Anonymously
Around the clock
Attention! The material contains information about substances, the use of which can cause serious harm to your health!
Troubles in personal and social life, the loss of a loved one or health problems often provoke the development of mental illness. Many disorders are short-term and can be dealt with on your own. But, there is a more severe depressive state, which is characterized by a lingering effect. Experienced psychologists help you get rid of depression.
- What is depression?
- Disease statistics
- Causes of the condition
- Biological
- Psychological
- Social
- Signs of clinical depression
- Physiological
- Psychological
- Behavioral
- Stages of development of depression
- First stage
- Second stage
- Third stage
- Complications of depression
- Sleep disturbance
- Apathy
- Lack of interest in life
- Biochemical processes in the brain
- Types of depression in psychiatry
- Classical
- Psychiatric
- Moderate
- Heavy
- Expressed
- Chronic
- Acute
- Black
- Behavioral
- Resistant
- Consequences of prolonged depression
- Prevention of depression
- How to get rid of depression on your own?
- Treatment methods for depression in Moscow
- Diagnostics
- Drug therapy
- Treatment at home
- Psychological help
- When should you go to the hospital?
Treatment prices:
| Service | Price, rub) |
| Types of therapies | |
| Standard detoxification therapy | 3 500 ₽ |
| Double Detox Therapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Enhanced Detoxification Therapy | 7 500 ₽ |
| Maximum detoxification therapy | 9 500 ₽ |
| Quick sobering up at home | 7 500 ₽ |
| Hospital at home 1 day | 22 000 ₽ |
| Advanced hospitalization | 15 000 ₽ |
| Treatment in hospital | |
| Accommodation | |
| Economy chamber (6 beds) | 2 000 ₽ |
| Standard room (4 beds) | 3 000 ₽ |
| Increased comfort (2 seater) | 5 500 ₽ |
| VIP chamber (1 person) | 12 500 ₽ |
| Individual post 24/7 | 5 000 ₽ |
| Medical and social rehabilitation 21 days | 140 000 ₽ |
| Service | Price, rub) |
| Initial consultation with a narcologist | for free |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3 000 ₽ |
| Psychiatrist consultation | 5 000 ₽ |
| Coding at home Torpedo | 7 500 ₽ |
| Express output and encoding (doublet) | 13 500 ₽ |
| Coding using the Dovzhenko method | 12 000 ₽ |
| Hypnosis classic session | 13 000 ₽ |
| Ericksonian hypnosis session (NLP) | 8 000 ₽ |
| Coding method Torpedo | 5 500 ₽ |
| Double block | 8 000 ₽ |
| Esperal injection for 1 year | 9 900 ₽ |
| Tetlong for 3 months | 10 500 ₽ |
| Esperal gel for 1 year | 15 000 ₽ |
| Selincro course of therapy | 12 500 ₽ |
| Implantation of Disulfiram for 1 year | 18 000 ₽ |
| Vivitrol injection for 1 month | 26 000 ₽ |
| Naltrexone stitching for 3 months | 35 000 ₽ |
| Neuroimplantation Prodetoxon for 6 months | 47 500 ₽ |
| Narcopsychotherapy session | 50 000 ₽ |
| Neutralization of encoding | specify |
| Psychodiagnostics / pathological diagnostics | 7 500 ₽ |
| Psychotherapy session | 5 000 ₽ |
| Family psychotherapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Outpatient rehabilitation in Moscow | 33 000 ₽ |
Expand
We will select an individual treatment plan
Free consultation 8-800-200-27-23
Outpatient program
We work with patients until they fully recover. Treatment of depression by a psychiatrist in our medical center does not imply spontaneous actions, but the systematic elimination of symptoms and causes of depression. After a hospital stay, work does not stop. The patient continues to take medications and attend doctor's consultations. There are patients who, for certain reasons, do not want to go to hospital; for them, the outpatient treatment format will be an excellent solution in the treatment of depression.
Disease statistics
Depression is the most common mental disorder in the world. According to statistics, 280 million people experience depression, which is as much as 4 percent of the total world population. In our country, according to the Ministry of Health, every tenth person suffers from depression. This is about 15 million people of different ages and genders. Experts say that the female half of humanity is most susceptible to the development of mental disorders of a depressive nature.
Who is at risk?
The risk of developing depression among single and divorced people is 2-4 times higher than among married people. At the same time, divorced and single men are at greater risk than divorced and single women. But according to WHO, women suffer from depression almost 2 times more often than the stronger sex. According to some experts, such statistics are distorted and do not reflect reality, since men prefer not to see doctors. Many people “relieve” symptoms of depression by using alcohol or drugs. This is confirmed by studies that were conducted among some religious denominations. Male followers who strictly observe religious precepts and do not drink alcohol suffer from depression at the same rate as women. Do not forget that some depressive disorders occur only in women: PMS, menopause, the postpartum period. Not so long ago, the peak of depression was between the ages of 30 and 40, but today depression has become dramatically younger and often affects people under 25 years of age. Approximately 60% of all suicides on the planet were committed in a depressed state.
