Medical information is reliable Checked by Shaidullin Renat Flyurovich
Panic attacks are attacks that occur unpredictably, accompanied by severe fear and anxiety. They are characterized by vegetative symptoms: increased sweating, chills, hot flashes, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat and others. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the level of anxiety. If a person is in good health, he does not complain of weakness, and is not registered in the hospital - this condition is easier to tolerate.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture, if somatic pathology leading to similar attacks is excluded. The treatment of panic attacks at Dr. Isaev’s Clinic is complex, consisting of drug relief of symptoms and psychotherapeutic methods of influencing the patient. The period between crises can be kept under control if the patient is promptly trained in ways to independently overcome such a condition.
Our doctors work with patients anonymously. If you are afraid that your secret will leave the hospital, these fears are unfounded. We do not enter information into special databases and do not record the fact of contacting a psychiatrist. This means that people who contact us have no reason to worry about the confidentiality of facts relating to their mental state.
Signs of panic attacks
The term “panic attack” was introduced into medical use in 1980. Currently, it is included in the International Classification of Diseases; the patient is not able to independently cope with periodic attacks. He needs the help of a specialist; perhaps other pathologies will be identified during the examination.
A similar condition was previously considered within the framework of vegetative-vascular dystonia, but now this version is not relevant. The psychological factor is considered primary, and vegetative symptoms are considered secondary. Attacks are classified as neuroses, and the accompanying disorders at the physiological level are classified as autonomic dysfunction.
Panic paroxysms are common, especially common among residents of megacities. They experience frequent stress; the dynamic rhythm of life leaves no chance for relaxation and good sleep. The typical age for the first attack is between 25 and 45 years. In older people, panic paroxysms occur with less severe symptoms; they affect the emotional sphere to a greater extent.
Panic attack symptoms
A sudden and uncontrollable attack of anxiety with various somatic disorders indicates a disorder of the nervous system. If a person is in danger or feels his life is threatened, he has a peculiar reaction to a stressful situation. Increased heart rate, trembling in the limbs, vomiting - for such a case this is the norm. As soon as the danger passes, all physiological disturbances disappear and the condition returns to normal.
The difference between a panic attack is that the patient cannot explain its cause. Such attacks often begin in places where there are large crowds of people. This can happen on the subway, in a store, or on the street. Panic often occurs in a confined space, its intensity varies. If paroxysms are observed frequently and are regular, the patient may have a more serious mental disorder that requires immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Typical symptoms of panic attacks include:
- fear of death - it seems to a person that he will die right now, without having time to do what seems so necessary to him;
- a feeling of doom and unreality of what is happening;
- general physical weakness, infirmity;
- loss of control over your thoughts and actions;
- rapid heartbeat, there is a feeling that the heart is actually jumping out of the chest, that it cannot cope with the load and will stop;
- numbness of the limbs;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills, fever;
- dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- dry mouth;
- difficulty breathing, shortness of breath similar to an asthma attack
These symptoms can intensify, which brings significant discomfort to a person’s life. He cannot predict how each next attack will end, and is constantly worried about what others will think of him at this moment.
The average duration of a panic attack can take from 10 minutes to 1 hour, an acute state - about 15 minutes. After an attack, patients feel overwhelmed and empty, they cannot work or perform household duties, and want to retire and relax.
In some cases, the symptoms are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract: heartburn, vomiting, nausea, pain in the epigastric region. Patients complain about the loss of a sense of their own “I”; the personality seems to be watching itself from the outside and cannot intervene. Sounds become muffled and objects around you become blurry.
Panic attacks: if it's not a mental issue
There is an opinion that panic attacks are a very rare mental pathology, and many have never heard of this. In fact, the attack has quite a few different forms, including “banal” depression and apathy. How to distinguish a true attack from the consequences of other diseases? And what diseases are at risk of attack?
12 signs of an attack
Perhaps everyone knows that a panic attack is accompanied by a sudden attack of fear. However, few people know that this symptom alone is not enough to make a diagnosis.
According to accepted recommendations, the conclusion “panic attack” is valid only if at least 4 of the following signs are present.
1. Mental
- fear of death,
- fear of going crazy or losing control of behavior,
- a feeling of unreality and alienation from oneself (depersonalization).
2. Somatic (bodily)
- pain, discomfort, feeling of tightness in the chest (as with angina and heart attack),
- dizziness,
- difficulty breathing, suffocation,
- feeling hot or chills,
- nausea, sometimes vomiting,
- numbness, tingling, "pins and needles"
- rapid heartbeat (tachycardia),
- increased sweating,
- tremors and tremors of the hands.
At the same time, panic fear, which seems to be the main sign of an attack, may not be among the symptoms, but only strong internal tension (anxiety) is present.
Thus, the vegetative form of attacks is characterized by sudden dizziness, increased heart rate, sweating and severe trembling in the body.
Ventilation – shortness of breath and muscle pain.
And, affective – mood lability with a predominance of depressive disorders (sadness, unbearable fatigue, apathy).
However, no matter what form the attack “appears” in, the patient remembers the situation that provoked its occurrence, and subsequently panicky avoids its repetition.
Similar conditions
The reliable mechanism for the development of attacks has not yet been revealed. However, it is already known that such symptoms can be present in a number of physical diseases:
- thyrotoxicosis (extreme excess of thyroid hormones),
- hypertensive crisis,
- heart disease (arrhythmia, angina, heart attack),
- asthma and other diseases of the respiratory system accompanied by shortness of breath,
- diseases of the adrenal glands (excess stress hormones - cortisol, adrenaline).
Panic attacks can be caused by: regular stress, lack of sleep, excessive mental and physical stress.
The point here is an imbalance of calming (gamma-aminobutyric acid) and excitatory (glutamate) neurotransmitters in the brain, and the risk factor is the excessive action of certain hormones (cortisol, adrenaline, T4), a decrease in the amount of beneficial intestinal microflora and some other factors.
If symptoms similar to a panic attack appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, and take the test results with you:
1. TSH + and free = to exclude thyroid pathologies,
2. blood cortisol
3. urine catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine) = to exclude adrenal pathology.
