Hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunction The basis of a woman’s reproductive system is an interconnected chain of neuroendocrine organs - the hypothalamus - pituitary gland - ovary, the correct functioning of which ensures the maturation of a full-fledged egg, changes in the structure of the endometrium necessary for normal implantation of the embryo, the correct functioning of the epithelium of the fallopian tubes to promote the fertilized egg into the uterus, implantation and maintenance of early pregnancy.
The highest organ of regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian system is the central nervous system, which through a whole complex of direct and reverse interactions ensures the stable operation of the reproductive system.
The hypothalamus (brain structure) is the center of regulation of the menstrual cycle. With the help of releasing hormones, the hypothalamus controls the functioning of the underlying gland, the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland, in turn, regulates the functioning of all endocrine glands - it produces follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Under the influence of pituitary hormones (FSH, LH and prolactin), cyclic changes occur in the ovaries: egg maturation and ovulation. With most hypothalamic-pituitary diseases, women develop menstrual dysfunction until the cessation of menstruation.
Pituitary hormones:
The pituitary gland produces the following hormones:
- Prolactin - ensures the formation of milk during lactation, and also inhibits the production of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones. Numerous other functions (eg, regulation of the immune and nervous systems) are currently being studied.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone - ensures the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries of women and spermatogenesis in men.
- Luteinizing hormone stimulates estrogen secretion and ovulation, and in men is responsible for the formation of testosterone.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone, according to statistics, is the most frequently prescribed hormone for research. Ensures the growth of the thyroid gland and the production of peripheral thyroid hormones - thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone - controls the production of hormones from the adrenal cortex.
- Somatotropic hormone is the most important stimulator of protein synthesis in cells, glucose formation and fat breakdown, as well as body growth.
Preparation and diagnostic process
MRI of the hypothalamic-pituitary region does not require special preparation, so you can take food and medications as usual.
Relative contraindications and complicating factors that should be discussed with your doctor before diagnosis:
- non-ferromagnetic implants, inner ear prostheses, hemostatic clips;
- external pacemakers, pumps;
- metal dentures and implants in non-scanable organs;
- the need for physiological monitoring;
- permanent permanent makeup and tattoos made with paints with metal components.
Before diagnosis, it is necessary to remove all metal objects and accessories from the body (jewelry, piercings, hairpins, hairpins, buttons, buttons, etc.). Electronic gadgets, mobile phones, tablets, watches, magnetic cards and other devices cannot be left in the same room as the tomograph. Clothing for diagnostics should also not contain metal parts. You can bring household items with you or change into a gown provided at the diagnostic center.
Depending on the type of tomograph, the patient lies on the open scanner table or is partially placed inside the magnet tunnel. During the scan, you need to breathe evenly and keep your head completely still. Communication with the x-ray technician is carried out through a mini-headset, so as not to hear the clicks of the device, you can use earplugs or headphones. The procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes.
Pituitary gland diseases:
Pituitary diseases are a large group of diseases that can be caused by the presence of a tumor of the pituitary gland or nearby structures, vascular pathology and inflammatory diseases, including granulomatous diseases.
Ultimately, this can lead to hypofunction, hyperfunction of the pituitary gland, and sometimes to mass effect.
Mass effect:
The mass effect of a large pituitary tumor causes blurred vision (due to compression of the optic chiasm) and headaches. If visual field impairment due to a pituitary tumor is suspected, consultation with an ophthalmologist . To diagnose the presence of a formation, MRI of the chiasmal-sellar region with contrast is used.
Hyperfunction of the pituitary gland:
Symptoms of pituitary hyperfunction are varied. Excess prolactin in women often causes lactorrhea, infertility and amenorrhea, and in men it can cause hypogonadism (decreased sexual function). An excess of somatotropic hormone causes gigantism in children, and characteristic changes in appearance (acromegaly) and organomegaly in adults. With an excess of adrenocorticotropic hormone (Cushing's disease), symptoms such as obesity with typical redistribution of fatty tissue on the arms and face, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and osteoporosis are described.