Causes of the condition
Disturbances in neurotransmitter activity in the neurons of the brain system play an important role in the development of depression. Serotonin deficiency manifests itself in increased irritability, sleep disturbances, and decreased libido. Lack of dopamine leads to disruption of mental and motor activity. Mental and physical symptoms include loss of interest in life, apathy, and muscle weakness.
Biological
Experts have proven that women are most susceptible to developing depression. Emotional instability caused by pregnancy, postpartum, menopause, provokes endocrine changes in the body. Biological reasons include:
- Immune.
- Neurobiological.
- Asthenia of the body against the background of severe infectious diseases.
Psychological
Psychological reasons include the inability to find the right strategy in solving problems. A person does not understand how to act correctly in a given situation. Against this background, he seems to be stuck in a problem with all the ensuing consequences. Also susceptible to depression are people who, due to their temperament, have a tendency to worry for a long time about any reason.
Types of depression in psychiatry
Depression includes a complex of somatic and psychological syndromes. There are several types of this disorder, which differ from each other in the characteristics of their clinical picture.
Classical
A classic depressive episode lasts from several weeks to one year. The complex of classical syndromes affects not only mood, but also performance. A person experiences stiffness of movement, apathy, impaired concentration and even mental functions. After the initial episode, depression may return.
Psychiatric
Any type of depression is a mental disorder. General restorative procedures and occupational therapy, contrary to what some people believe, do not help get rid of long-term oppression! You should contact an experienced psychiatrist.
Moderate
Moderate depression is accompanied by a persistent decrease in mood and performance, but does not include suicidal tendencies. Despite its moderate severity, such a disorder in any case requires professional help.
Heavy
Severe, progressive depression includes the following symptoms:
- Loss of interest in life;
- Lack of self-esteem;
- Unreasonable feelings of guilt;
- Persistent feelings of grief and depression;
- Suicidal thoughts, self-aggressive behavior.
Expressed
Severe depression is accompanied by lethargy, lethargy, and decreased mental function. Outwardly, the person is unkempt, speaks quietly, and has a mournful expression on his face.
Chronic
Depression can become chronic if it is not treated in time. In addition, with somatic diseases such as hypothyroidism, depressive episodes occur periodically.
Acute
During an exacerbation, a person experiences overwhelming sadness. Depression of mood can have a chronic form: it becomes a kind of “norm of life” for a person. During an exacerbation, a person can commit suicidal actions: it is necessary to provide the person with timely psychoneurological assistance.
Atypical
Atypical depression occurs in a hidden form. A person feels depressed, but this does not stop him from joking and laughing; there is a high appetite. It is difficult to determine this type of disorder; it is more common in men.
Recurrent
In recurrent disorder, depressive phases alternate with periods of normal mood. Recurrent depression develops in childhood and periodically manifests itself in adulthood.
Agitated
This type of depression includes low mood and anxiety. In this case, a person feels irrational anxiety, general depression is accompanied by periodic panic attacks. A person develops obsessive phobias and typically expects the worst outcome of any event.
Resistant
An obligatory sign of resistant depression implies the ineffectiveness of pharmacotherapy. Several courses of medication may not provide significant improvement. Antidepressants may have insufficient clinical effect. In this case, the patient must be under the constant supervision of a doctor.
How to get there
Social
Perhaps these are the most common reasons that lead to the development of depression. The following factors negatively affect the human psyche:
- Acute and chronic stress. For example, the loss of a loved one, divorce, betrayal, violence.
- High work loads.
- Job loss and change.
- Retirement.
Older people do not adapt well to changes in life. Therefore, any change, even positive, can lead to the development of stress or depression.
Is it possible to cure depression?
The specialists at our medical center tend to give a positive answer. With the participation of experienced specialists, you can overcome your disease. To do this, you need to undergo a full course of treatment. A well-thought-out treatment program will eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the root causes of depression. Many people believe that the treatment for depression involves the use of antidepressants. This is a false belief. Medicines correct visible disorders, that is, the symptoms through which the disorder manifests itself. Without a properly selected course of psychotherapy, it is impossible to cure depression.
Signs of clinical depression
A key sign of clinical depression is low mood. A person loses the ability to receive joy from anything. There is a negative assessment of others and oneself. The person experiences psychological inhibition and decreased physical tone.
Physiological
Physical activity decreases due to a lack of desire to do work or household chores. A person becomes lazy and gloomy, unable to start and finish any activity. Sleep is disturbed, appetite is lost or increased, libido decreases.
Psychological
In a state of depression, the functioning of the brain and central nervous system is disrupted. A person becomes indifferent to everything, his memory deteriorates, and his self-esteem decreases. In a severe stage, it is impossible to cope with this condition on your own.
Behavioral
A person has passivity, it is difficult to involve him in active activity. He begins to avoid contact with other people and refuses entertainment. Often, when people are depressed, they begin to abuse alcohol and drugs.
How our psychotherapists treat
Anonymously. Your application to our clinic for the treatment of neuroses and depression will remain confidential. We do not register patients with the state and do not disclose information to third parties. The reputation and peace of mind of our clients always comes first.
