Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder is one of the clinic’s priorities. Our specialists participate in international scientific research to improve and implement the most modern, safe and effective methods of treating GAD.
Call and make an appointment! We help even in the most difficult cases!
Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder in our clinic is carried out on the basis of modern differential diagnosis, methods approved and recommended by international research centers and the European Ethics Committee for Medicine. We use the most effective and latest techniques for treating GAD.
Generalized anxiety disorder - GAD
If you constantly feel anxious, you may have generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
GAD is a long-term mental disorder that makes you feel restless (anxiety, panic) in a wide range of situations and problems, and not just in the situation of one specific event, and is a “non-fixed” and not tied to a specific place or event condition. In many cases, one can say about GAD that one is constantly worried about everything and for every reason.
Generalized anxiety disorder, in English version
Generalized Anxiety Disorder, literally translated as - generalized
anxiety disorder.
According to the syndromic diagnostic index ICD-10 (which is currently used in Russia) it is encrypted as F41.1.
People with generalized anxiety disorder spend much of their time worrying, trying to remember the last time they felt free from anxiety.
In generalized anxiety disorder, both psychological (mental) and physical symptoms may appear, which are often mixed and manifest as psychosomatic disorders. These manifestations vary depending on the personality type, upbringing, education, physical condition and characteristics of human development. GAD may involve feelings of irritability or restlessness and often include difficulty concentrating and/or sleep disturbances.
Generalized anxiety disorder is very debilitating for patients, both mentally and physically. Symptoms of an anxiety disorder exhaust a person, “eat up” vital energy, interfere with sleep, and reduce appetite. In most cases, people with GAD are unable to engage in full-time work, study and adapt to new conditions. With anxiety disorders, patients are unable to free themselves from this chronic worry and calm their anxiety.
Diagnostics
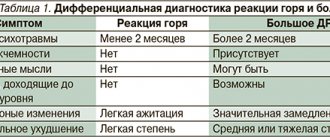
Even doctors often confuse anxiety-depressive disorder with neurocirculatory dystonia (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
The reason is that the somatic symptoms of neurosis are similar to VSD. The result of an incorrect diagnosis is incorrect and ineffective treatment. Therefore, if you suspect neurosis with complaints, it is better to consult a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, rather than a general practitioner. Anxiety disorder is more difficult to diagnose than depression. The reason is that the list of diagnostic criteria is rather “erased”, not clear, built according to the method of exclusion. At the first consultation, the psychiatrist collects anamnesis, asks the patient questions about his well-being, and inquires about the presence of mental pathologies in relatives. During the diagnosis, the patient undergoes a series of questionnaires. The Zung scale and the Beck test indicate the presence of signs of depression. The Hamilton and Montgomery-Asberg scales reveal the level of severity and neglect of a depressive state.
A general blood and urine test is needed in order to exclude somatic pathologies of an inflammatory, immunological and hormonal nature. It is advisable to use instrumental examination methods.
Electroneuromyography is prescribed for muscle pain syndrome to assess the condition of peripheral nerves and muscles. An EEG is needed to refute epilepsy, since some of its symptoms overlap with manifestations of neurosis. MRI of the brain allows you to see the organic causes of the disease and assess the state of blood flow. Electrocardiography is prescribed in case of frequent attacks of suffocation, feeling of pressure in the chest area. The method helps to exclude cardiovascular pathologies.
What is generalized anxiety disorder
History of GTR Valeria
Valeria has always been restless, but this has never interfered with her life before. Lately, however, she had been feeling edgy all the time throughout the day. She felt an omnipresent sense of fear, paralyzed by constant influxes of thoughts about the future. All her efforts to get rid of this anxiety and concentrate on work were to no avail. When she returned home, she could not relax.
