- Home >
- Clinic services >
- Neurology >
- Cerebral vasospasm
In the human body, the brain is the most important organ, which not only regulates the functioning of all other organs and systems, but is also responsible for our consciousness, perception and memory.
The human brain, like any other organ, must be supplied with blood and receive the required amount of oxygen and metabolic substances. Therefore, the microvasculature of the brain is one of the most complex vascular networks in our body. Indeed, when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, pathological processes occur, many of which are irreversible. One of the common causes of circulatory disorders in various parts of the brain is vascular spasm. Nowadays, cerebral vasospasm is a condition that most often occurs in people over 30 years of age. What is a spasm, how and why does it occur in the vessels of the brain, and how should this condition be treated?
The definition is: a spasm is a case of sudden contraction of smooth or striated muscle. It is known that our vessels have a wall consisting of smooth muscle, when a vessel spasm (angiospasm) occurs, the lumen of the vessel closes, which is always fraught with complications.
Causes of cerebral vascular spasms
Like any disease or pathological condition, spasm of the blood vessels of the brain has its causes. This condition has been studied quite thoroughly, and knowing the etiology (origin) of this disease is extremely necessary, because treatment of vasospasm is always symptomatic.
The causes of vasospasm in the brain (cerebral vasospasm) can be divided into two groups of etiological factors: cerebral and extracerebral.
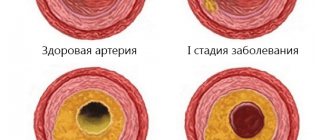
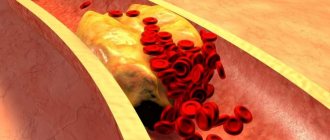
- Brain: Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the process of formation of the so-called atherosclerotic “plaque” on the inner vascular wall (endothelium). In essence, a plaque is an accumulation of clumped elements of circulating blood and various salts and fats. As a result of recent studies, it was found that atherosclerosis already affects 90% of adolescents aged 14 to 16 years around the world. This, of course, is due to the dietary habits and lifestyle of modern people, as well as a number of aggressive environmental factors.
- Hemorrhages in the brain. In these conditions, a reflex vasoconstriction occurs. The process takes some time, but ultimately ends with a complete narrowing of the damaged vessel, and as a result, a stoppage of blood supply.
- Osteochondrosis. As a rule, vasospasm occurs with osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebrae. This process entails a narrowing of the lumen of the vessels supplying blood to parts of the brain. Thus, as a result of a decrease in the volume of incoming blood, vasospasm occurs.
- Cerebral aneurysm. These are various changes and defects in the structure of the walls of blood vessels in the brain.
- Vasculitis (angiitis). Pathological changes in blood vessels are based on inflammation, which can be primary (independent) or secondary (as a symptom or complication of certain diseases).
- Vascular embolism. This should include thromboembolism as the most common cause of cerebrovascular accidents. Thromboembolism is a pathological condition in which a blood vessel is blocked by a blood clot. In this condition, spasms in the blood vessels of the brain are also noted.
- Tumors and tumor-like diseases of the head. In such conditions, spasm occurs due to compression of the vessel by the tumor.
- Circulatory disorders in diseases of the cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system). As a rule, vasospasms of the brain occur in diseases such as ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease), chronic heart failure, and increased vascular stiffness.
- lack of sleep;
—>
At the MART clinic on Vasilyevsky Island
- Evidence-based medicine
- Experienced specialists
- Monitoring of patients for 6 months.
- Diagnostics (MRI, ultrasound, tests)
- Daily 8:00 – 22:00
Make an appointment
Signs of involuntary muscle contraction are:
- with bruxism – grinding of teeth during sleep, a feeling of overexertion in the jaws after waking up;
- with spasms of the head muscles - hoop-shaped pain in the temples, in the forehead, in the back of the head;
- pressing, pulsating, squeezing nature of pain;
- feeling of heaviness in the area of spasm;
- pain when pressing trigger points (try to palpate the area of the head when it hurts: when you press certain points, the pain increases significantly);
- nausea, vomiting, dizziness;
- painful reaction to light, loud sounds (infrequently).
When to see a doctor:
- headaches appeared suddenly and do not go away;
- you are experiencing muscle pain for the first time after 50 years;
- pain is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, numbness of the limbs;
- pain lasts more than two weeks in a row;
- painkillers either do not work at all or give an insignificant short-term effect;
- the pain is localized on one side of the head/neck.
Muscle spasms that provoke pain indicate a disruption in the healthy functioning of the body. To prevent the development of the disease, it is important to consult a doctor in time. We advise you to visit a therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, who will prescribe detailed laboratory diagnostics for you. Based on the research results, specialists of another profile may be involved in your treatment: an orthopedist, a cardiologist, a chiropractor. Complex treatment may include taking medications, a massage course, and therapeutic exercises. A good doctor will definitely give you recommendations on nutrition and daily routine.
MIGUNOVA ANASTASIA ANDREEVNA
Cosmetologist
Initial consultation: RUB 4,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
VYATKINA IRINA SERGEEVNA
Gynecologist-endocrinologist
Initial consultation: RUB 8,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
KALININA EKATERINA ALEXANDROVNA
Cosmetologist
Initial consultation: RUB 4,500
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
KOZLOVA EKATERINA NIKOLAEVNA
Gynecologist-endocrinologist, oncologist
Initial consultation: RUB 5,000
Make an appointment with a doctor Instagram
Clinical manifestations of vasospasm
It must be remembered that cerebral vasospasm is a kind of circulatory disorder, and since the brain is associated with the regulation of neuropsychological processes, the main clinical manifestations are associated with a violation of neurological and psychological functions. To describe the symptoms of cerebral vasospasms, it is convenient to identify two groups: neurological and psychological lesions.
I. Neurological lesions in cerebral vasospasms.
- Headache, migraine. One of the early symptoms of vasospasm.
- Dizziness. As a rule, they arise spontaneously. They can occur together with loss of orientation in space.
- Feeling sick or suddenly vomiting.
- Visual, auditory, taste or olfactory disturbances, including hallucinations.
- Sometimes patients experience pain in various parts of the body (although the connection with cerebral vasospasm has not been established).
- Decreased performance.
- Increased fatigue.
II. Psychological disorders:
- The main and most alarming signs are memory impairment and amnestic syndrome.
- Various types of preservation (multiple repetitions of words or actions).
- Violations of psychological orientation. Patients are not able to talk about themselves, their profession, etc. This state is sometimes accompanied by apathy and indifference to the environment.
What can you do at home if:
Head muscle spasms
To relieve spasm and pain, you can take aspirin, a painkiller tablet like Ibuprofen, or a painkiller in powder form (for example, Nimesil). Give yourself peace of mind. You can try pressing trigger points and stretching your earlobes.
Jaw muscle spasm
If trismus manifests itself, before the doctor arrives, you can self-massage the masticatory muscles, accelerating the blood in them, alternately pressing on the muscles constrained by spasm. It is also possible to use compresses (alternate warm and cold compresses, apply them to the lower third of the face).
Cervical muscle spasms
Make gentle rotational movements with your head, lower and lift it (without throwing it back too much), turn it right and left. You can try stretching your neck muscles with your hands. Warm compresses and rubbing are effective.
*Attention! The information is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Reviews
Tatiana
I am happy to be among your guests at the clinic, I enjoy our communication, I am grateful for your super professionalism, for giving beauty and a sense of confidence in your professional actions, protection from “age-related changes”