Carefully. Psychiatrist help for depression should not only be effective, but also sensitive. Our specialists treat their clients very carefully. Considering the diagnosis, this fact is very important. Every action of the doctor is verified and thought out to the smallest detail.
Around the clock. We are ready to receive patients at any time of the day or night. Our hotline specialists answer calls around the clock. If necessary, they will provide all the necessary information, tell you about prices, special promotions, and also arrange for a doctor to visit your home.
Stages of development of depression
Depending on the cause and individual characteristics of the individual, the development of depression can be divided into three main stages.
First stage
Performance decreases significantly, mood deteriorates for no reason, and interest in what is happening is lost. If a person tries to entertain himself and get rid of problems, he can easily get out of this state.
Second stage
Negative symptoms increase, in addition to psychological discomfort, physical discomfort is involved - sexual desire decreases, sleep is disturbed, and appetite is lost. There is a complete loss of work activity.
Third stage
There is a pronounced agitated state or complete inhibition. The mood is always bad, there is low self-esteem and a feeling of guilt. During the third stage, suicidal tendencies may appear.
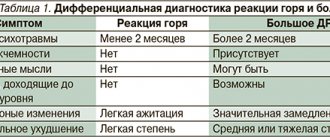
Severity of depression
It is incorrect to distinguish stages in depressive disorders, since the development of the clinical picture varies from person to person. The disease can manifest itself acutely or last for a long period with hidden symptoms.
More significant is determining the severity of the disorder by the number of symptoms, severity of symptoms, and level of decline in quality of life. According to ICD-10, depression is classified as:
- Mild – 2-3 symptoms that impair social functioning, but the person retains the ability to perform most activities.
- Moderate (moderate-severe) – 4 or more manifestations that create significant difficulties in everyday life.
- Severe – a full picture of a depressive episode that significantly impairs social and professional functioning. With ideas of worthlessness, suicidal thoughts and actions.
There are some differences with the DSM-5 approaches. Much also depends on the reliability of the diagnostic scales used and the qualifications of the doctor.
Events
08.12.21
Parents' Day in
Support from loved ones is an integral part of the rehabilitation of a person with alcohol or drug addiction. Since the use of telephones and other...Read more (~1 min.)
«
08.11.21
Residents' trip to the Zvenigorod club "Goliath"
Leisure activities are an integral part of the rehabilitation program for residents. Team games, visiting museums, theaters, exhibitions, picnics...Read more (~2 min.)
«
13.10.21
Travel of rehabilitators of the “Zdravnitsa” Center to “Ruzskaya Alaska”
One of the important tasks of a rehabilitation center for addicted people is to teach them to enjoy life in sobriety, to find...Read more (~2 min.)
«
21.09.21
Guests from the Moscow Regional Duma in
In September, a delegation of candidates for deputies of the Moscow Regional Duma, the head of the election headquarters of the Rodina party, visited. [zdravnews] Employees...Read more (~1 min.)
«
All events
Reasons for development
Any type of depressive disorder can develop due to:
- loss of a loved one;
- sudden and significant deterioration in health;
- problems at work;
- experienced physical/psychological violence;
- conflicts in the family;
- economic difficulties;
- change of place of residence (especially when moving for permanent residence to another country).
In rare cases, mild depressive disorders are a response to a joyful event. In this case, psychiatrists talk about “goal achieved syndrome.” A person receives what he has been striving for for many years, and realizes that he does not know why he should live further. He fails to form new goals, which makes his life empty and meaningless, uninteresting. In any case, depression is the result of the influence of a traumatic factor. The patient realizes when and why it began to develop in him, but cannot help himself. People who have been subjected to violence, participants in military operations, and creative individuals are prone to depressive disorders. Some women experience mental problems during menopause. This is due to hormonal changes. Whatever causes the problem, you should seek medical help. Then you will be able to quickly eliminate the negative impact of the traumatic component and fill your life with joyful moments.
Complications of depression
If a person suffers from chronic diseases such as hypertension, heart disease, asthma, gastritis or ulcers, oncology, then with the development of a depressive state the course of these pathologies becomes more severe. At the same time, the severity of the pain syndrome increases. The patient's sleep is disturbed, he becomes indifferent, and loses interest in life.
Sleep disturbance
With depression, a person is in an anxious, confused state. He can't sleep at night and then falls asleep during the day. The biological rhythm goes astray, and negative changes begin to occur in the functioning of other organs.
Apathy
Indifference or apathy is a consequence of prolonged stress or depression. A person’s desires disappear, he lacks the motivation to take care of loved ones and do household chores. Apathy fetters a person who becomes self-absorbed, while internal anxiety grows.
Lack of interest in life
A depressive state is characterized by a loss of interest in what is happening around. Complete apathy and indifference are the body’s protective reaction to a stressful situation. You can cope with this condition on your own only at the initial stage of development of the disorder. In the chronic form, you need to consult a psychologist.