Hypofunction of the pituitary gland:
With hypofunction of the pituitary gland, hypogonadism develops (decreased sexual function), secondary adrenal insufficiency (low blood pressure, weight loss, decreased glucose levels), secondary hypothyroidism - decreased thyroid function (brittle hair and nails, drowsiness, swelling). Children may also experience delayed growth and sexual development.
Features of MRI of the hypothalamic-pituitary region
During MRI diagnostics of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, contrast techniques are always used. A precisely calculated dose of a special contrast agent based on the paramagnetic gadolinium is administered intravenously during the scanning process using a syringe or injector.
Gadolinium-based drugs enhance the contrast between affected areas and healthy tissue, which greatly facilitates image analysis. Gadolinium is a non-toxic substance and rarely causes allergies. However, if you suspect intolerance to gadolinium-based drugs, it is necessary to perform allergy tests in advance.
MR scanning of the hypothalamic-pituitary region is carried out on open and closed tomographs with a power of 1 to 3 Tesla. Open-type tomographs are less powerful, but are suitable for examining claustrophobic patients, children and patients requiring physiological monitoring.
Closed-type scanners more accurately visualize pathological changes, but have a number of limitations related to technical parameters. The table with the patient is completely or partially placed inside the magnet, so its parameters should not exceed the diameters of the scanner, and its weight should not exceed 150 kg. During the diagnosis, be sure to keep your head completely still.
Absolute contraindications for which MRI diagnostics is impossible:
- implanted pacemakers;
- electronic or ferromagnetic middle ear implants;
- ferromagnetic intracranial clips;
- metal prostheses, foreign bodies and fragments in the eye sockets;
- metal bracket system.
Radiofrequency pulses can mimic heart contractions, which puts patients who wear permanent pacemakers at risk. The magnetic field disables electronics and magnetizes ferromagnets, so in all cases where electronic devices and metal prostheses cannot be temporarily removed, MRI cannot be performed.
Also, pregnant women should not be scanned in the first trimester, since the effect of intense fields on fetal development has not been studied. Contrast is contraindicated for pregnant and nursing mothers; non-contrast MRI can be done during these periods.
Diagnosis and treatment:
Pituitary gland disease can be suspected at an appointment with an endocrinologist during a detailed questioning and examination of the patient, after which, if necessary, hormonal and instrumental examinations are prescribed. Often, the primary diagnosis of pituitary diseases is carried out by the level of the hormone at the peripheral level (for example, if Cushing's disease is suspected, excess cortisol, an adrenal hormone, is excluded). It is worth noting that when studying the levels of many hormones (prolactin, cortisol, ACTH, etc.), certain rules must be followed, since the values of these hormones change significantly depending on the time of day, the menstrual cycle and other conditions. For further diagnosis, functional tests may be required (for example, a test with dexamethasone when diagnosing Cushing's disease).
Depending on the specifics of the disease, the patient may be offered surgical treatment (for example, for a pituitary tumor). However, it is worth knowing that prolactinoma is one of the few tumors that can be treated conservatively (with the help of medications). If a hormone deficiency is detected, hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed.
Diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system
Symptoms, diagnosis, therapy and prevention of diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system at the Diadent clinic.
Wide range of diagnostic methods, carefully selected treatment. Make an appointment at the clinic.
free consultation
Discount 500 ₽!
When making an appointment for treatment with specialists from the Diadent Group of Clinics, use the “last minute” windows of the current day (does not apply to consultations). Check with the administrators for the list of “burning” windows.
cost of endocrinology services
Consultation
- 1,500 rub. Primary consultation with an endocrinologist
- 1,500 rub. Repeated consultation with an endocrinologist
Tests and diagnostics
- 1,500 rub. Performing a glucose tolerance test
- 1,600 rub. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands
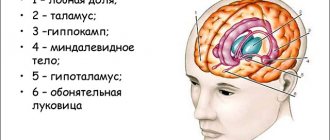
The hypothalamic-pituitary system is a complex of structures consisting of two sections and their connections. The components of this system are the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and stalk.