Prerequisites and causes of panic attacks
There are several factors that can become prerequisites for the occurrence of such a condition.
- Genetic predisposition.
If the patient's close relatives suffered from uncontrollable attacks of anxiety and fear, there is a high probability that this disorder will manifest itself in adulthood.
- Severe stress.
Chronic nervous tension, constant quarrels and conflicts in the family or at work, divorce or the loss of a close relative lead to the emergence of inexplicable fear. This feeling is irrational, the patient often cannot explain why he experiences it, he has no objective reasons to be afraid.
- Thyroid gland dysfunction.
This organ is responsible for producing hormones that affect the condition of the body. Increased or decreased production of these substances provokes the occurrence of symptoms characteristic of panic attacks. Perhaps this is autonomic dysfunction that will not develop into paroxysm; in any case, a thorough examination is necessary.
- Low self-esteem.
If a person is guided by the opinions of strangers, is afraid of disgracing himself in society, is a suspicious person, he belongs to the risk group.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
Often, in order to normalize their condition, patients use various medications - sedatives, sedatives, and blood pressure lowerers. The availability of such drugs and the lack of need for a prescription leads to the constant use of questionable self-prescribed drugs. If a certain dose does not help, the patient increases it, thereby harming his body. Negative consequences include exhaustion of the nervous system and frequent disruptions in its functioning. Also, mental disorders are a consequence of regular consumption of large volumes of energy drinks or drinks that contain a high percentage of caffeine - black tea, natural coffee.
- Alcohol.
Chronic addiction disrupts the functioning of the entire body, primarily affecting the nervous system. In the morning after drinking a large dose of alcohol, a feeling of irrational fear may arise. It often accompanies asthenic syndrome, in which all the patient’s thoughts are only about the next portion of alcohol. Panic attacks caused by alcoholism do not go away on their own; only qualified medical help will help you get rid of paroxysms and overcome addiction.
- Sleep disturbances.
If a person is awake at night and constantly lacks sleep, this depletes the nervous system. It begins to malfunction and gives incorrect commands to the body, which are expressed in fear and anxiety for no reason. Experts recommend sleeping at night; the daily sleep requirement is at least 8 hours. Daytime sleep for 1-2 hours is allowed; it is important during the period of recovery of the body.
- Phobias.
These are mental disorders in which a person is afraid of something specific. This could be a fear of heights, enclosed spaces, or places with large crowds of people. It is impossible to get rid of them on your own; you need the help of a psychologist or psychotherapist; in advanced conditions, you need to consult a psychiatrist.
Also among the possible causes of panic attacks are mental disorders; in this case, PA develops as a secondary disorder. For such conditions, a specific treatment regimen is selected.
If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, the intensity of symptoms increases with each new attack. As a result, a person strives for social isolation; the only true way out for him is the decision to stay at home and not go out. Our doctors will teach the patient to cope with attacks, he will be able to fully prepare for the onset of a panic attack, and will not be afraid of embarrassing himself in front of others.
Sympatho-adrenal crises (panic attacks)
It is an uncontrollable, irrational, debilitating and very intense attack of panic and anxiety, which is accompanied by physical and psychological symptoms. The condition can affect cognition and behavior.
They are quite common in the population, in about 5% of cases and, most interestingly, they affect young working citizens from 20 to 40 years old, and women suffer from this disease 3 times more often.
Due to the huge number of similar symptoms, doctors of different specialties call panic attacks differently , but in general all these names are synonymous and very similar (therefore, in the text we will use all names):
- Vegetative crisis
- Sympatho-adrenal crisis
- Vegetovascular dystonia
- Cardiopsychoneurosis
- Cardioneurosis
I would like to immediately note that with adequate, timely, and most importantly comprehensive treatment of this problem, complete regression of symptoms , this will allow the patient to take control of mental processes and he will be able to continue to lead full life activities without compromising the quality of life. Unfortunately, if untreated , the disease can progress from rare, infrequent attacks to a chronic form , in which the frequency and severity of attacks constantly increases and can develop into more serious mental problems . Therefore, we advise you to make an appointment with our specialists - they very effectively treat panic attacks in Ust-Kamenogorsk at the Pulse center. Call and they will help you.
Before moving on to the manifestation of the disease, let us turn to a small classification for a better understanding.
There are 3 types of panic attacks.
- A spontaneous panic attack is the most unfavorable form of the disease, when the patient cannot identify a clear trigger factor after which the attack begins, and accordingly cannot prepare for it.
- Situational panic attack - has psycho-somatic “roots”, manifests itself in a specific traumatic situation or in anticipation of such a situation. Here are a few examples that our patients often tell: waiting for an exam, an imminent public speaking, a quarrel with loved ones, a premonition of conflict, stuffy spaces and even an unfamiliar environment.
- Conditional situational attack - in this case, a chemical or biological trigger is added to the psychological trigger. For example, drinking coffee, tea, alcoholic beverages, changes in hormonal levels, etc.
A little about the symptoms and pathogenesis of the disease.
What exactly happens to the body? What causes these symptoms? Why did this happen? These are the questions patients ask themselves and this is not surprising ! After all, the clinical picture of the disease can be very confusing and it is very difficult to understand it without the help of an experienced specialist.
The attacks are clearly somatic, i.e. physical and physical character, its symptoms are very reminiscent of a classic heart attack, accompanied by fear of death , etc., so patients may assume they have heart pathology (hence one of the names - cardiac neurosis). However, even the most severe manifestations of attacks are a consequence of an imbalance of the nervous and humoral systems. The main mechanism for the development of a crisis is the activation of the sympathetic nervous system and a powerful release of the “stress hormone” adrenaline - hence another name “sympatho-adrenal crisis”.
As we have already said, vegetative crises are characterized by an abundance of abruptly occurring symptoms. First of all, this is phobic anxiety , i.e. uncontrollable panic fear. As adrenaline is released, the heart rate pain in the chest and heart area may appear pressure rises. There is a chill, muscle tremors, the person sweats, the limbs turn pale, the mouth becomes dry, there is a lack of oxygen, it becomes difficult to breathe and the full picture ends with an unpleasant symptom - the fear of death appears.