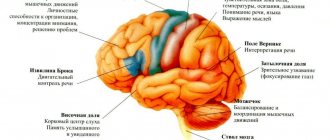
Biochemical processes in the brain
In patients with depression, biochemical processes in the brain are disrupted. The balance of hormones is disrupted, making the condition even worse. If drug treatment is not started in time, this will lead to irreversible consequences.
OUTPATIENT REHABILITATION
- Classic
Characterized by depressed mood and lack of pleasure from previously enjoyable activities. Negative changes in cognitive functions occur, memory deteriorates. Motor activity decreases, and loss of strength often occurs. - Psychiatric
A mental disorder is observed in which a decrease in mood occurs and indifference to everything that happens. A person is often sad and depressed. To treat this condition, doctors prescribe effective antidepressants. - Moderate
Characterized by a depressed state for two weeks. However, it does not improve under the influence of external factors. Sleep and eating behavior are disturbed; a person may sleep little, but at the same time experience hyperactivity in the morning, which is then replaced by apathy. - Severe
A serious mental disorder that combines mental, physical, and behavioral symptoms. It is characterized by a persistent pessimistic mood, depression and melancholy. A severe form of depression develops as a result of severe stress or a traumatic situation. - The severe
severe stage of the development of the disease includes all negative manifestations. A depressed depressed state, a constant feeling of mental pain and guilt coexist with a loss of strength and indifference. Particularly emotional people begin to have thoughts of suicide. - Chronic
Symptoms in the chronic course of the disease persist for about two years. A prolonged form of depression is accompanied by constant apathy, decreased mood, and anxious thoughts. A person’s self-esteem decreases, he moves less, and his mental abilities decrease. Chronic depression requires qualified treatment in a clinic. - Acute
Genetic factors lead to an acute form of depression. Gene mutations predetermine congenital deficiency of serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine. As a result of a lack of these substances, depression develops, manifested by rapid fatigue, bad mood, and apathy. - Black
Black depression is characterized by a hopeless negative state. A person begins to feel guilty in all situations that do not even depend on him. He always has anxiety, a gloomy mood, and for all troubles he blames himself and those around him. - Behavioral
Depression is often perceived by others as a character trait. With a mental disorder, a person’s behavior changes for the worse. He becomes indifferent to social affairs, avoids communication and entertainment, and often begins to use alcohol or drugs. - Permanent
Depression is often perceived by others as a character trait. With a mental disorder, a person’s behavior changes for the worse. He becomes indifferent to social affairs, avoids communication and entertainment, and often begins to use alcohol or drugs. - Resistant
is a mental disorder that has not responded to treatment by specialists in one or two courses. Resistant depression includes severe depression and partial remission. To achieve the effect of treating such a disorder, a long period of hospital stay and complex treatment, including with the participation of a psychologist, are necessary.
Types of depression in psychiatry
Based on the nature of its course, mental disorders are classified into several types, each of which poses a danger to the human psyche.
Clinical depression: signs, symptoms and treatment
What is clinical depression? What are the signs of clinical depression? What are the symptoms of depression and is it always necessary to treat it? How do antidepressants work?
The answers to all these questions are very important, because depression is one of the most famous mental disorders that is mentioned inappropriately in modern society.
Clinical depression is not a medical term, but a colloquial expression that some people use to describe depression that requires treatment from a psychiatrist.
The term “depression” is most often referred to in films, literature and even in everyday communication. But often the concept of depression as a disease is misunderstood by people and is taken as a temporary condition when there is a loss of energy, lack of motivation and low mood. Meanwhile, depression is a disease that often requires specific therapy.
What is depression, how to recognize it, in what case is the expression “clinical depression” appropriate, and when is it necessary to apply treatment?
Signs of clinical depression
To understand what depression is, you need to know its main signs. Although the phrase is common, “clinical depression” is a colloquial expression that means depression is severe enough to warrant treatment.
The key signs of clinical depression are hypothymia (consistently low mood), complete or partial loss of the ability to experience joy, a negative assessment of oneself and the world around us, in which the patient notices only gray tones and bad events. “Intellectual inhibition” and decreased physical tone also occur.
There is a lot of discussion and debate among experts around the nature of depression.
Depressive syndrome is observed not only in clinical depression, but also in other diseases, both mental and somatic.
The depressive symptom complex is low-specific, that is, it is not always sufficiently specific for the disease that causes it. In addition, difficulties with differential diagnosis in the presence of depressive syndrome are associated with its polymorphism (variety of manifestations). Signs of clinical depression may include other symptoms: chronic pain of unknown origin, difficulty concentrating, libido disorders, lack of motivation and much more.
The famous psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin considered all affective pathologies within the framework of one disorder - manic-depressive psychosis. With his views, he provoked a huge number of discussions that continue to this day. E. Kraepelin said that all types of manic-depressive psychosis (which included depression) are characterized by a positive outcome of the disease. But subsequent studies have shown that this view is not always correct and cannot be applied to all types of depression.