Valeria also had difficulty sleeping, tossing and turning for several hours before falling asleep. In addition, she felt frequent stomach cramps and diarrhea, and tension in the neck muscles. Valeria even began to feel like she was going crazy.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a common disorder that involves chronic anxiety, nervousness, and tension. Unlike a phobia, where fear is associated with a specific object or situation, the anxiety of generalized anxiety disorder is somewhat vague, not attached to an object. This anxiety is less intense than panic attacks, but much more persistent, making normal life debilitating and impossible to relax. With panic attacks, as a rule, the state remains normal between panic attacks, but with GAD, anxiety continues in a constant background.
If you have generalized anxiety disorder
If you have GAD, you may worry about the same things that other people worry about: health issues, money, family problems, or difficulties at work, etc.
But you take these worries to a new level.
An employee's careless comment on economics becomes a vision of imminent dismissal; A phone call to a friend who does not return immediately raises strong concerns that something bad has happened. Sometimes just thinking about the events of the day leads to anxiety.
The thought of one's own work is filled with exaggerated anxiety and tension, even when there are no problems or there are minor preconditions that could provoke a problem. Therefore, there are very significant features of the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder with modern inpatient replacement techniques.
Anxiety in GAD is more intense than the situation requires, and this anxiety no longer performs a protective function, does not protect you (after all, for a healthy person, anxiety is just a defensive reaction, a normal reflex). With GAD, you can't turn off your anxious thoughts. They continue to work beyond the reach of your will and desires, endlessly repeating themselves.
Doesn't remind you of anything?
- “I can’t control my thoughts to… it’s driving me crazy!”
- “He's late, he should have been here 20 minutes ago! My God, he must have had an accident! "
- "I can't sleep - I just feel some kind of fear (anxiety) ... and I don't know why!"
The Difference Between “Normal” Anxiety and GAD
Worries, doubts, and fears are a normal part of life. It's natural to worry about your upcoming exam, your finances, your situation at work, your family, etc. The difference between “normal” anxiety and generalized anxiety disorder is that the anxiety in GAD can be described as:
- excessive
- obsessive
- permanent
- exhausting
It has been scientifically proven, for example, that after watching a report about a terrorist attack in the Middle East, a person may feel a temporary feeling of anxiety and anxiety for several minutes. If you have GAD, a person may feel anxious about this all night and still worry about the worst-case scenario for several days, imagining that your hometown will become a target of terrorism, and you or your relatives (relatives, acquaintances) may become victims of this terrorist attack.
The main differences between normal and generalized anxiety in self-diagnosis.
"Normal" Anxiety
- Your anxiety does not stand in the way of your daily activities and responsibilities.
- You are able to control your anxiety.
- Your worries and troubles do not cause significant feelings of distress.
- Your concerns are limited to a small number of specific real problems.
- Your anxiety attacks occur for a short period of time.
Generalized anxiety disorder
- Your significant concern disrupts your work rhythm, activities, and social life.
- Your anxiety is uncontrollable.
- Your worries are very upsetting, make you tense, and are perceived as a disaster.
- You worry about all sorts of things that may not directly concern you or your family and, as a rule, expect the worst.
- Worry almost every day for at least six months.
Maintenance pharmacological therapy
A meta-analysis showed that long-term use of SSRIs (6–12 months) was effective in preventing relapse (odds ratio for relapse = 0.20).
Relapse after 6-18 months of duloxetine, escitalopram, paroxetine and venlayaxin XR was observed in 10-20% of cases, compared with 40-56% in the control group. Continuing pregabalin and quetiapine XR also prevents relapse after 6-12 months.
Long-term RCTs have shown that escitalopram, paroxetine and venlafaxine XR help maintain benefit over six months.
Signs of generalized anxiety disorder
The symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder vary greatly and can vary within the same person over time. A person may notice both improvements and deteriorations in their overall condition as the disease progresses. Stress, shock, negative emotions, and alcohol may not cause acute manifestations of generalized anxiety disorder, but this aggravates the course of the disease, and symptoms may become more severe in the future.
Not every person with generalized anxiety disorder has the same symptoms as another. As discussed, symptoms can vary greatly, but most people with GAD experience a combination of the following emotional, behavioral, and physical symptoms.