The pituitary gland is a lower cerebral appendage located in the area of the sella turcica, which is the central organ of the endocrine system of the human body.
Hypothalamus , located above the pituitary gland and below the thalamus, is part of the diencephalon responsible for autonomic function. The stalk, or instep, is the area connecting the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland.
The hypothalamic-pituitary system connects the nervous and endocrine systems of the body with each other, regulating the synthesis of hormones, without which the correct functioning of many organs is impossible. Each of the departments included in the system complex produces a special type of hormones that have a direct effect on the activity of organs and systems.
What are the hormones of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus responsible for?
The hormones of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus closely interact with each other. The functions of our body such as:
- feeling of hunger and satiety;
- feeling of thirst;
- natural thermoregulation;
- maintaining the circadian rhythm of sleep and wakefulness;
- feeling of need for procreation;
- manifestation of aggression;
- the ability to experience different emotions.
Hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary system
The main function of the pituitary gland is the production of hormones involved in the regulation of the activity of peripheral endocrine glands. These hormones are responsible for reproductive functions, tissue growth, metabolic processes in the body, and ensure the normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones, liberins and statins , which support the functioning of the adrenal glands, thyroid and pancreas and reproductive system, as well as those involved in the processes of regulating body temperature and supporting the normal functioning of internal organs.
Any disturbances in the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system can result in extremely negative consequences, even death. Unfortunately, quite often the pathologies of this system develop latently, manifesting themselves only in the form of concomitant diseases, which, at first glance, are not related to the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems.
Find out the cost of treatment at a free consultation by phone +7 (812) 40-000-60
your benefit of treatment with us
- Any payment methods We offer you many ways to pay for the clinic’s services for individuals and legal entities: cash and bank transfer, card or using a certificate.
- No queues
Make an appointment and it will take place at exactly the appointed time. - Complete safety of procedures
Diadent has developed a perfect safety system that reduces the risk of disease (protection against HIV, hepatitis and other diseases) to zero.
The reception is conducted by:
Smirnova O.V.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, endocrinologist Vlasova K.A. Endocrinologist
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system
A comprehensive examination may include:
- anamnesis analysis;
- visual inspection;
- MRI;
- CT;
- radiography of the sella turcica;
- spinal puncture;
- blood tests for hormones - pituitary gland and hypothalamus, adrenal glands, thyroid gland and sex hormones.
Only after receiving accurate data on the state of the entire system as a whole and each of its components separately, an endocrinologist can accurately diagnose and prescribe appropriate treatment that will normalize the functioning of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and the entire body.
To assess the functioning of the system, a blood test is performed for a complex of hormones involved in the functional connection of its elements. If the development of hormonally inactive adenomas is suspected, a blood serum test for the concentration of chromogranins is used.
Treatment of diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system is strictly individual, directly depends on the diagnosis and associated factors, such as the degree and severity of the disease, the presence of allergic reactions, intolerance to certain medications, gender and age of the patient, etc.
It is important to remember that the earlier treatment is started, the lower the likelihood of developing serious complications, which often pose a serious threat to the patient’s life.
Find out the cost of treatment at a free consultation by phone +7 (812) 40-000-60
Where is Diadent Clinic located?
Multidisciplinary clinic
St. Petersburg, Bukharestskaya st. 110, building 1
Phone: + 7 (812) 40-000-60
To assess the functioning of the system, a blood test is performed for a complex of hormones involved in the functional connection of its elements. If the development of hormonally inactive adenomas is suspected, a blood serum test for the concentration of chromogranins is used.
Treatment of diseases of the hypothalamic-pituitary system is strictly individual, directly depends on the diagnosis and associated factors, such as the degree and severity of the disease, the presence of allergic reactions, intolerance to certain medications, gender and age of the patient, etc. It is important to remember that the earlier treatment is started, the lower the likelihood of developing serious complications, which often pose a serious threat to the patient’s life.