Modern statistics on depression clearly prove that it does not always end in a positive outcome. About 40% of patients suffer from the same episode (attack) of depression a year after its onset, 20% of patients have a history of depression for more than 2 years, 17% suffer from depression all their lives. As you can see, this is not the most positive statistics. In modern medical practice, depression that lasts more than two years is defined as a chronic illness, no less serious than asthma or diabetes. It is unlikely that anyone will argue with the fact that it affects the overall quality of life and social status, in particular. In addition, depression negatively affects the patient’s family and his environment as a whole.
The most difficult cases are the combination of depression with any other physical illness. This complicates the diagnosis and treatment of such patients, and also has a negative impact on the course and possible complications of both diseases.
Symptoms of clinical depression
Symptoms of clinical depression in different patients can be both very similar and significantly different. But all of them are determined using diagnostic criteria for depression, which in most countries are based on DSM-V and ICD-10. The earlier a depressive state is diagnosed and treated, the less its negative impact on all areas of a person’s life will be observed.
Unfortunately, most patients with depression come to the doctor at the insistent request of family and friends. How often do we think that anything can happen to others, but not to us, we are afraid to look directly at the fact that the disease has already fully developed and is feeling very well, unlike ourselves. Depression is not always easy to diagnose and begin effective treatment immediately. Symptoms of clinical depression are not always pronounced; it can be hidden under various “masks” in the form of somatic symptoms. Therefore, people with depressive syndrome, due to existing stigma and their own ignorance, often come for help not to specialized specialists, but to somatic doctors: therapists, cardiologists, gastroenterologists, neurologists, etc.
In historical terminology, a division of mental illnesses into endogenous (where the main role belongs to heredity) and exogenous (caused by external factors) has been established. This division also applies to depression.
Clinical manifestations of depression
Depressive symptoms are caused by a decrease in the concentration in the nervous system of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine and, less commonly, dopamine. Clinical manifestations of depression can vary significantly depending on the pathogenesis and severity of the disorder, and the personal characteristics of the patient.
Clinical picture of endogenous depression
The clinical picture of endogenous depression is characterized by a depressive triad - low mood, slower pace of thinking and motor activity. There is also a predominance of the affect of melancholy, which is perceived as a very painful experience. Previously, this feeling was the key symptom of depressive syndrome. Recently, the pathomorphosis of mental illnesses has changed, and now the clinical picture of endogenous depression is often more characterized by anxiety. Along with anxiety, sleep disturbances are observed (shallow sleep, frequent and early awakenings). Also, with endogenous depression, a decrease in general tone, mental detachment and alienation, lethargy, asthenia, loss of the ability to feel pleasure, unreasonable fears about one’s health, indifference to what is happening around, motor retardation, along with possible depressive delusional ideas of one’s own inferiority, insignificance and self-deprecation may occur. , as well as sometimes a lack of understanding of the need to continue one’s own life. This can lead patients with endogenous depression to suicidal intentions and attempts.
Clinical picture of psychogenic depression
Psychogenic depression is one of the types of exogenous depression, along with traumatic, vascular, intoxication, etc.
Psychogenic depression is a disorder caused by the action of external or internal negative or traumatic factors.
The main causes of psychogenic depression are family and professional problems, stressful situations, difficulty in adapting to new conditions, distance from home, the presence of intrapsychic conflict, and psychological trauma.
From history... In the territory of the former Soviet Union, many authors used the term “neurotic depression”, however, they were never able to finally agree on its meaning. Some perceived it as a certain form of neurosis or one of the stages of neurotic development, others - as symptoms of a neurotic level in depression, which occurs in neurosis-like conditions. Depressive neurosis was also identified, which was considered identical to neurotic depression, and it was not isolated as an independent form, adhering to the opinion that the symptoms of depression can manifest themselves in all neuroses.
Factors leading to the occurrence of psychogenic depression are mainly individually significant and depend on the personality type. People with certain premorbid characteristics (those that were personality characteristics before the onset of depression), characterized by rigidity, straightforwardness, a strong sense of duty and uncompromisingness, are more likely to develop clinical depression of a psychogenic nature. In addition, they constantly try to restrain their emotions, thereby worsening their condition.
The clinical picture of psychogenic depression reflects the severity of the traumatic situation and the personal characteristics of the patient. The characteristic features of psychogenic depression include a person’s fixation on the stress factors that caused it, a pessimistic view of the future combined with an adequate or overestimated assessment of the past, attempts to escape from memories of a traumatic event, and tearfulness.
It should be noted that in the clinical picture of psychogenic depression, especially in its mild form, the classic melancholic triad and other symptoms that are observed with endogenous depression may be absent.
But there are cases when a stress factor leads not to psychogenic depression (depressive adaptation reaction according to the ICD 10 classification), but to the first attack of endogenous depression. And then, over time, the fixation on traumatic factors goes away, and the clinical picture reveals symptoms that are characteristic of endogenous depression.
Treatment of depression. Clinical guidelines
The treatment of depression is determined, first of all, by the nature of its occurrence. The treatment of various types and degrees (stages) of depression, including psychogenic and endogenous, has its own characteristics and, accordingly, different clinical recommendations. Treatment tactics for depressive disorder are determined after differential diagnosis.
