Dissociative fugue is a psychological pathology that occurs acutely against the background of unfavorable life events. The patient leaves his place of residence due to complete amnesia. The duration of the disorder ranges from several days to several months. Symptoms disappear suddenly. The diagnosis is based on studying the medical history. To eliminate the traumatic situation and change the attitude towards it, the patient undergoes a course of psychotherapy.
In movies, there is often a plot about “a man without a past.” The hero suddenly finds himself in an unknown place - without things, companions and any memories of what happened to him up to this moment. By the end of the film, the intrigue is usually revealed, and the memory returns. This kind of story is not the imagination of screenwriters, but a description of a real psychiatric phenomenon - dissociative fugue.
What is a fugue
Dissociative fugue is considered a disorder that separates a person from previous memories of past experiences, feelings, or people in their life. People suffering from it have no memory of their identity or any details of their lives.
Dissociative fugue describes the disease as follows: a split of consciousness occurs, while simultaneously reproducing actions. At the same time, people around, seeing the patient, do not understand that something is wrong with him. A common example of dissociation is driving a car and missing your turn because you are daydreaming. Thoughts inside split the consciousness about where the car was at the moment. The realization that a person has missed his turn usually puts him back on the opposite route. Thus, dissociation can occur in healthy people, but it does not last as long.
Diagnostic measures
It is difficult to identify the disease in the acute period. Doctors work more often with patients after the end of the fugue. This is due to the fact that people do not feel sick and do not complain. Experts note two main signs of dissociative fugue that help confirm the diagnosis:
- During the period of manifestation of symptoms, the patient leaves his permanent place of residence, in most cases this is another city. Less often to another region or country.
- During the fugue period, memories of the individual are partial or completely absent. When recovering from an acute state, the patient forgets about the events that occurred. General skills and knowledge are retained.
During the diagnosis process, psychiatrists and psychotherapists must exclude other dissociative disorders and organic brain lesions. In this regard, a general clinical examination is carried out, as well as special methods for studying the central nervous system:
- electroencephalography (EEG) - allows you to evaluate the electrical activity of individual areas of the brain and identify pathological foci of activity in the nervous system;
- examination of urine and blood for toxic substances, including narcotic drugs;
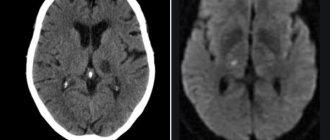
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging (CT or MRI) are aimed at visualizing individual areas of the brain, allowing them to detect tumor formations, areas of hemorrhage, etc.
A doctor must interpret the results. Attempts at self-diagnosis can lead to progression of the underlying pathology against the background of a late start of treatment.
Is it possible
After severe stress, some part of the memory is blocked and a dissociative fugue occurs. Examples from life:
- The 57-year-old husband and father of two, a Boy Scout, left the garage near his office and disappeared. Six months later he was found, living under a new name in a Chicago homeless shelter, not knowing who he was or where he came from.
- A middle-aged woman buys a newspaper to find out the date and what city she is in, and then contacts social services to determine her identity. As it turned out later, she had been considered missing for 5 years.
- Agatha Christie was perhaps the most famous writer of all time. In 1926, on the evening of December 3, 36-year-old Christie mysteriously disappeared from her home in England. The next morning, her abandoned car was found, but she was nowhere to be found. Before her disappearance, her husband Archibald was threatening divorce. On December 14, Christie was found alive and registered under the name Teresa Neil at the Harrogate Hotel. She claimed that she did not know how she ended up there. Some believe that this disappearance was a performance for PR and a reunion with her husband. However, there is evidence that Christie was in a fugue state and actually lost her memory. On the day of her disappearance, people saw her and stated that she was not wearing warm clothes, despite the cold season, she seemed confused and discouraged. There is speculation that her impending divorce and the recent death of her mother have caused her to become deeply depressed. Agatha Christie died in 1976 and took the truth about what really happened with her to the grave.
Which doctors should you contact if you have dissociative amnesia:
Psychiatrist
Is something bothering you? Do you want to know more detailed information about Dissociative amnesia, its causes, symptoms, methods of treatment and prevention, the course of the disease and diet after it? Or do you need an inspection? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Eurolab clinic is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, study external signs and help you identify the disease by symptoms, advise you and provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home. The Eurolab clinic is open for you around the clock.
Important Two Sides of Bipolar Disorder
How to contact the clinic: Phone number of our clinic in Kyiv: (+38 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our coordinates and directions are listed here. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on its personal page.
What to do
Patients experiencing dissociative fugue should be under close medical supervision. The patient's medical history should be reviewed to rule out an organic cause for the disease (eg, epilepsy or other personality disorder). If no cause is found, a psychologist or other mental health professionals will interview the patient and conduct psychological evaluations. These assessments may include dissociative experiences, a structured clinical interview for a disorder called dissociative fugue. The causes and symptoms of the disease may occur with the use and abuse of certain medications and illegal drugs. For example, patients with alcohol addiction are often in a state of “blackout”, while performing some actions, and sometimes making unplanned trips; a striking example of such a dissociative fugue is the film “Enjoy Your Bath.”
Causes
- Experts believe that the pathology in question acts as a protective mechanism, the purpose of which is to preserve the patient’s health in the presence of intolerable worries and unbearable tension. Patients feel that they want to escape from the current situation. The psyche tries to realize this desire in all possible ways.
- Often, the disorder appears when there is a direct threat to physical integrity or there is a likelihood of a break in a relationship with a loved one.
- It is extremely rare that illness is caused by less large-scale experiences: money problems, problems at work. Whatever the disorder, the basis will be a strong intrapersonal conflict.
- The chances of developing such a disease become higher if there are chronic problems with alcohol, an increased level of restlessness, and phobias.