Since the psyche is often involved, its short-term disorders can be observed: it seems to a person that all this is not happening to him, there is a feeling of the unreality of what is happening, one’s own mental processes are alienated, there is a fear of losing control of one’s behavior - such processes are called derealization and depersonalization.
The clinical picture and its severity have a wide range and vary greatly; there is even a so-called “ non-insurance ” form of panic attack or “panic without panic,” when physical disorders come to the fore.
Just like the symptoms, the duration of the attacks is variable. They can appear for a few minutes, or they can last for hours, but on average they last 15 – 30 minutes. The frequency of such attacks also does not have a clear relationship: for some it is once a month, for others it is 3 times a day.
Such crises, as a rule, are not isolated in nature. The experience of a terrible episode leaves an imprint on a person’s subconscious, because of this, a phenomenon called “fear of anticipation of an attack” is formed. This naturally creates a favorable background for more and more attacks. If a repeat of the crisis happens again and the conditions of the repeated attack are similar to the original ones, chronic panic disorder , and the patient develops “ avoidance behavior” - the person begins to consciously, independently avoid and limit his stay in potentially “panic situations.” All this can significantly complicate everyday life.
The causes of panic attacks as such are not fully understood, here are some possible ones:
- Violation of the circulatory system, in particular due to the vertebral arteries and pathological processes in the cervical spine.
- Hormonal imbalance, often involving the thyroid gland.
- Chronic somatic pathology, organic lesions of the central nervous system, recent infectious disease.
- Stress (positive and negative), being in an unfavorable environment (death of a loved one, frequent quarrels in the family, birth of a child).
- Improper upbringing, children's fears (excessive demands and criticism from parents).
- Peculiarities of mental functioning, personality traits, temperament.
- Genetic predisposition.
There is an interesting opinion that people who live in cities, who are intellectually developed, anxious and responsible by nature, are most often susceptible to the disease. There are practically no people with vegetative crises among residents of remote areas and villages.
Due to the multifactorial nature of the causes of the disease, only experienced specialists can . These are the doctors who see and successfully treat panic attacks at the Pulse Medical Center at the address: Ust-Kamenogorsk, Krasina St., 1.
Diagnostics.
This diagnosis can be established for the following objective reasons: repeated occurrence of an attack with an increase in peak at 10-15 minutes and the occurrence of at least 4 of the symptoms described above. But diagnosis is not so simple ; the difficulties lie in the fact that there are a large number of somatic diseases with a similar clinical picture. Many of them are potentially life-threatening and under-diagnosis would be a costly mistake. Here are some: bronchial asthma, angina pectoris, mitral valve prolapse, transient ischemic attacks, pheochromocytoma and others. Therefore, it is very important to consult a competent doctor who can rule out dangerous diseases and make a correct diagnosis. Our clinic successfully diagnoses panic attacks with the most confusing clinical picture and guarantees you highly qualified assistance.
How is panic attacks treated in Ust-Kamenogorsk?
After excluding other somatic pathologies and determining the cause of the disease, the turn of treatment comes. Since this disease affects the psycho-emotional sphere, we cannot do without rational psychotherapy . You should not be afraid of this, because in fact, the main therapeutic tool in such therapy is the use of reasoned logical influence on the distorted internal picture of the disease, the use of reason and thinking. With the help of a doctor, the patient learns to cope with his anxieties on his own and prevent crises from developing.
To restore the balance of excitation and inhibition processes in the nervous system, acupuncture , magnetic and laser therapy are used. Transcranial brain stimulation provides good results in the treatment of panic attacks.
If the cause is associated with hemodynamic disturbances at the level of the brachiocephalic arteries, then manual therapy, massage, and spinal traction are used.
The combined experience of our doctors, the ability to properly provide psychotherapeutic assistance, a large base of physiotherapy equipment and knowledge of reflexology allows us to successfully treat panic attacks in the Pulse center . In our clinic, any patient will be understood, supported and definitely helped. Make an appointment by calling 8-7
What happens during an attack
The patient’s first attacks occur after a strong emotional shock; it is this that provokes the severity of the disease increasing each time. Next, a certain trigger is needed for the paroxysm to take possession of the person again.
A similar factor may be close contact with other people, strong sound or unpleasant smell. Most often, triggers are associated with a traumatic situation. At first, the heart rate increases, the sweat glands begin to work to the maximum. They produce a large amount of sweat, perspiration appears on the forehead, and their hands become damp.
After a few minutes, panic sets in, the manifestation of which will vary from person to person. Some experience a strange feeling of confusion, forget where they are going, others are overcome by severe fear. They seem to freeze in one place, not finding the strength to make any movement.
The attack can last several minutes, for some it ends after one or two hours. The specificity of PA is the high rate of increase in symptoms. After the first attack, there is constant anxiety and concern for one’s health on a subconscious level. All organs and systems can operate uninterruptedly. Our clinic provides treatment for mental disorders; here you can undergo treatment for mental retardation and schizophrenia, and receive professional help in correcting the consequences of dementia and other pathologies.
Mechanism of attack
The human brain reacts to external stimuli in different ways, but triggers a single defense mechanism at the first sign of approaching danger. During a panic attack, a threat is signaled even if it does not actually exist. Tension in all parts of the nervous system increases fear. On a physiological level, this manifests itself in the production of large amounts of the stress hormone (cortisol), followed by a powerful surge of adrenaline.
The brain gives a command to the body to save life in any way, increasing the intensity of the manifestation of physical symptoms. If the threat is real, such hormonal surges can make a person stronger and more resilient, in this state he can do a lot. But if this happens in a state of rest, when there is no need to run anywhere and defend yourself, then there is a negative impact on mental health. The danger lies in losing control over your actions and thoughts.
