PERSONALITY, one of the centers. concepts of philosophy and psychology, a person considered primarily. as an autonomous bearer and subject of culture, historically established forms of world relations, which he implements in his activities. Along with this, in psychology there is also a widespread understanding of personality as an individuality, a stable specific structure that develops during life. psychological characteristics of the individual that underlie his characteristic forms of behavior.
Definition of personality in different sciences
In sociology, the concept of personality is studied in the process of relationships between people, as well as as a separate element of the social system. In addition, sociology conducts the study of personality when it is still being formed, in the process of its formation and the acquisition by an individual of certain qualities characteristic only of him. In contrast to legal science, which looks at this as a completely ready-made and formed concept.
In jurisprudence, a person is understood as an individual who has certain rights, freedom of action and obligations as an ordinary person and as a citizen in general. This concept refers to the personality of a specific person who has a number of socially important qualities that manifest themselves in relationships with other people.
The concept of personality in sociology and philosophy
In sociology, personality is considered as part of social connections:
- Personality is the social status that a person occupies, which determines his responsibilities and rights. A person can have many such statuses, depending on the presence of relatives, friends, work, activities, etc.
- Personality is a structure:
- Irrational (It) – instincts, desires, passions.
- Rational (I) – consciousness.
- Super-Ego – guilt, conscience, moral control.
All three components must be harmoniously combined in the personality: It must be controlled, just like the Self. Everything is controlled by the Super-Ego.
In philosophy, personality is understood as an individual who is aware of his own essence, the meaning of life and purpose. A person becomes a person when he realizes his arrival in life, his purpose, his ultimate goal. The individual is able to freely express himself and control his own motives.
Basic approaches to studying personality
There are many different theories of personality in the social sciences. Among them, the following main approaches can be distinguished:
- Dialectical-materialistic approach , according to which the personality develops according to a dialectical process determined by the following factors: the origin of the individual, the society surrounding him, upbringing and self-education skills. From the very beginning, a person is considered a social being, his personality is formed in the process of interaction with society, that is, when a person interacts with the world around him in the process of his formation and self-awareness.
- Anthropological approach . In this approach, the concept of personality is perceived as the bearer of the characteristic properties of all humanity. Personality is equated with the individual. This approach compares the understanding of personality, person and individual. He ignores the fact that the social environment plays an important role in shaping personality.
- Normative approach . According to this approach, the concept of personality is associated with the acquisition of good qualities that relate to a person's consciousness and actions.
- Sociological approach . Its essence lies in the fact that every person is an individual, regardless of his socially significant characteristics. The concept of personality in this approach is considered as an object and products of relations with society.
- Personal approach . In contrast to the anthropological and sociological approach, this concept makes it possible to understand personality as an individual and unique organism independent of any factors.
- Biological-genetic approach . According to this approach, it is believed that such behavior in people is embedded in their genes. What can be considered primitive determinism. This approach neglects the importance of social conditions and cultural heritage in the formation of an individual in society.
Article “The concept of the definition of “personality” by foreign and domestic psychologists”
Definitions of the concept of “personality” by different authors, indicating their names and synthesis of a general definition based on the analyzed data.
1. Z. Freud. Personality as a trinity: the psyche consists of three layers - conscious (“Super-I”), preconscious (“I”) and unconscious (“It”), in which the main structures of the personality are located. At the same time, the content of the unconscious is not accessible to awareness under almost any conditions. The content of the preconscious layer can be realized by a person, although this requires significant effort from him. In the unconscious layer there is one of the personality structures - “It”, which is actually the energetic basis of the personality.
2. A. Adler. The human personality is one, self-consistent and integral. The main determinant of personality development is the “will to power,” which is present in a person from birth.
3. K. Rogers. Personality is a unique holistic system, open to self-actualization, inherent only to man. Every person is endowed with the ability for personal self-improvement. At the same time, an important component of the personality structure is the “I-concept”.