Emotional symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder
- Constant worries running through your head
- Anxiety is uncontrollable, there is nothing you can do to stop the anxiety
- Intrusive thoughts that create anxiety; You try not to think about them, but you can't
- Intolerance of uncertainty; You must know what will happen in the future
- Widespread (pressing) feeling of apprehension or dread
Behavioral symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder
- Inability to relax and enjoy peace of mind
- Difficulty concentrating
- Quitting activities because you feel depressed
- Avoiding situations that make you anxious
Physical symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder
- Feeling of tension in the body or part of the body, sensation of pain, heaviness, pressure
- Having trouble falling or staying asleep
- Feelings of extreme anxiety or nervousness
- Stomach problems, nausea, diarrhea
Treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
The core symptom of generalized anxiety disorder is chronic anxiety. It is important to understand what is the “trigger mechanism” in the body for this massive anxiety, since these mechanisms play a huge role in triggering and maintaining GAD. Therefore, first of all, a complete and high-quality diagnosis is required that will answer this basic question and determine success in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder.
The main, most effective method in the treatment of GAD has been and remains complex therapy, which should simultaneously include several mandatory components.
Neurometabolic treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
Neurometabolic therapy, which helps the body quickly cope with the general background of mood, relieves obsessive thoughts, normalizes sleep and gives the brain the ability to self-heal with the help of additional substances that are introduced into the body.
Psychotherapy for generalized anxiety disorder
Rational psychotherapy, which gives a person a critical attitude and awareness of the true causes of this anxiety and intrusive thoughts. Provides insight into what is counterproductively draining your mental and emotional energy without leading to resolution of any specific tasks or actions. How to distinguish between productive and unproductive anxiety.
Autogenic training in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder
Relaxation training makes it possible to learn how to resist anxiety and anxious thoughts. When you are relaxed, your heart rate slows, you breathe slower and deeper, your muscles relax, and your blood pressure stabilizes. It is the opposite of anxiety and worry, which strengthens your body's relaxation responses. This is a powerful impetus for relieving symptoms. Regular practice is necessary. Your nervous system will become less reactive and you will be less vulnerable to anxiety and stress. Over time, the relaxation response will become easier and easier until it comes naturally.
Group therapy for GAD
Communication within group psychotherapy. Generalized anxiety disorder gets worse when you feel powerless alone. It is better to overcome this condition together with those who experience the same problems. The more connected you are to other people, the less vulnerable you will feel.
Psychological help
Meta-analyses clearly show that CBT significantly reduces GAD symptoms. A small number of studies have compared the effects of CBT and pharmacotherapy, which have shown approximately the same effect size. Individual and group psychotherapy are equally effective in reducing anxiety, but individual psychotherapy may be more effective in reducing anxiety and depressive symptoms.
Psychotherapy intensity was assessed in a meta-analysis of 25 studies. For reducing anxiety, a course of psychotherapy lasting less than eight sessions is as effective as a course lasting more than eight sessions. In reducing anxiety and depression, more intensive courses are more effective than courses with a small number of sessions. Several studies have shown the benefits of ICBT.
The meta-analysis found no significant difference between the effects of CBT and relaxation therapy. However, more recent research suggests limited effectiveness of relaxation therapy. A large RCT found that balneotherapy, a relaxation therapy with spa treatments, was better than SSRIs in reducing anxiety; however, there are doubts about the validity of the study.
The effectiveness of behavioral psychotherapy based on acceptance, metacognitive psychotherapy, CBT aimed at correcting the perception of uncertainty, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy has been proven.
Psychodynamic psychotherapy can also provide results, but at the moment there is no clear evidence of its effectiveness.
Adding interpersonal and emotional-process therapy to CBT does not provide significant benefits compared to CBT without the addition. A preliminary conversation before starting a CBT course helps reduce resistance to therapy and improve compliance - this strategy is especially useful in severe cases.