Causes
Doctors believe that the appearance of panic attacks during VSD is provoked not by one, but by several factors at once. Among the reasons are:
- unhealthy sleep;
- constant presence in stressful situations;
- headache;
- fatigue, overstrain;
- the appearance and further development of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine;
- character traits of a person. For example, suspiciousness;
- presence of a diagnosis of PA in relatives;
- unhealthy lifestyle: drinking alcohol, using drugs, smoking.
What happens if PA is not treated?
Each subsequent attack is accompanied by more acute sensations. A person may develop a new phobia - a strong fear of repetition of paroxysms; he continues to live in constant tension, expecting the situation to worsen. Regardless of the intensity of the physiological symptoms, this disorder is not fatal. Treatment of panic attacks is necessary to prevent the development of phobias, increased anxiety and nervousness.
The patient begins to radically change his life and adapt to his condition. He avoids places with large crowds of people, supermarkets, and stops using any public transport. Gradually, such a person isolates himself from society, prefers not to engage in professional activities, and spends all his time indoors. He stops communicating on confidential topics with his loved ones, and there is a risk of developing serious mental complications. Patients with panic attacks often suffer from neurasthenia, neuroses, sleep disturbances, depression, and asthenia. The nervous system is exhausted, the person tries to relieve the symptoms with self-selected medications.
Regularly recurring attacks lead to loss of appetite and disruption of the functions of important organs, in particular the gastrointestinal tract. Conscious refusal of food leads to physical exhaustion. In this case, treatment of dystrophy is often required; this process is lengthy and is not always completed successfully. It all depends on the condition of the body, the presence of internal reserves to fight the disease.
How to help a pregnant woman with panic disorder
The main tool for combating panic attacks in pregnant and lactating women is psychotherapy. Antidepressants used as maintenance therapy are extremely undesirable in the first trimester, and in the second and third they are prescribed only for severe panic disorder, when the benefit to the mother is higher than the risk to the fetus (the woman’s condition requires it).
It is working with a psychotherapist that will help to identify the hidden reasons that caused panic disorder. Treatment is carried out based on these reasons - negative attitudes are worked through and replaced with positive ones, hidden fears are revealed, self-esteem and self-confidence are improved.
The specialist will explain why panic attacks occur during pregnancy, what to do when an attack approaches and during it, and teach relaxation and control over thoughts and emotions. These skills will help stop an impending attack in the bud. Gradually, the frequency and intensity of attacks will decrease, and pregnancy and motherhood will give only positive emotions. Do not self-medicate, contact a professional to give peace and happiness to yourself and your baby.
We know how to help expectant and nursing mothers suffering from panic disorder. The Center’s doctors have the most modern and effective methods of psychotherapy in their arsenal, which will help you completely get rid of panic attacks without the use of antidepressants. A mother’s good mood and calmness are the key to the harmonious development of the baby. Therefore, you don’t need to fight fear on your own - come, we will definitely help you.
Diagnosis of the disease
PA is a specific mental disorder that causes difficulties in diagnosis. It is not always possible, even after an examination and conversation with a psychiatrist, to determine what caused this condition - problems with the cardiovascular system, autonomic dysfunction, mental disorder. The neurologist checks reflexes, listens to the lungs, measures blood pressure, and examines the patient's abdomen to rule out internal bleeding. It is important to establish that these are paroxysms, and not a heart rhythm disorder or a heart attack. The patient undergoes an electrocardiogram, MRI, breathing tests, and an ultrasound examination.
Panic attacks: how to deal with it yourself
We categorically do not recommend self-medication. Such events aggravate the patient's condition. He cannot independently determine whether he has concomitant mental disorders.
Pharmacology taken uncontrolled can provoke an increase in symptoms and make the patient’s condition more severe. This complicates further therapy in the hospital, increases the time of recovery and complete restoration of the body. The Clinic of Dr. Isaev provides round-the-clock care for patients in serious condition who, due to mental disorders, are unable to care for themselves.
How to treat panic attacks
When you notice the first symptoms of PA, you need to contact a psychiatrist or neurologist. Drug treatment consists of prescribing sedatives and antidepressants that reduce anxiety and calm the nervous system. Such medications have a cumulative effect, the effect begins on the 3-4th day of administration, the result lasts for more than 7 days. Doctors prescribe mainly those medications that are not addictive. Stopping their use does not lead to a sharp deterioration in health.
Psychotherapy is very popular; a course of sessions allows you to get rid of uncontrollable attacks of fear for a long time, in most cases forever. Depending on the condition and form of the disease, the following directions are used:
- cognitive-behavioural;
- body-oriented;
- hypnosis;
- psychoanalysis;
- family therapy.
The cognitive behavioral approach has proven itself in the field of eliminating panic attacks, fears and phobias. Psychotherapists are of the opinion that informing the patient as fully as possible about his condition is the first step towards recovery.
The doctor explains the principle of the occurrence of paroxysms, as well as the reasons why they periodically appear. A set of classes aimed at teaching methods of meditation, visualization, and breathing techniques helps the patient, when he senses an approaching attack, to normalize his condition.
The technique of “breathing into a paper bag” is often used, which the patient should have with him, especially in crowded places. A sharp inhalation and exhalation reduces the supply of oxygen, stopping the attack. A body-oriented approach helps reduce anxiety and relax the nervous system. It is based on various breathing exercises that help achieve complete relaxation. Alternately tensing and relaxing the muscles of the limbs allows you to normalize your emotional state and get rid of fear.
Hypnosis is a popular technique that involves placing the patient in a trance state. He disconnects from the influence of external stimuli, but retains the ability to listen to the therapist’s commands. The patient is instilled with the idea that an attack of PA is not life-threatening; it is important to find ways to overcome the paroxysm. The doctor offers patients various auto-training techniques that act as prevention.
Psychoanalysis is a line of work that will be effective only in individual cases. The process itself takes several months or even years. The doctor’s goal is to find an internal conflict in the unconscious, to determine which psychotrauma became the trigger for the occurrence of attacks.