4. K. Jung. Personality (psyche) consists of 3 main levels: Ego (I), personal unconscious and collective unconscious (Super-Ego).
5. E. Fromm. Personality is the product of a dynamic interaction between innate needs and the pressures of social norms and regulations.
6. P.A. Florensky. The personality of a person is a hidden inner core, which is known by a person only from the inside, in his free self-revelation before the face of God, in his dialogue with God, which arises through questioning God as his Creator and prayer efforts. A person’s personality is not a fact, but only an ideal, a certain “limit of aspirations and self-construction.”
7. V.S. Soloviev. Personality is the key element that determines the progress of society from “lower forms of society to higher ones due to its inherent unlimited desire for more and better.”
8. G.I. Chelpanov. Personality is an expanded image of the Self, which combines a person’s ideas about his inner world with the idea of his body.
9. G.G.Shpet. The personality must become entirely responsible: all its moments must not only fit side by side in the time series of its life, but penetrate each other in the unity of guilt and responsibility. A person, in accordance with his choice and efforts to implement it in actions, may or may not become a unique self, a personality, creates for everyone living an essentially existential problem of responsibility for their choice.
10. L. S. Vygotsky, A. N. Leontiev. A person is a person, as a representative of human society, who freely and responsibly determines his position among others.
Conclusion: A personality is a person developing in society, with his own views, beliefs, values and worldview, endowed with both innate and acquired qualities, as well as the opportunity to improve.
Personality structure
When studying and analyzing personality as a complex social phenomenon of society, it is important to highlight its structure, which is based on the following elements:
- biological level : it includes natural qualities inherent to all humanity (anatomical structure of the body, gender, character, etc.);
- psychological level : includes the psychological state of the individual such as the manifestation of feelings, freedom of choice, memories, way of thinking. Such features are closely related to hereditary personality traits;
- The social level is usually divided into the following sublevels:
- The sociological proper determines a person’s behavior in society, as well as his personal interests and pursued goals.
- Cultural-specific shows personal values, as well as behavioral factors corresponding to the norms of society.
- The moral sublevel demonstrates the moral qualities of a person, which he is guided by in any of his choices.
The concept of criminal personality in criminology
In criminology, it is also important to know personality psychology. To conduct an investigation and find criminals, you must understand their essence and internal motivations. By observing the behavior of criminals, you can do the following:
- Prevent future crimes by introducing new laws and regulations.
- Find the criminal, knowing his psychological profile, behavioral characteristics and motives.
Some believe that a person acquires the “personality of a criminal” from the moment he commits a crime. Others believe that a person becomes a criminal even before he commits an inappropriate act. In any case, a person loses his identity as soon as he commits a crime, while he retains it if he repents of his crime.
The influence of society on personality
Personality and social environment are inextricably linked. Its future depends on the environment in which a personality is formed. Seeing bad examples and irresponsible behavior in front of him, the child perceives this as a model. After some time, he may begin to behave the same way as his friends and people close to him. He may start drinking, smoking, stealing, without knowing that such behavior is the result of formed views on the world, the bad influence of his immediate environment.
Sometimes a person can fall under the bad influence of the social environment despite his desire. A schoolboy begins to smoke, fearing the ridicule of his classmates, who have long been addicted to cigarettes. A teenager decides to steal because of his friends’ obsessive persuasion to get easy money. An employee deceives his superiors after much persuasion from his colleague.
The positive influence of the environment on personality development is also manifested. Seeing before him examples of successful, happy and respected people, the child strives to imitate them and copy their behavior. Therefore, at school a lot of time is devoted to studying the biographies of national heroes, patriots, and outstanding personalities. A good example becomes an inspiration for work, creative activity, and activity in society.
()
Different structures of society have varying degrees of influence on the individual.
- Parents and close relatives have the greatest influence when raising a child from infancy.
- Second in terms of influence are school teachers.