Treatment of psychogenic depression
In the case of treatment of psychogenic depression, if its level does not exceed a mild degree, help from a psychologist or psychotherapist is possible without the use of antidepressant therapy. For moderate and severe depression, even caused by external causes, psychological correction and psychotherapy do not bring sufficient effect, and the use of medications (antidepressants) is necessary.
Treatment of endogenous depression
Pathogenetic therapy for depression is aimed at the mechanism of development of the disease. Endogenous depression is caused by a decrease in the amount of certain neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft, resulting in disturbances in the transmission of nerve impulses.
Antidepressants restore the balance of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine, which, in fact, is the treatment of endogenous depression.
Medicines used to treat depression differ in their mechanism of action, clinical effect and other characteristics.
Antidepressants in the treatment of depression
Antidepressants can be roughly divided into large and small. The former are capable of providing a complete therapeutic effect both in mild or moderate and severe depression; these are drugs that are polyvalent in their effect on receptors. The second (minor) antidepressants are effective for mild and moderate degrees (stages) of depression, at the same time they are better tolerated and have fewer side effects.
That is, for mild and moderate degrees (stages) of depression (masked or latent, somatized, cyclothymic), you can use monovalent antidepressant drugs that affect only serotonergic neuromediation or polyvalent, but weak in their effects on depressive syndrome. For severe degrees (stages) of depression (melancholic, paraphrenic), large polyvalent antidepressants should be used, which increase the level of norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine in the synaptic cleft through various mechanisms.
The duration of active treatment for depression is the same as the duration of the depressive episode itself. Symptoms resolve much faster, but active antidepressant therapy cannot be stopped immediately, as depressive symptoms will quickly return.
Seek help from professionals in a timely manner! Only they know the intricacies of diagnosis and necessary treatment! Only they can help a patient with depression return to a normal, fulfilling life!
Consequences of prolonged depression
With chronic depression, not only the functioning of the brain is disrupted in a person. Due to a mental disorder, the immune system malfunctions. As a result, the body’s protective functions weaken, and the risks of developing diseases, including infectious ones, increase. It is difficult for a person after depression to socialize in society. If treatment is not started, depression becomes severe.
Find out treatment recommendations without leaving home for free
To select a treatment plan, you just need to leave a request, we will contact you to select the time and specialist you need
Submit your application
Anxiety depressive disorder symptoms and signs
Since depressive disorder has acquired the status of a modern international problem, a whole classification of symptoms and signs has been compiled in medicine. It is important to note that we can only talk about a disorder if a person has symptoms on an ongoing basis for at least 1 month. To make a diagnosis, as a rule, 4-5 signs of the following must appear:
- Difficulty concentrating. To solve at least one task, a person has to make enormous efforts, since increased absent-mindedness prevails
- Lack of a normal sleep cycle. Sleep does not occur immediately; intermittent sleep is often observed (waking up after a short period of time), resulting in constant fatigue.
- Feeling as if strength is leaving the body. As a rule, with increased attention, the patient begins to feel anxiety and irritation.
- Increased irritability. Most often it manifests itself in an ordinary reaction to external stimuli in the form of tears, screams, even if the person is asked an ordinary question
- Groundless worry. Accompanied by a feeling of unreasonable fear and lack of self-confidence
- A tearful state. The patient begins to cry under any circumstances: observing a touching moment, an ordinary meeting with friends and relatives
- The emergence of unfounded fears. Any event, even one without any danger, seems suspicious to a person
- Constantly prepared for the worst. The patient develops a strong belief that the future does not promise him anything positive and the situation will only get worse every day
- A state of hopelessness. When any action seems completely ineffective, luck has turned away from the person and one should not hope that something good will happen in the future
- Low self-esteem. As a result, one’s own importance is devalued.
Any of the symptoms must be present for a month to indicate the occurrence of a depressive disorder.
Prevention of depression
To avoid the development of depression, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Properly distribute workload and rest. Sleep should be full for at least eight hours.
- Maintain a daily routine. The day is for being awake and the night is for resting.
- Proper nutritious nutrition will strengthen the body.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle. To feel good, you need to play sports, you can just go jogging every morning.
- Avoid stressful situations.
You should try to find interesting hobbies that bring joy and satisfaction. Positive emotions are the main prevention against depression.
Questions about depression
Is it possible to cure depression without pills?
- This is possible only at an early stage of the disease. If you contact a good psychiatrist or psychotherapist in time, who is competent in this area, you can do without medications. It is important to consider the causes of depression. If they are not related to physiological problems and the patient is ready for treatment, the doctor will select an effective type of psychotherapy.
Is it possible to treat depression at home?
- Several specialists are involved in diagnosing and treating depression in a hospital. This mental disorder requires in-depth analysis and accurate diagnosis. The patient cannot make a diagnosis on his own, and therefore cannot select adequate treatment.
How to get rid of depression on your own?