Family psychotherapy implies the involvement of all family members in the process, regardless of how many people from this microsociety suffer from attacks of uncontrollable fear. During a conversation with a specialist, relatives understand what feelings their loved one is experiencing, what the threat is, what words and actions can be used to support.
Anxiety and depressive disorders in women
Yuri Aleksandrovich Vasyuk presented an overview report on the topic of anxiety and depressive disorders in women and the possibility of drug correction of depression.
00:00
Ivashkin Vladimir Trofimovich , academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences:
“I will now give the opportunity to make a message to Professor Yuri Aleksandrovich Vasyuk. "Anxiety and depressive disorders in women."
Yuri Aleksandrovich Vasyuk , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor:
— Good afternoon, dear colleagues.
Today we will talk about anxiety and depressive disorders in women and the possibilities of their medical correction.
First of all, we need to remember the definition of depression. As you know, depression is characterized by a state of low mood, depression, sadness, decreased or loss of interest in any activity, and decreased activity.
If current trends continue, by 2020 depressive disorders will take second place (after coronary heart disease) among all diseases in terms of the number of years lost due to disability.
Speaking about the epidemiology of depression, it would probably be very revealing to reflect the situation that has developed in such a rich and prosperous country as the United States.
It is known that 10 million people in this country currently suffer from clinically significant depression. Another 20 million suffer from adjustment disorders. The economic burden of depression in the United States is $83 billion.
Great Britain is also an equally prosperous country. The concept of “iceberg depression phenomenon” has even been introduced. Its essence lies in the fact that only a third of patients with depression turn to doctors. Only a third of those applying are diagnosed with an affective disorder. This part of the patients is prescribed adequate treatment.
The total cost of depression in the UK is more than 15 billion pounds. 65% of patients with depression are a consequence of insufficient diagnosis and untimely correction. 65% of patients with depression have suicidal ideation, 15% of them commit suicide.
Speaking about risk factors for depression, we can recall quite a lot of unfavorable circumstances. History of anxiety disorder, unfavorable heredity, lack of social support, postpartum period, drug or alcohol addiction, severe somatic illnesses, old age, low socioeconomic status. But the female gender occupies a special place in this list.
02:37
Risk factors for mental disorders in premenopausal women. In fact, there are quite a lot of disorders. But it is necessary to note the most significant of them. First of all, this:
- - stressful life events:
- - divorce;
- - childlessness;
- - loss of social security;
- - history of mental disorders;
- — low level of education;
- - postpartum period, premenopause, oophorectomy, luteal phase of the menstrual cycle.
We will try to discuss in detail all of the listed conditions.
The so-called “female depression”. This is premenstrual syndrome (PMS). It is characterized by depression in combination with somatic disorders (vegetative-vascular and neuro-endocrine).
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder is the same, but in combination with pathocharacterological manifestations (up to suicidal thoughts, affective lability).
If we talk about epidemiology, it should be noted that in the population the frequency of PMS is 30–70%, depending on age. In mentally ill women, the incidence of PMS is 100%.
Clinical criteria for this syndrome boil down to the following key points:
- — PMS occurs 2-14 days before menstruation and disappears with its onset or in the first days of menstruation;
- — it is a complex of vegetative-vascular, metabolic-endocrine and mental disorders;
- — in the premenstrual period, aggressiveness, suicidal activity, the frequency of offenses and suicide attempts increase.
04:28
Postpartum depression is also a fairly common situation.
Manifestation or repeated attack of endogenous depression. Typically, postpartum depression occurs 10–12 days after an uncomplicated birth without an external cause. The clinical picture is characterized by classic depressive symptoms, anxiety and an atypical form (tearful).
Neurotic depression is distinguished separately. It manifests itself before childbirth (stress, fear of childbirth) or after childbirth (psychogenies associated with family and child). The clinical picture of neurotic depression is manifested by asthenic-depressive and anxiety-depressive symptoms.
Another type of depression in women is associated with menopause. Her options:
- - menopausal depression;
- - psychogenic depression;
- - endogenous depression;
- - involutive depression;
- - depression during surgical menopause.
Emotional-affective syndrome is known to be characterized by:
- - decreased mood;
- - loss of interest in one’s own personality and in the environment;
- - unmotivated anxiety;
- - suspiciousness, anxiety;
- - feeling of internal tension;
- — alarming fears for one’s health, etc.
05:50
Asthenic syndrome is very well known to all of us. There is probably no need to dwell on it for a long time. It is enough to recall such key manifestations as increased fatigue, decreased activity, increased vulnerability, touchiness, excessive sensitivity, mood lability, tearfulness and irritability.
Somatovegetative disorders occur in almost every second or third woman at an outpatient appointment. These are palpitations, arrhythmia, discomfort in the left half of the chest, fluctuations in blood pressure (BP), a feeling of lack of air, dyspeptic disorders, chills, trembling, sweating.
Finally, dissomnia disorders (or sleep disorders). They manifest themselves in women by an increase in the time it takes to fall asleep, frequent awakenings at night, low subjective assessment of sleep quality and the so-called “sleep apnea” syndrome.
A fairly large part of depression in women is occupied by depressive disorders during surgical menopause. The frequency of these disorders (according to some authors) reaches 60–80% of cases. But most of the literature indicates the detection of this syndrome in 40–45% of patients.
The clinical picture is characterized by a combination of affective (anxious, melancholy, apathetic, dysphoric) and somatovegetative disorders (which we just talked about).
For the treatment of affective disorders of the depressive spectrum, combination therapy is optimal. It is possible to use small doses of antidepressants in the treatment of these conditions.
Diagnosis of depression with concomitant somatic pathology. This is a very important point. I would like to draw your attention to the main clinical manifestations. A targeted search for the most significant symptoms of depression:
- - yearning;
- - sleep disturbance;
- - guilt, low self-esteem;
- - suicidal ideas/thoughts about death;
- - frequency of manifestation of painful symptoms.
This makes it possible in most cases to suspect the presence of a depressive syndrome.
Assessing the dynamics of these symptoms (especially improvement while taking antidepressants) is a direct indication of its presence. In doubtful cases, treatment is carried out ex juvantibus.