- They are followed by friends, acquaintances, colleagues.
- The media play an important role (mass media: Internet, television, print media).
In addition, the individual is influenced by the socio-cultural environment characteristic of the state and the area in which he lives. So in Russia, the USA, India, Israel - the conditions for the formation of a personality are significantly different. Thanks to this, individual peoples and the population of different countries have their own distinctive character traits and individual characteristics.
Methods of social philosophy
Modern approaches in social philosophy have helped researchers determine not only the patterns of possible development of complex political situations, but also crystallize personality types. This approach greatly helps psychologists and analysts in individual and collective work with people. Today the following basic methods have been formulated:
- Participant observation
. The researcher infiltrates the team, as one of the employees or activists of the movement, in order to create an internal picture. Disadvantage: it is impossible to influence the course of the process. - Social experiment
. Studying an object in specially created conditions. Plus: you can repeat the situation many times for the purity of the experiment. Disadvantage: strict exclusion of trial and error methods. It also includes modeling a situation when an object is inaccessible or the situation is only predicted.
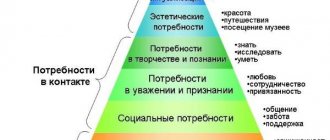
Motivational-need sphere as the basis of personality
Needs are the driving force of a person’s activity.
- Need is the body’s need for certain conditions, without which life is impossible.
- Motive is an objectified need.
- A set of motives aimed at a goal is motivation.
The need to understand the world is the most important for an individual. It frees a person from the captivity of fears, misunderstandings and superstitions, and allows him to be the creator of life.
Other spiritual needs are no less significant for the individual:
- in aesthetic pleasure;
- in labor;
- in social activities;
- in communication.
The development of needs (from lower to higher) is a condition for personality development.
Qualities inherent in personality
Personality is the totality of a person’s qualities. Each personality has its own unique set of qualities, there are a lot of them, sometimes one contradicts the other. So, a good-natured person may have greed in his character. He treats people around him well, but never lends money or gives expensive gifts.
Distinctive personality traits are:
- Worldview. This is a whole system of views on the world, ideas about it, values that can be realistic or illusory.
For example, a seven-year-old boy, Vasya, believes that all doctors are cruel and evil. He formed this opinion after Vasya suffered from a purulent sore throat. The doctor gave him injections for a whole week; a strong painful reaction was left in the boy’s memory for a long time.
But the worldview can change over time, so, having matured, Vasya will understand that he was mistaken about doctors in childhood.
- Character. Each person has a set of personal characteristics and qualities that determine his behavior. Character is closely related to emotionality, so excessive sensitivity can lead to touchiness, hot temper makes a person angry.
- Degree of responsibility. You can tell whether a person is serious or not by his actions. Individuals who are constantly late, fail to fulfill their obligations, promises, or refuse responsibilities are called irresponsible. A responsible person, on the contrary, strives to bring all matters to the end, keeps his word, and is responsible for his own actions. Such people are always respected and valued in society, they are entrusted with responsible tasks, and appointed to higher positions.
- Self-esteem. An individual can distinguish himself from the rest of society and evaluate his own activities, appearance, habits and other characteristics. Self-esteem is developed through the process of comparing yourself to others.
Self-esteem largely determines how society will accept a person and whether others will love him. You can notice how in the school class they tease narcissistic children who do not respect teachers and peers, considering themselves superior and much better than others. But guys with low self-esteem are also shunned; they often have few friends due to shyness and indecisiveness.
- Mental capacity. From birth, everyone has their own intellectual potential, that is, the ability to develop their minds. But a person can surpass his natural abilities thanks to perseverance, determination, and his work.
()
Example. Petya Ivanov has innate mathematical abilities. But he gets 4s and 3s because of laziness and unwillingness to do his homework. Sasha Sidorov is not good at mathematics, but he devotes a lot of time to extracurricular activities, and has already begun to earn his first A's.
