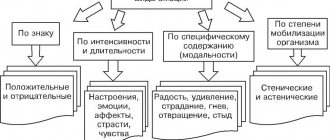
Victim psychology is a section devoted to a special, learned type of victim behavior. A separate branch of psychological science, victimology describes not only the characteristics of the victim’s psychology, but also the situations in which this behavior is formed, and the moments of the best way out of stereotypical destructive behavior. If we leave such a serious scientific section, then what remains is a more social psychology of the victim’s behavior on an intuitive level, understandable to many. It is common in society to accept suffering as something positive, something that purifies the soul or demonstrates the positive aspects of a person’s character. This is especially true for women who are constantly forced to pull the burden, who do not have the right to allow themselves insolent pleasure, but who receive support and attention when they begin to complain, get into trouble, or ask in a voice that breaks into tears.
The position of victim psychology spoils life, like bad water - the river itself and everyone who comes into contact, because people are not blind and do not want to be in the trap of manipulation. There is no personal development, as well as her ability to take care of herself, there are only constant complaints and demands. The desire of those around them to do something for such people is less and less, because then they are presented as a tyrant at the slightest refusal.
A child’s infantile position of deliberately reducing one’s own strength and disabling one’s capabilities does not come from the internal innate structure of the personality, but only under the influence of the attitudes of the entire society, which uses negativity in relation to everything as the same manipulation scheme that is used by victims. The victims are not taken into account, their opinion is not asked, but they easily make cutting remarks, physical pushes, betrayals, humiliation, lack of salary increases, etc.
Who is a victim and its signs
The victim syndrome in psychology, although extensive, has a very clear and targeted description. You can diagnose this condition both in yourself, by familiarizing yourself with the symptoms, and in others. With yourself you will have to think about whether to leave everything as before or whether there is an opportunity to bring positivity into life, but with others you will need to learn to resist manipulation or completely exclude the person from your life.
Constant complaints regarding one’s own health, work, the situation in the country, or even the weather are considered classics of sacrificial behavior. Absolutely any reason and opportunity to whine is suitable and the victim uses them. If nothing hurts, it means they were overloaded with documents, and if they gave you time off, it means it started raining nasty. Concentration on the negative, its active search and almost drug addiction to notifying others about existing problems. It is difficult for the victim to switch to positive things or even think about what can be done to improve the situation.
The psychology of the victim is such that the feeling most often inherent in it, one might even say the emotional background, is resentment. Everyone around does not understand, they offend and do not care enough about the poor and unhappy person, speak with an offensive intonation or mean something bad under plausible phrases. Grievances are not expressed, they are accumulated, nurtured and carefully stored, but still those around them find out about them, only not through constructive dialogue, but through heavy silence or by a martyr’s expression on their face. This gives rise to a lot of claims to others and a style of interaction with society appears, as if a person is owed everything, and a lot, regularly and on an unrequited basis.
In relation to oneself, a decrease in self-esteem and perception of oneself as a small or teenager is characteristic. Other people always seem smarter, their advice is correct, they reason sensibly. This is a way of shifting responsibility - you don’t think about it, and you’re not responsible for the consequences, because the one who came up with it is to blame. And since the world does not particularly care about those who do not think with their own heads, all sorts of troubles begin and then the victim recognizes the reality as frightening and unsafe. It’s like considering a saucepan bad just because it burned when you touched it without a protective glove. The victims’ perception of reality is very specific and, although it is subject to some kind of logic, it is quite distorted in relation to common sense and the principles of responsibility.
Manipulation is an integral part of the victim’s behavior, because if she suffers, then there must be an offender causing this suffering. When such a person is not found on his own, he is made from someone nearby. The husband can be blamed for the loss of youth, the parents for the ruined fate, the boss for the bad appearance, and so on ad infinitum. The victim always has an enemy who receives maximum claims and provocations. Even the ideal ones will be taken out, they will find something to complain about, they will ask for opposite things at the same time, so that there is a reason to be offended by the failure to fulfill one. For example, they may tell you not to help with cleaning, complaining about your health. Another person falls into a trap where helping means violating a request, and not helping means ignoring that the other is feeling bad. There will be complaints in any type of behavior, because victims can specifically do something for others, even when they are not asked, in order to later be reproached for this.