People with depression rarely go to the clinic for help. If you experience a depressive reaction to a stressful situation or mild depression, it is not necessary to consult a doctor, since the consequences will not lead to serious consequences. A person can cope with the disorder on his own. It will be enough to get carried away by something interesting and learn to let go of problems. The condition will improve if loved ones provide psychological support. At a more severe stage, all measures will be ineffective; here the help of a psychologist and psychotherapist will be required.
Treatment methods for depression in a clinic in Moscow
Each aspect of treatment includes pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. Therapeutic measures are selected on an individual basis: they actively resort to art therapy, yoga, massage... The most effective method of treating depression in Moscow is combined. A comprehensive, modern approach is what helps achieve remission.
Diagnostics
The main method for diagnosing depression is interviewing the patient. There are several main manifestations of the disease:
- Depressed psycho-emotional background for several weeks;
- Anhedonia (the inability to experience positive emotions even from things that previously brought joy);
- Apathy (lack of motivation to perform daily activities).
An extensive range of diagnostic measures is also prescribed. They examine brain activity, study analyzes of the thyroid gland and sex hormones to exclude endocrine and hormonal pathologies.
Drug therapy
Depression is a disease that is often accompanied by organic pathologies. Due to disruption of the biochemical processes of the brain, severe depression of mood and apathy are observed. To stabilize sleep, sleeping pills are used, and antidepressants are prescribed without fail, but the exact treatment regimen depends on the specific case.
Treatment at home
Treatment for depressive disorder cannot be done at home. Traditional recipes for treating depression do not help in any way to get rid of this disease. Depression is often caused by bereavement. This means that psychotherapy is simply necessary: only a professional will help a person work through the problem.
Psychological help
This disease requires the participation of a psychologist. Several types of psychotherapy are used:
- Cognitive - aimed at changing thinking patterns that support a depressive state;
- Gestalt therapy - support in difficult life situations, working through underlying problems, feelings of loneliness. abandonment;
- Psychodynamics - awareness of the root cause of the problems that have arisen. Working through childhood traumas and grievances, being in an unfavorable environment.
Together with a psychologist, a person with depression changes their way of thinking, fights traumatic memories of the past, and correctly experiences the stages of grief. Thanks to high-quality psychotherapy, a person quickly returns to normal life.
Need for a hospital
This mental disorder should be treated in a clinical setting. People suffering from depressive disorder are prone to suicide. This means that a person in deep depression, left alone, can commit rash actions that can lead to death.
In a hospital setting, the patient is under constant supervision of medical personnel. Due to compliance with safety rules, the risk of committing suicidal acts is practically absent. It is impossible to achieve the same high effectiveness of treatment and safety of the environment at home.
How to recognize depression?
How to get an answer to the question: “Am I depressed”? If you have any suspicions or notice any of the above signs in yourself or a loved one, you need to confirm the diagnosis - consult a psychotherapist.
Diagnosis of depression is an assessment of the patient’s symptoms and complaints by a psychotherapist. It is important to establish after what the disease began (after stress, overwork or “out of nowhere”) and how it developed.
The doctor uses the following techniques:
- Clinical and anamnestic examination is the basis for diagnosing depression. The specialist evaluates the possible causes of depression, analyzes all symptoms (including subtle and hidden ones), and compares them with diagnostic criteria. An experienced doctor can diagnose even those patients who are in a state of apathy, constantly cry or refuse to make contact with others.
- Pathopsychological examination performed by a clinical psychologist. For differential diagnosis (for example, with schizoaffective disorder) and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment (is there an objective improvement or not), the psychologist gives an opinion about the patient’s thinking, memory, concentration, and emotional-volitional sphere.
- Examination by a neurologist or therapist - if a person has complaints of pain, sensory disturbances, digestive disorders, heart pain, it is necessary to identify general somatic diseases, since in some cases the presence of the main signs of depression and nervous exhaustion are associated with them. For this purpose, specialists of related profiles are involved: a neurologist, a therapist, an endocrinologist.
- Laboratory and instrumental examination - if the doctor suspects another disease in a person based on the symptoms, he can prescribe an analysis for the level of thyroid hormones (differential diagnosis with hypothyroidism), EEG, CT or MRI of the head (organic brain damage), Neurotest or Neurophysiological test system (endogenous diseases - schizophrenia, schizotypal disorder).
It must be remembered that depressive symptoms may be part of the symptoms of another mental illness: schizophrenia, bipolar or schizoaffective disorder.
Clinical prognosis
The overall prognosis is always positive. Modern psychotherapy has a sufficient set of proven tools and techniques for the successful treatment of reactive depression at any stage of the disease. At the same time, you need to understand that the timing of such therapy is determined by the advanced state of the disorder, and therefore, if a person shows clear signs of depression, it is recommended to visit a specialist as soon as possible.
Psychiatrist, narcologist, psychotherapist Viktor Nikolaevich Antipenko
Share the article
What happens in the body with depressive personality disorder
There are many theoretical assumptions that explain the origin of dysthymic abnormalities.