If desired, a person can develop his memory, logical thinking, willpower and even physical abilities.
The qualities of a person’s personality are manifested and developed in the process of communication, interaction and work activity.
Personality formation
Factors
The psychological development of a person is influenced by hereditary factors, on the one hand, and factors of the physical and social environment, on the other. Mental development, like psychological development, continues throughout a person’s life. The prerequisite for individuality, the root cause for the formation of human originality, is, first of all, the environment where the future personality grows. An important role is played by the associations accumulated by a person in childhood, the model of education that instills moral guidelines, the peculiarities of the family structure and the principles of treating a child.
Genes control human development from birth, just as the lifestyle of the expectant mother affects the fetus. After birth, caring for the child supports his physical life, but at the same time directly affects the mental development of the future personality.
Different stages of a person’s life take into account certain tasks of mental development. Of course, successes occur regularly, but problems often arise. Psychological information is used to find solutions to any child's developmental problems - for example, in terms of language skills or schooling.
There are a number of opinions about which age periods of the individual are most important for the whole life. Psychology of life is the detailed study of human development at each stage of life. Individual development can be viewed through different methodologies and perspectives.
Stages of psychological development of personality, their features and connections with changes in physiology
Childhood. A child's first task is to learn that the world is a safe place and people can be trusted
That is why it is important that what is perceived and viewed by the baby during this period of life is appropriate for his age.
The children's sensory world, due to its immaturity, is still very small. Children under three years of age observe everything at a subconscious level of understanding. By school age, the boundaries of fairy tales and truth begin to be perceived visibly and tangibly.
Boyhood
The most important thing in adolescence is the formation of personality: who I am, how I behave. Today, thanks to technology such as social media, you can even get reactions to your own comments and photos.
At the same time, it all becomes surprisingly fragile: feedback can become a problem if she is not resilient enough to accept it.
Youth. This is a period of active self-determination and self-searching. There is often a strong tendency to create idols and negative self-identification in order to strive for a feeling of personal irresistibility. At the end of this stage, people often come to independence and a clear definition of their future life path.
Youth, which lasts approximately from 20 to 25 years, has such characteristic features as the desire to create a family and personal attachments, including intimacy. In first place in importance comes such a feeling as love, a feeling of attachment to a loved one, caring for him.
Maturity is one of the longest periods of personal formation
During this time, a person who has already achieved certain successes in life no longer focuses on his own personality, but on others. He strives to share his accumulated experience, unique knowledge, skills, and finally, simply life wisdom
Aging. During this phase of development, there is an active rethinking of one’s actions.
Therefore, it is very important for a feeling of happiness to be able to find joyful moments in the past and, of course, maintain physical health as much as possible
Essence
Thus, personality is the sum of a person’s ideas, attitudes and values that determine his role in society and form an integral part of his character. It is acquired as a result of his participation in group life. As a member of a group, he learns certain systems of behavior and symbolic skills that determine his ideas, attitudes and social values. These ideas, attitudes and values are the constituent elements. When considering the main definition, it should be taken into account that the concepts of “man”, “individual”, “individuality” and “personality” in philosophy are of the same order, but not identical.
Borders
The concept of personality in philosophy defines its limits much wider than the limits of the human body and its internal intellectual world. These limits can be compared to circles spreading on water: the closest ones are the fruit of creative activity, then there are circles of family, personal property and friendship. Distant circles merge with the seas and oceans of all social life, its history and prospects. Here, the way philosophy considers the concepts of “individual,” “individuality,” and “personality” comes to the fore.
The completeness of the latter is expressed in its uniqueness, in its uniqueness. This is what is called individuality. Personality as a whole is an abstraction that is concretized in real people, in individual, rational beings with all the unique properties of their psyche and physique, the color of their skin, hair, eyes, and so on. She is a unique representative of the human race, always special and unlike any other person in the fullness of spiritual and material, physical life: each “ego” is unique.