Meaning
The explanatory dictionary gives the historical meaning as the first one. But let’s look at them all to see the whole picture:
- In ancient religions: an object or living creature brought as a gift to a deity (killed), as well as the offering of this gift (sacrifice). For example: “We have made a sacrifice to the gods, then our journey should be easy.”
- Voluntary abandonment of someone or something in favor of another, self-sacrifice. Characteristic of high style. “He sacrificed his career for her well-being.”
- A victim of someone or something. A person suffering from violence, failure, misfortune. For example: “He fell victim to a villainous fate.”
- The meaning of the noun “donation” is similar. Currently considered obsolete.
What meanings of the word “victim” are most popular now? From the list of positions 2 and 3. The first meaning is relevant only for those who love books about ancient cults and sometimes reread the Old Testament. 4 meaning is hopelessly outdated, so we will work today only with the essential.
Psychology of the victim - causes and consequences
The position of the victim in psychology is considered as a formed skill, the development of which is influenced by several reasons. From childhood, the formation of a victim type may begin due to reduced self-esteem. Such children look different, cannot fight back or have a verbal argument, they are more easily singled out by aggressive children and it is on them that they take out their anger. Indeed, aggressors feel weak and afraid, and if the child is not confident, then he begins to get into trouble, which further reinforces the fear. Those who were constantly made fun of in the family become targets in adulthood, and those who received their mother's love only after breaking their knee on a bicycle understood that if it became emotionally cold, then you need to get into trouble and they will love you.
The lack of one’s own opinion completely destroys a person’s position, and he begins to adapt to the opinion of a significant other. Over time, someone who changes like a chameleon becomes uninteresting, because you can inspire him with anything. So they stop listening to them and taking their protests seriously, they can cheat on such people, then say beautiful words and know that there will be forgiveness. Such treatment is impossible with those who know their own worth and have their own position in relation to any event - you won’t fool them, but the attitude will be respectful, more careful or something, because it’s scary to lose.
Despite the superficial negative consequences, being a victim turns out to be very profitable, because increased attention is paid to them. Through manipulation, the sufferer can achieve much more than through honest and hard work; in addition, inside this creates a certain image of his own holiness. When a person is a martyr, he gradually becomes a great martyr, and the rest become mere mortals, and this significantly increases the decrease in self-esteem characteristic of victims. It’s just that the method is somewhat clumsy and does not work with everyone, but the object of complaints and worries can always be replaced.
Emotional Freedom Technique
One way to get out of the victim position is the “Emotional Freedom Technique” developed by Harry Craig. This is a direct impact technique, it is very simple and easy to learn. Its essence lies in the fact that once again, when a person remembers a negative event, a traumatic situation, he needs to lightly press several times with his fingers on certain points on the body, which are points of energy flows. In most cases, this method reduces fears and negative emotions. You can learn how to correctly perform the Emotional Freedom Technique by watching the video.
(
3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Psychology of the victim in a relationship with a man
The psychology of the victim in a relationship is revealed most fully, because these are close people who find themselves in long-term interactions and often even in moments of psychological dependence. In pair interaction, if a woman chooses the position of the victim, then the entire surrounding world does not become catastrophic; she can solve any problems at work, manage a company of especially dangerous criminals and make complex plans. It all begins at home, where this same woman falls into powerlessness and stupor.
The most popular manifestation is when a man begins to humiliate, insult, beat a woman and in all other ways make life together impossible. From the role of a victim, she will complain to others - this is important, because... if a woman simply lives with a gaslighter or there is violence at home, then she either tries to hide it or solves the problem. The victim does not solve the situation and continues to tell everyone about his misfortunes. As a result, even the most ordinary man turns into a demon, everyone around only advises her to run away, but she remains. There can be many reasons, for example, a woman herself understands that she provokes a man and if she changes her behavior, then he is not a bad person, or she is pleased that she can use the help and support of her friends at any time - this is all a secondary benefit from the psychology of behavior victims.
Typically, this role is played by infantile women who do not make direct adult and open contact with their partner, which causes misunderstandings to accumulate, and all experiences are endured independently in depression. The second type is adrenaline junkies who are looking for a tough man for a special relationship, full of passion and storms; in an ordinary family circle they are bored and it seems that love is gone and only a swamp remains. Also, extremely strong ladies find themselves in similar situations, constantly competing with their husband, which drives him to extreme manifestations of his character and then complains about how they are treated unfairly.