08:26
It should be noted that, as a rule, depression is masked by somatic manifestations. Clinical manifestations of most somatic diseases, which are also characteristic of depression:
- - weakness, fatigue;
- - headache;
- - tachycardia, chest pain;
- - feeling of difficulty breathing, tachypnea;
- - arthralgia, myalgia;
- - loss of appetite;
- - constipation, abdominal pain;
- - urination disorder;
- - decreased libido;
- - menstrual cycle disorders.
Very wide range of clinical manifestations. With such a range of manifestations, it is very difficult to suspect the presence of an anxiety-depressive disorder.
But if the clinician has such suspicions, it is necessary to use widely available, very simple tools for detecting depression: subjective and objective scales.
09:28
Subjective scales: Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Zung scale.
Objective scales: Hamilton anxiety and depression scales, Montgomery-Asberg scale.
I will not draw your attention to the technology of using these tools. It is described in sufficient detail in the literature. A list of questions, answer options, each of which has a certain number of points. Their summation allows one to suspect the presence of depression.
(Slide show).
This slide shows a fairly typical appearance of a woman with a depressive disorder. Notice the dull look, the downcast face. Appearance speaks volumes.
The treatment strategy for depressive disorders during menopause is reduced to symptomatic treatment, the use of phytoestrogens, hormone replacement therapy, antidepressant therapy, and psychotherapy.
Cognitive therapy or psychotherapy is a very important component of complex treatment, not being an alternative to pharmacological treatment, but very actively increasing its effectiveness. It is aimed at changing self-esteem. The most important thing is to develop emotional self-regulation skills that allow patients to endure difficult stressful situations without falling into depression.
Even in ancient times, philosophers Fr. About his attitude to this stressful situation, to the possibility of self-regulation.
Of course, antidepressants are the first choice drugs. Their common property is a positive effect on the emotional sphere, accompanied by an improvement in general and mental state and, in particular, an improvement in mood.
The therapeutic effect of antidepressants (this must be remembered) develops gradually. It usually appears within 2-4 weeks from the start of therapy.
11:48
Undesirable effects. Unfortunately, there are quite a lot of them. This:
- - sedative effect (for some drugs, especially classic tricyclic antidepressants);
- - orthostatic hypotension;
- - high potential for drug-drug interactions (especially sedatives, hypnotics, antiarrhythmics, antihypertensive drugs. Most of these drugs are prescribed to patients with cardiac pathology);
- - weight gain is also an undesirable effect of antidepressants (with long-term use of tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants);
- - slow development of the therapeutic effect, the need for dose titration;
- - the need to gradually reduce the dose of the drug upon completion of treatment.
Anxiety and anxiety disorders are satellites of depressive disorders. Anxiety is a feeling of restlessness, nervousness, tension, nervousness, anticipation of trouble, internal tension. All these components of anxiety are well known not only to doctors, but also to most of our patients.
The severity of anxiety in stressful conditions ranges from mental discomfort without a clear understanding of the causes of anxiety to the appearance of symptoms of psychological maladaptation of the individual.
Anxiety disorder is a group of neuroses associated with unreasonable and destabilizing feelings of fear and tension for no apparent reason.
13:24
We often hear the phrase “anxiety-depressive disorder.” They usually accompany each other. If we talk about symptoms of anxiety, they can be divided into mental and somatic.
The former include tension, inability to relax, restless thoughts, bad feelings and fears, irritability and impatience, difficulty concentrating and sleep disturbances.
Somatic symptoms include hot or cold flashes, sweating, palpitations, shortness of breath, “lump in the throat,” dizziness and headache, trembling, “crawling” sensation, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, urination problems, and sexual disorders. Very common clinical manifestations.
In developed countries, anxiety disorders are detected in 10–20% of the population.
According to the National Comorbidity Survey, 25% of the world's population will experience some form of anxiety disorder at least once in their lives. Their prevalence among general medical practice is several times higher than in the general population.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that women suffer from anxiety disorders 2 times more often than men. The cause of these disorders: everyday life, home, husband, child, work.
The medical and social significance of anxiety disorders is very great. They are characterized by a long course and a tendency to recur.
Somatization of psychopathological disorders is a very common phenomenon. Patients with anxiety symptoms turn to a cardiologist 6 times more often, 2.5 to 3 times more often to a rheumatologist, and 2 times more often to a neurologist, urologist, or ENT doctor. According to the literature, people turn to a gastroenterologist 1.5 times more often than in the population.
The worsening prognosis of concomitant somatic pathology is also a very important component of medical and social disorders. A significant decrease in quality of life and ability to work, impairment of social functioning is a very important medical and social aspect of anxiety disorders.
15:40
Speaking about drug therapy used to treat anxiety conditions, you must first of all turn to tranquilizers (or anxiolytics - anti-anxiety drugs). They are classified into benzodiazepine and non-benzodiazepine (Afobazol). In addition, the use of antidepressants and herbal drugs.
Undesirable effects of benzodiazepines:
- - sedative and hypnotic effects;
- — the phenomenon of “behavioral toxicity”;
- — paradoxical reactions;
- - systemic side effects;
- — formation of mental and physical dependence, development of the effect syndrome (rebound effect);
- - high potential for intercellular interaction (especially when combining a class of drugs with beta blockers, adrenergic agonists, calcium antagonists, ACE inhibitors and ethanol).
Contraindicated for use in severe diseases of the cardiovascular system, kidneys and liver.
Herbal preparations are used quite actively nowadays. In particular, "Persen" ("Persen"). It is not by chance that I focus on this drug, because one of the questions that came to me is related to the desire of listeners to discuss the issue of the evidence base for Afobazol, Persen and antidepressants.
Weaknesses of herbal preparations:
- - low efficiency - the anxiolytic effect is very weakly expressed, as a rule, only when a pronounced sedative effect is achieved;
- - they (in particular, “Persen”) are characterized by the presence of a hypnosedative effect in the daytime;
- — individual sensitivity of patients;
- - a large number of side effects that limit the use of the drug (nausea, epigastric pain, dry mouth, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation, anorexia, anxiety, fatigue, headache);
- — a large number of herbal components in combination preparations (which are quite popular in our country), unfortunately, significantly increases the risk of allergic reactions.
