinov, such people are almost constantly in a state of crisis and are distinguished by:
- sudden change in mood;
- often experience bouts of anger;
- have poor control over their rage.
In addition, the “border guard” is prone to various impulsive self-destructive actions. An unstable psyche can push him towards gambling addiction, bouts of shopaholism, sexual promiscuity, and the use of alcohol or drugs.
A characteristic manifestation of the disease is self-harm and suicidal tendencies. Borderlines can easily attempt suicide. Moreover, the ultimate goal of such an act is not to die, but to feel something and thereby prove to yourself that you are alive.
Symptoms of the disease also include:
- instability of interpersonal relationships with sharp transitions from idealization to devaluation of the partner;
- emotional sensitivity (any look or word can cause painful emotional experiences);
- distorted thinking and a tendency to see everything in black and white;
- paranoid ideas;
- inadequate perception of oneself and reality;
- inability to control emotions and actions;
- chronic feeling of emptiness;
- constant fear of being abandoned.
The latter, according to practicing psychologist Lina Dianova, turns “border guards” into tyrants, manipulators or ordinary egoists.
However, the problem is much deeper. Fear of loneliness often causes people with BPD to cling to relationships. They strive to constantly be close to the object of love, to spend all the time with him without interruptions for sleep, work or, for example, going to the store.