Origin
According to the etymological dictionary, the word is borrowed from Old Church Slavonic. It contained the verb “to eat,” which meant “to sacrifice.” Scientists see here the influence of the Greek language, for the word geras and the object of study go back to the same basis. By the way, the Greek word means “honorable gift,” because sacrifice was originally understood as “a gift to the deity.”
Victimological prevention
In our country, there is very little statistical information about victims of crime, which makes it difficult to collect and develop methods for preventing victimized behavior. We can highlight some countries in the world where victimology is developing most intensively: the USA, Germany, Canada, Switzerland, Japan, Italy. They actively develop not only theoretical problems of victimology, but also practical aspects of the victimological direction of crime prevention.
Thus, research centers in some US universities conduct research on various indicators of victimization of the population and organize special victimology clinics. In German police educational institutions, a special course on the basics of victimology is taught, lectures are given and seminars are held on the application of the provisions of this course in police practice. Victimology has also received a certain development in Japan, where victimological research is carried out by a comprehensive legal research institute and a police research institute, which have special laboratories of psychology and educational work that study the personality and behavior of victims, the damage suffered by them, and the forms of relationships between victims and offenders.
Attempts to protect people from criminal environments in foreign countries are even made through architectural planning. This is a fairly new direction, but has already received development. For example, in one of the areas of London (Stonebridge), the development features made it difficult for police officers to apprehend criminals. Soon, at the request of law enforcement agencies, the municipality decided to demolish a number of houses and redevelop Stonebridge. Architectural features that created a crime-prone landscape were eliminated, and residents of Stonebridge were allocated £1,000 by the Housing Ministry to equip each apartment in the block with an alarm system and other security measures.
Synonyms
We are considering a simple definition, and yet synonyms for the word “victim” will not be superfluous. Analogues always help to understand the meaning better and deeper. The list of replacements is as follows:
- gift;
- victim or victim;
- patient;
- client;
- self-denial;
- sufferer.
As can be seen from the list, there is no full synonym for the word “victim”. You can treat this reality as you like, but the main thing is not to despair. No matter how far the words presented above may be in meaning, they can still be used on occasion.
Pseudo-victim
After the main part has been completed, it is worth understanding the intricacies. To truly explain the meaning of a definition, you need to understand that sometimes it does not mean what it seems.
For example, a father and son (or daughter) are playing chess, and the parent, having explained the rules, wins several times against a beginning chess player, he wins again and again, but why “accidentally” loses. Why does he need such a sacrifice (what this is is already clear)? From the point of view of education, there are two irreconcilable positions: some parents believe that the child should not give in, because this humiliates his dignity, and others believe that it is necessary to give in, since otherwise the boy or girl will quickly lose interest in the game. Everyone decides for themselves which side to take in this pedagogical debate, but one thing is clear: if you don’t give in once, then the child can really give up everything. In addition, victory will give him strength and confidence and a desire to move on.
Factors of victimization
Victimization is often proposed to be understood as the ability of a person to become a victim of a crime due to certain subjective qualities inherent in the individual. With this understanding, crimes such as waging aggressive war or terrorism have no victims. What subjective qualities of Iraqi citizens determined the aggression against this country? What are the “victimological abilities” of people who found themselves at the performance “Nord-Ost” on October 23, 2002 or September 1, 2004 at school No. 1 in Beslan? Victimization is precisely the likelihood (of individuals, groups of individuals, groups of people, residents of a region, country, etc.) of becoming victims of criminal acts. With this approach, attention is focused not on the search for the subjective qualities inherent in the individual (the “guilt” of the victim), but on the interaction of objective circumstances and subjective characteristics that increase the likelihood of being a victim of a crime.
Victimization is a quality of the social environment, a property that is largely objective. Theoretically, it always exists in relation to all people and can only differ in small values. It is clear that these values are minimal in the “monastic republic” (a special unit of the Greek Republic, a self-governing community of 20 Orthodox monasteries under the ecclesiastical jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Constantinople) on the Greek Athos peninsula, where no one except monks and novices resides. Nevertheless, victimization exists here too; it is no coincidence that Mount Athos has its own police.
