Stress, psychological and physical tension, prevents us from working and generally living with pleasure. The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration even considers stress an occupational hazard. Research shows that up to 80% of all visits to doctors are related to illnesses and problems caused by stress. Finally, it reduces productivity—after all, tired people tend to make poor decisions.
In this article, we figured out how to relax psychologically and physically, so that tension does not interfere with living and working effectively.
Manage different stages of stress
Experts divide professional stress into three stages:
- Growing tension.
- Actually stress.
- Reducing internal tension.
Our task is to control our condition and prevent the transition from the stage of increasing tension to the stage of stress. You can track the transition by observing behavior: we suddenly change it to the opposite when we become stressed. For example, a calm and reserved person suddenly becomes fussy, irritated, even aggressive and cruel, while a lively, active and sociable person can suddenly become gloomy, withdrawn and inhibited. Other signs of increasing tension: we stop looking the other person in the eyes, we feel the urge to move from meaningful conversation to personal attacks.
Being in the first stage, we can still be constructive, but gradually our self-control weakens. This means that it is important at this stage to take a break in communication, identify factors influencing tension, and remove them.
Symptoms of anxiety neurosis
The clinical manifestation of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms of a mental, somatic and vegetative nature:
- causeless anxiety of varying intensity: from a state that the patient describes as “anxious in the soul” to a paroxysmal feeling of an impending catastrophe;
- persistent intrusive thoughts of disturbing content with detailed thinking about dialogues or actions in response to various imaginary events;
- anxiety or fear over the most insignificant reasons;
- increased irritability;
- panic attacks during exacerbation;
- the occurrence of concomitant mental disorders during a long chronic period of the disease - hypochondria, depression, obsessive-compulsive neurosis;
- vegetative-vascular hyperactivity, which can be expressed in pain in the heart, rapid heartbeat, respiratory distress (feeling of lack of air), discomfort in the epigastric region (between the navel and sternum), dry mouth, increased sweating;
- sleep disorders - insomnia, interrupted sleep, disturbing dreams, nightmares;
- muscle hypertonicity, inability to relax, fussiness, tension headaches, trembling due to impaired motor functions;
- feeling of constant fatigue, lightheadedness, dizziness, loss of orientation;
- nausea, stool disorder (IBS - irritable bowel syndrome), appetite.
The main symptom of generalized anxiety disorder is the patient’s inability to clearly identify the cause or object of a long-lasting (from several weeks to several months) state of fear and anxiety.
Learn breathing practices
Psychologists consider breathing control one of the effective methods of dealing with stress. Scientists say that breathing exercises have a positive effect on all systems of the body, including the nervous system.
See also: How to increase stress resistance
To relieve tension, try concentrating on your breathing, the movement of your chest, rhythmically rising and falling in time with your breathing. Or on the flow of air passing through the lungs. At this moment, thoughts are distracted from the source of stress and attention switches from the traumatic situation to the breathing process.
Self-help for panic attacks: body
The most common recommendations and advice on self-help regarding the body are:
- intense exercise in the morning and (or) physical activity at the first signs of anxiety;
- long walks in the fresh air;
- deep calm breathing, or “diaphragmatic breathing”, or “belly breathing”, other types of breathing exercises;
- avoidance of alcohol and stimulants;
- cold and hot shower;
- sufficient sleep;
- plenty of warm drinks;
- medicines, herbal medicine, homeopathy;
- acupuncture.
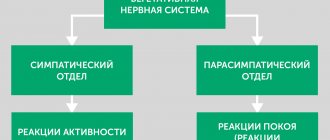
Separately, it should be said about methods of targeted activation of the parasympathetic division of the ANS and reducing heart rate by inducing specific reflexes:
- according to Aschner - close your eyes and use the pads of your thumbs to press intensely on the eyeballs for 15–20 seconds;
- “diving dog” reflex - hold your breath and immerse your face in a basin of ice water;
- Valsalva reflex - strain at the height of a deep breath;
- induce a gag reflex (the urge to vomit, but not vomiting itself) - press on the root of the tongue.
Attention! These actions are contraindicated in the following conditions:
- severe chest pain;
- shortness of breath and cough with foamy sputum;
- severe weakness, decreased blood pressure;
- convulsions, disturbances of sensitivity and movement in the limbs.
- loss of consciousness.
These methods work “through the body” - they affect the autonomic nervous system through one of three mechanisms:
- Promote relaxation in its sympathetic department.
- Activate the parasympathetic department.
- Harmonize and stabilize their activities.
How some self-help methods affect the ANS
Click on the title to read the text
- For example, intense physical activity releases tension in the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system - it allows you to “blow off steam.”
- Deep breathing and inducing vagal reflexes stimulate the parasympathetic system, which is an antagonist to the sympathetic system, thus balancing it.
- Avoiding stimulants allows you to avoid excessive stress on the sympathetic department.
- A contrast shower balances both departments.
- Sufficient walks and sleep help restore the body's own strength and resources.
Try to loosen your control
In a state of tension, we often experience anxiety, slight excitability, and an excessive desire to control everything. You can get rid of this feeling through meditation.
Experts from the University of Michigan recommend starting to meditate like this:
- Focus on the things that are happening right now.
- Listen to your body: what kind of breathing are you doing, fast, slow, deep or shallow?