- In individuals with multiple personality disorder, the pathology can manifest itself more than once. In other cases, this condition does not recur.
Dissociative fugue: symptoms of the disease, prevention
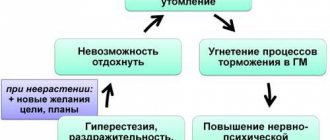
It is not easy to explain the cause of the fugue state, but people who suffer from the disorder have usually had some kind of serious trauma or stress in their lives. War veterans or people who have suffered extreme violence or disaster scenarios may be more prone to these symptoms. Some psychologists believe that fugue sufferers may have unresolved conflict in their lives, which can add to the likelihood of abnormal dissociation. It is possible that drug abuse may contribute to the development of this disease.
Forecast
The prognosis is quite favorable. If there are no other mental disorders, complete recovery will occur. If, before the onset of the fugue, the patient had to experience an event of high mental trauma (violence, observation of a situation of abuse, severe loss), most likely there will be a remainder of dissociative amnesia
Whether it is worth restoring traumatic memories is a purely individual decision. You should take into account how severe the events were, as well as the patient’s character traits.
How common is the disease?
Dissociative fugue is relatively rare, with a prevalence rate of 0.2% in the general population. The length of a fugue episode is believed to be related to the severity of the stress or trauma that caused it. In most cases, it appears as single episodes without repetition. In some cases, a person will not remember events that occurred during the fugue state. In other situations, amnesia associated with the traumatic event that initiated the fugue may persist to some extent after the episode is completed. Prevention of this disorder can be a conversation with a psychotherapist after a tragic episode in life, good family support and close, trusting relationships with friends. If there is no way out for traumatic thoughts, the brain blocks the memory for protection and amnesia occurs.
Symptoms
To make a diagnosis, in addition to the general signs of dissociative disorders, additional criteria must be met:
- an attempt was made to unexpectedly leave and distance oneself from the usual social environment;
- forgetting the episode, which corresponds to 2 dissociative amnesia.
If an organic brain disorder is the cause of the disease, behavior is not determined by a stress factor and is not as complex and socially adaptive as it is in psychogenic fugue. The situation is similar with fugue during temporal lobe epilepsy.
Psychology according to Freud
Freud suggests that psychogenic amnesia is an act of self-preservation, where the alternative may be traumatic anxiety or even suicide. Unpleasant, unwanted or psychologically dangerous memories are blocked from entering consciousness. Neurologically, normal autobiographical memory processing is inhibited by imbalances of stress hormones such as glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids in the brain, especially in regions of the limbic system involved in memory formation.
Such repressed memories may be recalled spontaneously by a particular smell, taste, or other identifier, years or decades after the event. Because this is due to psychological rather than physiological causes of psychogenic amnesia.
Differential diagnosis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and the collected anamnesis.
For these purposes, a toxicological study, EEG, MRI or CT, and X-ray of the skull are performed.
Features of the course of dissociative amnesia that help a psychotherapist or psychiatrist make a diagnosis:
- a mental assessment of the patient’s condition gives the following picture: the patient is oriented in place and time, his thinking is slightly inhibited. He analyzes and recalls current events with ease, but has difficulty retelling a certain time in the past;
- It is difficult to bring the patient to openness. He refuses to talk about the required time period or is confused about the information provided;
- the patient’s condition indicates self-examination, hidden aggression, and a predisposition to suicide;
- the disease develops suddenly and is directly related to a tragic event in a person’s life.
A psychiatrist or psychotherapist works with a person suspected of having dissociative amnesia. The doctor must determine whether he is at risk by assessing his mental profile by examining childhood memories and impressions.
Dissociative fugue: symptoms, treatment
When treating dissociative fugue, the focus should be on helping the patient come to terms with the traumatic event or stress that caused the disorder. This can be achieved through various types of interactive treatments that explore the trauma, and work must also be done to build the patient's coping mechanisms to prevent further recurrence. Some therapists use cognitive therapy, which focuses on changing maladaptive thinking patterns. It is based on the principle that inappropriate behavior, in this case a fugue episode, is initiated by inappropriate or irrational thinking. The cognitive therapist will try to change these thinking patterns (also known as cognitive distortions) by exploring the reasonableness and validity of the assumptions behind them with the patient.
Medication may be a useful adjunct to treat some of the symptoms a patient may experience in relation to dissociative episodes. In some cases, certain antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed.
Multiple personality.
Also on topic:
MENTAL HEALTH
The condition of multiple personality was described back in 1840 by a doctor who treated a painful 11-year-old girl with hypnosis and observed the appearance of two personalities in her. Subsequently, various variants of this disorder were described. Split personality has been studied earlier than others and most often occurs, in which one personality replaces another, and the initial one does not have access to the memories of the second, and the second has the memories of both. Subsequently, more complex cases were reported, in some of them the number of personalities resulting from the splitting of the original one exceeded 100. Usually, at least two personalities control the patient’s behavior, and the transition from one to another occurs almost instantly. Interactions between individuals can be very complex; in some cases, they do not know about each other's existence. Personalities can be of different ages and genders, very different and even opposite in external behavioral manifestations.
Although this disorder usually begins in childhood or adolescence, due to various masking symptoms it is often recognized in adults. Recent studies have shown that in almost every case there was sexual or other violence.
Treatment with therapy
Creative therapies (art therapy, music therapy) allow patients to express and channel thoughts and emotions into “safe” channels. They empower the patient by encouraging self-knowledge and a sense of control.
Group Therapy - A therapist or counselor may be helpful in supporting the patient on an ongoing basis. It also provides the patient with opportunities to gain self-confidence and interact with colleagues in a positive way.
Family therapy can be part of the treatment regimen, both in exploring the trauma that caused the fugue episode and in educating the rest of the family about the illness.