Among them are the following theories:
Biochemical disruptions in the homeostasis system. For a number of reasons, the level of serotonin and other transmitters in the nervous structures decreases, which leads to persistent dysthymia.- Behavioral, according to which the central nervous system, trying to cope with stress, turns off positive emotions in a person, thereby provoking an aggravation of the stress response. Thus, a vicious circle is formed.
- Alternative social reaction (secondary, reinforcing the problem). In this case, the patient is perceived by loved ones as an annoying negative factor. Misunderstanding pushes people away, creating even greater isolation in the patient.
- Unforeseen circumstances. According to this version, the dysthymic state is a consequence of the lack of a positive response from society to the positive type of behavior of the patient.
How depression manifests itself
Below is a general portrait of depressed people:
- Women between twenty and forty years of age are more often exposed to this disease;
- Most likely one of the parents, or worse, both, died when they were little;
- The person is divorced and does not have a permanent life partner;
- Perhaps there was a difficult birth, and the child is being raised without a father;
- If the patient’s relatives were depressed due to mood changes;
- There was a desire to do something to oneself for no good reason;
- The man buried his spouse;
- There were troubles along his life's path;
- There is an addiction to alcoholic beverages, painkillers, and worse, drugs;
- For a long time he drinks hormonal drugs, sleeping pills-barbiturates, reserpine;
- Basically, a person suffering from a psychological disorder tries to distance himself from the world around him and becomes uncommunicative. No one comes to see him, and he tries not to communicate with anyone; his friends are becoming fewer and fewer. They do not spend free time with him and do not care for him;
- Something happened to him of a personal nature: a disagreement with close friends or family;
- Does not have a high level of education;
- He has no interest or passion for anything;
- Stops believing in anything.
Service price
- HOSPITAL Day hospital5 000
- Day hospital with intensive care8,000
- 24-hour hospital (all inclusive, cost per day) 12,000
- 24-hour hospital (all inclusive, cost per day). Single occupancy24,000
- 24-hour hospital (all inclusive, cost per day). Single occupancy in a superior room 36,000
- Primary family counseling for relatives of patients undergoing inpatient treatment free of charge
- Group psychotherapy for relatives of patients undergoing inpatient treatment free of charge
- Group psychotherapy for 24-hour and day hospital patients free of charge
- Individual post for a hospital patient (if indicated)6,000
Treatment options
The main method of treating reactive depressive disorders continues to be individual psychotherapy sessions, during which the doctor helps the patient accept or rethink what happened, develop new personal volitional qualities, increase stress resistance, etc.
In the most acute situations, when the patient withdraws into himself or contemplates suicide, antidepressants or corrective hypnotherapy sessions are prescribed, which helps to quickly normalize the person’s emotional state and protect him from irreparable actions.
From origins to modern times
Depression
- is not at all a phenomenon that suddenly became popular or seemed to be a consequence of superstition. This is a real disease, a problem that began around the time humanity appeared. Proof of this can be a written source that has survived to this day - the Bible. It describes the story of the first king of the Jews, Saul, who lived in the 11th century BC. His condition was a mixture of all negative emotions: Saul was angry and gloomy, angry, depressed. And only playing the lute was able to humble the king and ease his suffering. The brave and valiant David, who performed delightful music, helped Saul get out of his difficult situation. But Saul was not filled with gratitude. Envy of the brave warrior, who so easily gained fame and recognition of the people, burned the heart of the king and drove him into even greater despondency. Depression and anger forever left Saul painfully aware of reality. This story shows signs of depression. The aggravation of the causes of the king’s illness is also caused by his feeling of guilt for his broken promise to God. Being in deep prostration, the king, unable to stand it, kills himself with a sword.
Depression in people from wild tribes occurred in conditions in which the imperfect human psyche could quickly adapt, which allowed them to survive in the future. Ancient Egyptian priests several thousand years ago already knew how to treat patients with constant melancholy. Around 5000 BC, the thinker Pythagoras advised people who fell into a sick state to listen to music. A thousand years later, Democritus recommended reflection, that is, analyzing one’s condition in order to get rid of the causes of suffering. Around the same time, Hippocrates called the mental disorder melancholia and noted that it is the human brain that causes grief, sadness, and poor sleep and nutrition. Madness, anxiety and fear have their origins in the functioning of the brain. Hippocrates tried to “divide” melancholy depending on the reasons for its manifestation. For example, overwork and other external factors led to a semblance of melancholy, while the disease itself arose for no reason.
Today, such conditions are given names, namely, “psychogenic” and “endogenous” depression. Plato viewed disease carriers as creative individuals in comparison with healthy people living their everyday philosophy. Aristotle, by the way, in the 4th century BC wondered about the close connection between the activities of talented people and melancholy. In the 17th century, the English professor R. Barton, the author of “The Anatomy of Melancholy,” himself suffered from depression and in his work outlined everything he knew about the disease. Barton's views on the disease turned out to be close to the views of modern scientists. Thanks to the works of outstanding authors, it is now possible to use modern techniques in the fight against depression.