- Do you hear noise, such as traffic, or just silence?
The idea is to simply notice what is happening without trying to change it or thinking about how to change it.
Popular relaxation techniques
Autogenic meditation (visualization)
Research by scientists has shown that our subconscious does not distinguish between real events and high-quality visualized images. Vivid, peaceful fantasies can give a person the same pleasant sensations as possible reality. Positive emotions and a state of peace will move from the subconscious to consciousness, thereby producing a therapeutic effect. It’s enough to close your eyes, even out your breathing and imagine yourself in a picturesque and safe place. Experience all the details: colors, sounds, aromas, tactile sensations. The brighter your images are, the better.
Deep breathing
A very simple technique that can be practiced anywhere. Take a comfortable position and try to relax as much as possible. You will inhale and exhale slowly, concentrating on the air entering your lungs.
Inhale slowly, let it be cool blue air, feel it in your body. Now exhale slowly, this is warm pink air. Repeat the exercise several times until you feel an improvement.
Muscle relaxation
During mental arousal, the muscles of our body involuntarily tense and send corresponding signals to the brain. Voluntary muscle relaxation will reduce the number of signals going to the brain and, as a result, achieve a state of peace and relaxation.
Take a comfortable position and mentally say to yourself: “I relax and calm down. My shoulders (back, arms, torso, legs) relax and become warm.” Thus, go step by step through all parts of the body and relax them. End the session af.
Text: Natalya Bartukova
Set up power
Certain foods and drinks help relieve mental and physical stress.
- Start with green tea - it contains chemicals that help reduce the body's stress response.
- If you feel that thinking and making decisions has become harder than usual, treat yourself to a piece of dark chocolate. The main thing is that it contains more than 70% cocoa - such a product strengthens mental health and reduces stress. And it also has fewer calories.
- Eat honey. It helps relieve anxiety, fight depression and even protects the brain.
- Introduce mango into your diet - it contains linalool, which has a positive effect on a person’s nervous state.
Finally, just eat something that will make your jaws work hard - an apple, celery, carrots. Crunching helps you relax.
How to recover from neurosis
Comprehensive treatment of neurosis (neurotic disorders) has been accepted as the standard in the world. It includes the following methods:
- Individual psychotherapy is a course of several sessions with a specialist who helps to understand the underlying causes of the disorder.
- Drug therapy is prescribed with the consent of the client and if necessary - medications help to quickly cope with the symptoms, but have almost no effect on the cause of the disease.
- At the treatment and rehabilitation stage, in order to consolidate the result, patients are prescribed relaxation, massage, physiotherapy, and vitamin therapy.
Cognitive behavioral therapy sessions help cure neurosis: the therapist and the patient identify negative beliefs that led to neurosis. Many people experience stress and suffer from conflicts. But the disease does not occur in everyone - only in those who are predisposed: anxious, suspicious, defenseless people. They perceive everything negatively, pessimistically and further aggravate their condition. It turns out to be a vicious circle.
After a course of therapy, a person can take a fresh look at his problems. And then he either stops paying attention to them, or quickly finds a solution.
A psychotherapist helps replace negative thoughts with productive, optimistic attitudes.
Biofeedback therapy (biofeedback therapy) is relaxation and work with the reflex arc. A special device informs the patient about changes in autonomic functions. A person learns to control the body, control symptoms, and the device immediately shows him whether he is moving in the right direction. Biofeedback therapy teaches a person adaptive capabilities and helps to quickly pull oneself together in stressful situations.
Drug treatment of neuroses in adults is a prerequisite for effective psychotherapy. Depending on the severity of the manifestations (anxiety, restlessness, depressed mood, fears, dizziness, fatigue and fatigue), pharmacotherapy for neurosis is represented by the following medications:
- antidepressants;
- anxiolytics (anti-anxiety);
- nootropics;
- neuroleptics.
Medicines reduce anxiety, reduce the number and severity of panic attacks, restore sleep, which immediately improves overall well-being.
Practice daily exercise
According to Harvard Health, there is a direct connection between the mind and body: If you work on relaxing your muscles, it helps control and relax your mind. Regular physical activity normalizes blood pressure, increases cholesterol levels and lowers blood sugar levels.
If you have no contraindications, engage in physical activity every day. You don't have to train for a marathon or go to the gym if you don't want to. 30-40 minutes of brisk walking and 15-20 minutes of intense exercise are enough. Add in some strength training and stretching a few times a week and you have a great balanced program for health and stress reduction.
Relaxation: a little theory
The founders of this method are considered to be the German psychiatrist and psychotherapist Johann Schultz and the American psychologist Edmund Jacobson. In the first half of the last century, they developed a methodology based on spiritual and religious practices. It was aimed at eliminating psycho-emotional disorders, treating neuroses and correcting psychosomatic diseases. Jacobson proved that through muscle relaxation (one of the popular techniques) it is possible to reduce the hyperexcitability of the nervous system, allowing it to recover and return to a stable state.
The ability to achieve a state of relaxation is necessary for everyone, regardless of medical history. If you can devote at least 20-30 minutes a day to this technique, wonderful changes will occur in your life. Your heart rate, blood pressure and breathing will improve, blood supply to the brain and major muscle groups will normalize, muscle tension will go away, and mental activity will improve. You will feel a powerful surge of strength and increase your resistance to stress.