St. John's wort is highly recommended in wide practical activities. But it affects isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system and can interact with many drugs metabolized by this enzyme. Most of us are like that. At least in cardiology.
18:16
Weaknesses of barbiturate-containing drugs (Corvalolum, Valocordin, Valoserdin).
High toxicity. It manifests itself as depression of the respiratory and vasomotor centers, a decrease in myocardial contractility and vascular smooth muscle tone.
These drugs can be addictive, require increased doses, and are associated with withdrawal syndrome, which can lead to complete insomnia and the development of physical and mental dependence.
In most countries around the world, these drugs are not available over-the-counter. You simply cannot enter any EU country with this drug. In most countries of the world, phenobarbital has not been used as an anti-anxiety and hypnotic drug for many years.
The availability of the combination drugs that I spoke about often becomes the reason for their uncontrolled use. There are more problems than positive effects.
A few words about Afobazole. The systemic effects of the new generation anxiolytic “Afobazole” are associated with a vegetotropic effect. "Afobazole" increases heart rate variability under stress, tone n. vagus, which contributes to better adaptation of the cardiovascular system to stress.
Intravenous administration of Afobazole does not cause changes in blood pressure, cardiac output and contractile function of the intact heart.
During occlusion and reperfusion of the coronary artery, Afobazol has an antirhythmic and antifibrillatory effect.
19:56
The pharmacodynamics of this drug is due to the fact that it has an anxiolytic effect that is not accompanied by a hypnosedative effect. The anxiolytic effect occurs 5-7 days from the start of treatment. The maximum effect is by the end of the 4th week of treatment.
What features does Afobazol have? Drug dependence does not form and withdrawal syndrome does not develop. There are no muscle relaxant properties and no negative impact on memory and attention indicators, or cognitive disorders.
To the question I received: what is the evidence base for antidepressants and Afobazole?
Currently, quite a lot of research has been conducted with this drug. The format of our meeting does not allow me to dwell on many of them in detail. But I'll try to do it.
An open clinical trial was conducted at the Scientific Center for Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology. 56 patients with uterine fibroids and a control group - 32 healthy women. It has been shown that anxiety symptoms are detected in 72% of patients with uterine fibroids and mastopathy. You see what a large percentage of affective disorders there are.
“Afobazole” reduced sympathetic influences, restored compensatory and adaptive response mechanisms, and reduced the frequency of emotional and anxiety symptoms in these patients by 2.5 times. Afobazole was noted to be well tolerated.
Another open non-comparative clinical study was conducted at the First Moscow Medical Institute (Perinatal Center) and City Clinical Hospital No. 29 of Moscow. It studied the effect of Afobazole on PMS in women with autonomic disorders.
Results. The administration of Afobazole was associated with a decrease in the severity of autonomic disorders. The most pronounced effect was noted with sympathicotonia. The maximum effect is by the end of the 4th week. The effect persisted for two weeks after completion of therapy.
22:23
Another open-label, non-comparative clinical trial. It included women with psychopathological menopausal disorders. Afobazol was prescribed. Its effect was compared with other psychotropic drugs (Diazepam, Mebicarum).
It was shown that normalization of mood with the use of Afobazole, disappearance of anxiety disorders, emotional lability, and a decrease in depressive symptoms were noted already on the 5-6th day of therapy.
Compared to Diazepam, Afobazol more often stopped or significantly weakened the psychopathological manifestations of menopausal syndrome within the asthenic variant. More often than Mebicar, it stopped the manifestation of anxiety and depressive disorders.
Also in the group of patients receiving Afobazol, a decrease in vegetative-vascular manifestations was noted already in the second week, the disappearance of lethargy, fatigue, and asthenic manifestations. Normalization of sleep in most patients.
The use of Afobazole in the treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders during surgical menopause. A very important group of patients was studied in an open-label, non-comparative controlled trial. It included women with surgical menopause.
It was shown that treatment with Afobazole (20 mg/day for three weeks) led to improved well-being, mood, a decrease in the frequency of headaches, and a decrease in disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
No side effects have been reported.
Indications for use are already clear from what I said:
- — anxiety states: generalized disorders, adaptation disorders, such as a predepressive state in patients with various somatic diseases. Also for dermatological and oncological diseases;
- - sleep disorders associated with anxiety;
- - cardiopsychoneurosis;
- - PMS;
- - alcohol withdrawal syndrome;
- - to alleviate withdrawal symptoms when quitting smoking.
24:33
Contraindications:
- — individual intolerance;
- - period of pregnancy or lactation;
- - childhood.
Side effects of Afobazole:
- - increased individual sensitivity;
- — allergic reactions are possible;
- - rarely - headache;
- - non-addictive;
- - does not cause drowsiness;
- - does not affect concentration and memory (can be used by people whose activities require increased attention and quick response).
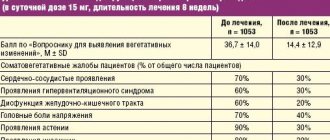
The regimen for using Afobazole is quite well known. 1 tablet 3 times a day for 2-4 weeks. If necessary, the dose can be increased to six tablets per day, and the course of treatment extended to three months.
Speaking about the advantages, I would once again like to emphasize the very high safety profile. Convenient release form. Low potential for intercellular interaction.
(Slide show).
A completely different face: glowing bright eyes, smile! Full of energy, cheerful woman.
Questions and answers
In the remaining 2 minutes I will try to answer the questions I received.
? Is there a non-drug treatment for depression?
Undoubtedly. We have already said that non-drug treatment is rational psychotherapy. Quite an effective method. It should be noted that it is used not as an alternative, but as an addition to psychopharmacotherapy. Only then can a sufficiently good effect be achieved.
? Does hormone replacement therapy reduce the risk of depression in menopausal women?