The nature and magnitude of victimization depend on many factors, and primarily on the type of crime. Some crimes (genocide, terrorist act, waging aggressive war, development, production, stockpiling, acquisition or sale of weapons of mass destruction) are characterized by mass victimization. The circumstances that determine the magnitude of its values are factors of global politics (American hegemony, the emergence of odious political regimes, regional wars and conflicts, religious and ethnic extremism, financial speculation, anthropophobic (misanthropic) theories such as the “golden billion”, etc.). The importance of mass victimization is increased by weak international and domestic control over the use of the results of scientific and technological progress (for example, cloning technologies, obtaining new strains of viruses and breeding chimeras - creatures with polar genetic properties). The breakthrough of adventurers and criminals into politics sharply increases the significance of mass victimization.
Mass victimization depends on historical (memory of generations, which stores not only positive, but also negative facts of history, transferring them to contemporaries), political (ideological intolerance and despotism) and geographical (places of residence of people, in particular near drug trafficking and in border areas) factors. A big contribution to the increase in the values of mass victimization is made by weak social policy, as a result of which huge groups of disadvantaged, powerless people appear in the state.
Group victimization is the likelihood of becoming victims of crime for individuals united according to certain social characteristics. Thus, group victimization is typical for vehicle drivers and pedestrians, law enforcement officers, women, children, and rich people. Here there is a relationship between the amount of victimization and factors such as profession, level of security, place of residence, intensity of traffic flows, etc. Thus, high values of group victimization are characteristic of criminal investigation officers, employees of private security companies, homeless children, taxi drivers, prostitutes, etc.
Individual victimization increases when a person is careless in choosing the place and time of leisure, promiscuity in acquaintances, flashy and provocative clothing, cheeky behavior, rudeness, offensive remarks, excessive gullibility, inattention, poor relationships with the criminal, etc. To a large extent, it depends on the psychological state of the victim, the ability to anticipate danger and resist possible threats.
The technique of victimological forecasting is based on determining the values and establishing combinations of victimization factors. Its logic is simple: the greater the number of victimogenic factors and the greater their significance, the greater the likelihood of being a victim of a crime.
This forecasting takes into account the magnitude of such factors as the prevalence of crime in a given region and place, the effectiveness of law enforcement agencies, assessment of one’s own security (including from the point of view of taking certain measures), readiness to behave in a criminal situation.
Victimological forecasting is extremely relevant in business activities. Modern Russian business life is in many ways similar to survival in an extreme environment, but with the caveat that the social environment is active and often criminal. In the process of victimological forecasting, risk factors such as legal (related to malicious use of legal gaps and legal incompetence of a partner) are taken into account; law enforcement (assessing the likelihood and consequences of the response of law enforcement and judicial authorities to a criminal situation); banking (taking into account the possibility of abuse by banking institutions); financial (related to the likelihood of material losses due to the existing payment model, including payments to criminal intermediaries or “curators”); transport (indicating the possibility of suffering damage due to attacks on vehicles, including pipeline transport); obligatory (arising from threats of non-fulfillment of obligations by the debtor); competitive (taking into account manifestations of unfair competition: provoked bankruptcies and sanctions of government and judicial authorities for the economic suppression of competitors); personnel (related to errors in personnel selection and management), etc. These risks are specified in relation to typical tasks solved in the process of business activity of a certain type.
Thus, when concluding transactions, it is recommended to pay attention to the following circumstances: a questionable source of initial capital at the time of starting business; participation in shadow and criminal business; engaging in criminalized types of business activities (gambling, etc.); presence of patrons; relationships with the administration, law enforcement, and judicial authorities; connections in the criminal environment, frequency and nature of contacts with criminals, including participation in joint “topics” (business projects); presence of deposits, real estate, other property abroad, second citizenship; moral deformations and pathologies (alcoholism, drug addiction, homosexuality and other sexual deviations); presence of unfulfilled debt obligations for the entire period of business activity; delays in settlements with creditors due to one’s own fault (including simulating the occurrence of force majeure); unfair competition, duplicity, deceit, non-obligation in relations with partners; negative image in law enforcement agencies, application of sanctions by them, initiation of criminal prosecution; criminal registration; the desire to attract interest from influential connections, exaggeration of one’s capabilities in the business world; discrepancy between the enterprise’s profits and the costs of meeting the needs and requests of the owners or management; evasion of providing collateral or other guarantees of fulfillment of an obligation. These signs indicate that their owner is an unreliable participant in the proposed transaction and there is a high probability of being a victim of fraud or another crime.
Victimological forecasting is an area of interest for any person who decides to buy or sell real estate, go on vacation to a foreign country, spend leisure time in a nightclub, etc. Criminological knowledge makes it possible to systematize and clarify relevant information.