Definitely. I talked about this. The format of our meeting does not allow me to dwell on this in detail. But in consultation with a gynecologist-endocrinologist, it can significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment for these patients. Naturally, the appointment of hormone replacement therapy.
? Is depression in men less important, both socially and economically?
The question is philosophical. But psychiatrists, psychoneurologists, and psychotherapists believe that depression still develops more often in women. In my opinion, there is no need to prove this for a very long time. This is an obvious fact.
? When is the use of antidepressants indicated?
The question is quite difficult. I have already spoken about the use of scales when testing patients. When you score a certain number of points (more than 20), it is advisable to consult a psychiatrist. We must keep in mind that in our country the number of psychiatrists is about 10 thousand people. The number of patients with anxiety and depressive disorders...
45% of all somatic patients at outpatient appointments have anxiety-depressive disorder. In 25% of them, clinical manifestations are detected that require correction. Psychiatrists, therapists, and cardiologists have agreed that when using modern antidepressants in small doses, with a moderate regimen, depression can be treated with antidepressants and not by psychiatrists.
It is difficult to say in a nutshell about the prescription of antidepressants. This is a separate topic.
Thank you for attention.
Vladimir Ivashkin : Thank you very much, Yuri Alexandrovich.
28:01
Symptoms of a panic attack in women
PA in women occurs for several reasons:
- severe stressful situation;
- unbearable mental stress at work;
- cardiac or oncological diseases;
- peculiarities of upbringing - overprotection, strict control or perception of the child as the center of the universe;
- schizophrenia and other mental disorders;
- changes in hormonal levels - the onset of sexual activity, menstrual cycle disruption, pregnancy and childbirth, lactation, menopause;
- tendency towards hypochondria, suspiciousness;
- physical inactivity.
During a panic paroxysm, a woman experiences depersonalization and derealization, a feeling of impending disaster, motor disinhibition or stiffness. This condition is not an obstacle to pregnancy, but symptoms may intensify after the birth of the child.
Panic attacks often accompany postpartum depression, fears for the child, fears of being a bad mother, and general dissatisfaction with life arise. During menopause or menopause, there is an intense release of stress hormones, which provokes the disorder. The quality of life is deteriorating, the woman does not feel happy, she is constantly in nervous tension, waiting for the next PA. Often women do not realize what exactly is happening to them at this moment, and this is more frightening than the physiological symptoms.
Our patients turn to the doctor with complaints of an incurable disease. They don’t yet know what happened to them, but they believe that some kind of system has suffered a serious failure. We act openly. We immediately stipulate that panic attacks are treatable, they can and should be fought by learning self-regulation in difficult life situations.
Vegetovascular dystonia and panic attacks
A person who has experienced a panic attack will forever remember the feeling of overwhelming, unconscious fear. It evaporates as incredibly quickly as it appears. This anxiety is not inspired by the outside world, and irritability is not the outcome of the problems that have piled up. The patient experiences characteristic symptoms in the form of rapid heartbeat, breathing discomfort and tremors. The body seems to have received a dose of adrenaline, as panic begins from an inexplicable condition.
People say they feel their own death approaching and their minds clouded. Internal organs react sharply to the condition, causing chills, vomiting and fever. Patients rarely realize that they have become a victim of a panic attack. Due to VSD, the situation may repeat itself again and again until action is taken.
How is a panic attack related to VSD?
The human body is a single network where each internal organ is coordinated in one way or another with another. This rule does not bypass the nervous system, which is associated with VSD disease. According to researchers, this happens due to the constriction of blood vessels, which quickly deliver stimulation to the nervous system. A sharp jump in pressure creates the effect of a state of panic. There are explanations in psychoanalytic reasons, as well as in genetics. It is a clear fact that the disease passes from parent to child in ninety-five cases out of a hundred. As for mental disorders, in general, everything depends on the emotional instability of the person.
What are the reasons for panic attacks and how to avoid them?
From childhood, we are instilled with a love for a healthy lifestyle. Constant physical activity is a vaccine against diseases, especially nervous diseases. It is necessary to drive away negative thoughts, filling them with fitness, walks and all kinds of trips. It is the lack of physical activity and dependence on substances such as nicotine and caffeine that slowly but surely leads the body to an accumulation of tension.
How are panic attacks treated with vegetative-vascular dystonia?
If a patient experiences groundless panic, containing a number of the above symptoms, then doctors advise not to aggravate the process with medications in large quantities. Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia begins with sedatives - validol and corvalol. In this case, the use of an abundance of pharmaceutical drugs will not eliminate the disease in which neuroses worsen, but will turn into another bad habit. Tranquilizers and antidepressants are in demand, taking the patient out of negativity and creating a feeling of peace. Such medications have a small chance of getting rid of the disease with individual manifestations. But none of them is a surefire way to kill a panic attack with pronounced symptoms.
One of the best methods of coping is to make an appointment with a psychotherapist. The goal of the doctor is to influence the connection between the environment, personal experiences and the patient. If necessary, psychotherapy is used together with prescribed pills for neurosis. In addition, you need to independently learn relaxation in order to apply the methods during the next crisis.
Self-help for panic attacks
As mentioned earlier, a hypertensive crisis dramatically disarms a person, appearing at any moment of the day or night.
During the next attack, you cannot rely on your family and the ambulance team. You need to realize that if you don’t help yourself, your chances of getting back to normal are reduced. In such cases, instructions on proper breathing are used, since the next wave completely disrupts the heart rhythm. The supply of oxygen through four breaths per minute normalizes the heartbeat. The patient must understand that his tense state will subside in the near future. Manipulate your consciousness. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Questions and answers
Have there been any cases of death due to PA in medicine?
No, the concept of PA implies a feeling of fear, as well as a number of other physiological changes. They are strong in intensity, but not so strong as to lead to the death of the body.
Who is more susceptible to the disease - men or women?
Individuals, regardless of gender or age, are prone to the disorder.
What mental disorders can cause the disorder?
At risk are schizophrenics, people diagnosed with bipolar affective disorder, manic-depressive psychosis, and various phobias.